Chapter 26 - Surgery of the Ear, Nose, Pharynx, and Larynx
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Cerumen
A substance produced by the cerumen glands of the ear (i.e., earwax)
Cholesteatoma
A benign tumor of the middle ear caused by the shedding of keratin
Effusion
Fluid in the middle ear
Epistaxis
Bleeding arising from the nasal cavity
Evert
To turn outward or inside out
Hypertrophy
Enlargement of an organ or tissue
Ossicles
The bones of the middle ear that conduct sound (i.e., the malleus, incus, and stapes)
Ototoxic
A substance that can injure the ear
Packing
A method of applying a dressing to a body cavity. In nasal procedures, 1/4- or 1/2-inch gauze strips are inserted into the nasal cavity to absorb drainage, control bleeding, or expose the mucosa to topical medication. "Packing" a wound may refer to any dressing that is introduced into an anatomical space or cavity.
Papilloma
A benign epithelial tumor characterized by a branching or lobular tumor (also called a papillary tumor)
Paranasal sinuses
Air cells surrounding or on the periphery of the nasal cavities. These are the maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid, and frontal sinuses
Paresis
Paralysis of a structure
Perforation
A defect in the tympanic membrane caused by trauma or infection
Phonation
Vibration of the vocal cords during speaking or vocalization
Polyp
Excessive proliferation of the mucosal epithelium
Sensorineural hearing loss
Hearing impairment arising from the cochlea, auditory nerve, or central nervous system
TM
The tympanic membrane
Transcanal
Surgical access through the external auditory canal (EAC)
Transsphenoidal
Literally, "across or through the sphenoid bone." Surgery of the pituitary gland may be performed by approaching it through the sphenoid bone
Tympanostomy tube
A tube that is placed in a myringotomy to produce aeration of the middle ear
A benign tumor of the middle ear caused by shedding of keratin in chronic otitis media
Cholesteatoma
Defect that can be caused by a blast injury or penetrating foreign body in the ear
Perforation
Enlargement of the tonsils that may prevent swallowing
Hypertrophy
A benign epithelial tumor characterized by a branching or lobular shape
Papilloma
Fluid in the middle ear
Effusion
Bleeding arising from the nasal cavity
Epistaxis
Vibration of the vocal cords during speaking or vocalization
Phonation
The most common cause of a break in the ossicle chain, which erodes the ossicles
Cholesteatoma
Paralysis of a structure, such as vocal cord paresis
Paresis
Excessive proliferation of mucosal epithelium
Polyp
Hearing impairment arising from the cochlea, auditory nerve, or central nervous system
Sensorineural hearing loss
Abnormal thickening of the bone in the middle and inner ear
Otosclerosis
A surgical opening is made in the tympanic membrane to release fluid
Myringotomy
Close a small, nonhealing hole in the tympanic membrane
Myringoplasty
Surgical removal of a cholesteatoma and mastoid bone, with or without reconstruction
Tympanoplasty
Removal of diseased bone, the mastoid air cells, and the soft tissue lining the air cell of the mastoid
Mastoidectomy/tympanomastoidectomy
The reconstruction of the ossicles to restore conduction to the oval window, performed to treat profound hearing loss related to sclerosis of the stapes
Stapedectomy/ossicular reconstruction
Is used to transmit external sound directly to the VIII cranial nerve, to treat sensineural hearing loss
Cochlear implant
Is performed to treat disease of the paranasal sinus, nasal cavity, and skull base and to improve nasal airflow
Endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS)
Maxillary sinus is exposed by making an incision in the gingivalbuccal sulcus (the junction of the gum and upper lip)
Caldwell-luc
Removal of the bony turbinate to increase airflow through the nose
Turbinectomy/turbinate reduction
Surgical manipulation of the septum to return it to the correct anatomical position or to gain access to the sphenoid sinus for removal of a pituitary tumor
Septoplasty
Is performed to reshape the external nose for aesthetic or functional purposes
Rhinoplasty
Is performed to reduce ear, nose, and throat infection, and improve the airway
Tonsillectomy
Surgical removal of the adenoids
Adenoidectomy
Performed to reduce and tighten oropharyngeal tissue to improve obstructive sleep apnea
UPPP
Endoscopic assessment of the larynx
Laryngoscopy
Is performed in the emergency department, ICU or operating room to create an airway for the patient
Tracheostomy/tracheotomy
Performed to enable jaw movement
Temporomandibular joint arthroplasty
Removal of the larynx usually with wide excision and skin grafting
Laryngectomy
Performed to treat malignant tumors; removal of all cervical lymph nodes and surrounding structures including the spinal accessory nerve, internal jugular vein, and sternocleidomastoid muscle
Radical neck dissection
Removal of the tongue for treatment of cancer
Glossectomy
Often performed for the treatment of a neoplasm neoplasm of the salivary gland
Parotidectomy
Tuning fork test (Rinne and Weber tests)
Test bone conduction and sensorineural hearing function of cochlea
Audiological testing (hearing test)
Usually conducted by an audiologist; can include air conduction, bone conduction, and speech recognition tests
Electronystagmography (ENG) testing
Tests for nystagmus
Head-positioning tests
Test for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
Balance testing
Tests stance, gait, and balance for signs of vertigo
Caloric testing
Tests for vertigo and nystagmus; warm or cool water is instilled into the external ear canal to determine whether those conditions are elecited
Auditory brainstem response (ABR)
Usually conducted by an audiologist or neurologist; measures the response of the brainstem to electrical stimulus as it relates to the ear
The knife used to make an opening into the eardrum is:
Myringotomy knife
Careful dissection around the Facial Nerve (CN VII) and its branches is essential in which of the following procedures?
Parotidectomy
With which of the following procedures should a patient be instructed to avoid blowing the nose, coughing, sneezing, swimming, and air travel?
Stapedectomy
Which of the following statements is true of cocaine hydrochloride?
It is used topically as an anesthetic and to decrease bleeding
A disease associated with bone conduction hearing loss whereby the stapes become fixed is:
Otosclerosis
Benign tumors that grow on a stalk and can be found on mucous membranes are called:
polyps
The surgical procedure performed to straighten a deviated septum in the nose is a/an:
Submucous Resection
Immediately following surgery of the mouth or pharynx, before consciousness is regained, the patient is positioned:
in the lateral position with slight Trendelenburg
The surgical procedure done to correct sleep apnea (absence of breathing for periods during sleep) is:
uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
The laryngeal cartilage which serves as the first tracheal ring and completely encircles the trachea is the:
cricoid cartilage
The salivary glands located alongside the ear and drained by Stenson's duct into the mouth are:
parotid
A tracheotomy would precede which of the following surgical procedures?
Laryngectomy
Surgical hazards associated with a Thyroidectomy include all of the following except:
Damage to the Facial Nerve
Surgical contouring of the teeth sockets in preparation for dentures is:
Alveoloplasty
For which of the following fractures would Erich arch bars and 25-gauge wire be applied?
Maxillary fracture
The drill used for ear surgery is a/an:
Ototome
Basic instrumentation for a Myringotomy would include all of the following except:
Yankauer suction tip
The transparent, absorbable sponge used to support a graft in the ear is:
Gelfilm
The anesthetic agent NOT used during middle ear surgery after graft placement is:
nitrous oxide
The type of Tympanoplasty which involves malleus damage and a graft placed between the tympanic membrane and the incus is:
Type II
Tissue used for a graft over the tympanic membrane is the:
temporalis fascia
The nerve which may be injured during Mastoidectomy is the:
Facial Nerve
The major nerve supply to the nose is the :
Olfactory Nerve
The medication used during nasal surgery that shrinks mucous membranes and relieves pain is called:
cocaine HCl
The surgical procedure to open the maxillary sinus by way of the canine fossa for removal of the sinus contents is referred to as:
Caldwell-Luc
Salivary glands includes:
Parotid glands, submandibular glands, and sublingual glands.
A sampling of the lymph nodes in the neck region is referred to as a:
Scalene Node Biopsy
Tonsillar fossa bleeders encountered during Tonsillectomy are ligated with:
surgical gut
Preoperative testing which should be reported for the patient undergoing Tonsillectomy would be:
PTT - 7 minutes
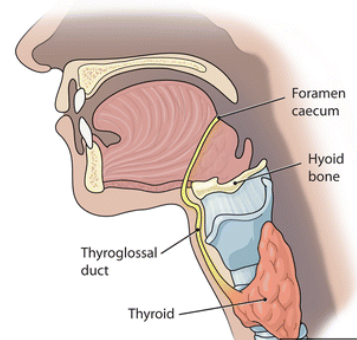
The embryologic structure of the tongue/neck region that may remain open, form a cystic pouch, and become infected is the:
thyroglossal duct
To create a Tracheostomy, a transverse incision is created in the neck, just below that _____.
cricoid cartilage
The parotid glands are located:
Under and in front of each ear
The procedure resulting in the patient's permanent loss of the ability to speak normally is a:
Total Laryngectomy
The facial bone which makes up the bony structure of the outer aspect of cheek is the:
Zygoma
The midface fracture which results in a "moustache" fracture is classified as a:
Le Fort I fracture
A Malar fracture is a fracture primarily involving which of the following bones?
b. Zygoma
Which of the following instrucments would be used to remove nasal polps?
Wilde Forceps
At what age is cohlear implant contraindicated in the children?
Under 2 years old
Earwax is known as
Cerumen
The ________ transmits the vibrations of the tympanic membrane (TM) and other ossicles to the inner ear via oval window.
Stapes