Atomic structure - Topic 1.2 - Definitions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Relative isotopic mass (RIM)
The mass of an atom of an isotope of an element relative to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Relative atomic mass (RAM)
The average (weighted mean) mass of an atom of an element relative to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Relative formula mass (RFM)
The average (weighted mean) mass of a formula unit relative to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Relative Molecular Mass (RMM))
The average (weighted mean) mass of a molecule relative to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Mass spectrometer
A machine that allows us to work out RAMs and isotopic abundances for elements
Orbital
A region in an atom that can hold up to two electrons with opposite spin
Principal quantum numbers/shell or energy levels
The shell
Ground state
An electronic configuration in which all the electrons are in the lowest available energy levels
First ionisation energy
The energy required to convert one mole of gaseous atoms into gaseous ions with a single positive charge
Second ionisation energy
The energy required to convert one mole of gaseous ions with a single positive charge into gaseous ions with a double positive charge
Across the period
e- is removed from the same shell
Increased in number of protons “ e- are held more tightly “ IE increases
Down a group
more shielding due to more shells
The e- removed is further from the nucleus “ further from the protons “ is not feeling the positive charge as much “ easier to remove. Ionisation energy decreases
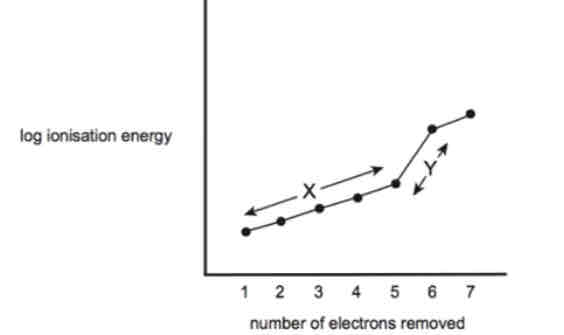
Region x explanation
As you remove e- , the proton to e- ratio is increasing so there is a higher effective nuclear charge. This hold the remaining electrons more strongly, making them harder to extract
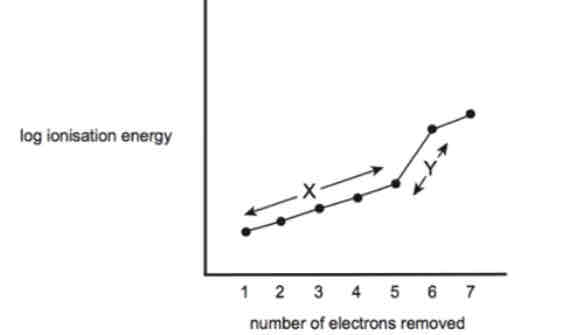
Region Y explanation
The e- is being removed from a full shell(that is stable) that is closer to the nucleus and experiences no (this is because it is in the inner shell but if its not the inner shell stay less) shielding
Dip between be and b
In Be you are removing an e- from a full 2s² orbital
In B you are removing from a 2p^1 which doesn’t have that stability, the electron is also further from the nucleus “ easier to remove “ B has a lower 1st IE than Be
Trend across the period is that IE increase across a period
Dip between nitrogen and oxygen
N has a half filled 2p sub shell that’s giving it extra stability O doesn’t has it so “ the IE decreases
High Ne energy explanation
Ne has a full 2nd shell
Big dip between Ne and Na
The electron you are removing from Na is from the 3s^1 sub shell which is even further from the nucleus and has more shielding “ easier to remove than Ne