ch 17 blood (bio163)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
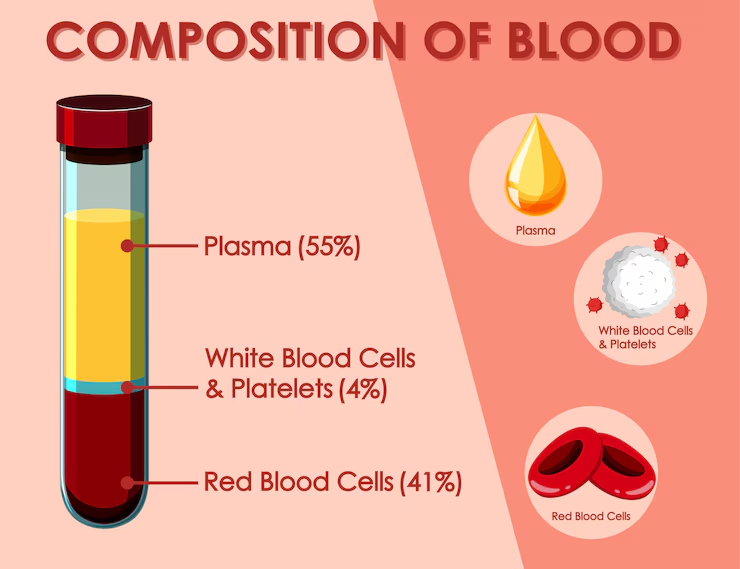
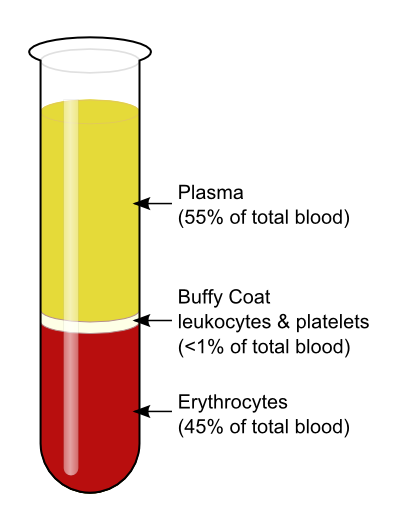
plasma
(not living fluid matrix)
55% of whole blood
least dense component
cardiovascular system
supplies all tissues with enough blood to meet energy demands
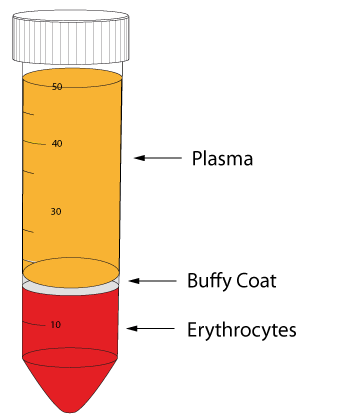
buffy coat
leukocytes and plates
<1% of whole blood
erythrocytes
45% of whole blood (hematocrit)
most dense components
formed elements
living blood cells suspended in plasma
contains-
erythrocytes: RBC
leukocytes- WBC
platelets
hematocrit
percent of blood volume that is RBC
47% ± 5% for males; 42% ± 5% for females
blood description
sticky opaque fluid with metallic taste (iron in hemoglobin in RBC)
has salty taste because of NaCl in plasma
color of blood
varies with oxygen content (red w/ oxygen and dark red (scarlet) without)
normal pH
7.35-7.45
average total blood volume
5 liters
hematopoiesis
forming blood (hematopoietic stem cells in red bone marrow)
erythropoiesis
forming RBC’s( increased by EPO from kidney in response to hypoxia: too few RBC)
leukopoiesis
forming WBCS
RBC definition
mature cell is biconcave disc ( decreased diffusion distance for oxygen),
full of hemoglobin (carries oxygen)
reticulocyte
immature RBC (# indicates the level of hematopoiesis)
hemoglobin
found in rbcs and is made out of:
heme and globin
heme
broken down in the body and turned into bilirubin, a yellow pigment that the liver usually gets rid of by sending it into the intestines as part of bile.
hyperbilirubinemia
too much bilirubin in the blood.
Can happen from liver failure or too much red blood cell (RBC) breakdown.
Causes jaundice (yellow skin and eyes).
Bilirubin goes to the intestines and turns into stercobilin, which makes poop brown.
contains iron that binds to oxygen (4 hemoglobin molecule)
globin
a protein that gets broken down into amino acids when recycled
spleen
where old rbcs are recycled
ex) RBC graveyard
anemia
decreased blood has abnormally low oxygen carrying capacity
-oxygen lvls are too low to support normal metabolism (body function)
-symptoms of fatigue, pale skin (pallor), shortness of breath and chills
causes of anemia
Blood Loss
Low Red Blood Cell (RBC) Production
High RBC Destruction
Increased Blood Plasma Volume
sudden blood loss in anemia
leads to hemorrhagic anemia
ex) stab wound
ongoing blood loss in anemia
leads to like chronic hemorrhagic anemia
ex) like a bleeding ulcer
low iron anemia
makes fewer, smaller and pale RBCS
low vitamin b12
occurs when you aren’t eating enough animal products
causes fewer and larger RBCs to be made
pernicious anemia
autoimmune disease where the stomach doesn’t make intrinsic factor, so the body can’t absorb B12
hemolytic anemia
when rbcs are being destroyed faster than the body can make them
ex) sickle cell disease
increased blood plasma volume
blood has more liquid than cells, making it watery
dilutes rbcs which makes it seem like there are fewer
ex) pregnancy: to support the baby
2 things that are normally not permeable thru a capillary
RBC and protein (mostly albumin)
hydrostatic
pushes fluid out of capillaries
too much hydrostatic pressure
pushes out too much fluid → edema (swelling)
too little hydrostatic pressure
pulls in too much fluid → lowers fluid in tissues, may increase blood volume
colloid osmotic pressure
pulls in plasma in a capillary
too little colloid pressure
not enough fluid pulled back in → edema (swelling)
too much colloid pressure
pulls in too much fluid → lowers fluid in tissues, may increase blood volume
white blood cells function
leukocytes fight infection/ disease
leukocytosis
WBC count over 11,000/mm3 which indicates infection
3 types of granulocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
neutrophils
most numerous
is a bacteria slayer
eosinophils
digests parasitic worms
basophils
contains histamine
histamine
an inflammatory chemical that causes vasodilation (blood vessels widen) to attract wbcs to inflamed sites but also in allergies
what are the 2 agranulocytes?
lymphocytes (b and t) and monocytes (in blood)
lymphocytes (b and t cells)
crucial to immunity
monocytes (in blood)
become macrophages in tissues
leukopenia
abnormally low wbc count (often drug induced)
leukemia
is a cancer
overproduction of abnormal wbcs
cancer leukocytes fill red bone marrow
other lines crowded out→ anemia & bleeding
platelets
cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocytes
act in clotting process
hemostasis
stopping of bleeding
vascular spasm
smooth muscle contracts which causes vasoconstriction
platelet plug formation
injury to lining of vessel exposes collagen fibers, platelets stick here
platelets release chemicals that make nearby platelets sticky
platelet plug forms
required von willebrand factors
coagulation
fibrin forms a mesh that traps rbcs and platelets
forming the clots
series of rxns using clotting factors (procoagulants) that converts soluble plasma protein (fibrinogen) into a insoluble fibrous protein (fibrin)
vitamin k needed to synthesizes 4 of them
pic on reveiw
write it
intrinsic pathway
triggered by negatively charged surfaces ( activated platelets, collagen, glass)
– Uses factors present within blood (intrinsic)
extrinsic pathway
triggered by exposure to tissue factor (an extrinsic factor) present on the surface of damaged tissues
bypasses several steps of intrinsic pathway so faster
vessel repairs
.
platelet derived growth factor
stimulates division of smooth muscles and fibroblasts to rebuild blood vessel wall
vascular endothelial growth factor
stimulates endothelial cells to multiply and restore endothelial lining.
plasminogen
clot is converted to plasmin by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) factor XII (12) and thrombin (negative feedback)
plasmin
is a fibrin digesting enzyme
what are the two mechanisms that limit clot size?
1) swift removal and dilution of clotting factors
2) inhibition of activated clotting factors
thrombin bounds onto?
fibrin threads
antithrombin III inactivates…
unbound thrombin
heparin in basophil and mast cells…
inhibits thrombin by enhancing antithrombin III
thromboembolic disorders
undesirable clot formation
thrombus
clot that develops and persists in unbroken blood vessel
may block circulation leading to tissue death
embolus
thrombus freely floating in bloodstream
embolism
embolus obstructing a vessel
ex) pulmonary and cerebral emboli
risk factors for thromboembolic disorders
atherosclerosis
inflammation
slowly flowing blood or blood stasis from immobility
bleeding disorders
abnormalities that prevent normal clot formation
thrombocytopenia
deficient number of circulating platelets
petechiae
apreas due to spontaneous widespread hemorrhage
impaired liver function affects ability for blood to coagulate
inability to synthesize procoagulants
hemophilia a
most common type (77% of all cases); factor VIII (8) deficiency (intrinsic pathway)
disseminated intravascular coagulation (dic)
involved both types of disorders
occurs as a pregnancy complication, in septicemia or incompatible blood transfusions
widespread clotting blocks intact vessels and causes ischemia and uses up clotting factors which results in bleeding
aspirin
inhibits thromboxane a2 (released by activated platelets for spasm and clotting)
often suggested to prevent strokes, heart attacks
heparin
anticoagulant used clinically for pre and post op cardiac care
warfarin (coumadin)
used for those prone to atrial fibrillation due to increased clot formation in blood pooling in atria> risk of stroke
interferes with action of vitamin k (required for formation of clotting factors)
what hemoglobin does the fetus form
hemoglobin f
-has a higher affinity for o2 than hemoglobin a (adult) formed after birth
helps fetus obtain oxygen from mom’s blood thru placenta