alkenes and alkynes ochem midterm 2
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what alkene rxn has X2 as the reagent and what is the mech, regio and stereochem
the concerted mechanism the alkene acts as a nucleophile and attacks the partial pos of the Br2 which creates a bromonium ion and a loss of LG to create BR-.
then there is another nuc attack in an SN2 tyope process, a backside attack, where the Br- attacks the more substituted carbon of the bromonium ion, leading to anti-addition of bromine to the alkene.
may produce a pair of EN and an inversion of configuration
what is thought process for Elimination vs substitution rxns
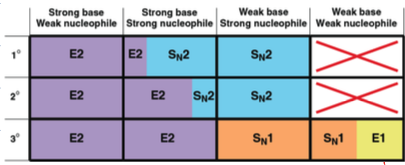
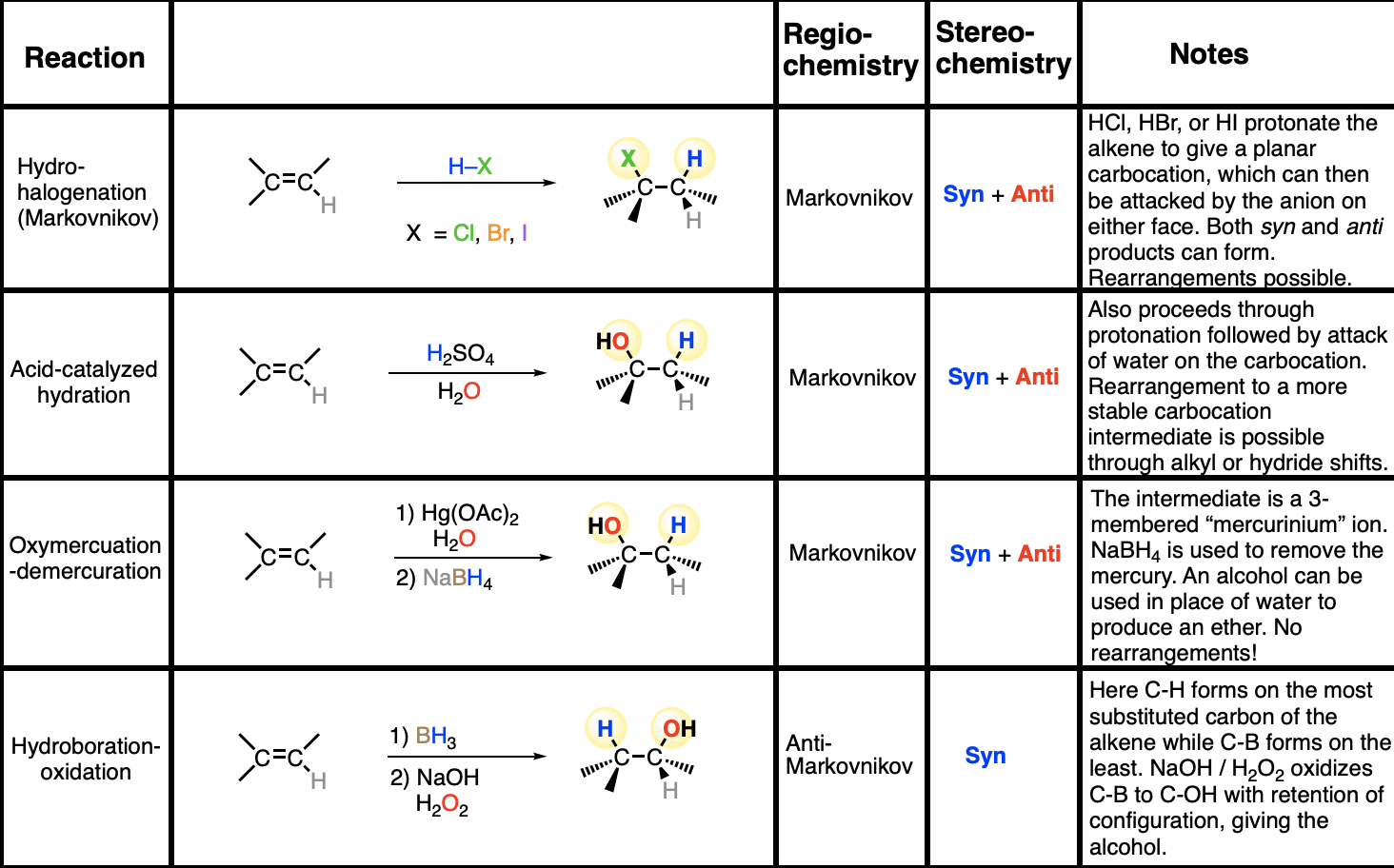
what are the rxn, mech, regio and stereo for alkene
hydro halogenation
acid catalyzed hydration
hydroboration oxidation
oxymercuration demurcuration
what rxn has Br2 and H20 as the reagent and what is the mech, regio and stereochem
halohydrin formation
same concerted mechanism as halogenation where the alkene forms a bromonium ion
then there is a nuc attack by water at the more substituted side , resulting in the addition of a bromine atom and a hydroxyl group to adjacent carbons in anti configuration.
may produce pair of EN and an inversion of confiuration
what is the rxn with MCPBA and H3o + what is stereo
anti dihydroxylation (adding 2 OH groups)
the alkene creates an epoxide from MCPBA which is then protonated by H3O+ and then the water acts as a nucelophile ot open the ring resulting in the addition of hydroxyl groups in an anti configuration across the alkene.
this is can create a pair of En and have an inversion of configuration
what is the rxn with OsO4 and H2O2 and stereo
syn dihydroxylation adding syn Oh groups
The reaction involves the alkene being treated with OsO4, forming a cyclic osmate intermediate, which is then hydrolyzed by H2O2 to yield two hydroxyl groups on the same face of the alkene, resulting in syn addition. This reaction can create a pair of enantiomers and may exhibit overall retention of configuration.
what is the alkene rxn with o3 and DMS
ozonolysis
where each c-c double bond is replaces with c-o double bonds
how can you to an alkyne from alkyl dihalides
by using 2 eq of a very strong base you can have two E2 rxns
what terminal alkene rxn with NaH or NaNH2 with an alkyl halide
acetylide formation or adding a carbon chain to an alkyne
This process involves the deprotonation of a terminal alkyne, allowing for subsequent nucleophilic substitution with the alkyl halide.
what rxn with H2 and Pt for an alkyne and lindlar’s catalyst
catalytic hydrogenation results in an alkane
if you use lindlars catalyst you stop at the cis alkeneinstead of forming an alkane.
what is the alkyne rxn if you use Na and NH3
The reaction involves dissolving metal reduction, which converts alkynes to trans alkenes.
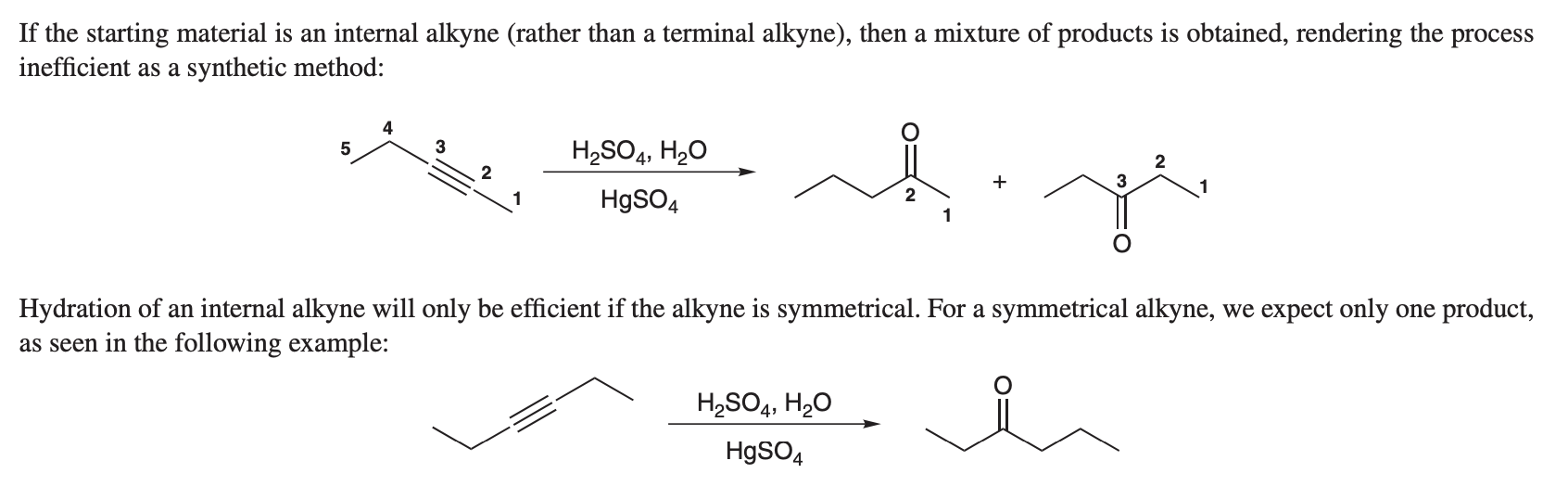
what is the alkyne rxn if you use HgSo4, H2SO4, and H2O
The reaction is known as hydratation of alkynes, leading to the formation of a ketone. where the ketone is formed at the more substitued position
if the alkyne is not symmetrical must draw botth forms
what is the rxn for an alkyne with HX as the reagent and what is regio chem
hydrohalogenation
where the halide is added at the more substituted spot (mark)
what is the mechanism for tautomerization (both acid and base)
the enol attacks the H3O^+ to form ketone, (has CC intermediate) or base abstracts a proton from enol to form the carbonyl compound.
what rxn with 9 BBN or R2BH and naOH and H2O2
what is regio and stereo
hydroboration oxidation of alkyne
it adds an aldehyde at the less substituted position if terminal alkyne
but if internal alkyne it will yield ketone
it is anti mark and syn
what rxn with xs X2 or 1 eq X2
halogenation of alkynes
the addition occurs twice in excess or once in 1 eq of the halogeen
what rxn for alkyne with O3 and H2O
ozonolysis of alkynes
for an internal alkyne it creates two carboxylic acids
but for a terminal alkyne it creates a carboxylic acid and CO2