Cartilage and Bone
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What are the main cellular components of cartilage?
Chondroblasts (immature), chondrocytes (mature in lacunae), and mesenchymal stem cells (in perichondrium).
What are the main extracellular components of cartilage?
Ground substance (GAGs, proteoglycans), collagen (type II or I), elastin, and chondronectin.
What is the function of chondronectin?
Mediates adherence of chondrocytes to the extracellular matrix.
What type of collagen is found in all cartilage types?
Type II collagen.
Which types of cartilage contain type I collagen?
Fibrocartilage (also contains type II).
What is the perichondrium?
A dense connective tissue layer surrounding cartilage (except articular hyaline and fibrocartilage); has outer fibrous and inner cellular layers.
What is the nutrient source for cartilage?
Diffusion from surrounding tissues; cartilage is avascular.
What are the two types of cartilage growth?
Interstitial (from within) and appositional (from perichondrium).
Which types of cartilage lack a perichondrium?
Articular hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage.
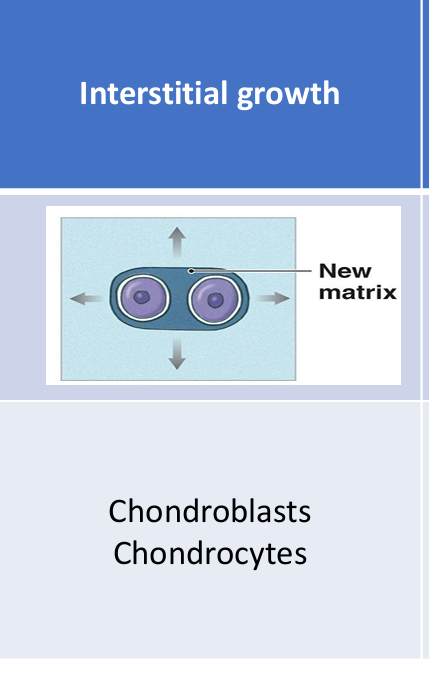
What is interstitial growth?
Chondrocytes divide within lacunae and secrete matrix, expanding cartilage from within.

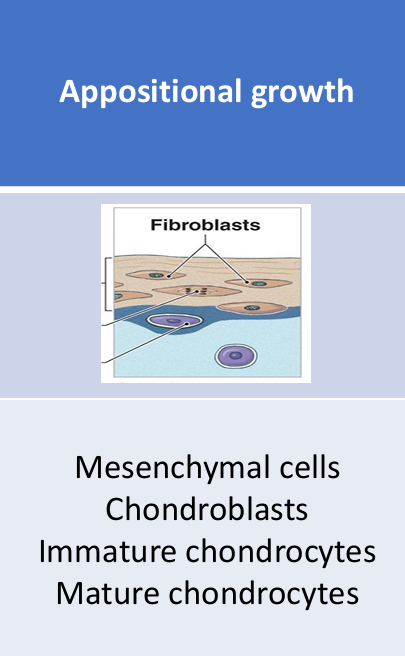
What is appositional growth?
Mesenchymal cells in the perichondrium differentiate into chondroblasts, which secrete matrix at the surface.

Why can't fibrocartilage undergo appositional growth?
It lacks a perichondrium.
What are the three types of cartilage? CHEF
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage.
What is the function of hyaline cartilage?
Provides stiff but flexible support; reduces friction between bones.
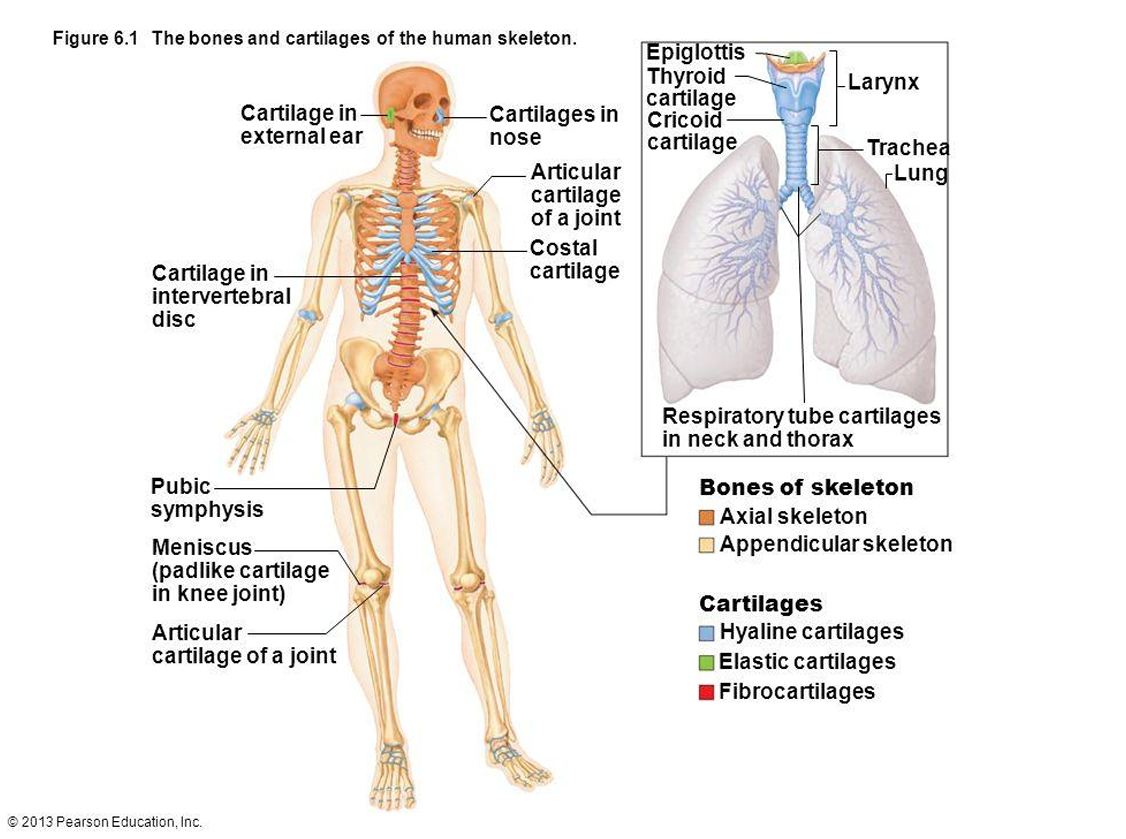
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Synovial joints, trachea, bronchi, nasal septum, costal cartilage.

What is the function of elastic cartilage?
Provides flexible support; tolerates distortion and returns to shape.
Where is elastic cartilage found?
External ear, epiglottis.
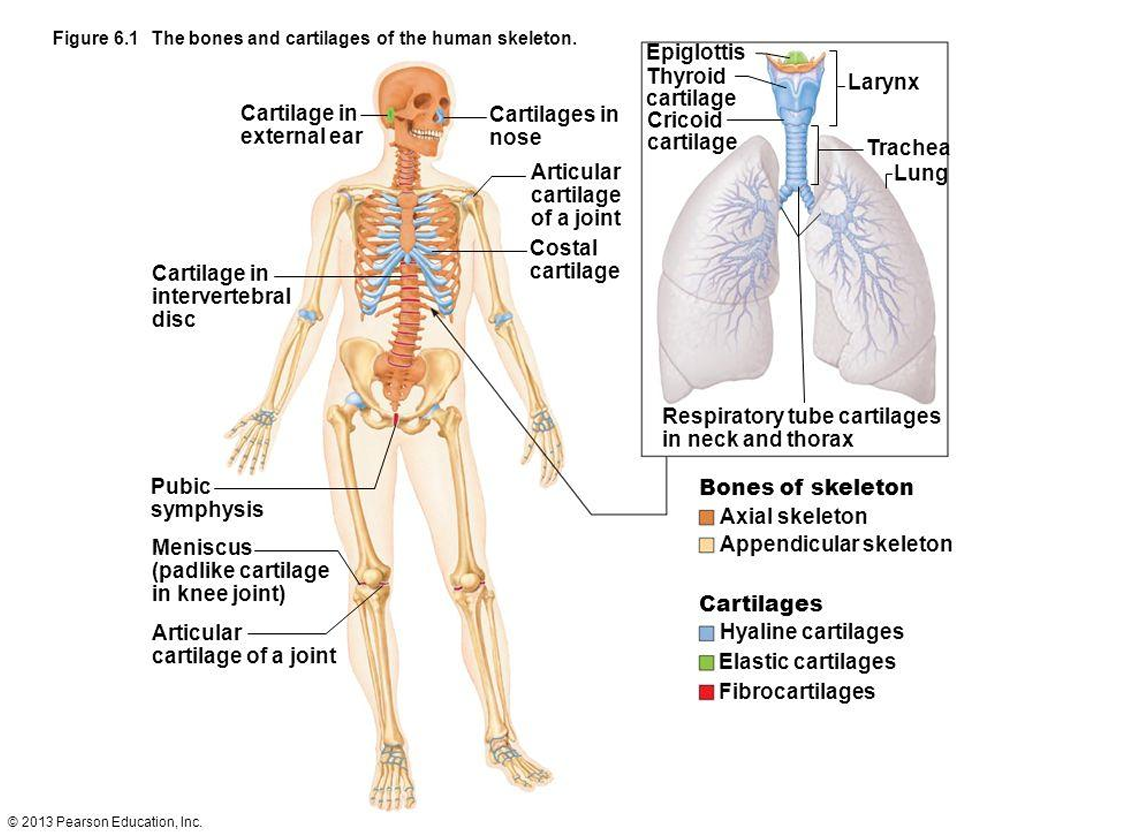

What is the function of fibrocartilage?
Resists compression, prevents bone-to-bone contact, limits movement.
Where is fibrocartilage found?
Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, menisci.
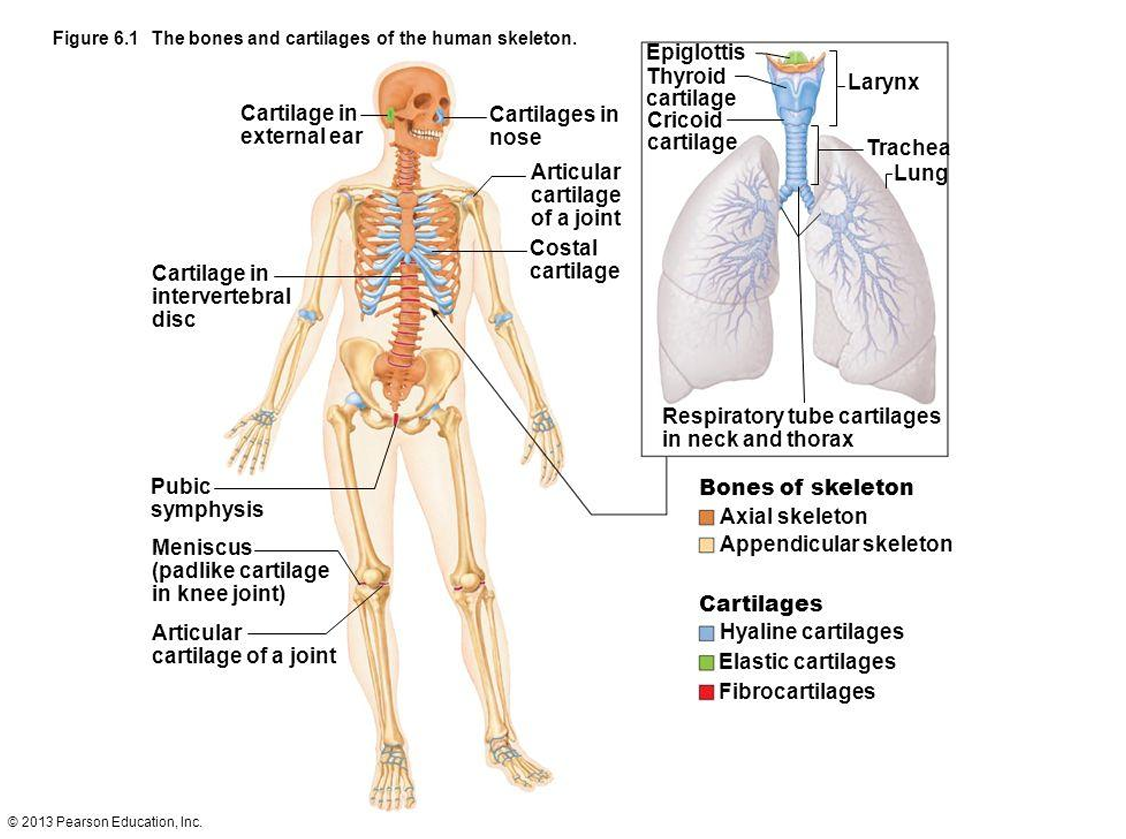

Which cartilage types have a perichondrium?
Hyaline (except articular) and elastic cartilage.
Which cartilage types have both interstitial and appositional growth?
Hyaline and elastic cartilage.
Which cartilage type has only interstitial growth?
Fibrocartilage.
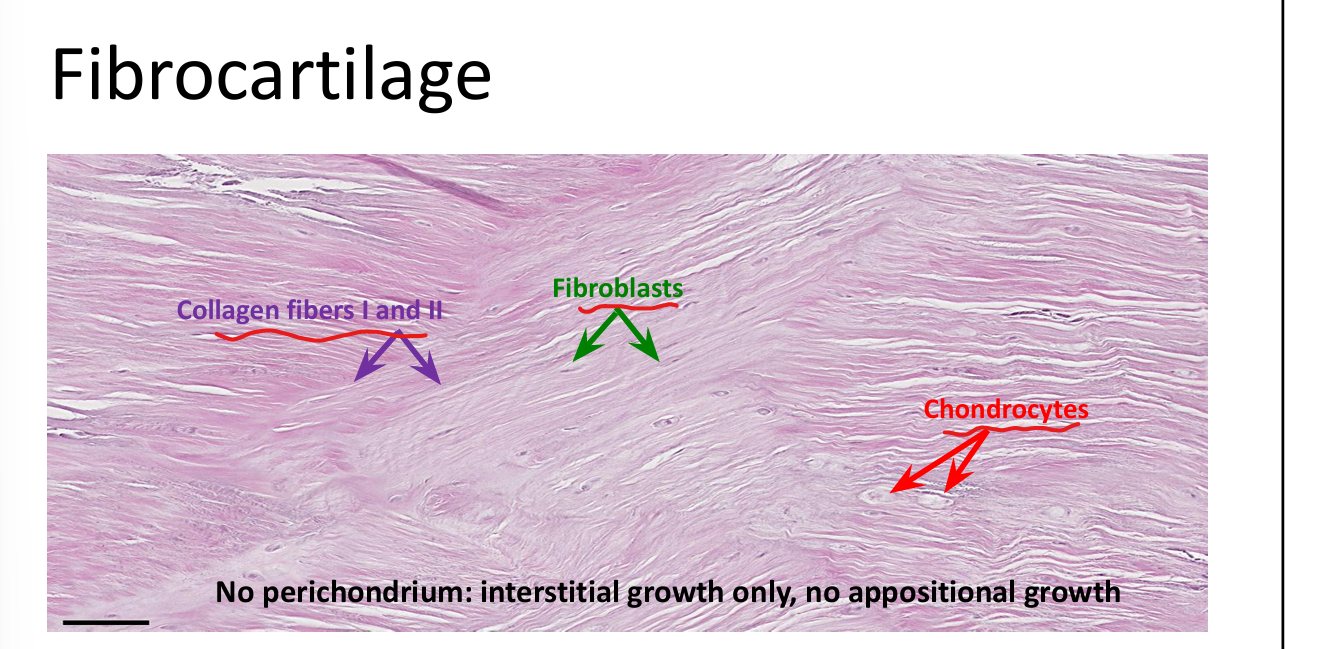

What are the major cells in hyaline and elastic cartilage?
Chondroblasts and chondrocytes.
What are the major cells in fibrocartilage?
Chondrocytes and fibroblasts.
What is the ECM composition of hyaline cartilage?
Type II collagen, high water content, glassy matrix.
What is the ECM composition of elastic cartilage?
Type II collagen and elastic fibers.
What is the ECM composition of fibrocartilage?
Type I and II collagen, dense fibrous matrix.
What are the four types of bone cells?
Osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts.
What is the function of osteoprogenitor cells?
Stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts; found in periosteum and endosteum.
What is the function of osteoblasts?
Build bone by secreting osteoid (type I collagen and matrix proteins); found on bone surfaces.
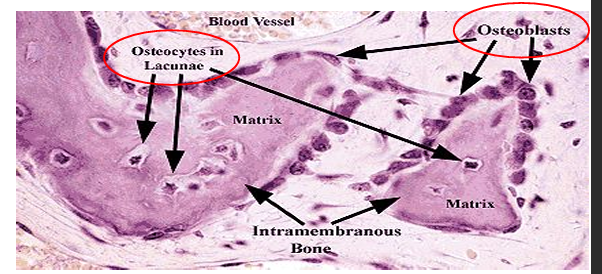

What is osteoid?
Unmineralized bone matrix secreted by osteoblasts.
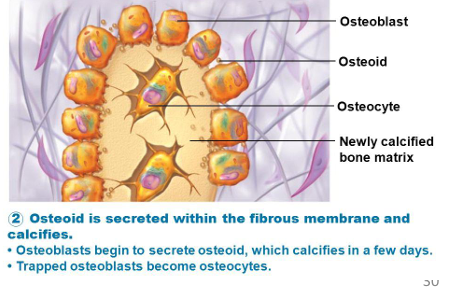

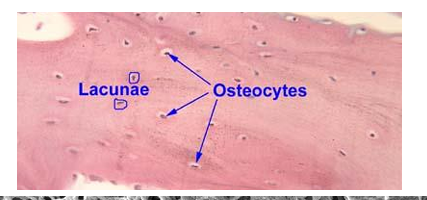
What is the function of osteocytes?
Mature bone cells in lacunae; maintain matrix and communicate via canaliculi.

What is the function of osteoclasts?
Large multinucleated cells that resorb bone by secreting acids and collagenases. Located at the edge of bone matrix
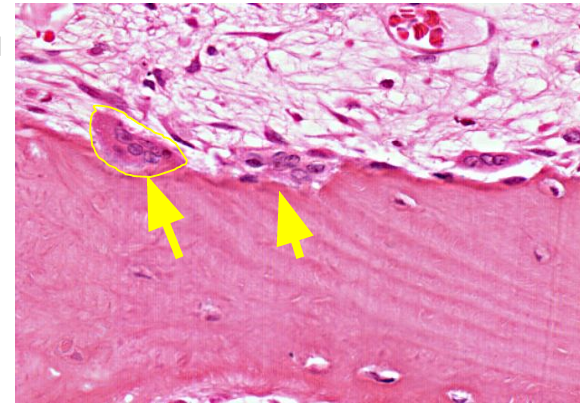

What is the origin of osteoclasts?
Fusion of bone marrow–derived monocytes (macrophage lineage).
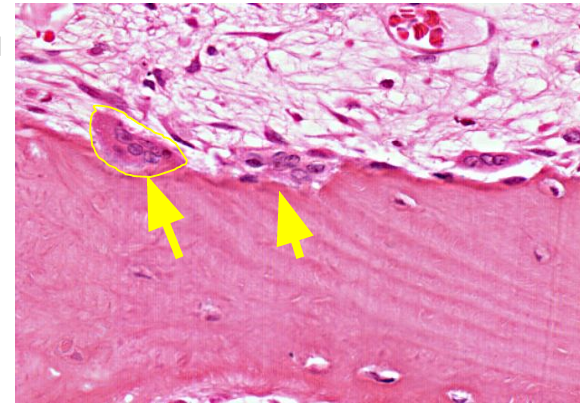

What hormone activates osteoclasts?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH); increases bone resorption and blood calcium.
When does an osteoblast become an osteocyte?
When it becomes encased in bone matrix.
Where is the periosteum located?
Outer surface of bone; has fibrous outer layer and cellular inner layer.
Where is the endosteum located?
Lines medullary cavity, trabeculae of spongy bone, and central canals of osteons.
What is the function of the periosteum?
Protects bone, provides vascular and nerve supply, assists in growth and repair.
What is the function of the endosteum?
Active in bone growth and repair; contains osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoprogenitor cells.
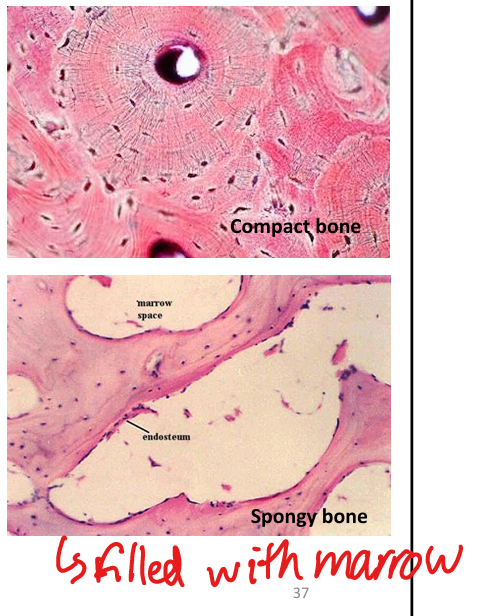
What are the two types of bone tissue?
Compact (dense) and spongy (cancellous).

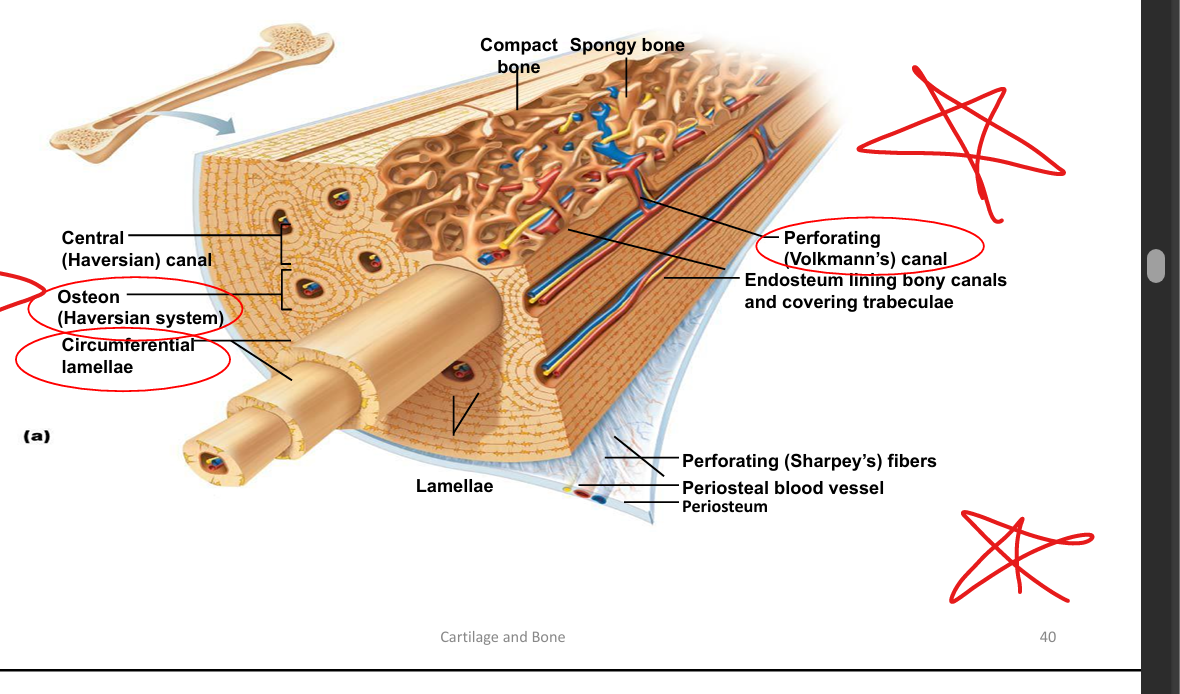
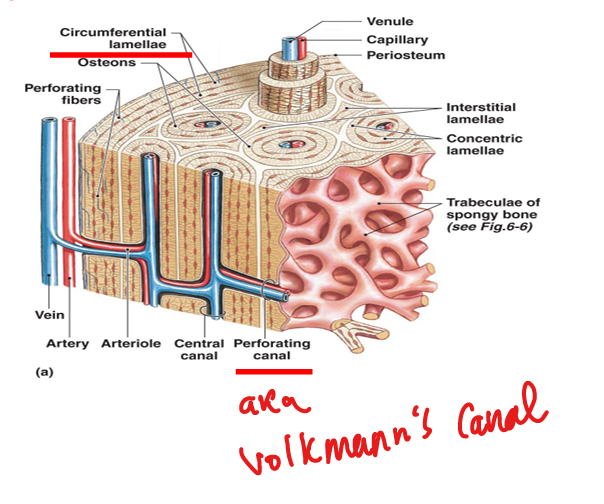
What is the basic unit of compact bone?
Osteon (Haversian system): concentric lamellae around a central canal.
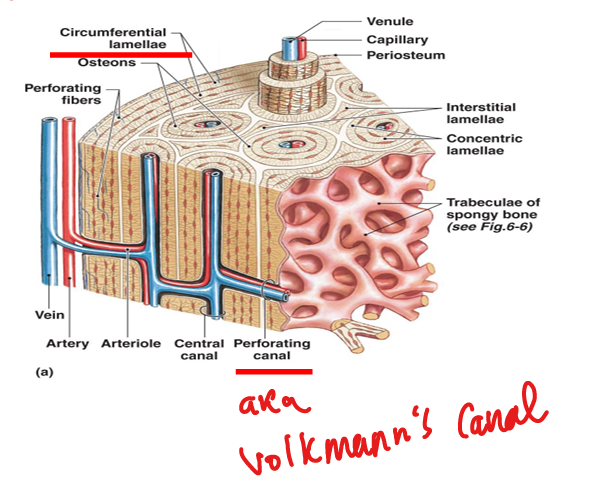

What are Volkmann’s canals?
Perforating canals that connect osteons and carry blood vessels from periosteum.

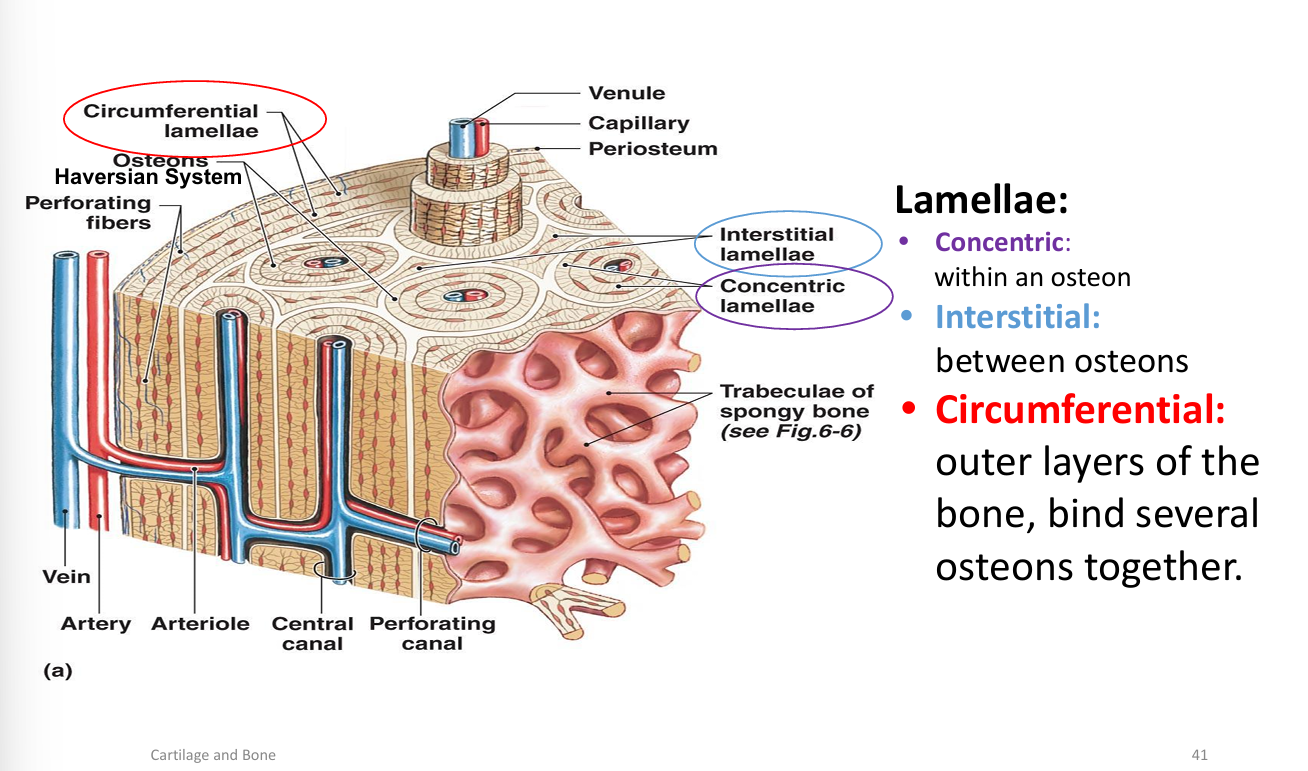
What are the three types of lamellae in compact bone?
Concentric (within osteons), interstitial (between osteons), circumferential (outer layers).

What is the structure of spongy (cancellous) bone?
Trabeculae with marrow spaces; no osteons; lined by endosteum.
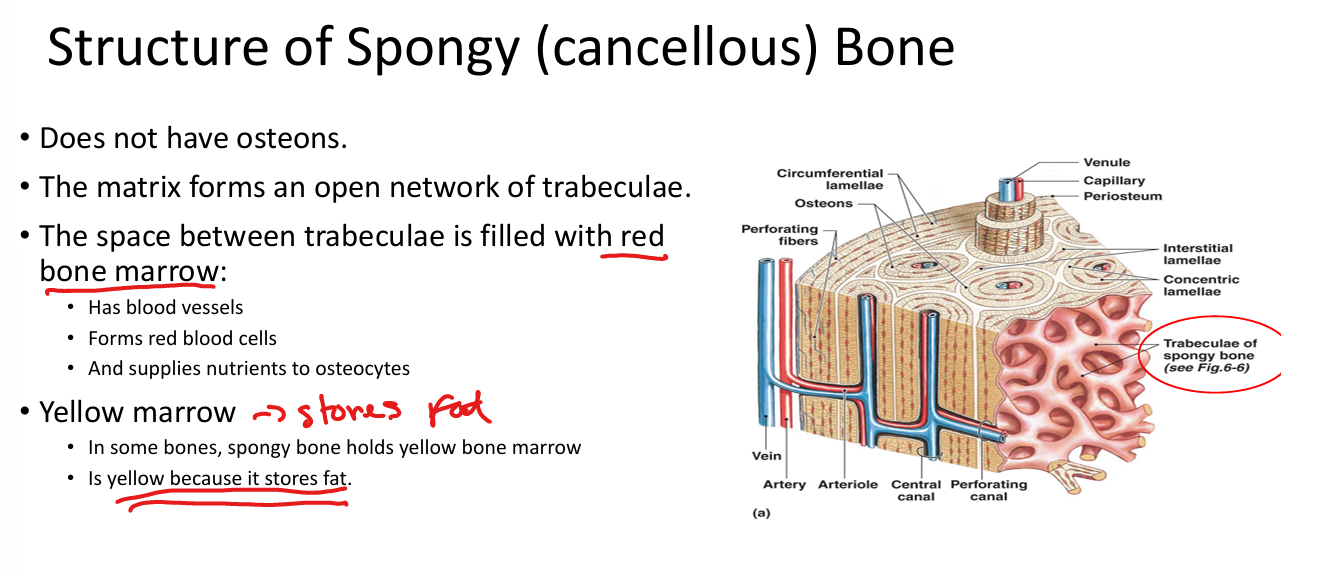

What fills the spaces in spongy bone?
Red marrow (hematopoiesis) or yellow marrow (fat storage).
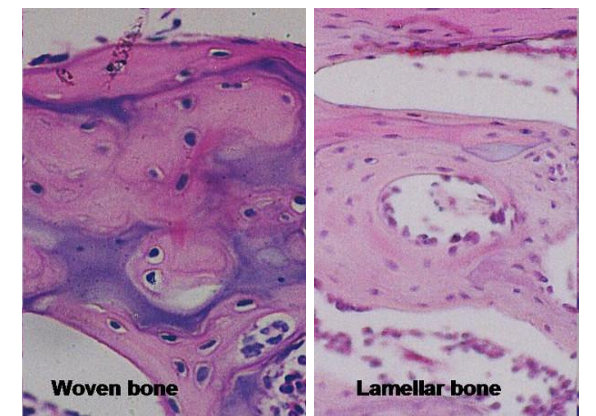
What is woven bone?
Immature bone with randomly arranged collagen; remodeled into lamellar bone.
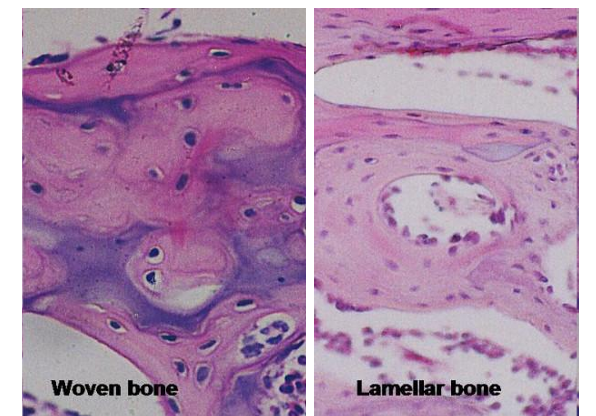

What is lamellar bone?
Mature bone with organized parallel collagen bundles.

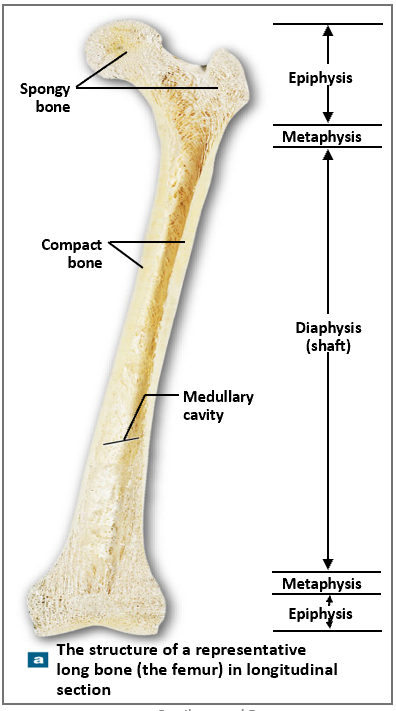
Where is compact bone located in long bones?
Diaphysis (shaft); thickest where stress is greatest.
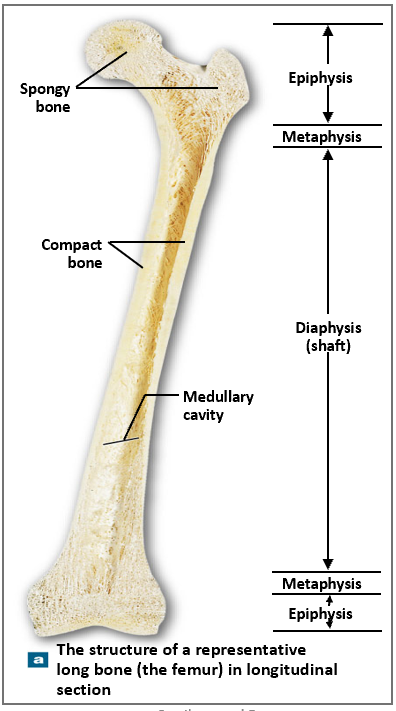

Where is spongy bone located in long bones?
Epiphyses and lining medullary cavity.

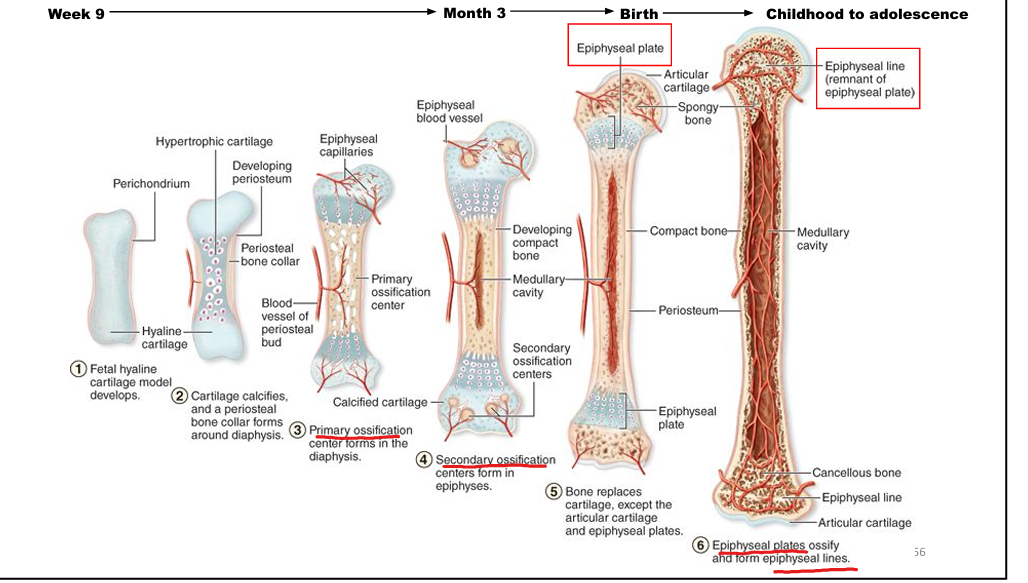
What is endochondral ossification?
Bone formation from a hyaline cartilage model; forms most bones.

What is intramembranous ossification?
Bone formation directly from mesenchymal tissue; forms flat bones (e.g., skull, clavicle).
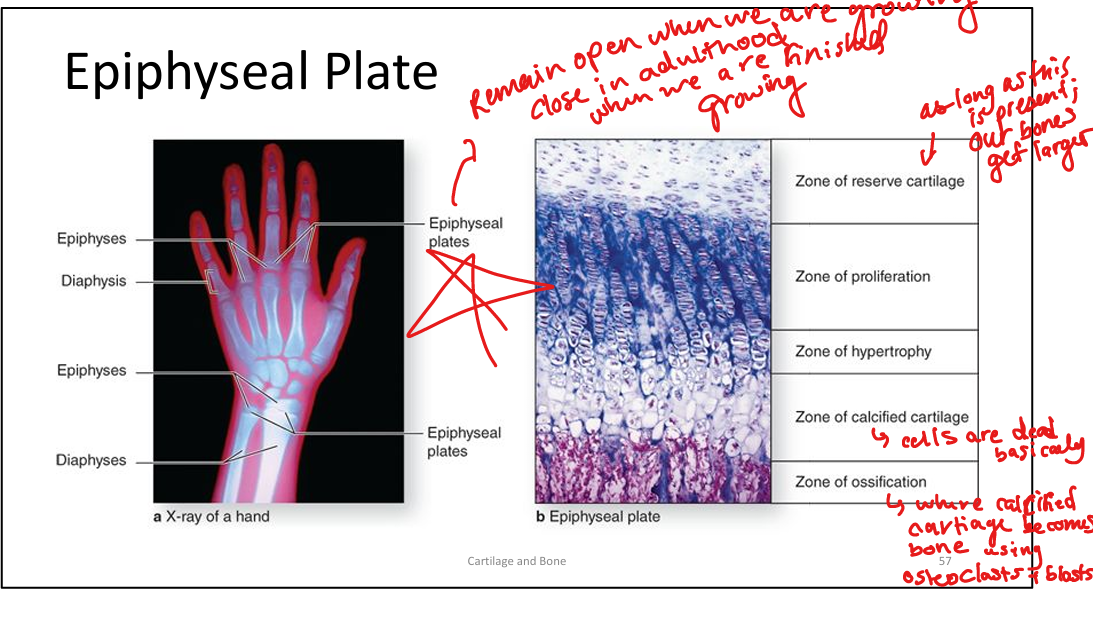
What are the zones of the epiphyseal plate? RPHCO>reserve pro hyper call ossi’s
Reserve cartilage, proliferation, hypertrophy, calcification, ossification.

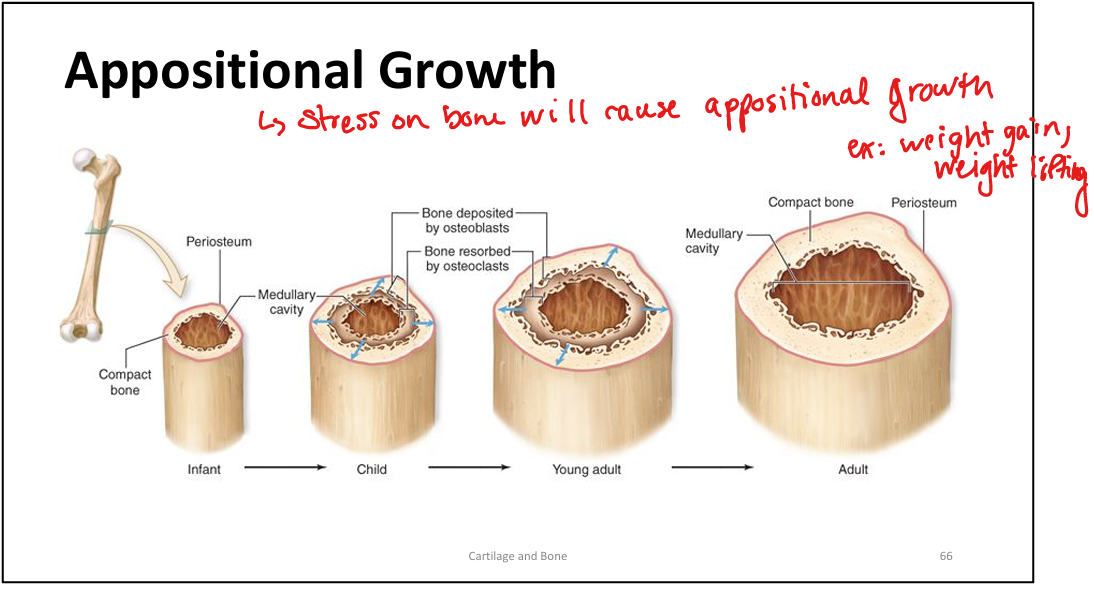
What is appositional growth in bone?
Bone growth in diameter via osteoblasts in periosteum.

What are the three regions of a long bone?
Epiphysis (ends), metaphysis (growth zone), diaphysis (shaft).

Is bone vascularized and innervated?
Yes; blood vessels enter via nutrient foramina and Volkmann’s canals; sensory nerves innervate periosteum and endosteum.
What vitamins are essential for bone health?
Vitamin A (osteoblasts), B12 (protein synthesis), C (collagen), D (calcium absorption), K (protein synthesis).
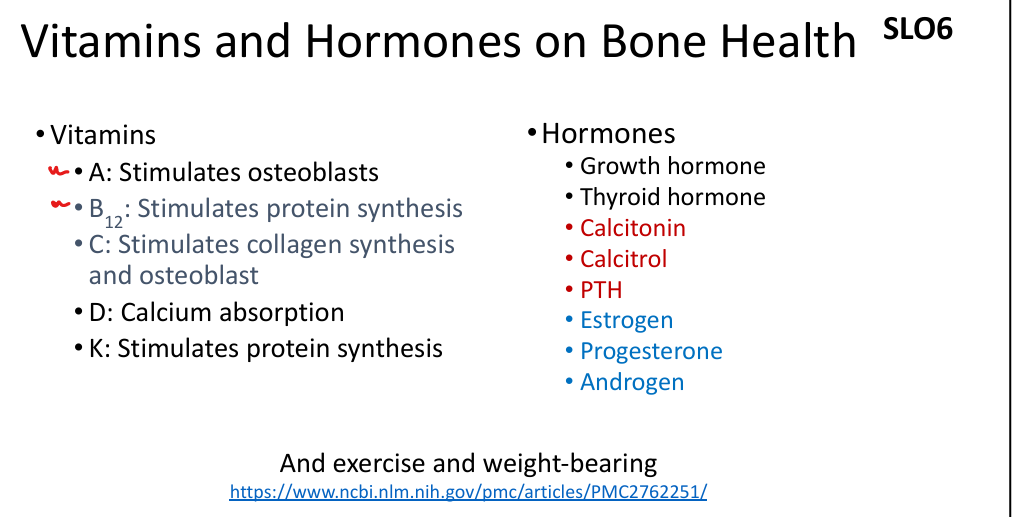

What hormones regulate bone metabolism?
PTH (↑ resorption), calcitonin (↓ resorption), calcitriol (↑ Ca²⁺ absorption), estrogen (↓ osteoclast activity).
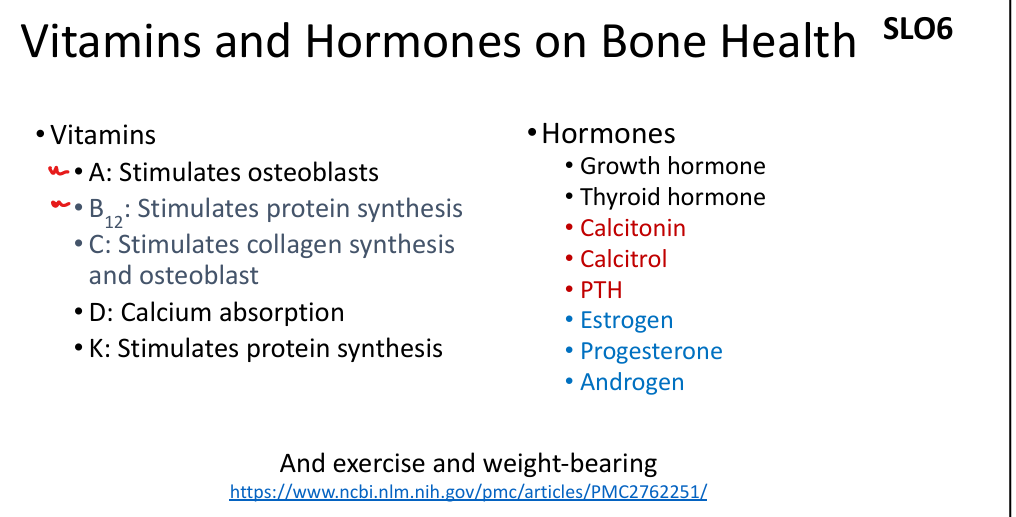

What is the effect of estrogen on bone?
Inhibits osteoclasts, promotes osteoblast survival; deficiency leads to osteoporosis.
What is the role of calcitriol?
Active vitamin D; increases calcium absorption in intestines.
What is the function of calcitonin?
Produced by thyroid C cells; inhibits osteoclasts, lowers blood calcium.
What is the function of PTH?
Produced by parathyroid glands; stimulates osteoclasts, increases blood calcium.
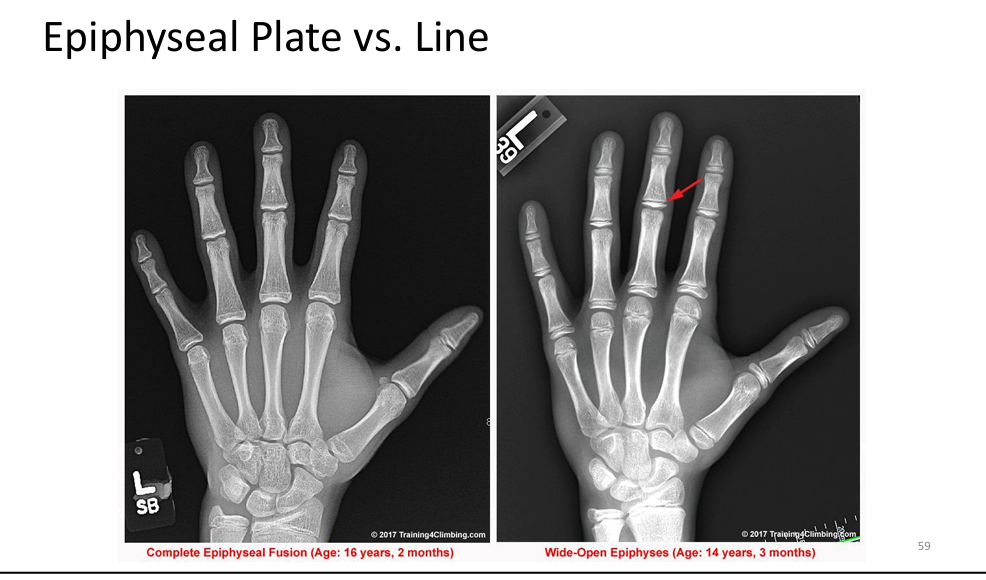
What is the difference between an epiphyseal plate and line?
Plate: active growth zone in children; Line: remnant after growth ends.

Compare cartilage and bone: vascularity, strength, repair.
Cartilage: avascular, flexible, limited repair. Bone: vascular, strong, extensive repair.
Know Me