superposition of waves and formation of stationary waves
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what is superposition
where the displacements of two waves are combined as they pass each other, the resultant displacement is the vector sum of each wave’s displacement
what are the two types of interference that can occur during superposition
constructive interference
destructive interference
what is constructive interference
when 2 waves have displacement in the same direction
what is destructive interference
when one wave has positive displacement and the other has negative displacement, if the waves have equal but opposite displacements, total destructive interference occurs
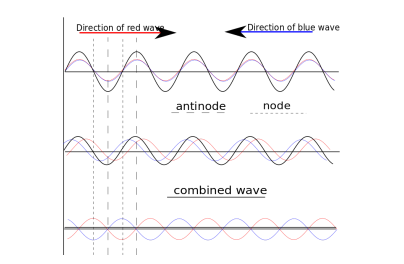
when is a stationary wave formed
the superposition of 2 progressive waves, travelling in opposite directions in the same plane, with the same frequency, wavelength and amplitude
how much is transferred by a stationary wave
0
what happens when wave meet in phase
constructive interference occurs so antinodes are formed (max amplitude)
what happens when two waves meet out of phase
destructive interference → nodes are formed
what is a good example of a stationary wave forming
A string fixed at one end, and fixed to a driving oscillator
what is the first harmonic
when the lowest frequency at which a stationary wave forms
what is a distance between adjacent nodes called
half a wavelength
what are examples of stationary waves
stationary microwaves
stationary sound waves
how can stationary microwaves form
by reflecting a microwave beam at a metal plate
what is the equation for the first harmonic
f = 1/2l (sqrt T/μ)
how can stationary sound waves be formed
by placing a speaker at one end of a closed glass tube, lay powder across the bottom of the tube, it will be shaken at the antinodes and settle at the nodes