help from Sarah
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
where is P highest & lowest in stenosis?
highest P: before stenosis
lowest P: w/in stenosis

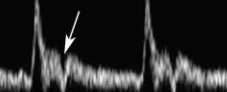
what does this waveform indicate w stenosis?
“tardus parvus”
distal to stenosis
bc P drop & resistance from stenosis

what does this waveform indicate w stenosis?
“staccato”
proximal to stenosis
high resistance & absent/reversed diastolic flow

what does this waveform indicate w disease?
“staccato”
arterial disease is distal to waveform
high resistance, blunted/monophasic, low flow in diastole
‘spikes’ bc flow struggles to overcome high resistance in obstruction

what does this waveform indicate w disease?
“tardus parvus”
arterial disease is upstream/proximal to waveform
round upstroke, low amplitude
VRT
place sensor on medial malleolus (seated patient w feet dangling)…
pt dorsiflexions (move blood to heart)…
record VRT
normal VRT: >20s
if VRT >20s w/out cuff…
normal venous filling
if VRT <20s w/out cuff & then >20s w cuff below knee…
SSV reflux
if VRT <20s w/out cuff & >20s w cuff above knee…
GSV reflux
if VRT <20s w & w/out cuff…
deep & superficial reflux
CRT
time it takes for blood to refill capillary beds after applied P
apply P to fingertip until white & time to return to color
normal CRT: 1-3 sec
CRT >3s (poor tissue perfusion, dehydration, shock)
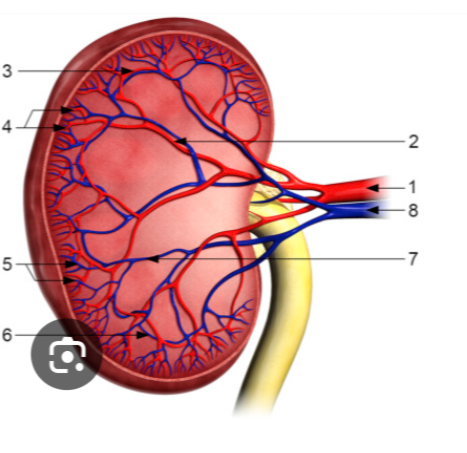
order of renal vessels
renal a…segmental a
interlobar a
arcuate a
interlobular a
interlobular v
arcuate v
interlobar v
renal v
RI
peripheral resistance of flow in renal arteries
normal<0.7
*high RI=less diastolic flow

RI for renal transplants
<0.7 (good perfusion)
0.7-0.9 (possible rejection)
>0.9 (probable rejection)
RRA runs…
post to IVC
ant to vertebral
*longer than LRA
RRV vs LRV
RRV
into post-lat IVC
sup to RRA
no tributaries
LRV
btwn AO & SMA
inf to panc
larger & longer than RT
accepts LT adrenal, LT gonadal, LT inferior phrenic
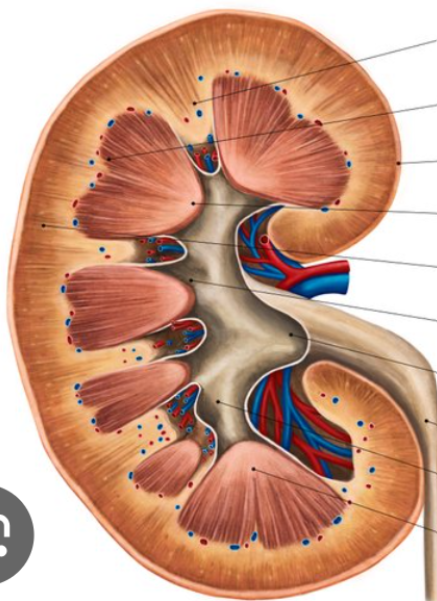
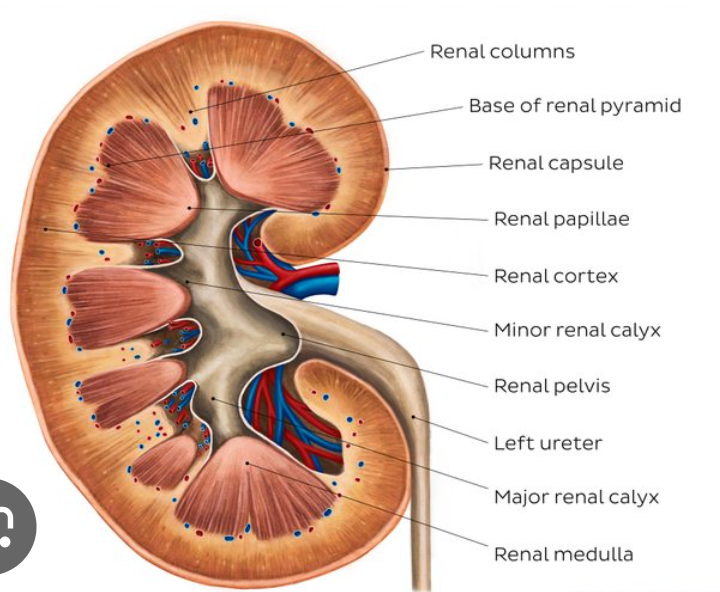
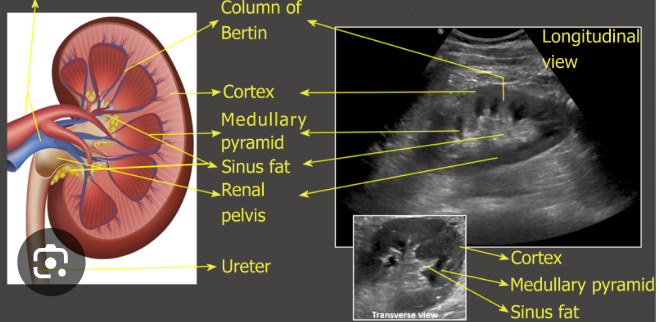
kidney anatomy
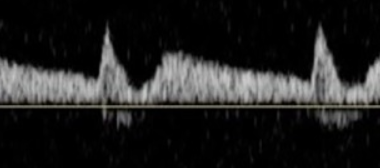
bunny rabbit sign is seen w what disease?
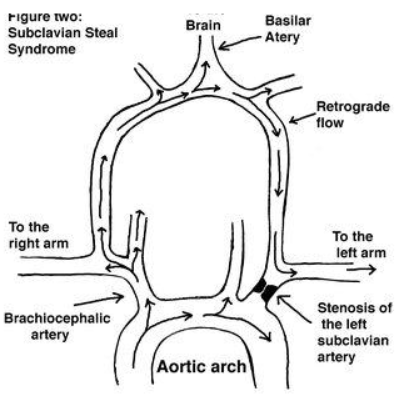
subclavian steal
vertebral waveform @pre-stenosis/pre-steal
subclavian steal
retrograde vertebral flow
bi-directional or bunny sign if ‘pre’
LT subclavian/innom occlusion that is proximal to vertebrals
brachial BP difference 15-20mmHg
ICA
larger
posterolateral (95%)
post to mastoid
NO extracranial branches
low resistance & high diastolic flow
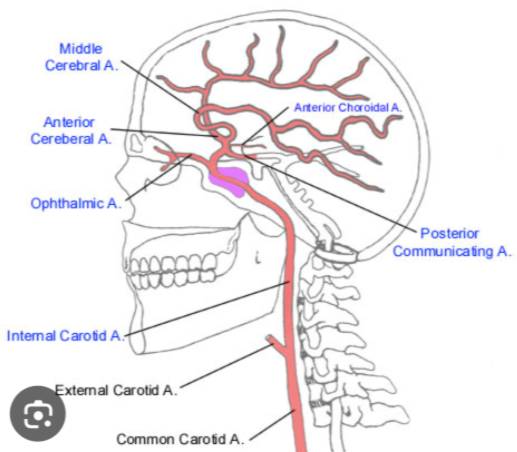
ICA branches
ECA
smaller
anteromedial
ant to face
high resistance
*temporal tap
*supplies neck, face, scalp (not brain)
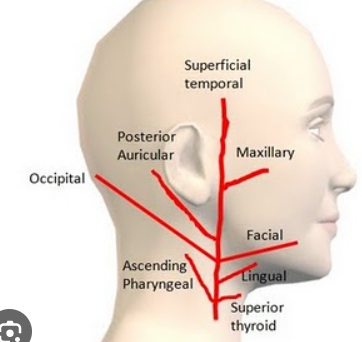
ECA branches
super thyroid
ascending pharyngeal
lingual
facial
occipital
posterior auricular
maxillary
superficial temporal
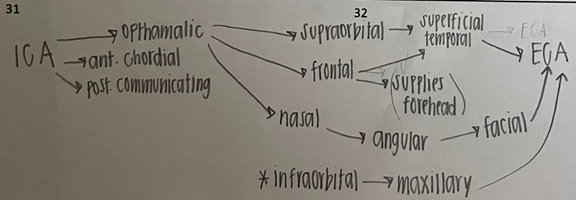
when ICA is occluded, what are collateral pathways?
from ECA…OP branches
supraorbital
frontal
nasal
AT
time from systolic onset to systolic peak
long AT (slow flow) may suggest arterial stenosis

paget-schroetter syndrome
‘stress/effort thrombosis’
compression & thrombosis of subclavian/axillary v
w intense, repetitive activity
*form of TOS
*young active people
pop entrapment syndrome
pop artery compression by gastrocnemius
bc repetitive trauma or pop artery stenosis/thrombosis
*calf pain w exercise
*<30yo men
buergers disease
“thromboangitis obliterans”
small vessel ‘fixed’ occlusive disease
spares vessel walls
mc arteritis
*<40yo male smoker
*rest pain, claudication, ulcers
raynauds color change order
pallor (white), cyanosis (blue), erythema (red)
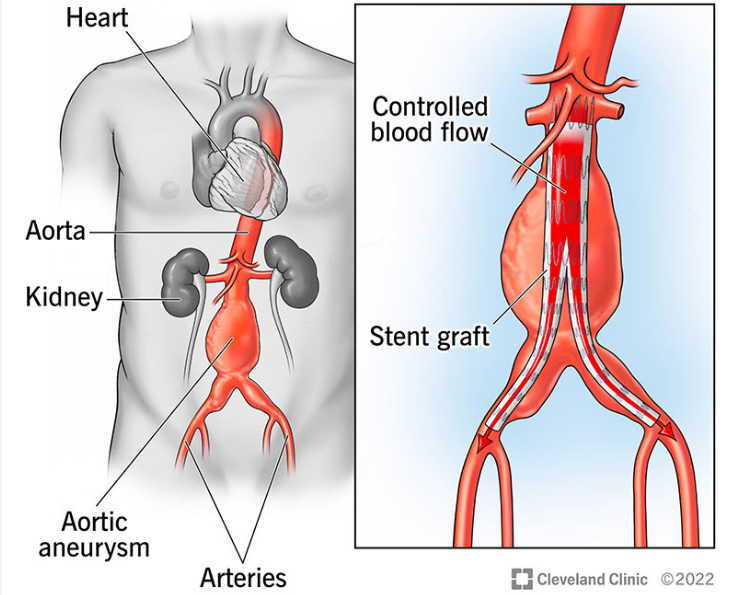
EVAR endoleak types
**repairs AAA w stent graft (groin-AO)
type I: incomplete seal at ends
type II: sac fill via branch vessel (retrograde)
type III: stent defect/tear
type IV: porous graft
type V: AAA expansion w/out leak site
kidney AT
normal <0.07s (<70ms)
kidney size
normal: 10-13cm (4-5in)
12cm (long)
8cm (wide)
5cm (thick)
nutcracker syndrome
LRV compressed btwn AO & SMA
*flank pain, hematuria
breathing affects venous flow
inspiration…decreases thoracic P & increases abdominal P
less flow from LE
expiration…increases thoracic P & decreases abdominal P
less flow from UE
median arcuate ligament syndrome
“celiac artery compression syndrome”
celiac a compressed by diaphragm fibrous band (median arcuate lig)
recurrent abdominal pain
in expiration…celiac is compressed
phlegmasia alba dolens
‘painful white inflammation’
DVT progresses to occlusion of LE w/out ischemia bc collaterals present
swelling, no pulse
phlegmasia cerulea dolens
‘painful blue inflammation’
complete LE thrombosis including collaterals
worsening edema, gangrene, tissue death
may thurner syndrome
LIV compressed by RIA
*high risk of left LE DVT
*left LE pain & edema
*<20yo female
*oral contraceptives, pregnancy
post enhancement vs post shadowing
post enhancement:
sound waves easily pass thru
increased echos; brighter
post shadowing:
sound waves blocked
less echoes; darker
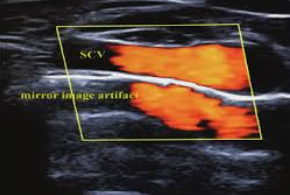
likely artifact at subclavian artery
mirror image
waves bounce off strong reflector (pleura) to create duplicate image

1: AO
2: CHA
3: splenic artery
4: celiac artery
5: IVC
spectral broadening
vertical thickening in systole
filling in spectral window bc lots of frequencies
high flow V
vessel branching
small d vessels
SMA & celiac disease V markers
SMA: significant stenosis (PSV >275cm/s)
celiac: significant stenosis (PSV >200cm/s)
PSV >200cm/s also w celiac artery compression syndrome (median arcuate ligament)
pre-prandial & post-prandial SMA/celiac
pre-prandial:
(SMA) high resistance
(celiac) low flow
post-prandial:
(SMA) low resistance
(celiac) high flow
MPV vs HA
MPV:
hepatopetal, low V, monophasic, slight respiratory variation
SMV + SV
supplies 70-75%
nutrient rich
HA:
hepatopetal, biphasic
supplies 25-30%
oxygen rich
MPV vs HA ultrasound
MPV:
post to pancreas & ant to IVC
echogenic walls
HA:
ant to MPV
hypoechoic

TIPS
shunt to reduce portal HTN
RPV-to-RHV
normal V: 90-190cm/s
suspect stenosis if…
-TIPS V <90cm/s or >190cm/s
-dizziness, dehydration
brescia cimino
for dialysis (radial artery & cephalic vein)
@wrist
low infection & clot risk
requires 1-3M to mature
****common place for cephalic stenosis is at cephalic arch over shoulder
MCA identification
transtemporal
40-60mm depth
antegrade
ACA identification
transtemporal
65-75mm depth
retrograde
PCA identification
transtemporal
60-75mm depth
antegrade
opth identification
transorbital
40-60mm depth
antegrade
vert identification
transforamen (suboccipital)
50-75mm depth
antegrade
basilar identification
transforamen (suboccipital)
75-110mm depth
antegrade
AComA identification
transtemporal
68mm depth
retrograde
ICA identification
transtemporal
65mm depth
antegrade
ICA
MCA
ACA
AComA
PCA
OPH
VERT
BAS
ICA: 65
MCA: 40-60
ACA: 65-75
AComA: 68
PCA: 60-75
OPH: 40-60
VERT: 50-75
BAS: 75-110
malignant IVC blockage
bc cancer
direct tumor in IVC
external tumor compresses IVC
tumor causes thrombosis in IVC
edema, ascites, pain
S&S of blocked TIPS
ascites
dizziness
dehydration
hepatic encephalopathy (low brain fx)