Cultural Ecology of Food: Nutrition, Traditions, and Indigenous Perspectives
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What are modern traditional diets?
Diets like the Mediterranean and Japanese diets that emphasize unprocessed foods, local sourcing, and active living.
What are the characteristics of modern traditional diets?
They include plant-based foods with meat as an accent, active lifestyles, lower chronic disease prevalence, and longer life expectancy.
What are the low intake foods in modern diets?
Legumes, nuts, seeds, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and fiber.
What are the high intake foods in modern diets?
Refined carbohydrates, meat, dairy, ultra-processed foods, added sugars, sodium, and omega-6 fatty acids.
What are the four major cuisines of China?
Cantonese, Sichuan, Hunan, and Beijing (Northern) cuisine.
What is the average rice consumption per person in China?
300 lbs (136 kg) of rice per person per year.
What is a typical Japanese meal composed of?
A bowl of rice, soup, grilled fish, pickled vegetables, and fruit for dessert.
What are the two main types of Japanese noodles?
Soba (brown noodles made from buckwheat) and Udon (thick white noodles made from wheat).

What are common soybean foods consumed in Asia?
Edamame, tempeh, and tofu.

What health claim did the FDA allow for soy protein in 1999?
Foods high in soy protein may help lower heart disease risk.

What are common characteristics of Thai cuisine?
Often hot and spicy, wok-fried foods, and the use of partially hydrogenated oils in ultra-processed foods.
What is the smoke point of coconut oil?
About 360°F (180°C), making it suitable for high-heat cooking.
What recent studies indicate about coconut oil and cholesterol?
Coconut oil raises LDL cholesterol similar to other saturated fats, leading to recommendations against its use.

What are the staple foods in traditional Mexican cuisine?
Foods of Aztec origin such as prickly pear cactus, chili pepper, avocado, beans, corn, tomatoes, and cocoa beans.

What is the significance of the Columbian Exchange?
It refers to the transfer of animals, plants, culture, diseases, and technology between the Americas and Afro-Eurasia in the 15th and 16th centuries.
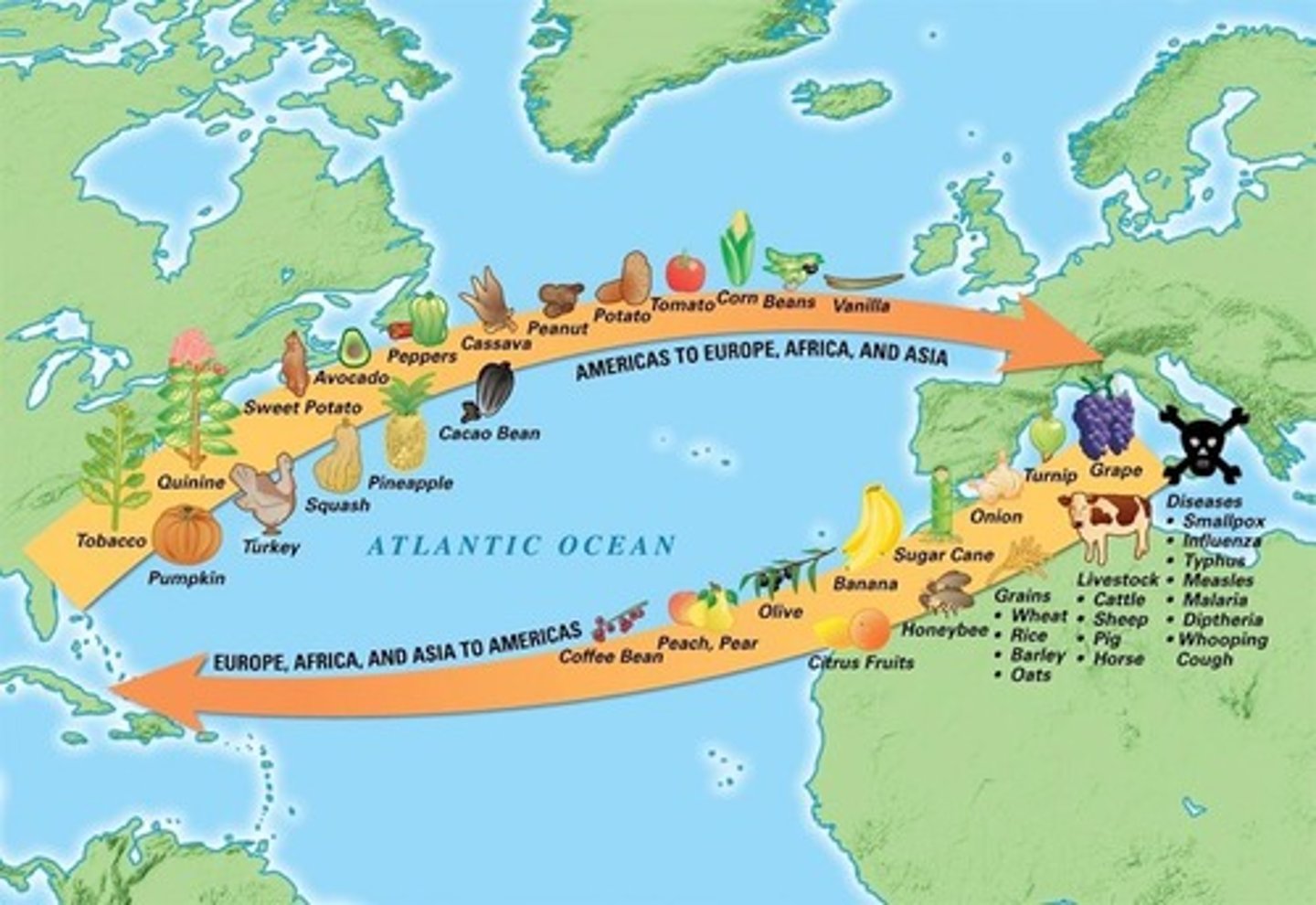
What impact did the Columbian Exchange have on Indigenous populations?
Highly virulent diseases like measles and smallpox decimated Indigenous populations who had no immunity.
What is the preferred rice type in Thailand?
Glutinous rice.
What is the preferred rice type in India?
Fragrant basmati rice.
What are the health benefits associated with traditional diets?
Lower rates of chronic diseases and longer health expectancy.
What role do vaccinations and sanitation play in nutrition transitions?
They have reduced the incidence of many infectious diseases, contributing to overall health improvements.
What is the cultural significance of food in traditional cuisines?
Food reflects cultural identity, history, and the ecological practices of a region.
What livestock was exchanged from the Old World to the New World?
Turkeys
What livestock was exchanged from the New World to the Old World?
Goats, sheep, cattle, pigs, and chickens
Name three significant crops native to the Americas.
Maize, tomatoes, and sweet potatoes

What are the main groups of significant American crops?
Grains, roots/tubers, legumes, fruits, melons, vegetables, and other
Which crop is known as Zea mays?
Maize
What is the significance of nixtamalization in corn-based diets?
It softens corn for grinding, allows dough formation, makes niacin bioavailable, adds minerals, and removes aflatoxins.
What is a common staple food made from maize in Latin America?
Tortilla
What are the results of nixtamalization on corn?
It increases the bioavailability of niacin and calcium, and enhances nutritional value.
What traditional method is used to increase calcium absorption in corn tortillas?
Lime treatment (using calcium hydroxide)
What is the effect of lime treatment on calcium absorption from corn tortillas?
It significantly increases calcium absorption compared to untreated tortillas.
What is the role of calcium in the diet, particularly concerning corn-based diets?
Calcium is essential for bone health and is often low in untreated corn-based diets.
What is the cultural significance of 'rice and beans' in Latin America?
It represents a staple food combination that reflects cultural food adaptation.
What European dietary contributions were introduced to Mesoamerican diets in the 16th century?
Rice, wheat, sugar, dairy, cows, pigs, sheep, and chicken.
What is the primary benefit of nixtamalization for niacin in corn?
It makes niacin bioavailable, preventing deficiencies like pellagra.
What are the main types of corn tortillas evaluated for calcium absorption?
Untreated corn flour, commercial lime-treated corn flour, and lime-treated home-prepared corn flour.
What is the calcium absorption comparison between lime-treated and untreated corn tortillas?
Lime-treated tortillas have significantly higher calcium absorption.
What is a common dish made from masa, the dough from nixtamalized corn?
Tamales
What is the result of consuming untreated corn as a dietary staple?
It can lead to niacin deficiency and conditions like pellagra.
What are some examples of cultural food adaptations mentioned?
'African' corn ugali, 'Swiss' chocolate, 'Irish' potato, 'Thai' chili peppers, and 'Italian' tomato sauce.
What are the calorically dense plants transferred from the New World to the Old World?
Maize, potatoes, and sweet potatoes.
What was the impact of switching to New World crops in Europe and Africa?
It improved caloric intake and food security.
What is nixtamalization?
A process that softens corn for grinding, allows dough formation, makes niacin bioavailable, adds minerals, and removes aflatoxins.
What are aflatoxins?
Toxins produced by certain molds that can contaminate food and are harmful to health.
What is the United Nations' definition of Indigenous Peoples?
Peoples with historical continuity with pre-colonial societies, distinct social, economic, or political systems, and strong linkages to territories and natural resources.
What are the main Indigenous groups in Canada?
Inuit, First Nations, and Métis.
What characterizes traditional Indigenous food systems?
Systems of harvesting, cultivation, processing, storage, trade, and consumption specific to geographic regions, generally predating industrial agriculture.
What are some disruptions to traditional Indigenous food systems?
Resource extraction, hydro-electric projects, oil and gas extraction, road construction, deforestation, and urbanization.
How did colonization affect Indigenous peoples in Canada?
European diseases devastated communities, colonizers displaced Indigenous people, and assimilation policies disrupted food systems.
What was the impact of bison hunting on Indigenous peoples?
Commercial hunting nearly led to bison extinction, which caused starvation and forced treaties that marginalized Indigenous peoples.
What is the significance of the Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump?
A UNESCO World Heritage Site that preserves over 6,000 years of Plains Buffalo culture.
What were the consequences of the Indian Act of 1876?
Declared First Nations as wards of the state and promoted assimilation policies.
What is the Nutrition Transition among Indigenous peoples?
A shift from traditional food systems to reliance on market foods, leading to health issues like obesity and diabetes.
What are some health risks associated with the Nutrition Transition?
Micronutrient inadequacies, excess intake of sugar, sodium, and saturated fat, leading to various chronic diseases.
How did Sir John A. Macdonald contribute to Indigenous marginalization?
He implemented policies that starved Indigenous peoples to clear land for European settlement.
What is the role of traditional food systems in Indigenous cultures?
They maintain cultural practices and provide nutritional sustenance linked to the land.
What are the differences in nutritional content between venison and beef?
Venison has lower calories and fat compared to beef, which has higher saturated fat content.
What is food sovereignty?
The right of peoples to healthy and culturally appropriate food produced through ecologically sound and sustainable methods.
What are the effects of urbanization on Indigenous food systems?
Destruction of traditional habitats and loss of access to traditional food sources.
Why are healthy environments important for healthy eating?
They support the availability of traditional foods and maintain cultural practices related to food gathering.
What is the significance of seal hunting for the Tlingit First Nations?
It is part of their traditional food gathering practices and cultural identity.
What are the implications of mining on Indigenous lands?
It leads to wastewater and air pollution, further disrupting traditional food systems.
What is the impact of cattle ranching on Indigenous habitats?
It destroys natural habitats and disrupts ecosystems critical for traditional food sources.
What does the term 'marginalization' refer to in the context of Indigenous peoples?
The process by which Indigenous peoples are pushed to the edges of society, losing rights to their lands and resources.
What are the fat-soluble vitamins found in seal fat?
Vitamins A, D, E, and K.
What are the consequences of deforestation on Indigenous food systems?
It destroys forests and disrupts ecosystems, impacting food availability and cultural practices.