Glomerular fitration (urine formation) T2 W9
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Glomerular filtration
Process in which high blood pressure forces fluids and solutes through a filtering membrane.
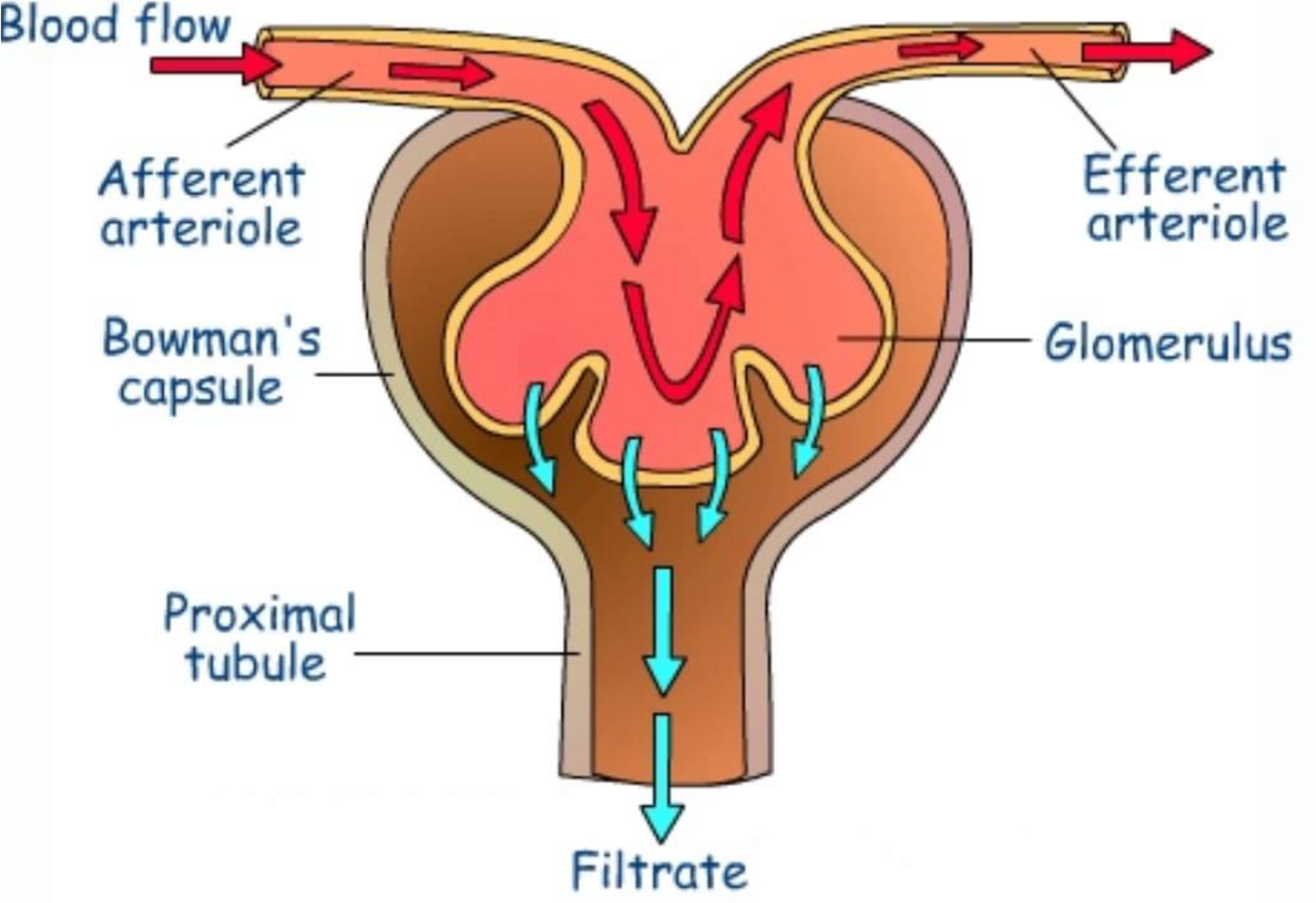
Where does glomerular filtration process occur
The process takes place in the renal corpuscle, as fluid moves from the glomerulus to the glomerular capsule.
What makes glomerular capillaries exceptionally permeable and why is it needed
They have many pores allowing for large amounts of fluid to pass from the blood into the glomerular capsule.
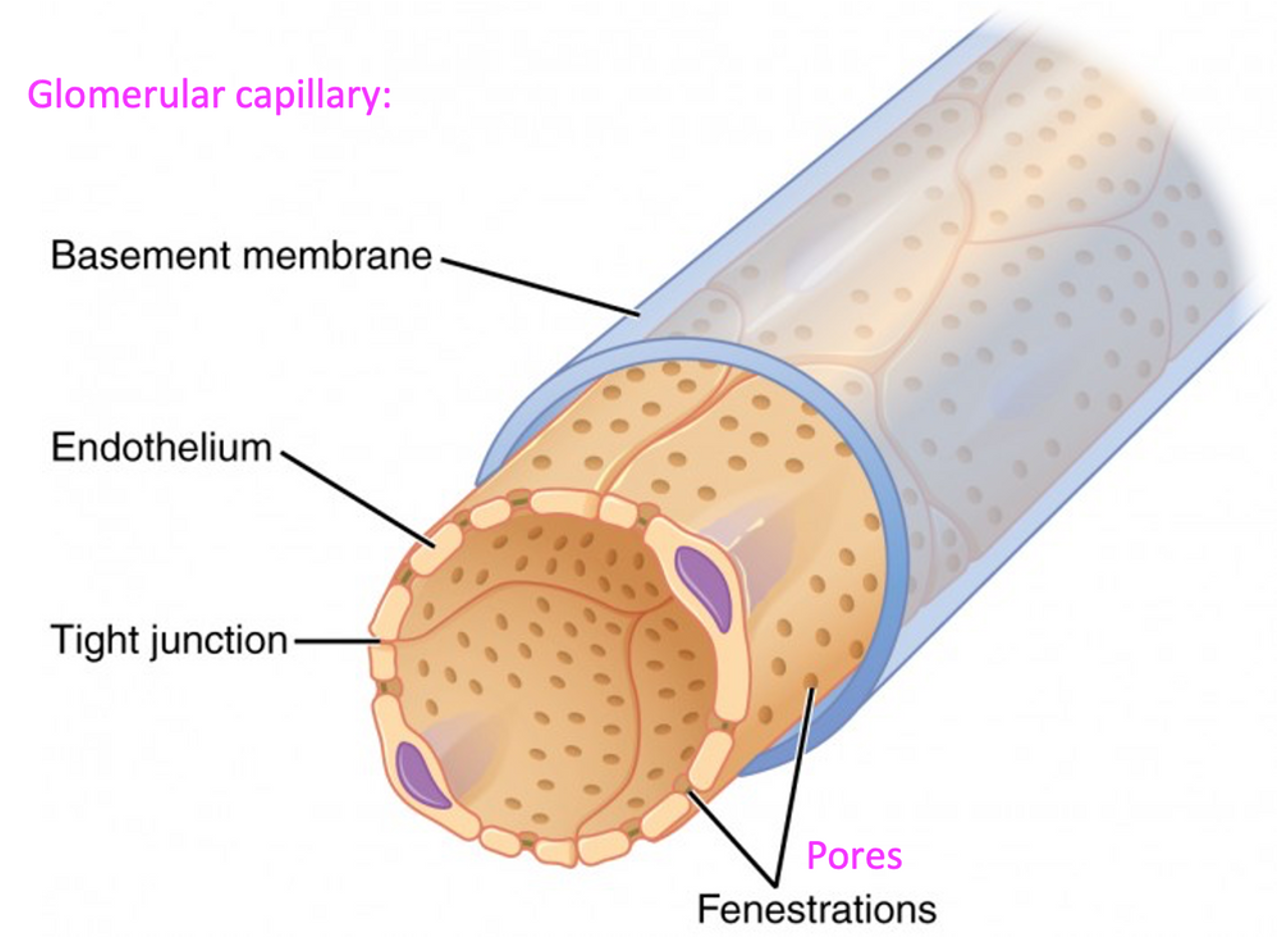
Glomerular capsule internal layer
Internal layer is made of epithelial cells that cling to the glomerular capillaries, forming a thin surface. The epithelial cells have openings that allow the filtered fluid from the blood to enter the capsular space insider the glomerular capsule. This fluid is now called a filtrate
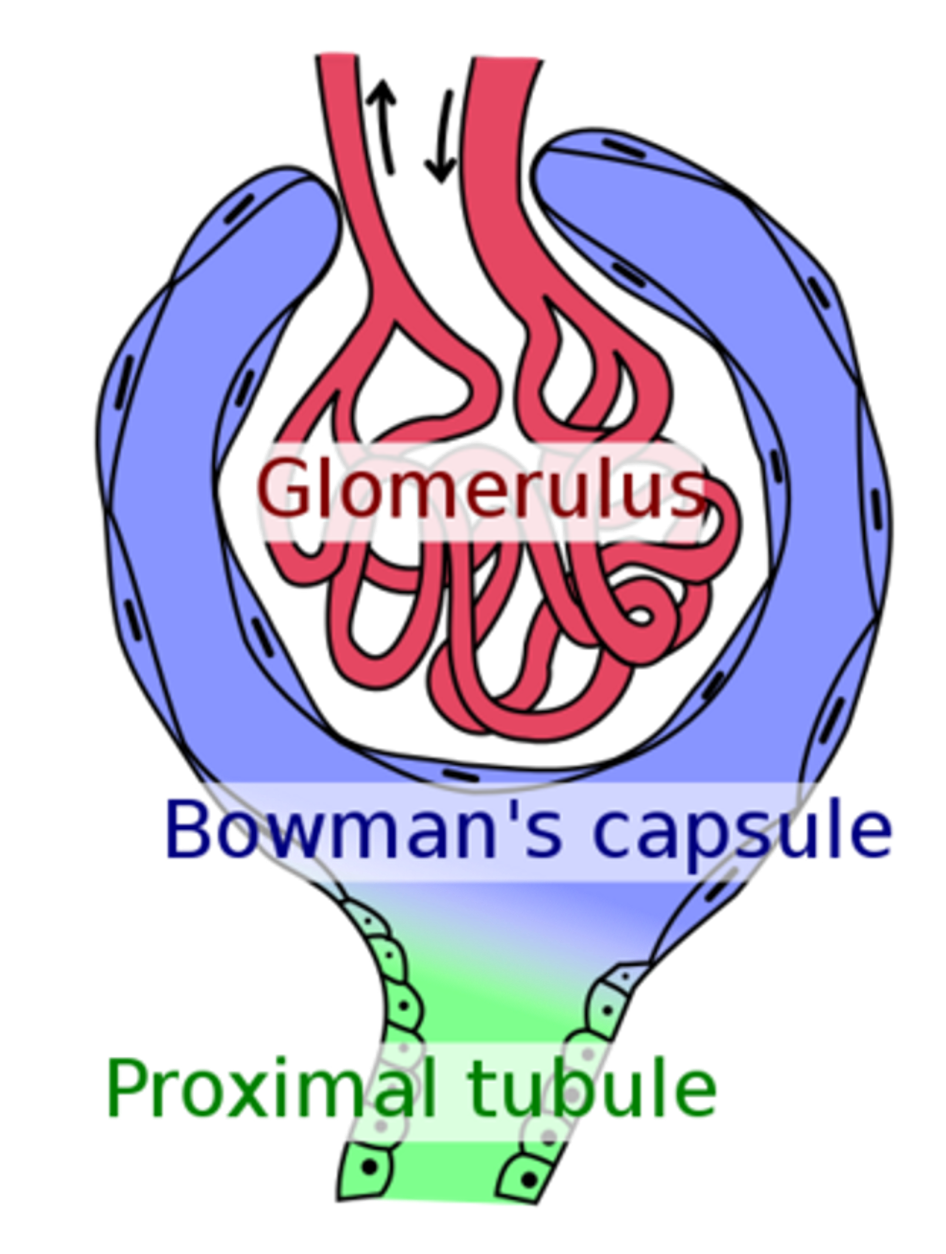
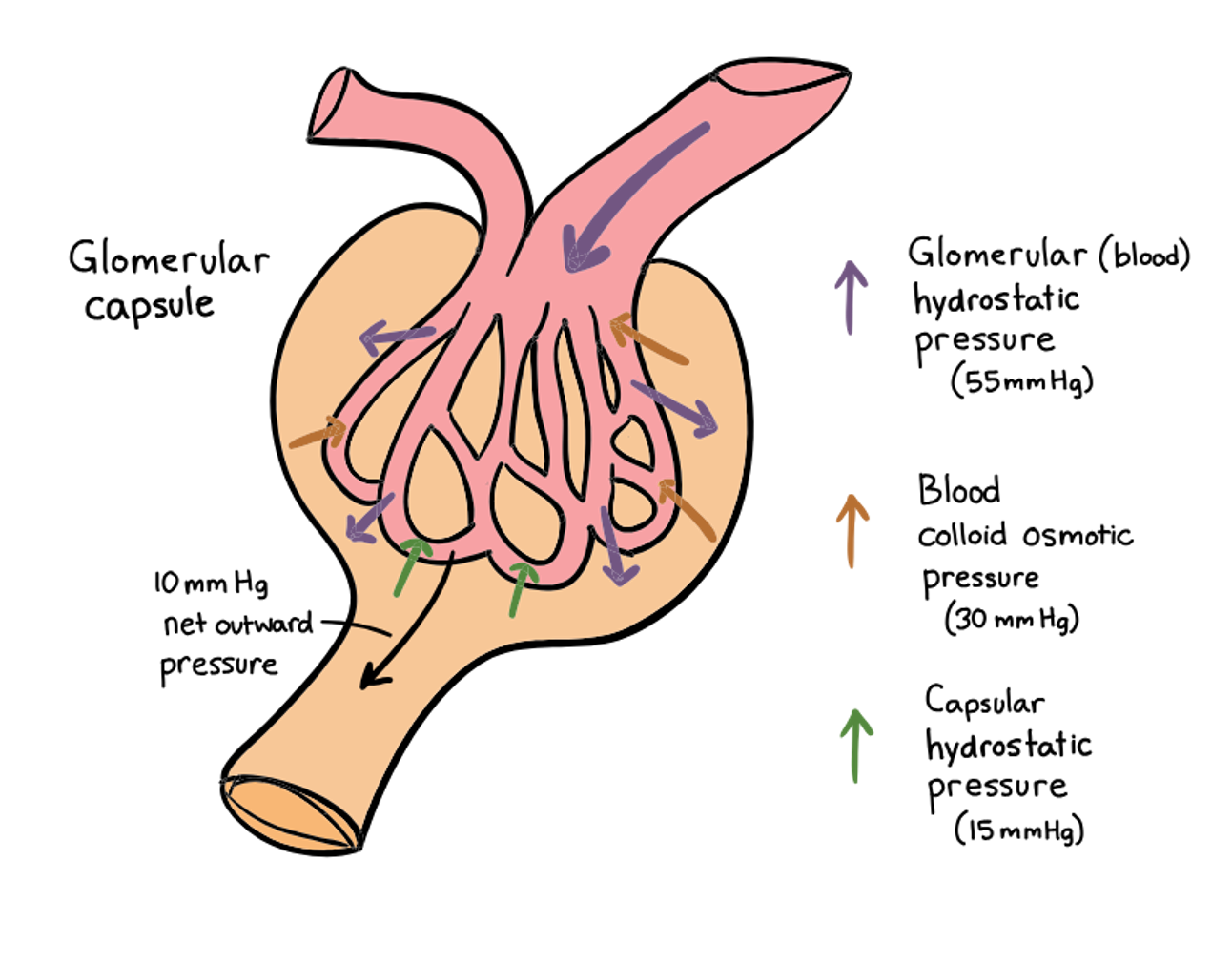
Why does glomerulus have high blood pressure
Promotes filtrate formation (hydrostatic pressure)
The blood pressure in the glomerulus is very high due to the high-resistance to blood flow of the efferent arterioles, whose diameter is smaller than the afferent arteriole.
As a result of this high blood pressure, filtration occurs along the entire length of each glomerular capillary and substances do not move back the other way into the blood.
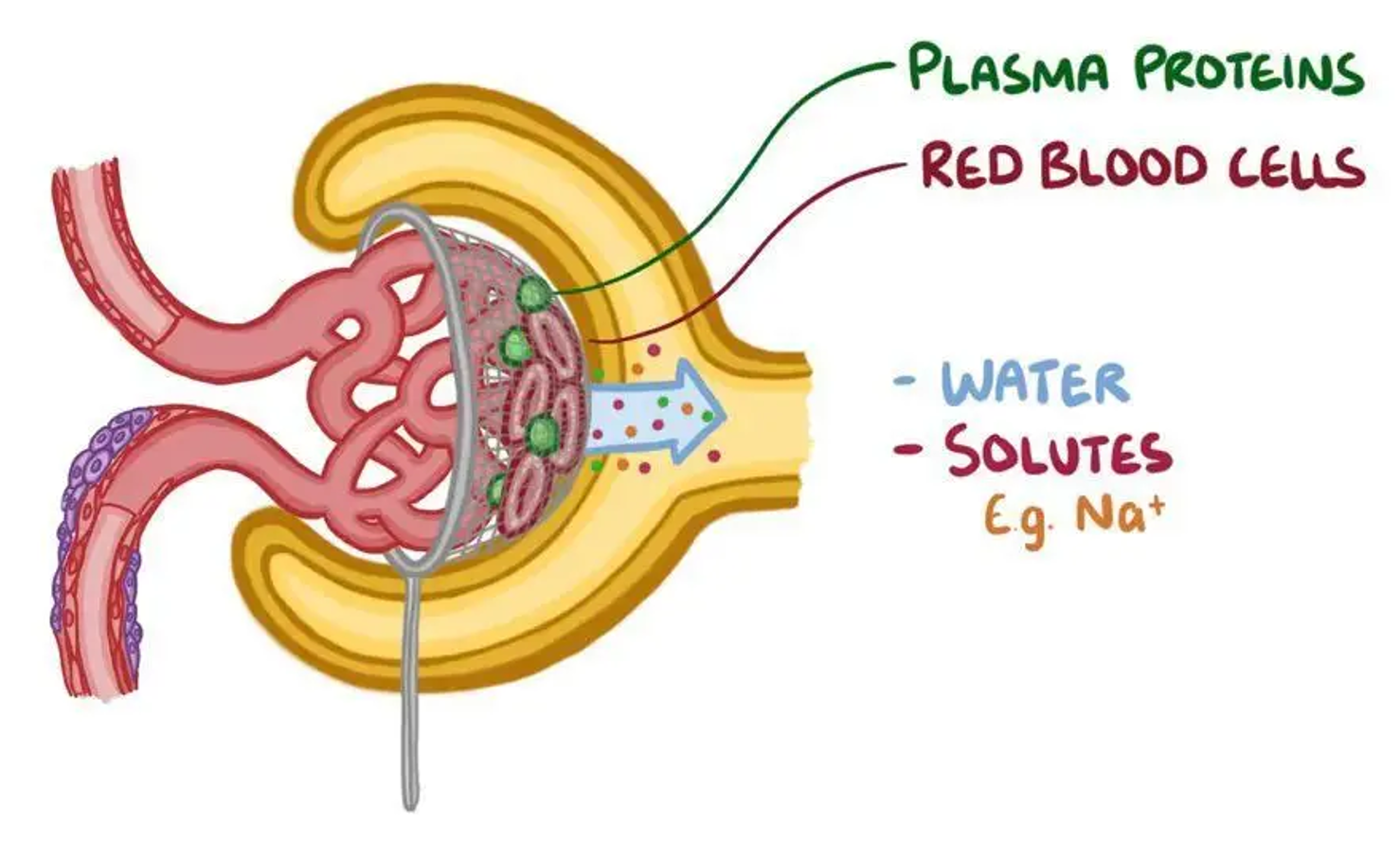
What does the glomerulus allow to pass through
All blood components except blood cells and plasma proteins.
Smaller molecules pass freely from the blood into the glomerular capsule and form the filtrate: water, glucose, amino acids, salts (ions) and nitrogenous wastes (urea, uric acid, ammonium ions, creatinine).
Therefore they’ve got similar concentration in blood and glomerular filtrate
How much filtrate is produced daily
180L
What does filtrate consist of
Water
Salts (ions)
Small nutrient molecules (glucose and amino acids)
Wastes like urea
Uric acid
Ammonium ions
Creatinine
Hormones
Drugs.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
The volume of filtrate formed each minute by the combined activity of all 2 million glomeruli of the kidneys.
What is glomerular directly proportional to
⚬Net filtration pressure: the blood pressure in the glomerulus
⚬Total surface area for filtration: glomerular capillaries have a huge surface area (collectively equal to the surface areas of the skin!).
⚬Filtration membrane permeability: glomerular capillaries are thousands of times more permeable than other capillaries due to their porous structure.
⚬Thin membrane surface of both the glomerulus and glomerular capsule.