Lecture 4 - Social Constructivism and Cultural Differences
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is culture?
meanings, conceptions and interpretive schemes that are activated, constructed or brought on line through participation in normative social institutions and practices, giving shape to the psychological processes in individuals in a society
system of meaning
the idea that cultures are ways of interpreting, understanding and explaining what is going on in the word around us, includes language, rituals, objects with culturally defined meaning
meaning through social participation
appropriate behavior is defined, cued based on culturally defined norms
gives rise to psychological processes
how we think, behave depends on the concepts we have learned and how they relate to eachother
systems of meaning example
cat as a word, consider several objects like the national flag or an autograph by a celebrity, in each case something has a certain meaning or significance in the context of a particular culture’s history and social structure
social participation
you might sit quietly during a symphony but not sit at all during a concert because you learn largely by imitation, you watch what other ppl do and you do the same
jodo
japanese word that includes considerate, motivated, lucky as well as angry, happy, sad and ashamed
semteende
refers to situations in which ppl might feel embarrassment or shame rather than emotion itself
sadness and pea pea
this is a Tahitian word that is used to describe someone who is sick, fatigue or troubled, they don’t have a word for sadness
culture in north america study
they had participants undergo semi structured interviews about what real love means, experiences with romantic love and what makes a relationship good vs bad, etc
culture in north america study results
they found that there were two concepts of love that participants would describe, hollywood love and prosaic love
hollywood love
this is the kind of love that you would see in movies, love at first sight and the concept of the one, it is based on destiny, flashy but shallow,
prosaic love
this concept of love is much more realistic, it is the love that grows slowly over time, you can have many possible partners, based on compatibility, it is deep, sure and lasting, it grows slowly over time, it revolves around personality, social connections and activities rather than overcoming obstacles
litost
comes from czech and it describes a state of torment caused by a sudden insight into one’s own miserable self
schadenfreude
this is a german word that describes the feeling of enjoying another person’s suffering
liget
it is like anger but its a positive, socially encouraged response to insult or injury, could be a successful hunt, celebrations or death of a loved one
amae
this is a japanese word that means pleasurable dependence on another person, license to be childlike
abhiman
it describes a combination of pride and hurt or self respect, it arises when someone feels unappreciated or slighted by someone close to them
display rules
certain social rules that we always follow, when in how one is appropriately allowed to display certain emotions
hypercognized emotions
they are emphasized in a culture, become objects of discussion and has elaborate cognitive structure usually seen with rich vocabularies, important for culture, distinctions lead to increased vocabulary
hypocognized emotions
underemphasized in a society, limited cognitive structures, there are few words for it, those for which a culture and language have little cognitive elaboration or detail
the sapir whorf hypothesis
this is the proposal that humans require language to think and therefore only have those experiences, thoughts and perceptions for which they have words, it implies that people should not be able to experience emotions for which their language has no word
sapir whorf hypothesis (strong form)
this is the idea that language completely determines thought and perception
sapir whorf hypothesis (weak form)
this is the idea that people might more readily experience or express an emotion for which they have a word than one for which they lack a word, language influences thought and percepton but it does not determine them (more supported form)
language and emotion concepts study
showed participants two different photos, one was the classic display of embarrassment and the other was the classic display of shame
language and emotion concepts study (results)
they found that americans could differentiate between the two types of photos but oriya speakers used one word (lajya) to describe both expressions, when the oriya ppl explained the situations that’s when they were able to distinguish between the two expressions showing that even without distinct words for emotions, ppl can still differentiate between emotional experiences based on context
individualism
cultural emphasis on individual uniqueness, personal rights, being true to one’s self, independence from others
collectivism
cultural emphasis on prioritizing group over individual, deference, social harmony and interdependence
individualism vs collectivism study
they had US and chinese students describe the behavior of these fish and found that americans would say the fish on the right is leading the others (individualism) but the chinese students would say the group of fish is chasing the one on the right (collectivism)
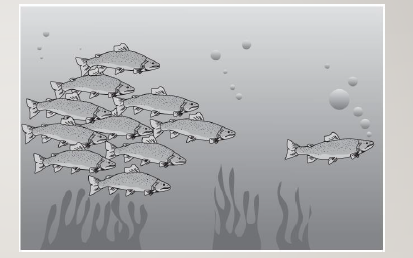
individualism/collectivism and emotion study
the premise was that the self in collectivist cultures is more defined by close others than it is in individualist cultures, they had participants read a scenario in which self or a family member is accepted into a prestigious university or is caught cheating on an exam, they then measured rating of pride, shame and guilt
individualism/collectivism and emotion study (results)
they found that for the prestigious university university the americans were equally proud of self or child but the chinese were prouder of the child, for the cheating scenario both groups said they felt more shame, guilt if they were the ones who were caught rather than a close relative but chinese reported more shame, guilt in both conditions, especially the brother, this shows that for the chinese they had stronger emotional responses to close others’ actions and outcomes
vertical society
this is the idea that people attend closely to social hierarchy, encouraging emotions and behaviors that respect status differences
horizontal society
this is the idea that people minimize attention to status differences, seldom acknowledging status differences publicly
power distance and emotion study
they had olympic judo competitors and measured their display of pride, dominance when they won/lost a medal, they found that competitors from more vertical cultures showed more dominance after winning a medal but there was no effect of power difference on behavior after losing
epistemology and emotion study
the researchers investigated whether asian americans experiences more mixed emotions than european americans, they found that european americans expressed more love and negative emotions but there was no correlation for asian americans showing that european americans tend to experience love and negative emotions seperately while aisan americans experience it at the same time (linear vs dialectical way of thinking)
methodological considerations
most studies of culture and emotion have compared people in two countries or ppl of two ethnicities within one country, this presents limitations like most research has compared ppl in the US or canada with another country (china or japan), cultures dont always follow national boundaries, it may influence how ppl interpret, use rating scales in questionnaires, same number might have dif meaning and studying group differences is not the same as studying culture
culture of honor
reputation for strength, self reliance, pride toughness are important for social standing, self protection, this is common in herding economies with sparse law enforcement
culture of honor and anger study
a man is bumped and verbally insulted by a confederate in hallway or the confederate walks by, they measured rater-observed anger, hormones cortisol, testosterone and dominant behavior
culture of honor and anger study (results)
they found that there was no difference in the no bump condition but southern men were more polite, less dominant and aggressive, implying that aggressive responses to insults may be heightened in cultures where self protection has historically required strong assertion of dominance
neurocultural theory of emotion
if you are angry then you will show emotion but you have display rules to control your behavior to be socially acceptable, display rules dictate how your emotions should be displayed in social contexts
socially constructed scripts theory
emotions are cultural beliefs about what events, thoughts, feelings and behaviors are supposed to go together in an episode of experience, some reflect universal, biological human nature while others are culturally learned, psychologically constructed, especially perceived causes of emotion and emotional behaviors
levels of analysis theory
emotions have functions at many levels of analysis and some are universal while others are culturally variable (intraindividual, dyadic, small groups and culture), intraindividual and dyadic are universal while small groups and culture are culturally variable
intraindividual
helps the individual survive and reproduce
dyadic
supports relationships
small groups
helps negotiate group members’ social roles
culture (levels of analysis theory)
emotional stories are used to teach cultural values
open ended attribution (priming study)
same as the fish study but the participants had to write explanations and results showed that american priming caused them to explain with more internal attributes but with chinese priming it was more external attributions
boy breaking diet story (priming study)
had to explain why a boy eats cake against doctor’s advice, they found that with american priming they attributed it to personality/self control failure but with chinese priming it was attributed to peer/social pressure and with controls it was a mix between the two