IB DT: Topic 4.e: Textiles
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://sites.google.com/view/designandinquiry/dp-sl-design/topic-4-final-production/4-2-materials/4-2e-textiles?authuser=0
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
diagram of different textile origins
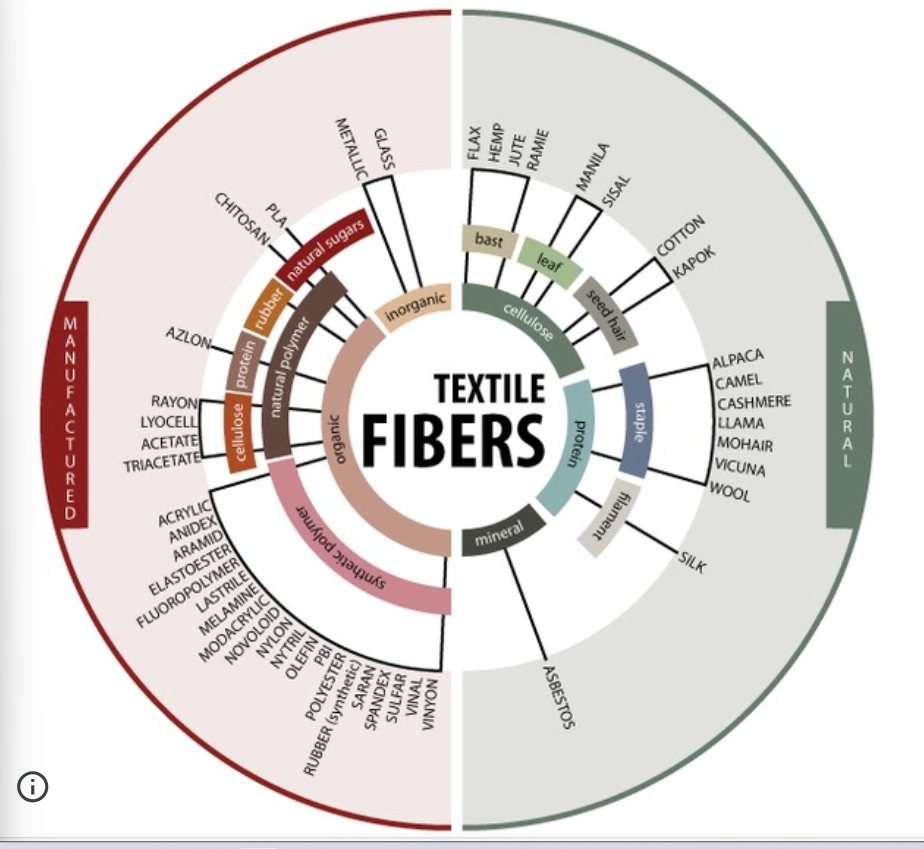
what is a fibre?
the raw form, used in the manufacture of other materials, called composites. can be processed into long forms called yarns.
what is a yarn?
a long, continuous fibre
what is a thread?
thin yarns used in sewing
what is fabric?
created by cloth produced by weaving, knitting or felting
what are the two types of textiles?
natural fibre or synthetic fibre
what are the properties of natural fibre textiles?
high absorbency
low tensile strength
low elasticity
burns but doesn’t melt
what are the properties of synthetic fibre textiles?
low absorbency
high tensile strength
high elasticity
burns and melts
what is wool and what are its properties?
originates from sheep
commonly used in clothing such as socks and suits
highly insulative
highly durable
highly absorbent
what is cotton and what are its properties?
the most common natural fibre, made from the cotton plant
highly absorbent
high tensile strength
durable
retains colour well
what is silk and what are its properties?
natural fibre made from silk cocoon
the strongest of all natural fibres
thermal properties make it cool in summer and warm in winter
very smooth and light to the touch
strength means it has medicinal uses such as stiches
what is nylon and what are its properties?
synthetic fibre derived from petrochemicals
good abrasion resistance
low absorbance
high elasticity
ideal for mass production
what is polyester and what are its properties?
versatile fabric that is strong, quick drying, resistant to scratching, resists mould and stains
synthetic and derived from petrochemicals
what is lycra and what are its properties?
synthetic fibre derived from petrochemicals
very highly elastic
what is a natural fibre?
materials produced by plants or animals that can be spun into a thread, rope or filament
what is a synthetic fibre?
materials made from man-made materials that are spun into thread - the joining of monomers and polymers through polymerisation
how are natural fibres converted from fibres to yarns?
yarn spinning
hand spinning: pre-industrial revolution, people made yarns by using a tool called a carder to align parallel the yarns before twisting
machine spinning
how are synthetic fibres converted to yarns?
most synthetic fibres are known as filament fibres - they are so long that they work as yarn themselves.
what is weaving?
the process of interlocking yarns at right angles to create a fabric
what is knitting?
the process of manipulating yarn in multiple lines to create a tube
what is lace making?
the weaving of yarns and threads into delicate, open patterns
what is felting?
the process of creating a fabric by compressing and matting fibres together. felted fabrics can be quite dense as the fibres are laid down in random, densely packed natures. (made from natural wool and synthetic fibres)
how are textiles recovered/disposed of? are they sustainable?
recyclable
donatable
however, the textile making process is energy and resource intensive.
what ethical considerations come with textile production?
labour intensive and poor working conditions: most raw material production and textile manufacturing takes place in developing countries, using low-skilled labour and under poor working conditions
treatment and genetic modification of plants and animals: the genome of goats has been modified by scientists to produce the same silk protein
what are the environmental considerations that come with textile production?
chemicals and pesticides used in production of natural fibres like cotton have a huge environmental impact
most synthetic fibres are oil based
cotton requires loads of water to grow
dying textiles relies on a range of chemicals and energy intensive processes - poor regulation means that toxic chemicals are released into the environment
large carbon footprint associated with transportation
regular cleaning of textiles requires lots of water, cleaning chemicals and energy