HBS 2.1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
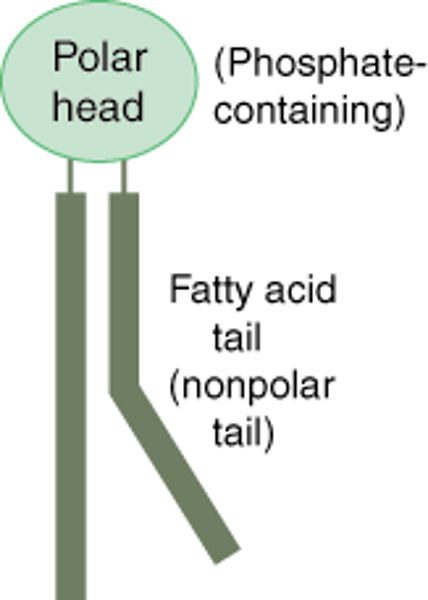
phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
phospholipid image
hydrophilic
water loving
hydrophobic
Water fearing
Sodium wants to move what way during action potential?
outward
Potassium wants to move what way during action potential?
inward
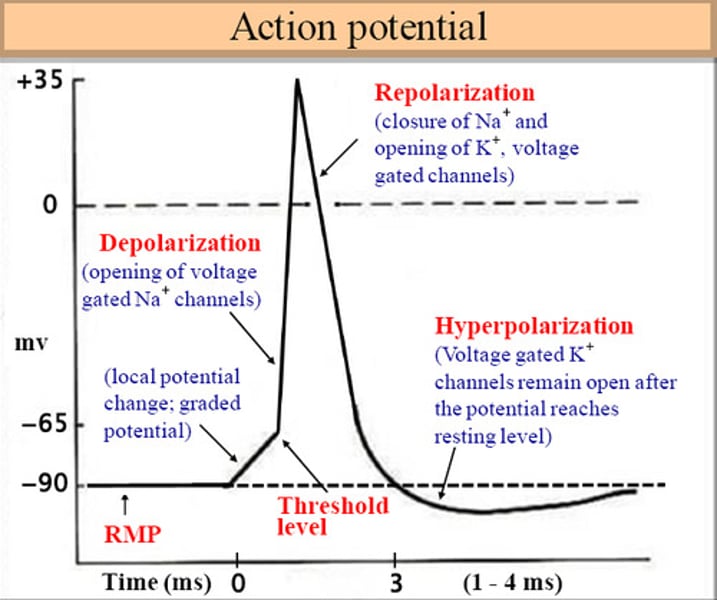
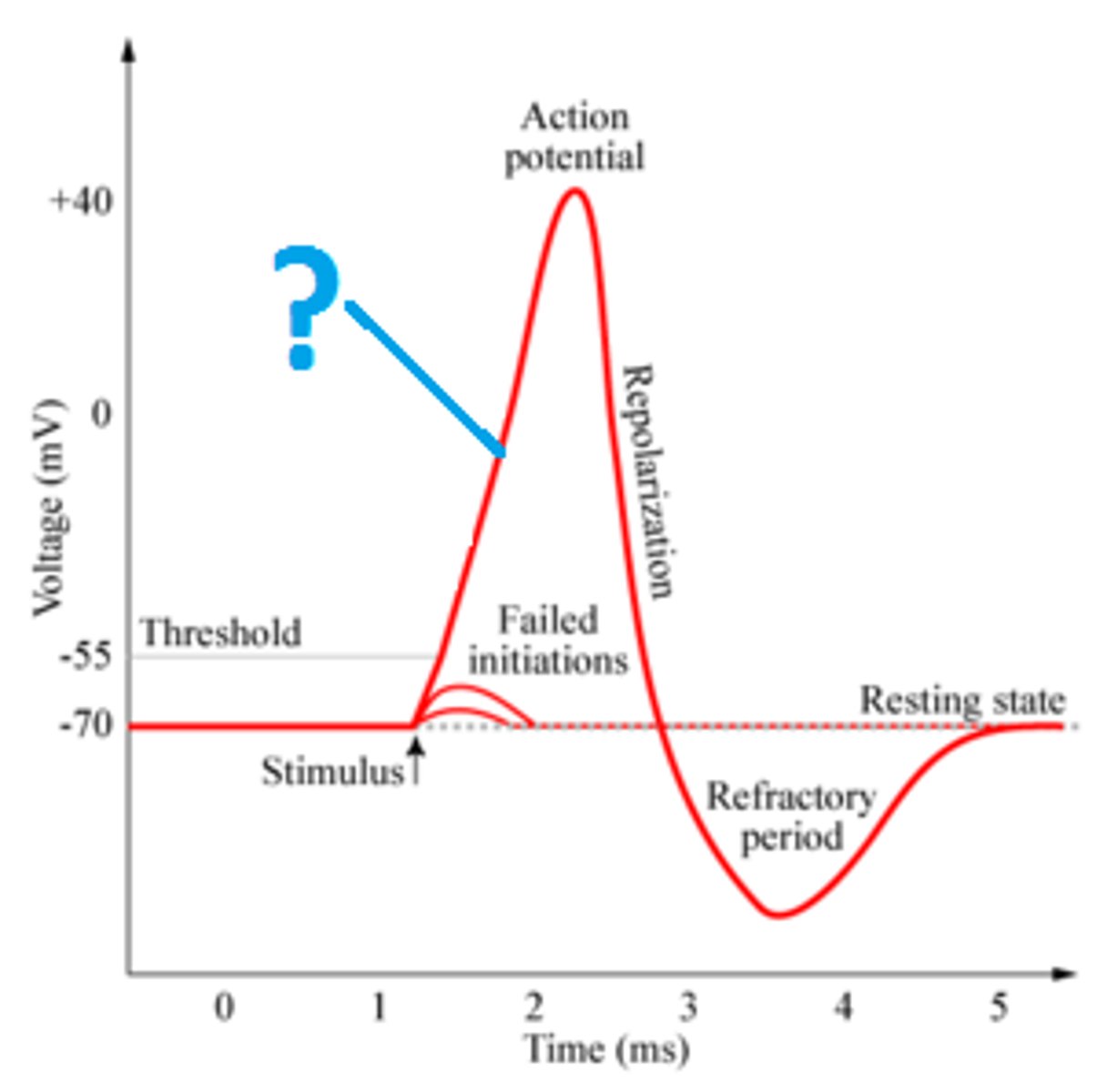
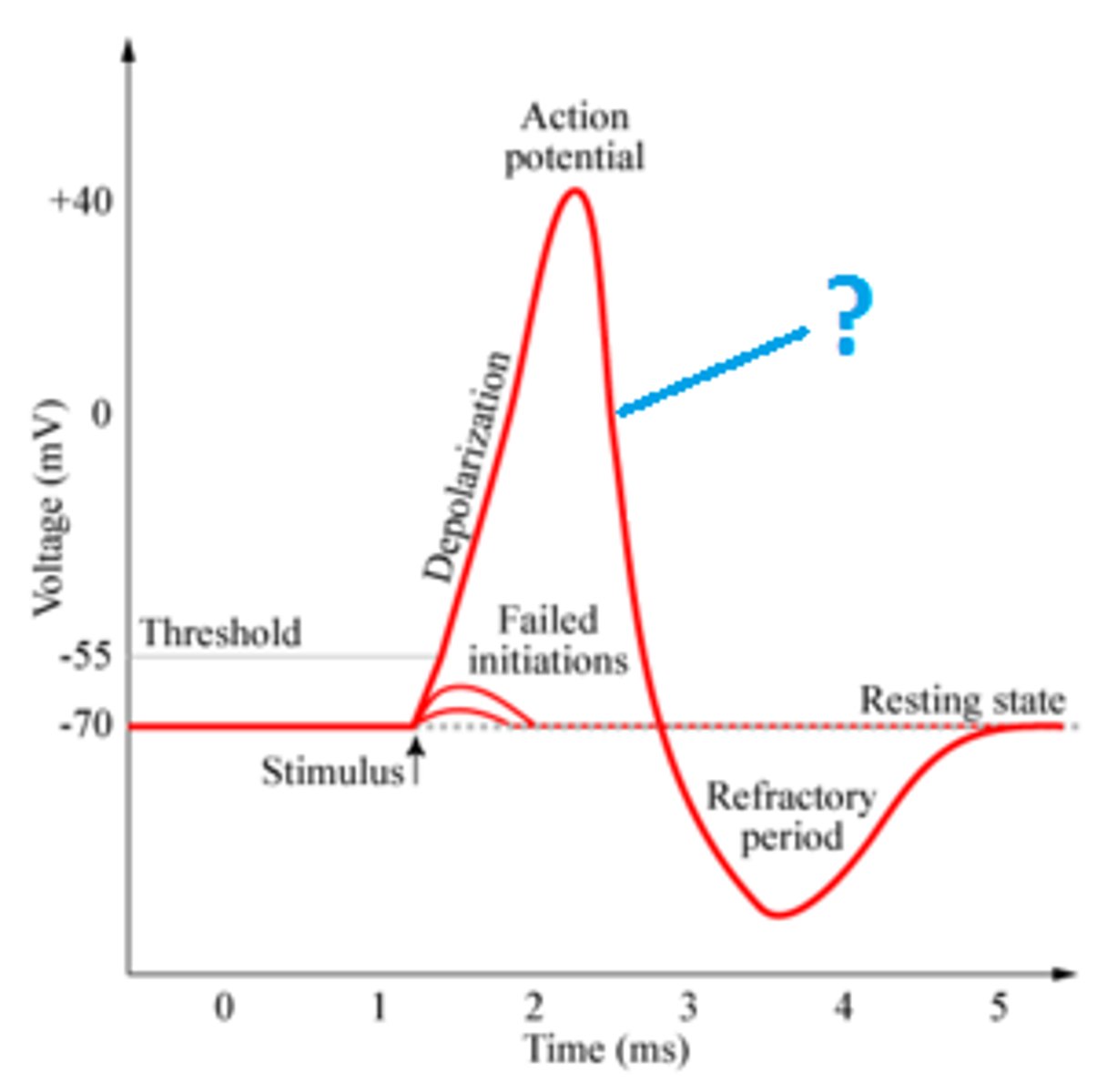
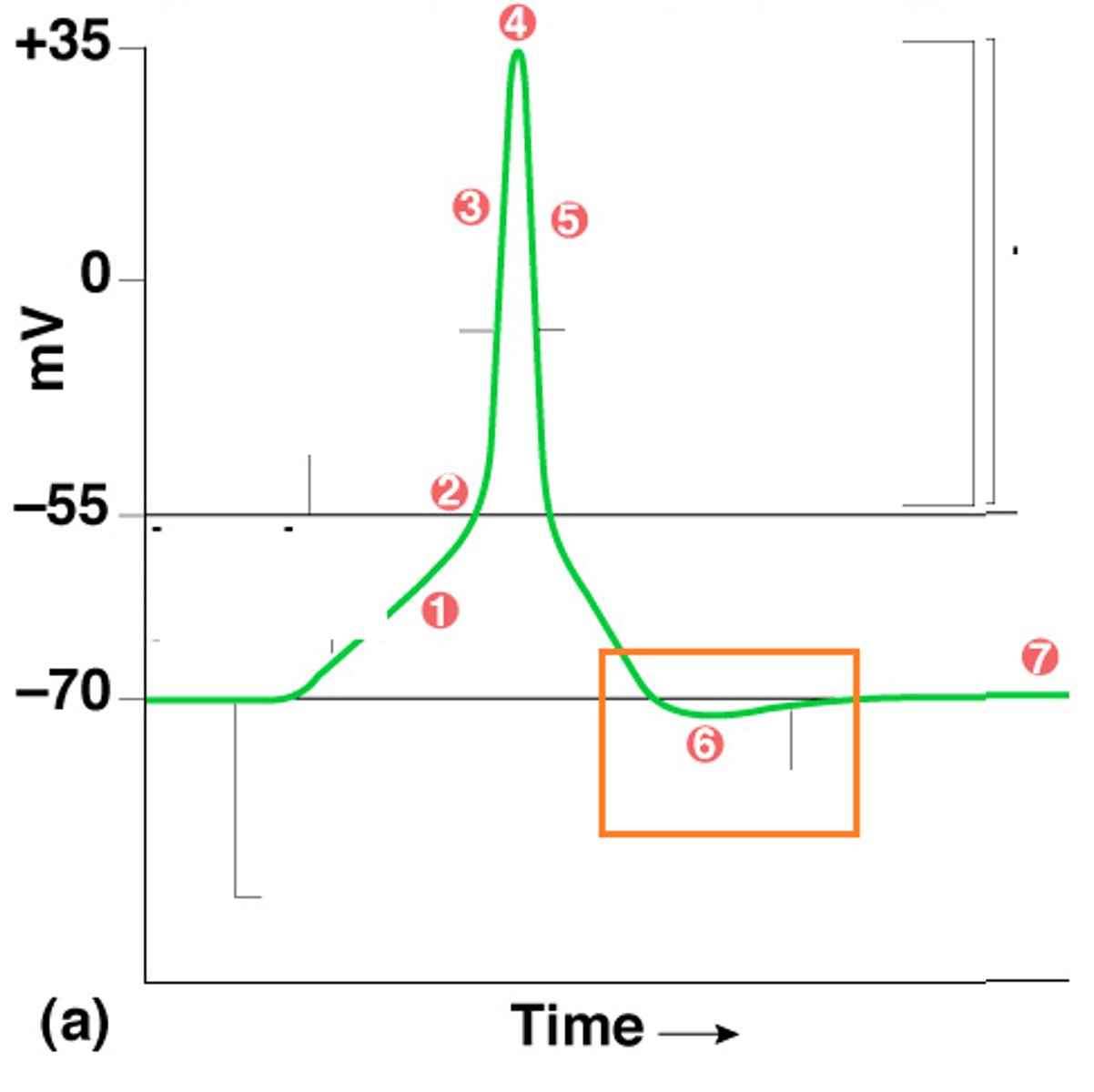
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
action potential image
How many potassium ions move through the pump at once?
2
How many sodium ions move through the pump at once?
3
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
The sodium-potassium pump maintains a higher _________ concentration outside the cell.
Sodium
The sodium-potassium pump maintains a higher _________ concentration inside the cell.
Potassium
Resting Potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane
sodium during resting potential
outside
potassium during resting potential
inside
during resting potential it is ______ on the inside
negative
during resting potential it is ______ on the outside
positive
depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell.
depolarization graph
repolarization graph
sodium channel
A protein channel in the nerve cell membrane that controls the movement of sodium ions into the cell. At rest, no sodium is flowing into the nerve cell. Passive transport.
potassium channel
A protein channel in the nerve cell membrane that controls movement of potassium ions out of the cell. Passive transport.
depolarization steps
sodium moves inward with open gates making inside positive and outside negative
repolarization steps
potassium moves outward making inside negative again and outside positive again
hyperpolarization
The movement of the membrane potential of a cell away from rest potential in a more negative direction.
hyperpolarization graph
action potential is...
electrical
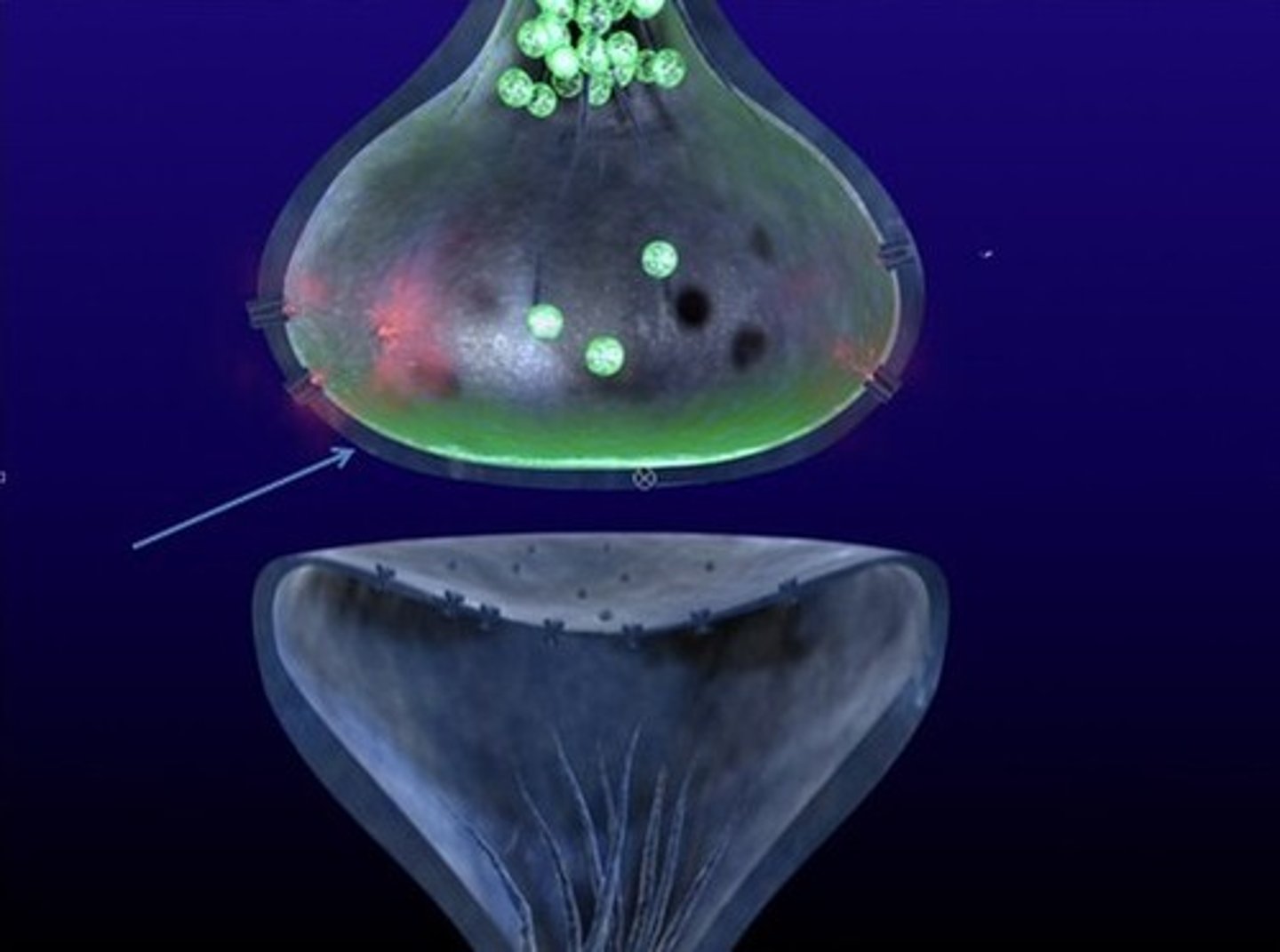
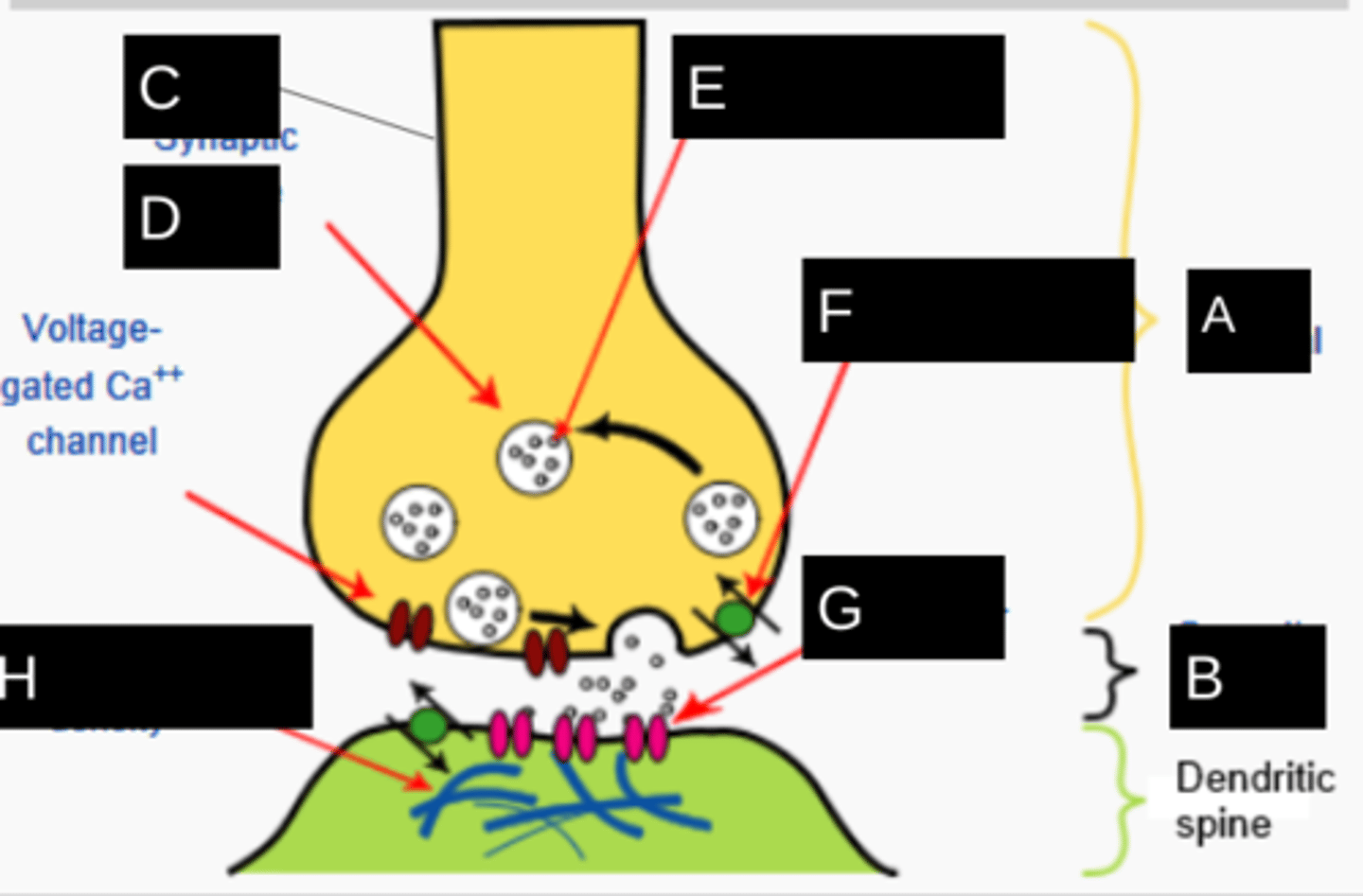
presynaptic cell
The transmitting neuron in a synapse.
postsynaptic cell
The neuron, muscle, or gland cell that receives the signal from a neuron.
presynaptic cell image
neurotransmitter
chemical used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
synaptic cleft image
receptor protein
a protein that binds specific signal molecules, which causes the cell to respond
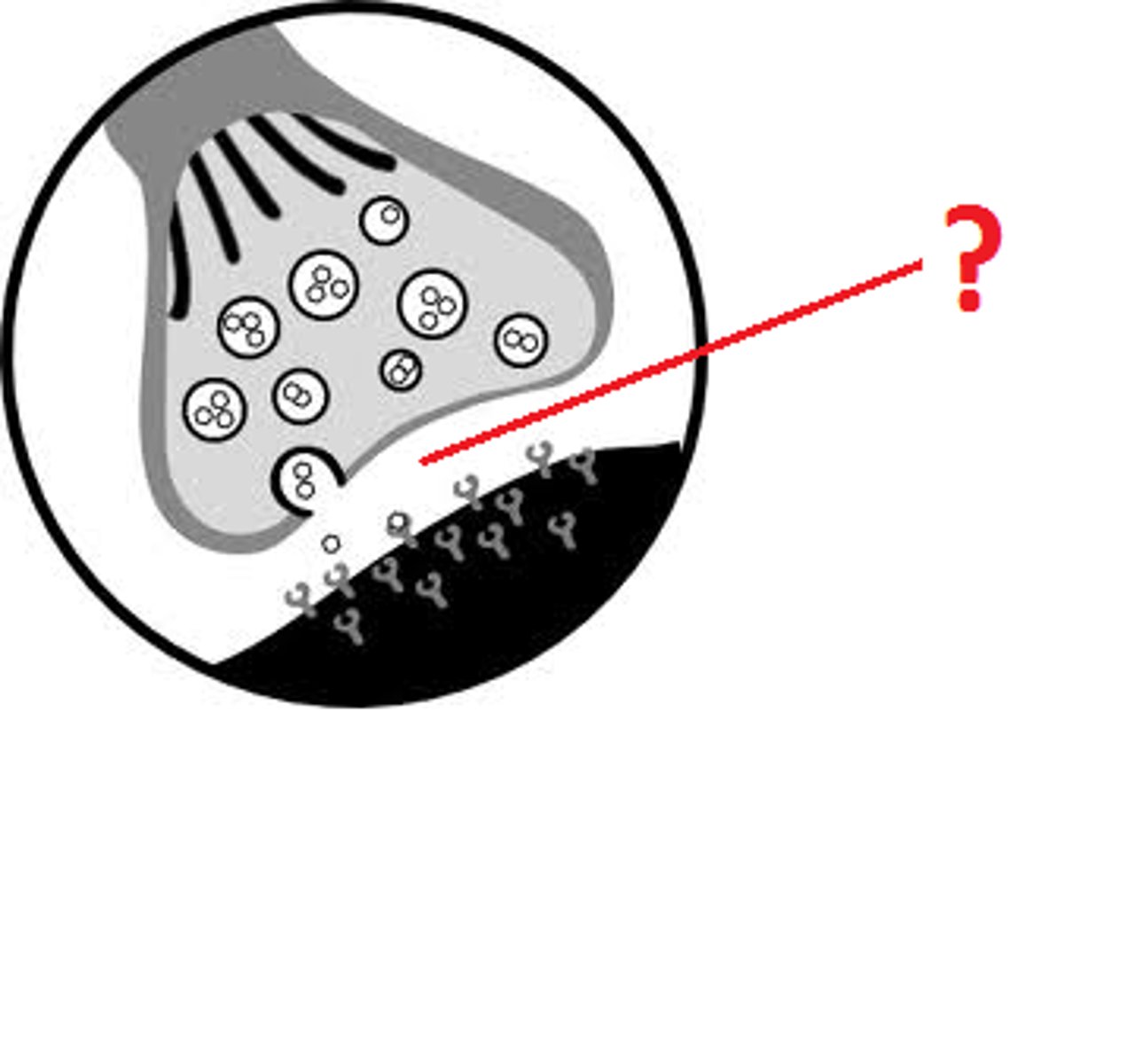
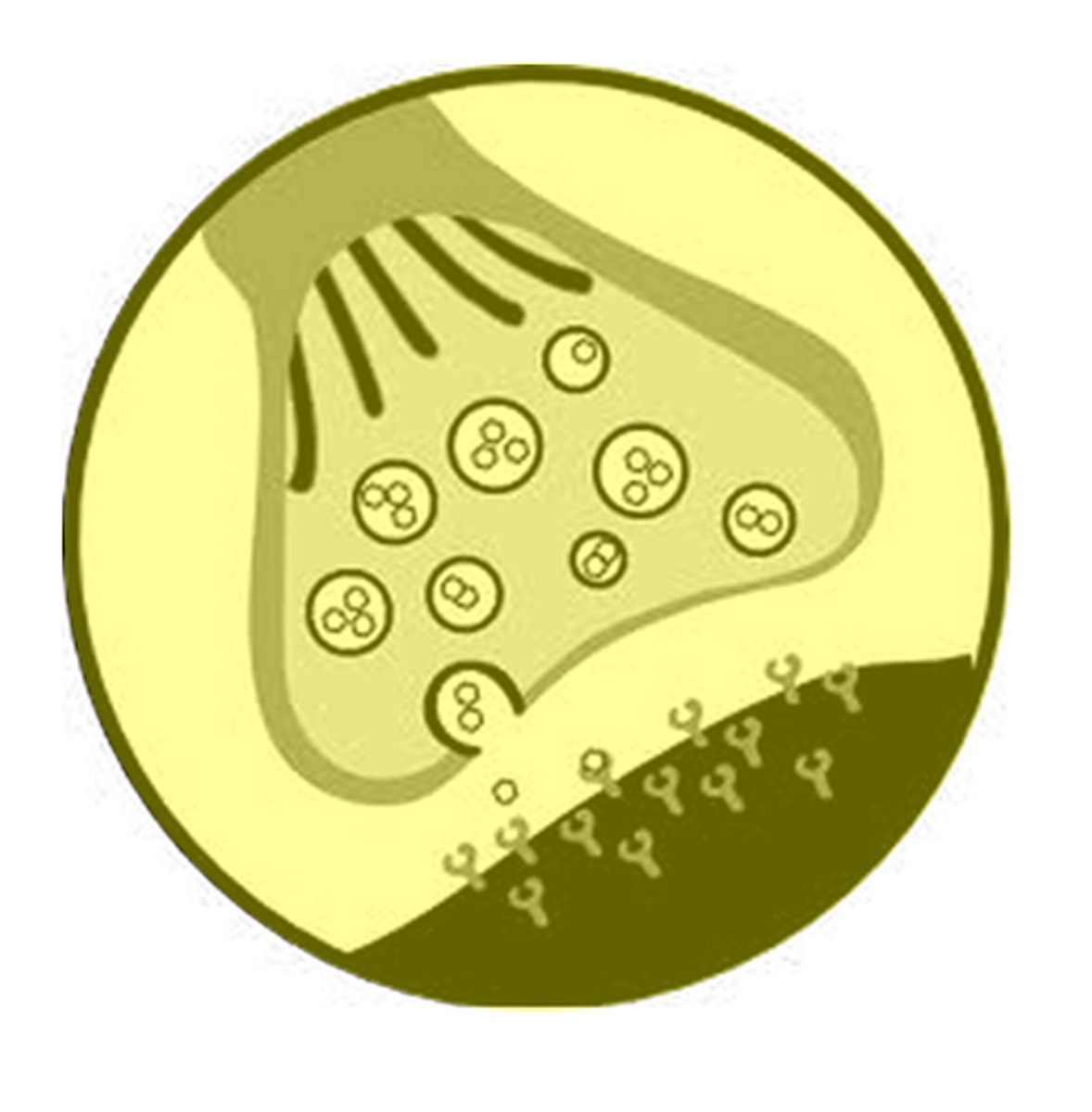
synaptic vesicles
Membrane-bounded compartments in which synthesized neurotransmitters are kept.
synaptic vesicle image
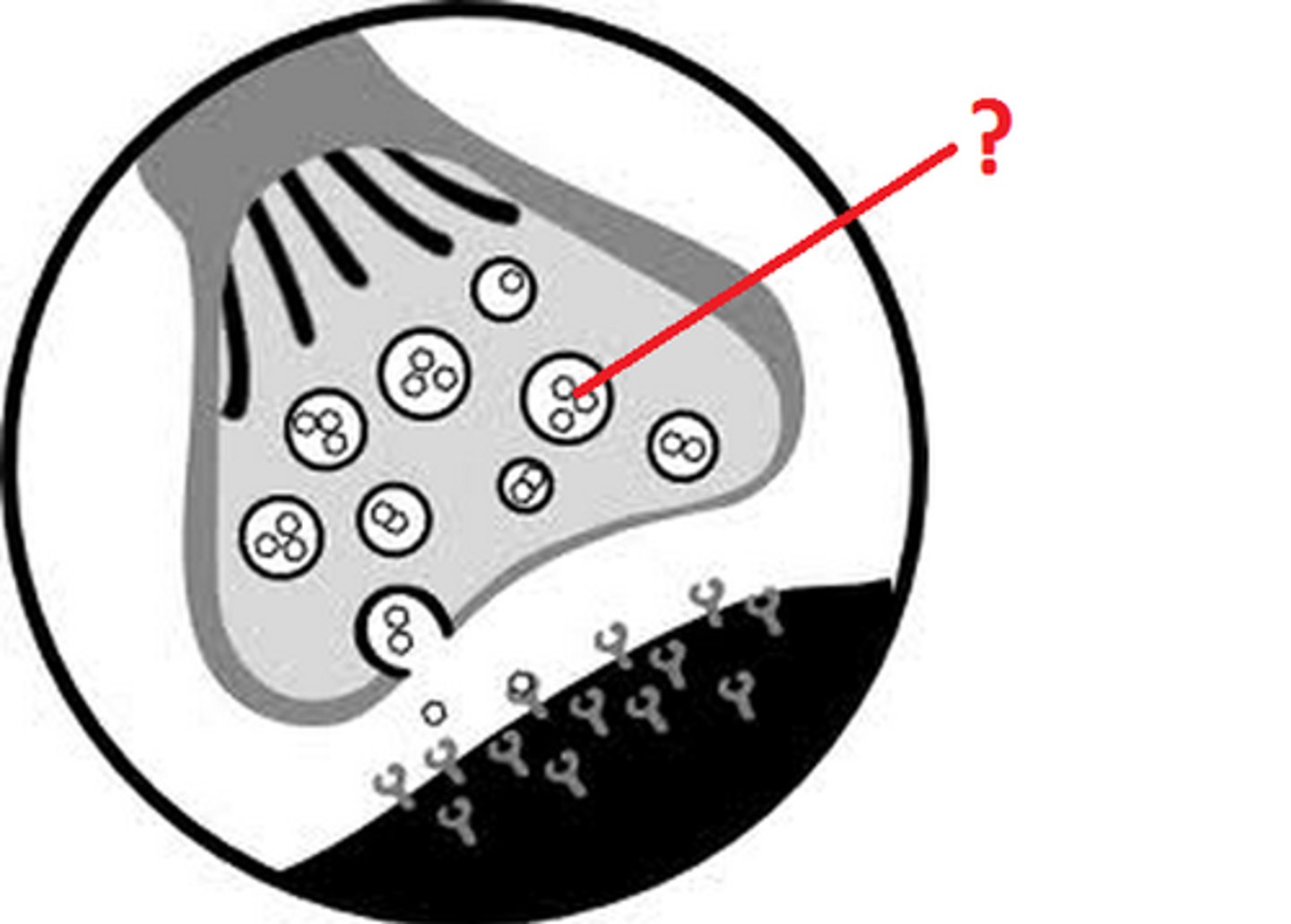
synaptotagmin
A specialized protein that responds to calcium ions to trigger vesicular exocytosis.
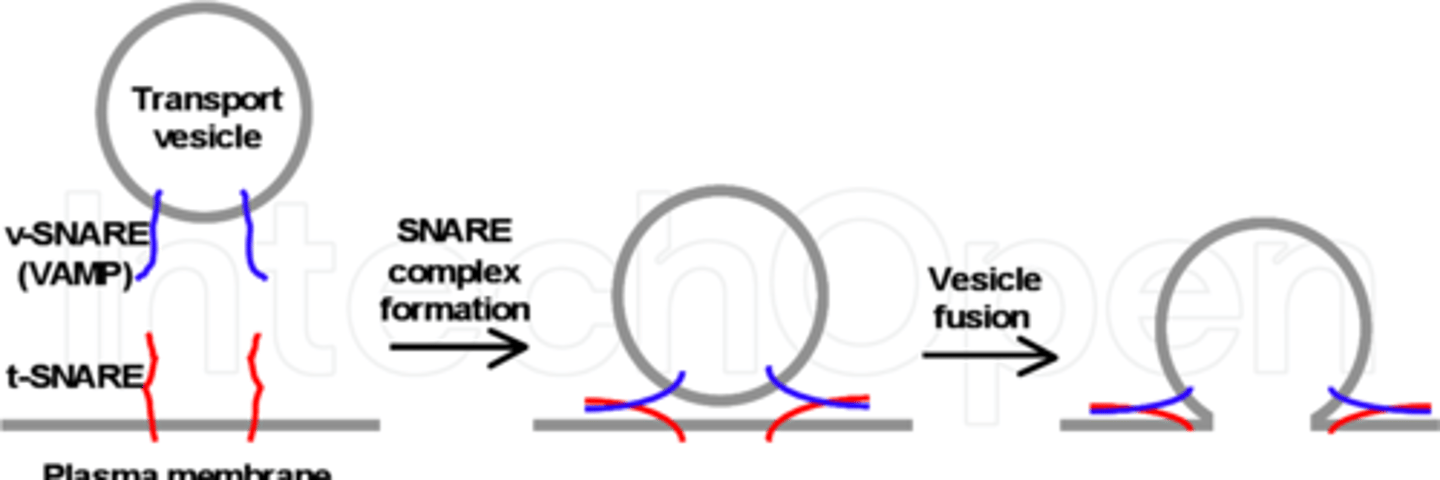
SNAP and SNARE proteins
proteins that allow neurotransmitters to exit the vesicle and into the synaptic cleft
SNAP and SNARE proteins image
reuptake channel
when neurotransmitters are reabsorbed they enter via reuptake channel
reuptake channel image
G
vesicular transporter
Channel located on a vesicle that allows passage of neurotransmitters
serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Epinephrine
Neurotransmitter secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress. Also known as adrenaline.
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
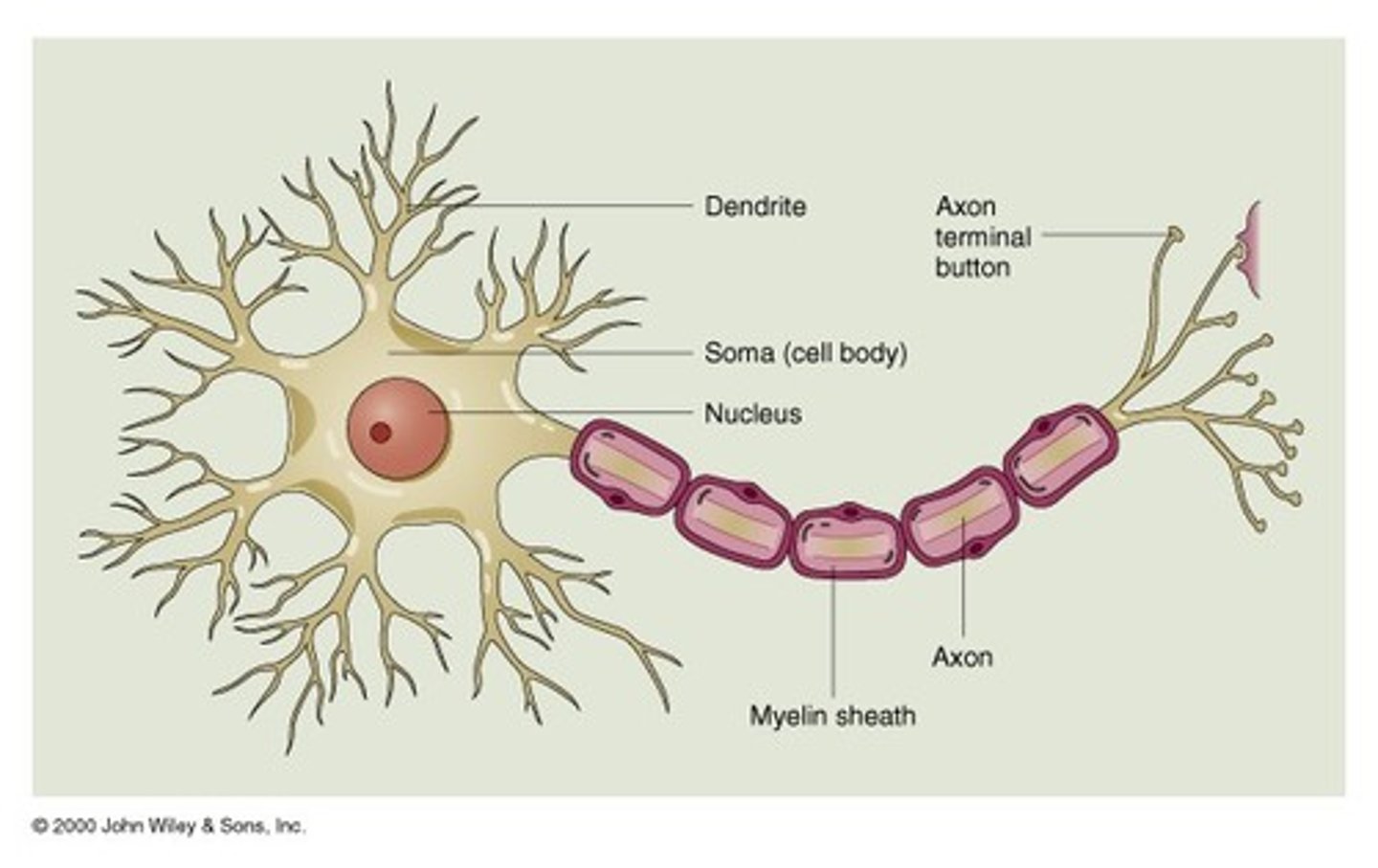
neuron
a specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses; a nerve cell.
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that provide protection and maintain homeostasis for neurons
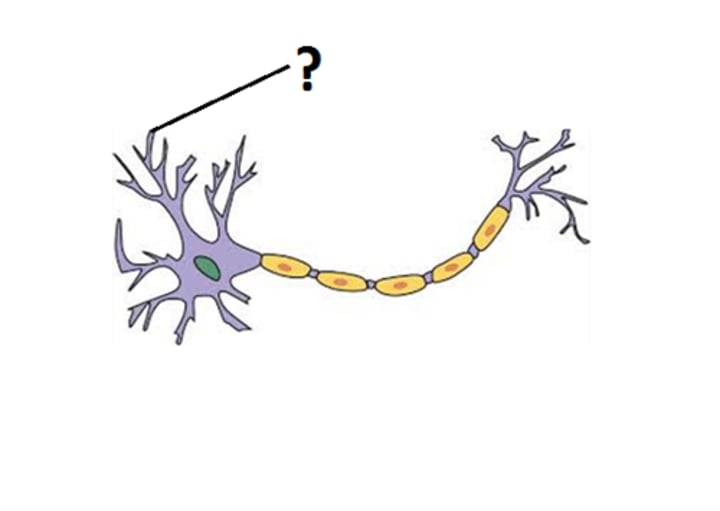
dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
dendrite image
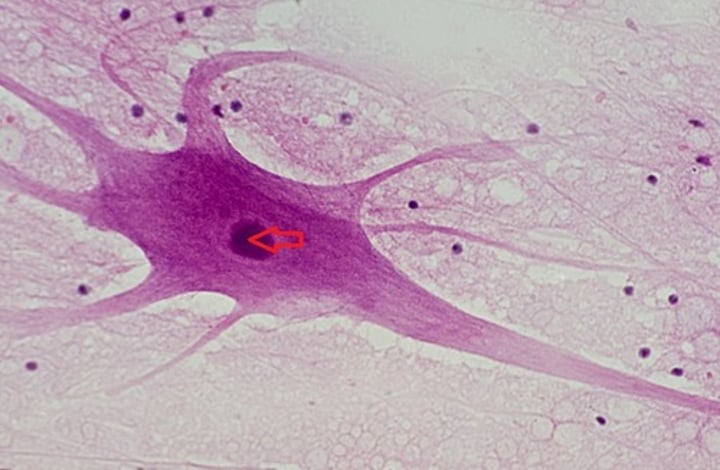
neuron body
contains nucleus and organelles
neuron body image
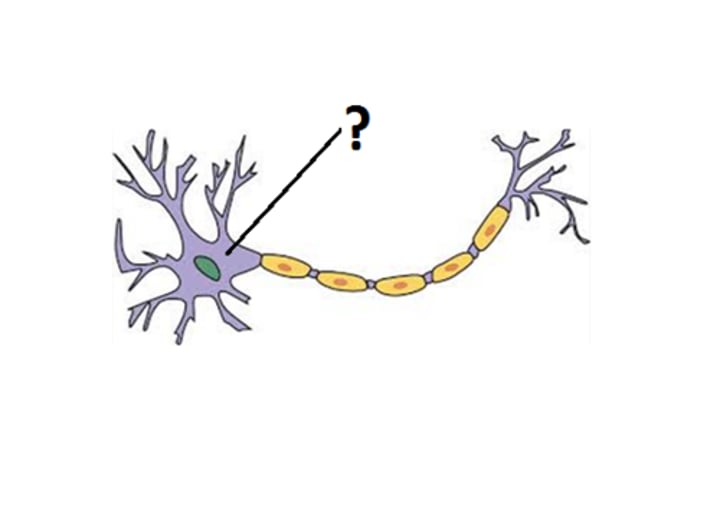
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
axon image
nucleus neuron
Control center of the cell
nucleus neuron image
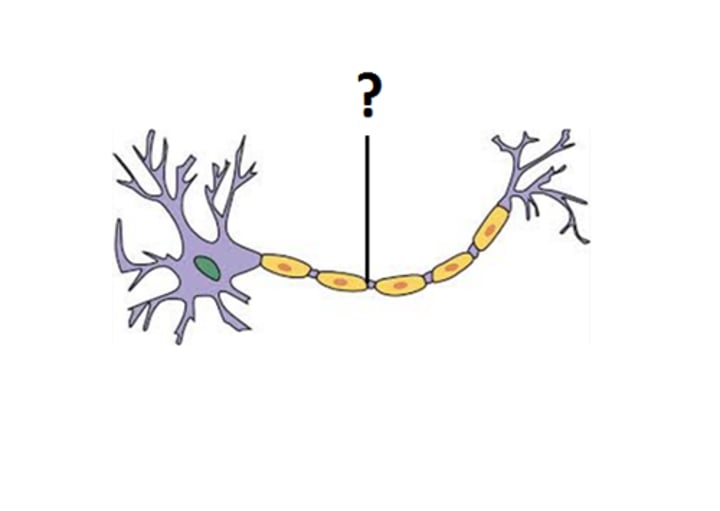
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
myelin sheath image
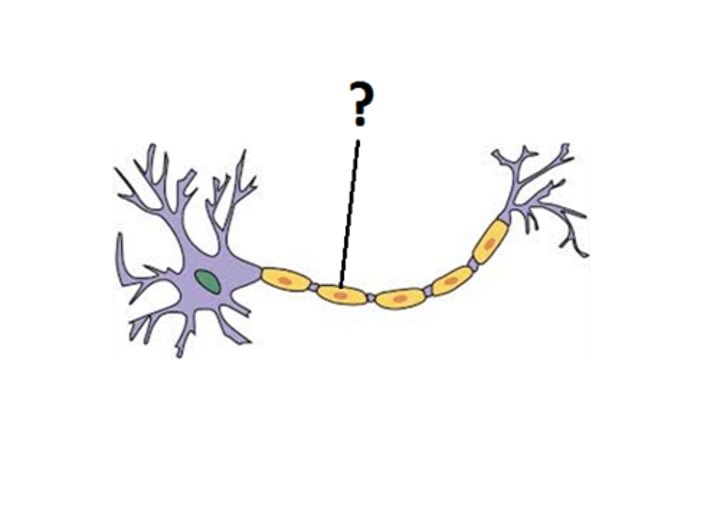
node of ranvier
A gap between successive segments of the myelin sheath where the axon membrane is exposed.
node of ranvier image
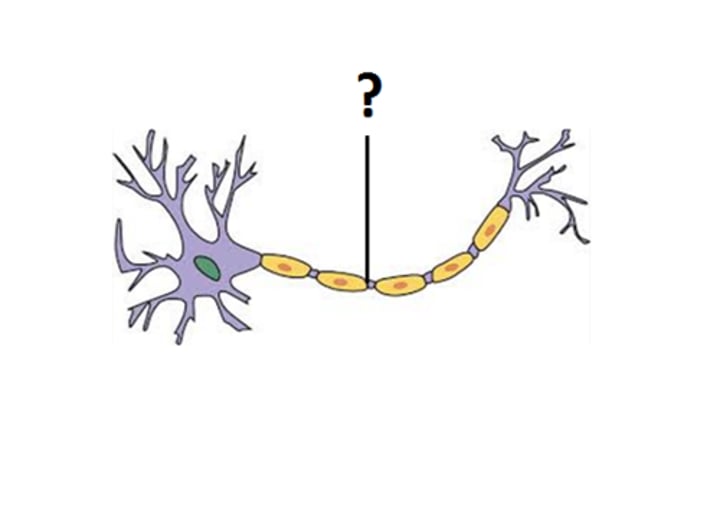
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
axon terminal image
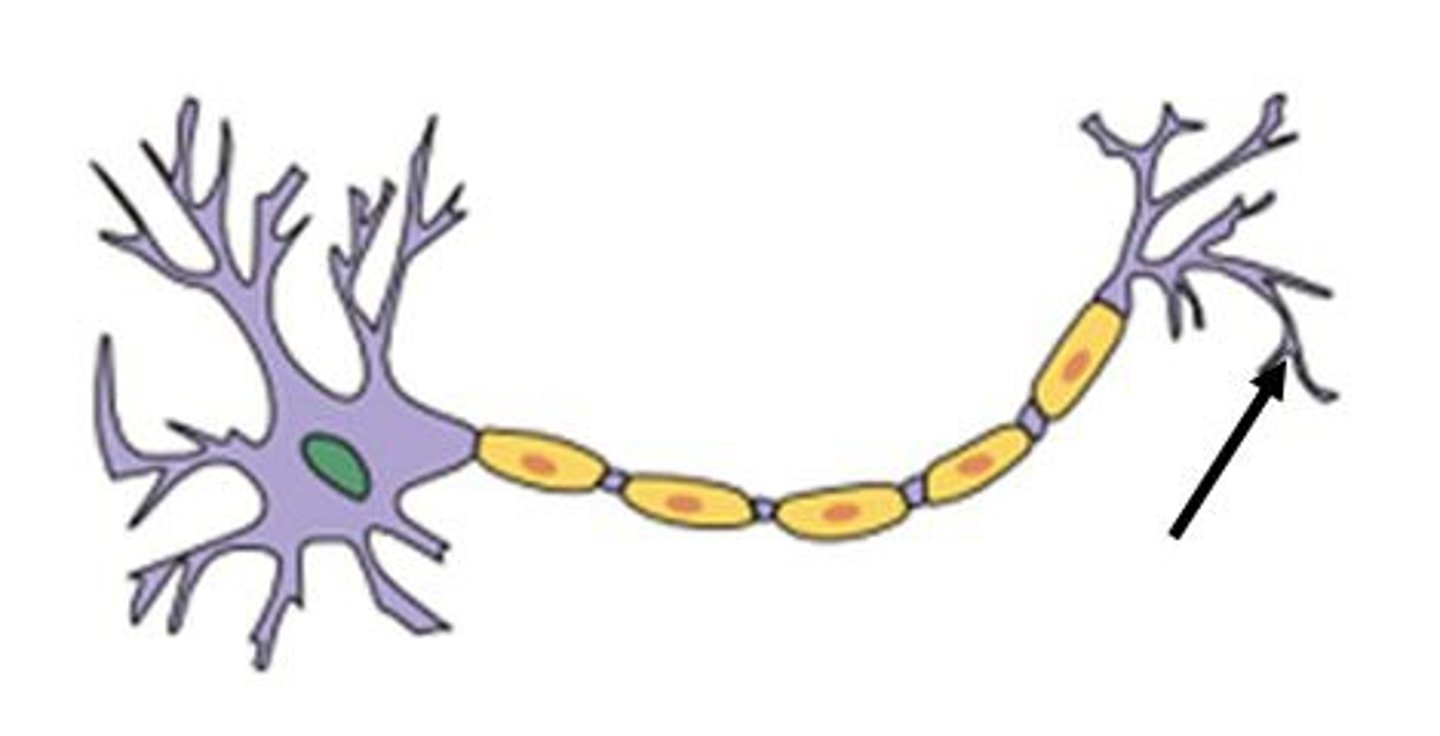
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
synapse image
soma
cell body
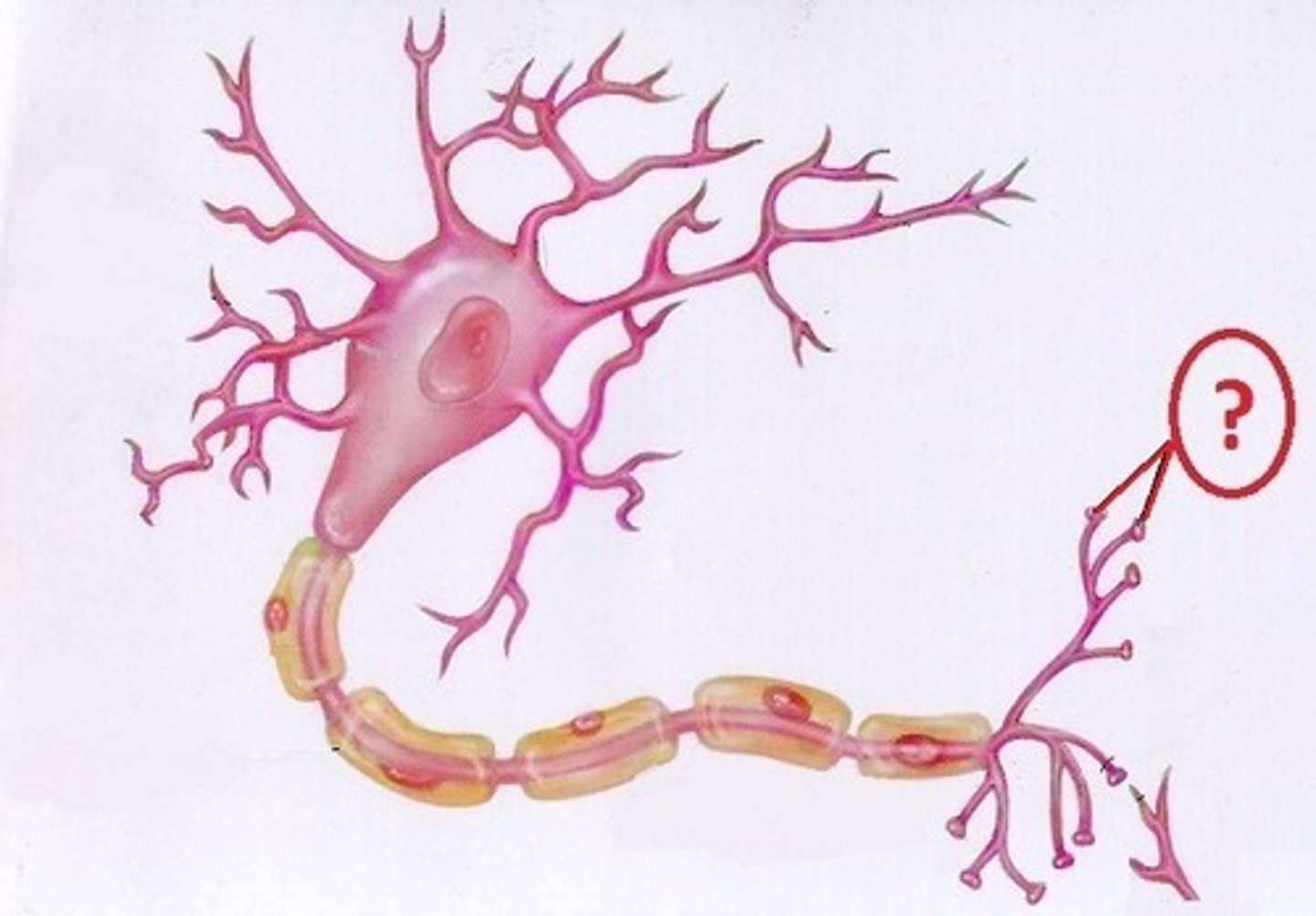
terminal buttons
Small knobs at the end of axons that secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
terminal buttons image
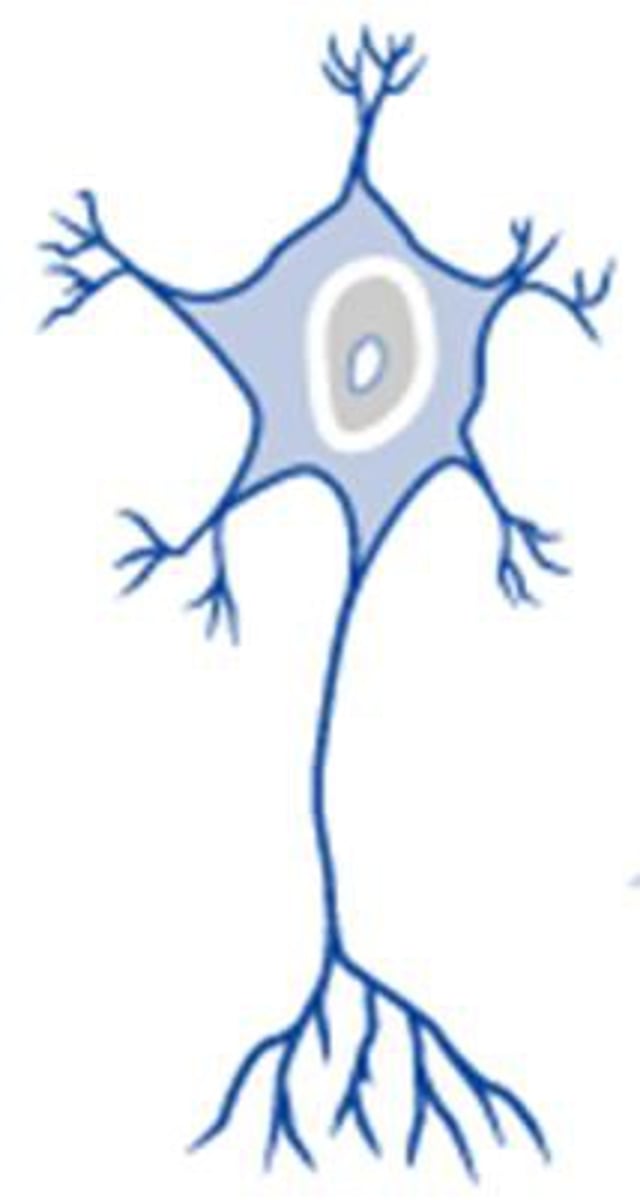
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system.
Multipolar type
motor neurons
multipolar image
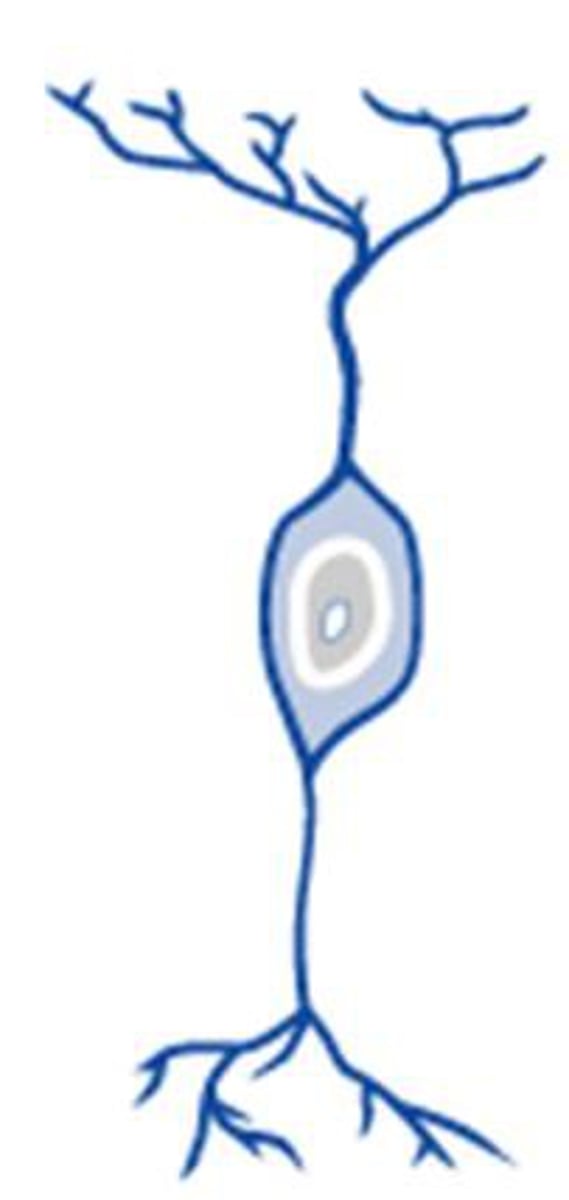
bipolar neuron
a nerve cell that has a single dendrite at one end and a single axon at the other end
bipolar image
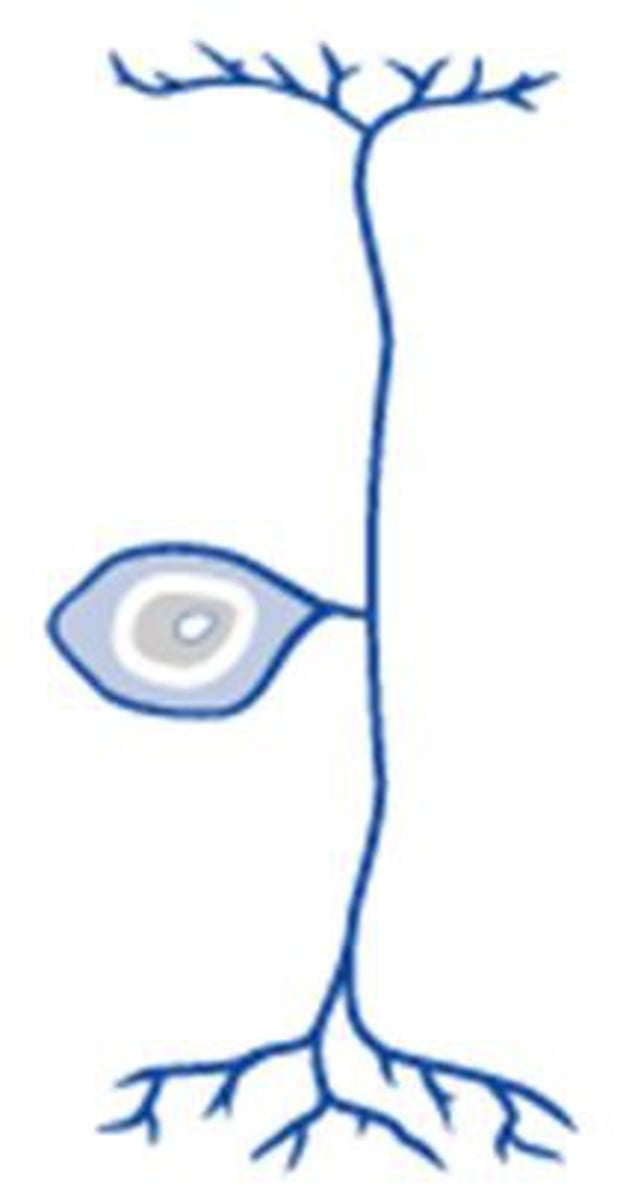
unipolar neuron
A neuron with one axon attached to its soma; the axon divides, with one branch receiving sensory information and the other sending the information into the central nervous system.
unipolar type
sensory neuron
pseudounipolar neurons
have a single short process that branches like a T to form a pair of longer processes
pseudounipolar image
pseudounipolar type
sensory neuron
sensory neurons are found where?
eyes, spinal cord, and through the body
interneurons are found where?
between sensory and motor neurons
motor neurons are found where?
connecting to muscles
sensory neurons go where?
towards CNS
motor neurons go where?
away from CNS
Dendrites of sensory neurons connect to?
sensory receptors (ex skin)
Dendrites of interneurons connect to?
sensory axon ends
Dendrites of motor neurons connect to?
interneuron
Axon terminals of sensory neurons connect to?
dendrites of interneuron
Axon terminals of interneurons connect to?
dendrites of a motor neuron
Axon terminals of motor neurons connect to?
muscle, organ, neuromuscular junction, ect.
What direction does the signal move in a neuron?
dendrites ---> axon terminals
experimental research
This branch of research is sometimes referred to as basic medical research and includes animal experiments, cell studies, biochemical, genetic, and physiological investigations, and studies on the properties of drugs and materials.
clinical research
This branch of healthcare science determines the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products, and treatment regimens intended for human use. These may be used for prevention, treatment, diagnosis, or for relieving symptoms of a disease.
neuron image
glial cell image