arch350 final
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Gabled roof
A roof with two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, creating end walls with a triangular shape.
Hipped roof
A pitched roof that has sloping gable ends, providing stability against high winds.
Parapet
A low wall or railing at the edge of a roof or balcony.
Eave
The part of a roof that meets or overhangs the walls of a building.
Siheyuan
A Chinese courtyard house dwelling with individual pavilions surrounding an open court.
Pit house (Yao Dong)
A dwelling that is partially or fully excavated into the ground, known for its temperature control.
Cantilever
An overhang that is supported at only one end by a wall or a column.
Talud-tablero
An architectural profile used in ancient Mexican buildings, consisting of an inclined plane supporting a cantilevered box.
Corbeled vault
A type of vaulted ceiling made by stacking stones or bricks in layers that project inward.
Chacmool
An altar shaped like a reclining person, used in ancient Mesoamerican cultures for sacrifices.
Cenote
A natural sinkhole or pit formed by the collapse of limestone bedrock, exposing groundwater.
Kiva
A circular room used by indigenous peoples of the American Southwest for religious rituals.
Dome
A rounded vault that forms the roof of a building, often seen in churches and mosques.
Gopura
A 2 story entrance gateway of a Hindu temple.
Mandapa
A columned hall in a Hindu temple, often situated before the garbha griha.
Garbha Griha
The innermost sanctum of a Hindu temple, where the main deity is located.
Torii
A traditional Japanese gate that marks the entrance to a Shinto shrine.
chigi
decorative rafters that stick out from the gables of Shinto shrine roofs. They are often gilded and are a key feature of traditional Shinto architecture.
shoden
the main hall of a Shinto shrine, where sacred objects representing the kami (spirits) are housed. It is a modest wooden structure that serves as the focal point for worship and rituals.
Imperial Shinto Great Shrine, Ise, Japan, begun 792 CE
Imperial Shinto Great Shrine, Ise, Japan, begun 792 CE
Fogong Si Pagoda, Yingxian, China, 1056 CE
Pagoda
A multistoried Chinese or Japanese prayer tower with elaborately projecting roofs at each story.
Foguang Monastery, Shanxi Province, China, 857 CE
Dougong
interlocking wooden brackets used in traditional Chinese architecture to connect columns to beams and rafters, distributing the weight of the roof and providing stability, especially during earthquakes.
Great Mosque of Damascus, Damascus, Syria, 704-715 CE
Minaret:
corner towers. 3 of them here, singing voices/ defense mechanism
Sahn:
: courtyard.had a fountain, surrounded by colonnades
Prayer hall:
The _________ of the Great Mosque of Damascus, also known as the Umayyad Mosque, is a long, east-west-oriented space with three aisles and a central nave
Mihrab
an alcove in the center of the qibla wall that focuses Muslims in their prayers
Qibla
wall that shows the direction Muslims pray towards
Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, Israel, 687-691 CE
Kailasanatha Temple, Ellora, India, 760 CE
Chaitya Hall, Karli, India, 200 CE
buddhist temple, contained nave(center line), vestibule ( space that leads to the main temple structure) ashoka column(upper left black circle)
Hagia Sophia, Constantinople (Istanbul), Turkey, ca 532-537 CE
San Vitale, Ravenna, Italy, 526-540 CE
Old St. Peter’s Basilica, Rome, Italy, 318-320 CE
Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine, Rome, Italy, 306-312 CE
Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine, Rome, Italy, 306-312 CE
Dura-Europos, (Christian Community House and Synagogue), Syria, ca 250 CE
Basilica Church Plan
Central Church Plan vs Basilica Church Plan
Pendentive
A curving triangular surface or spandrel that makes the transition from the corners of a square or polygonal room to a circular dome or its drum.
Clerestory:
A window, usually in a series, disposed at an upper level, above head height.
barrel vault
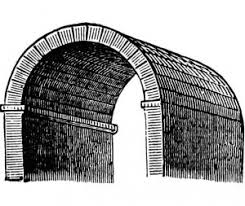
groin vault
Ambulatory:
A processional passageway around a shrine or flanking the apse of a Christian church.
catacombs
An underground system of passages used as a cemetery.
Apartment Compounds, Teotihuacán, Mexico, 100 BCE-200 CE
Ceremonial Center, (includes Pyramid of the Sun , Pyramid of the Moon and Temple of Feathered Serpent), Teotihuacán, Mexico, ca 100 BCE- 200 CE
Parapet
A low guarding wall at the top of a building
Great Zimbabwe, Zimbabwe, Africa, 1100-1400 CE
Silo
A well-sealed structure, usually without windows, for storing grain.
Chichen Itza, Yucatan, Mexico, ca 890 CE (Includes El Castillo (Temple of Kulkukan), Ball Court and El Caracol)
Cenote
a natural sinkhole or pit formed by the collapse of limestone bedrock, exposing groundwater underneath
El castillo
The great ball court
Caracol
Effigy
mounds shaped like animals (snakes, birds, bears) build along the great lakes
Platform
built with a flat top, intended to be the platform for a structure that was built on top. Usually rectangular.
Serpent Mound, Adena, Ohio, ca 300 BCE-1000 CE
Cahokia Mounds, (includes Monks Mound), Collinsville, Illinois, ca 1050-1200 CE
Plaza
Spanish word for an open public space in a city.
Pueblo Bonito, Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, 12th century CE
Kiva
Male meeting hall used by the indigenous peoples of the American Southwest, usually round and below grade