PSYC1030 quiz 3 (all module 3)
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
Social learning theory
-children learn by Imitating adults
-Shape behaviour and social learning by rewards/punishments
-Parents influence
Problems with social learning theory
-Children can be more moral than parents and Children learn morals from other sources
-Moral reasoning goes through changes over course of development: morphing and increasing with complexity along w cognitive ability
Main theorist involved in social learning theory
Albert Bandura
what did bandura’s bobo doll experiment find
If adult punches and hits bobo doll then children adopt behaviour
Children not exposed to aggressive modelling did not display same behaviour
Children will model any adults
Main theorist involved in cognitive learning of morals
-Jean Piaget
-Lawrence Kohlberg
Piaget and Kohlberg agree that
-Reasoning of moral dilemmas the focus not the outcome
Piaget's stages of moral development and ages they occur
-Heteronomous morality stage (4-8)
-Autonomous morality stage (8+)
Heteronomous morality stage (Piaget)
-Focus on rules or laws
-Rules have innate authority
-Rules not negotiable
-Rules don't serve a purpose
-Outcome focused
-Motivated by fear of punishment
Autonomous morality stage (Piaget)
-Laws relative
-Laws socially constructed
-Rules are negotiable
-Rules do serve a purpose
-Intention focused
-Not motivated by fear of punishment
-Internalised sense of morality
Kohlberg developed three levels of morality by testing 84 males
-Preconventional Morality
-Conventional Morality
-Postconventional Morality
Name all 6 stages of Kohlberg's moral development
1. Punishment orientation
2. Self interest
3. Social perspective
4. Authority and social order
5. Social contact orientation
6. Universal ethical principles
Kohlberg's Preconventional Morality: Two stages and what age
1. Punishment orientation
2. Self interest
-Progress through both by age 9
Kohlberg's Preconventional Morality: Stage 1: Punishment orientation
-Individual perspective
-Egocentric
-Concrete tangibles
would argue that $ should be given to dad bc if it is not joe will be punished. Operating using another person's law.
Kohlberg's Preconventional Morality: Stage 2: Self interest
-Individual perspective
-Egocentric
-Fairness
Joe shouldn't give $$ to dad bc it is his money
Kohlberg's Conventional Morality: Two stages and what age
3. Social perspective
4. Authority and social order
Between adolescence and adulthood
Kohlberg's Conventional Morality: Stage 3: Social perspective
-Social and interpersonal perspective
-Perspective of contributing member of society.
joe shouldn't give $$ because he sacrificed and worked hard and father lied. Social, interpersonal perspective.
Kohlberg's Conventional Morality: Stage 4: Authority and social order
-Reasoning re interpersonal orientations
-Reasoning about society as a whole
-Common rights people have
-Societal expectations of possession
-Principles dictate behaviours.
very justice system-y
Kohlberg's three levels of morality
-Pass at any age BUT
-Sequential
-Linear
Kohlberg's Postconventional Morality: Two stages
5. Social contact orientation
6. Universal ethical principles
Kohlberg's Postconventional Morality: Stages 5 and 6 commonalities
-Appliable for minority of adults
-Universal kinds of morals
-Applicable regardless of culture
-Prior-to-society perspective
Kohlberg's Postconventional Morality: Stage 5: Social contact orientation
-Free individual as long as it does not infringe upon others rights
-Basic fundamental human right
Kohlberg's Postconventional Morality: Stage 6: Universal ethical principles
-Mother Theresa.
-Personal conscience.
Limitations with what Kohlberg's experiment
-Only tested boys and men in his task.
In modern approaches to how we think about moral reasoning people have examined:
-Specific domains of reasoning within moral reasoning
-Role of parents
Carol Gilligan's view on morality
-Repeated Kohlberg's study
-Challenged his theory
-Tested men and women
-Kohlberg overestimated importance of progressing through the stages
-There are different kinds of moral reasoning that vary across people
What did Carol Gilligan find in women compared to men
-Women: stage three
-Men: stage four
-Women: Cooperative orientation
-Men: Justice orientation
Moral rules pertain to our concepts of:
-Harm and welfare
-Fairness
-Universal
Social conventional rules
-Social order
-Organisation
-Subjective
-Arbitrary
-Doesn't directly reflect our principles
can social conventional rules and moral rules intersect
yes. social conventions can be there to preserve moral rules
Baumrind's axes of parenting style
-Indulgent parents
-Authoritative parents
-Neglectful parents
-Authoritarian parents
Low control and low sensitivity
Neglectful parents
Low level of control and high sensitivity
Indulgent
High level of control and low sensitivity
Authoritarian parents
High level of control and High level of sensitivity
Authoritative parents
Authoritarian parents
-Punishment and reward orientation
-Thus children also have this
Indulgent and neglectful parents
-lack social responsibility
-Parents don't correct child's actions
-Children don't contribute to groups or partners
-Problems with authority
Authoritative parents
-Socially responsible
-Altruistic
Why do authoritarian parents have children less moral reasoning compared to authoritative parents
-Authoritative: Correction, control, sensitivity, understanding
-Authoritarian: Punishment, control, no sensitivity, no understanding
Cultural difference between Western and Eastern with parenting styles
Western: Authoritative parents
Eastern: Authoritarian parents
both eastern and western parenting styles produce similarly healthy children because
Parenting styles + culture + child= healthy child
not just one or the other
what happens in utero in terms of lang development
pick up elements of lang
more sensitive to sound
preference for hearing language they are going to speak
what is the hypothesis for the overregularisation error pattern (i.e. correct usage high, then decreases, then high again)
they're just mapping word to referrent (younger children 2-3). Something happens in kids mind where grammatical rule is extracted and then overapplied to lots of words (i.e. "I know that to make past tense you add -ed, so I will add -ed to blow). This is unrelated to schooling.
what did dare baldwin 1991 find
in a lab, when baby looked at 1 (of 3) objects, parent uttered word
Did baby link word with what they were looking at?
No!
When they hear new word, they turn and look at where the speaker is looking and follow where speaker is looking. Basically what the speaker is looking at is what the baby assigns the word to
Young as 16 months old
Called joint attention
what is the nature explanation and what is the nurture explanation for the naming explosion
Nurture explanation- learns how reference works and importance of social situations and then tries to figure out what is what and when
Nature explanation: something happening in brain at ~18 mos which allows them to absorb all this info
what is the regular developmental progression for language
First words around first birthday--> start stringing words together--> follow grammatical rules (not explicitly taught)--> between 4-5y/o they can properly talk basically
Phonetic distinction between V and B are not picked up in what country
Spain
Baby's are born with a universal ear, what does this mean
Infants under 1 are sensitive to all phonetic distinctions between all languages, less sensitive as they approach 1
What's infant directed speech also known as
Motherese
What are the factors involved in motherese pattern of speech
-Talk slowly
-Repetitive
-High and low intonations
Benefits of infant directed speech opposed to adult directed speech
-Segments speech stream
-Begins to map meanings from words
What's the meaning of babbling
Closer to 12 months babbling tongue tuned in to consonant vowel pairings common in the language they will be speaking
What's the significance of pointing
-Drawing ones attention to something
-Just proceeds infants first word
-Can be done with finger and language
-Only humans point spontaneously
The problem with simple association ?
If speaker looking at something and baby looking at something else.
Just hearing language in order to learn is not sufficient, what's needed to effectively learn
Social context
Part of the social context of language includes what and an example
-Pragmatic functors (Meaning wanting to convey)
-Example: 'bye-bye' 'ta'
First word is usually by what age and what is the age limit when you should test for hearing impairment
12 months
By 3 y/o
First word is usually what
-Noun
-Usually "middle sized thing in the environment"
Language errors occur in what age range ?
12-18 months (1-1.5 y/o)
Two types of language errors that occur
-Overextension error
-Under extension errors
What is the one-word stage
-Pointing at and uttering single word nouns
-Referential errors in the first 50 words or so
What is the overextension error and an example
-Overextend the reference
-common error by most babies
-Parent "moon" reference to the moon
-Child independently (without social reference) calling other round things "moon"
What is the under extension error and an example
Common noun treated as proper name
-Baby knows the name of the family pet as dog
-Doesn't extend that word to any other dogs that she sees
How many words have baby's learned by 18 months
50-75 words
What age do baby's stop making the under extension and overextension error
18 to around 24 months
Why do babies make extension errors
Maybe over extension occurs bc have very limited vocab and use as 'placeholder' OR (theory 2) until ~18mos when children have acquired 50-75 words, bbies don’t actually understand how language works. Don’t understand that words refer to specific thing.
By 18 to around 24 months what's happening with baby's language
-Naming explosion 9 words per day via "what's that" game
-Combining words (telegraphic speech)
What game creates a "naming explosion"
The what's that game
At what age have baby's got a critical mass of beyond 50 to 75 words
From around 18 to around 24 months
The "what's that game" with the "naming explosion" is a nature or nurture view
Nurture
How many words in a child's vocabulary by age 6
12,000-14,000
How many words in a adult's vocabulary
25,000
What is word order error
Grammar
What is telegraphic speech and an example
-Two and three-word stage
-Baby's make very few word-order errors.
"Teddy eat," and, "Eat teddy."
A developmental psycholinguist studying language acquisition up until three-word stage is most interested in what aspect ?
Utterances and context.
A developmental psycholinguist studying language acquisition after three-word stage is most interested in what aspect ?
Context
What is over regularisation errors and what age range do these appear/disappear
* Grammatical mistake
* Grammatical rule extracted and overapplied
* <3 Correct usage
* >3 over regularisation
* From 8: Correct usage
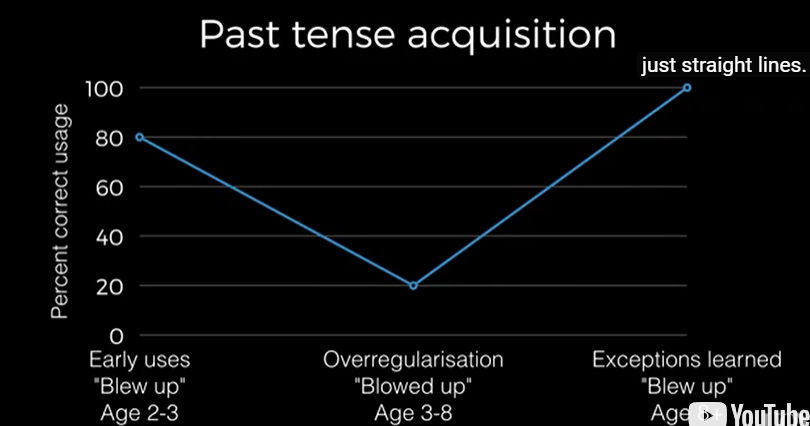
An example of over regularisation errors
"blowed-up"
The nature argument for language acquisition and an example that supports this argument
-Innate
-Biological
-Noam Chomsky
-Over regularisation errors
-developmental regularity
-poverty of input: input heard by children isn't varied enough to explain through simple processes of association or social learning. e.g. where did she learn blowed up?
The nurture argument for language acquisition
-Association
-Imitation
-Shaping (Social learning) reward/punishment
Problems with nature rationale for language acquisition
-Variation in languages
-No underlying principles that apply to all languages
-No universal grammar
-Proven environmental influence
-Increased language input, increased rate of language acquisition
Difference between high socio-economic status homes compared to low with language acquisition
high SES homes who are read to regularly have twice as many words in their vocabularies
Is there a critical period for language acquisition
Yes. unclear how it is characterised
What is Language Acquisition Device
-Noam Chomsky's view
-We learn language by genetically coded Language Acquisition Device
-Input generates output
What is the problem with the critical period hypothesis
-Cant test it
-Only humans have language
-Ethically cant deprive human of language
What did Genie teach us about language acquisition and the critical period hypothesis
-Unable to learn grammar
-The importance of gramma in language
-Limited telegraphic speech with word-Order errors
-Evidence for "critical period" for language acquisition
-lends some support to nature view
McGuires Chain of persuasion
-Presentation
-Attention
-Comprehension
-Yielding
-Retention
-Behaviour
what did regan 1971 find
participants who were given a drink by the confederate with no expectations bought more raffle tickets than participants given a drink by experimenter
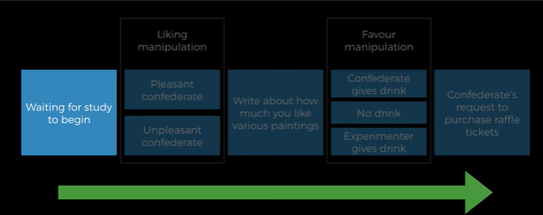
what did barry and kanouse 1987 find
participants who were given $20 as a gift had a higher completion rate of surveys than participants who were promised (and given) $20 as a reward after completing the survey
Brocks Cognitive Response Analysis
A persuasive message and associated things are the focus of elaborative thought
What's "elaborative thoughts" according to Brocks Cognitive Response Analysis model
Whether or not we think favourably about the message. This leads on to attitude change.
Elaboration likelihood model
-Dual process model
-Central route
-Peripheral route
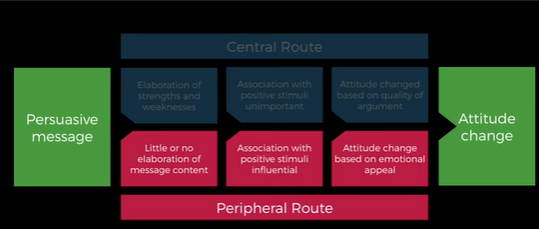
Central route (Elaboration likelihood model)
-Elaboration strengths/weaknesses
-Association with positive stimuli unimportant
-Attitude change based on quality argument
Peripheral route (Elaboration likelihood model)
-Little or no elaboration of content
-Association with positive stimuli influential
-Attitude change based on emotional appeal
Compliance
Agreeing to a request from someone who does not have the authority to make you obey
Principles of compliance by Robert Cialdini
-Reciprocation
-Consistency
-Social validation
-Liking
-Scarcity
-Authority
Robert Cialdini learned compliance from the following people
-Salespeople
-Advertisers
-Real estate agents
-Negotiators
-Con artists
How are persuasion/compliance techniques developed in sales people according to Robert Cialdini
Persuasion techniques developed via NATURAL SELECTION. The most adaptive compliance techniques will persist in these professions
Reciprocation
more willing to comply with a request from someone who has previously provided a favour or concession to us
If people display behaviours to us we will display behaviours of quivalent or greater value back
Ppl self disclose to us we are more likely to self disclose back
Why does reciprocation exist
Powerful norm for reciprocation in society
Obligation to return behaviour we receive
examples of reciprocity
-Liking
-Cooperation
-Competition
-Self-disclose
-Make concessions
-Gifts