Lecture 44: Cardiac output 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
what is the conduction system of the heart and the properties of the pacemaker and the cardiomyocyte action potentials?
the heart is the pump that moves the blood(creates a pressure difference)- its activity is described as the cardiac output
what is the equation for cardiac output?
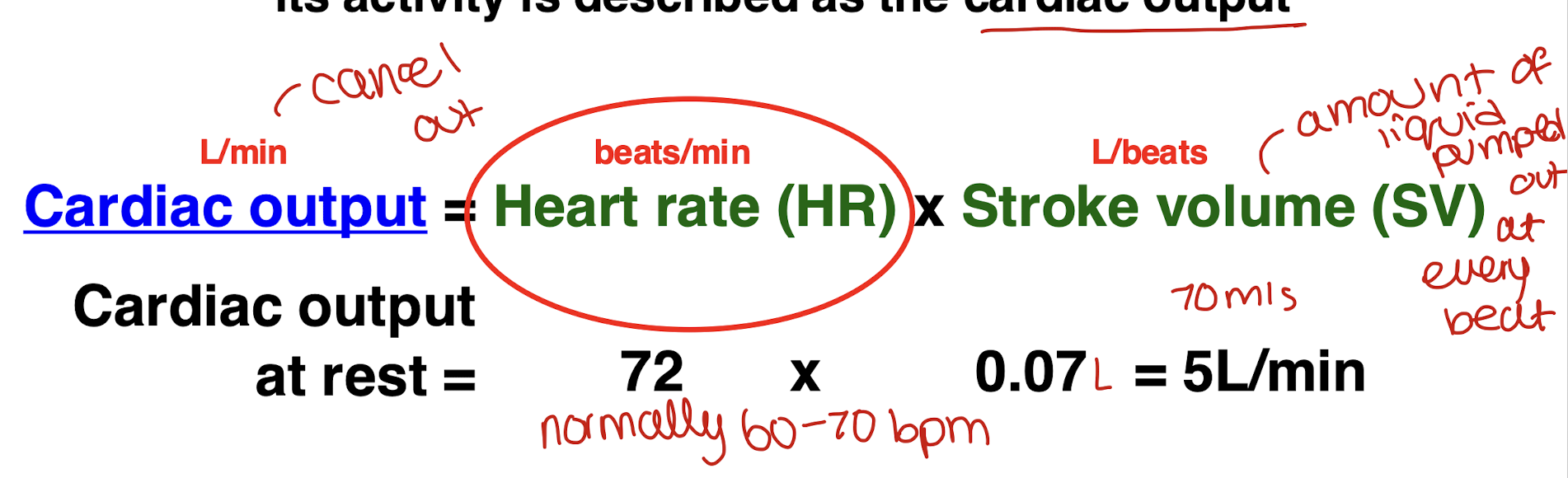
what are the changes in cardiac output?
sleep decreases cardiac output by 10%
excitement, stress increase cardiac output by 30%
pregnancy increases cardiac output by 40%
exercise increases cardiac output by 600%
what is heart rate driven by?
waves of electrical activity that induce the cardiac muscles to contract
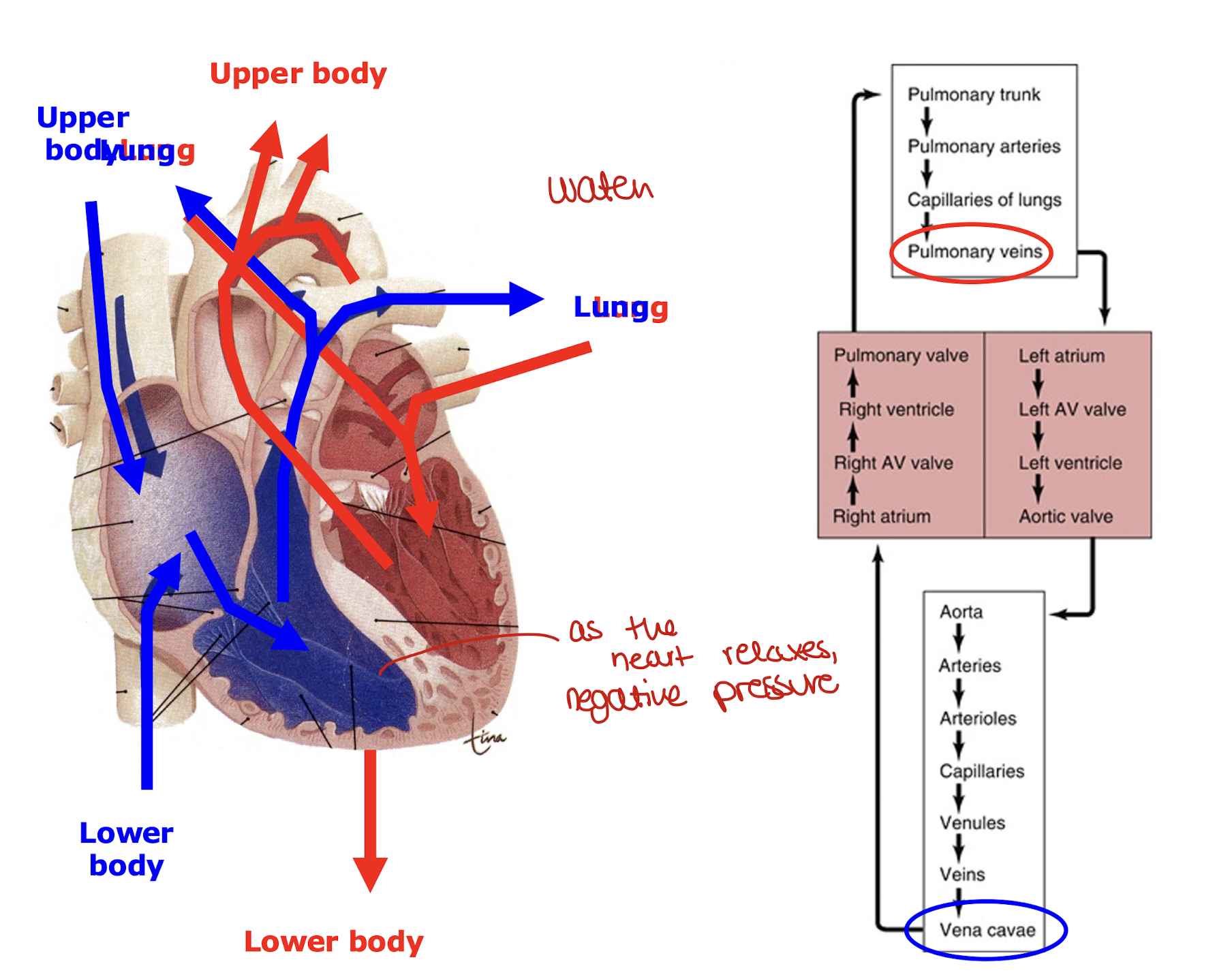
how does blood flow work around the heart
most of the liquid moves into ventricles due to negative pressure passively, only 15 % are pumped
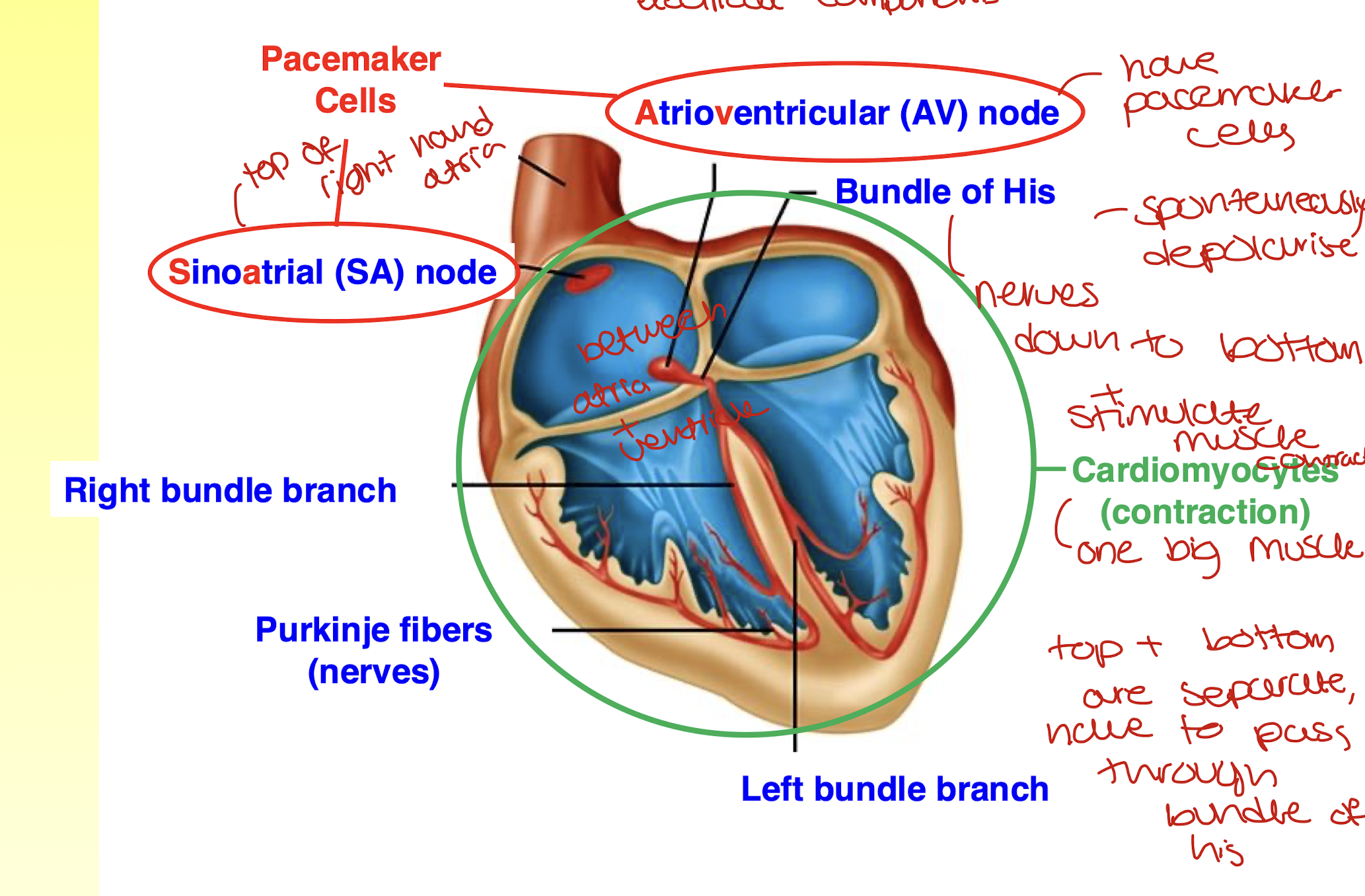
what are the electrical components of the conduction system of the heart?
the SA and AV node are made up of pacemaker cells
they spontaneously depolarise
the bundle of his sends electrical signals down to the bottom and they stimulate muscle contraction
the top and bottom of the heart are separate so electrical signals have to pass through the bundle of his
they then pass through the purkinje fibres to allow the ventricles to contract
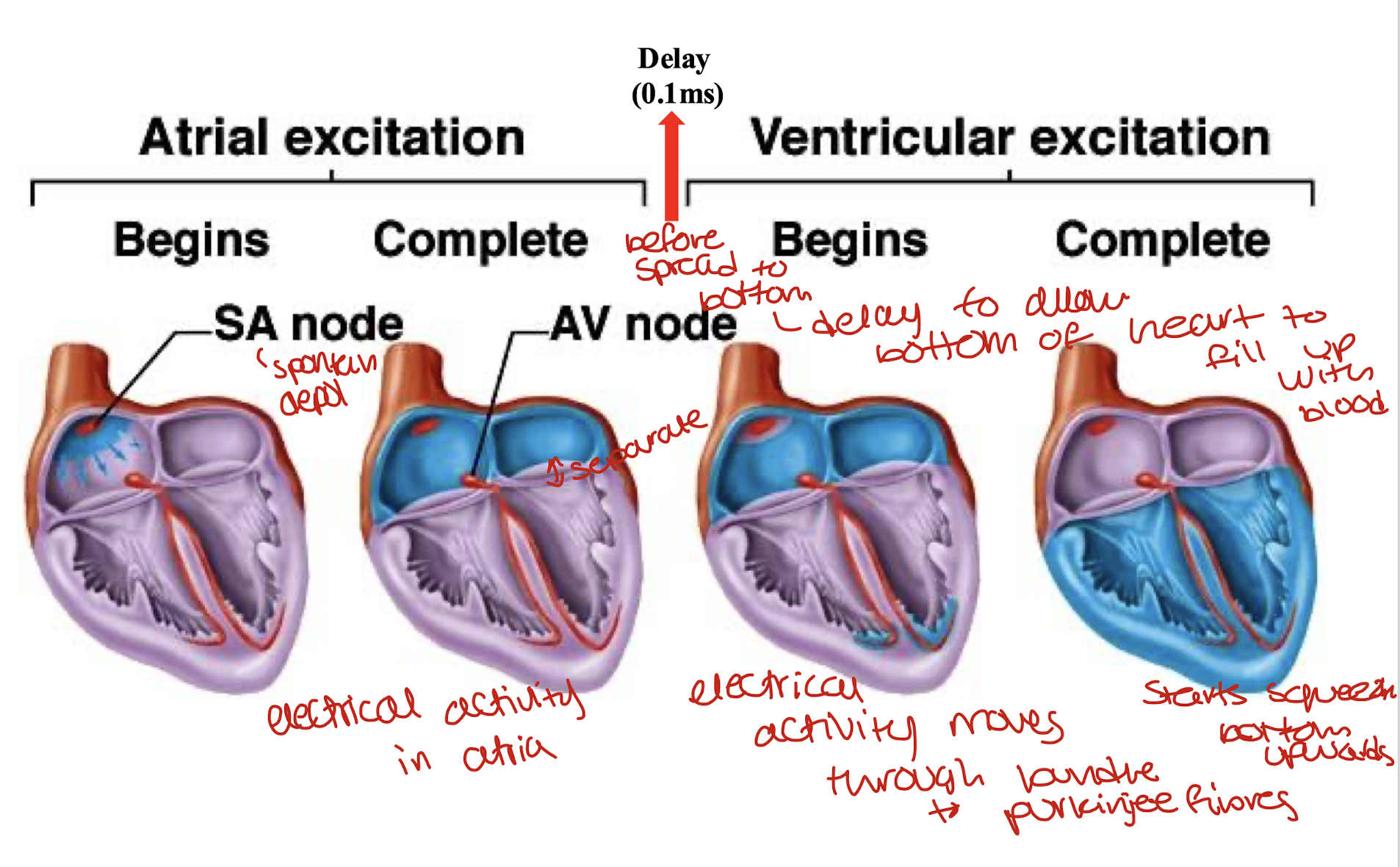
how does cardiac excitation take place?
atrial excitation
electrical activity in the atria
theres a delay of 0.1 ms before it spreads down to the bottom to allow the bottom of the heart to fill up with blood
ventricular excitation:
electrical activity moves through the bundle of his to the purkinje fibres and the heart starts to squeeze bottom upwards
what causes the pacemaker cells of the SA nodes to trigger an action potential?
pacemaker has low resting potential(-60- -70mv), the sodium channels allow Na+ to move in slowly which causes depolarisation which develops into an action potential
what is the mechanism underlying the spontaneous action potentials in the pacemaker cells?SA nodes
slow entry of sodium ions into the cell as well as these entry of calcium ions into the cell
sodium ions leak in through F-type(funny) channels and calcium ions move in through the T-type channels which over time cause depolarisation
the rapid opening of foltage gated calcium L-type channels is responsible for the rapid depolarisation phase
reopening of potassium channels and closing of calcium channels are responsible for repolarisation phase
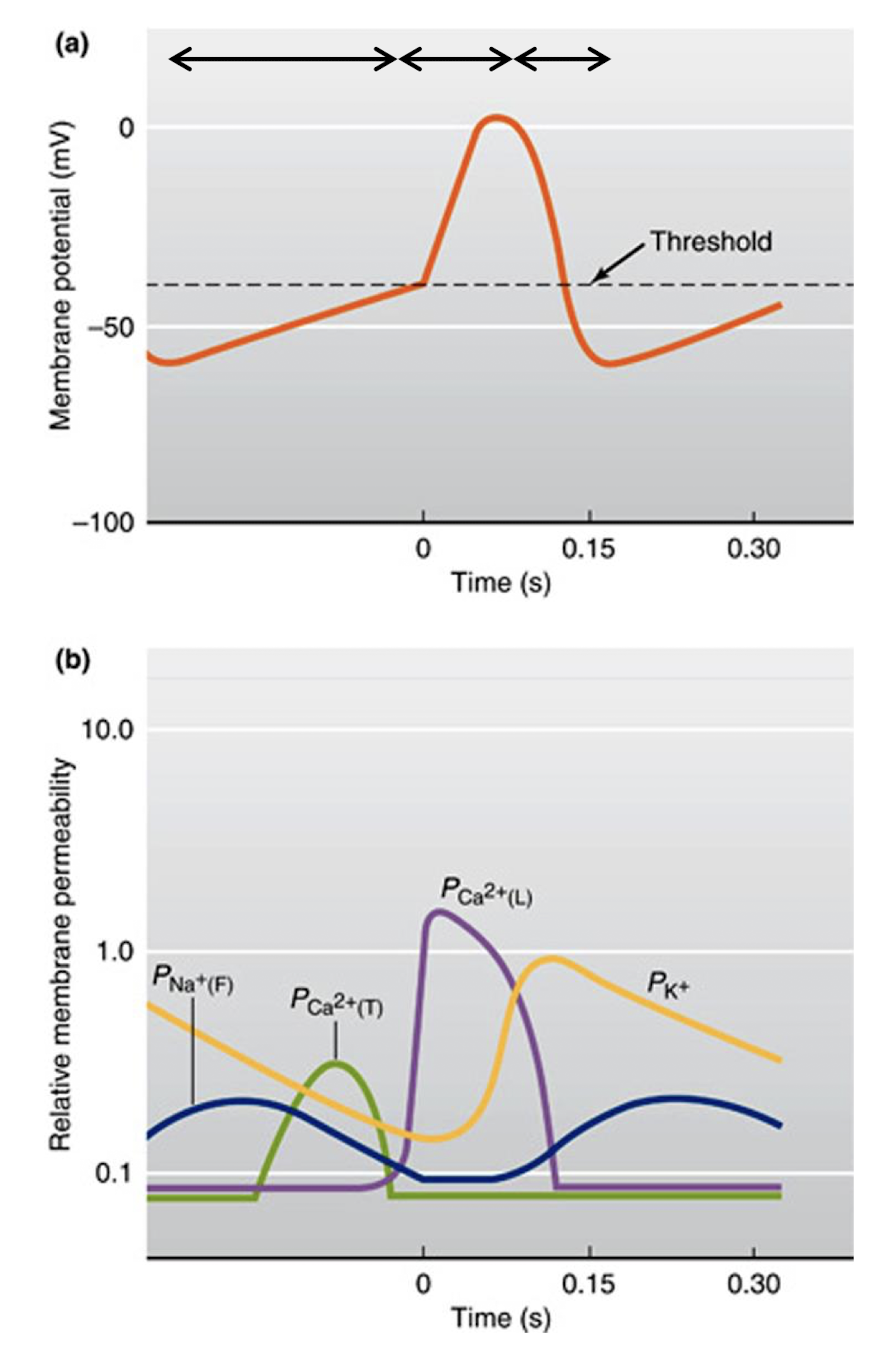
how fast do the cells in the SA, AV node and Purkinje fibers beat?
SA: 100 bpm
AV, has pacemaker cells: 40-60
purkinje, has pacemaker cells : 15-40
Because the SA node is the fastest it basically takes over the rest of the heart, it becomes the driver of the heartbeat in the heart
Damage to the SA node, AV node takes over to keep the heart beating
the loss of both, purkinje fibres will still keep the heart beating: fall back mechanism
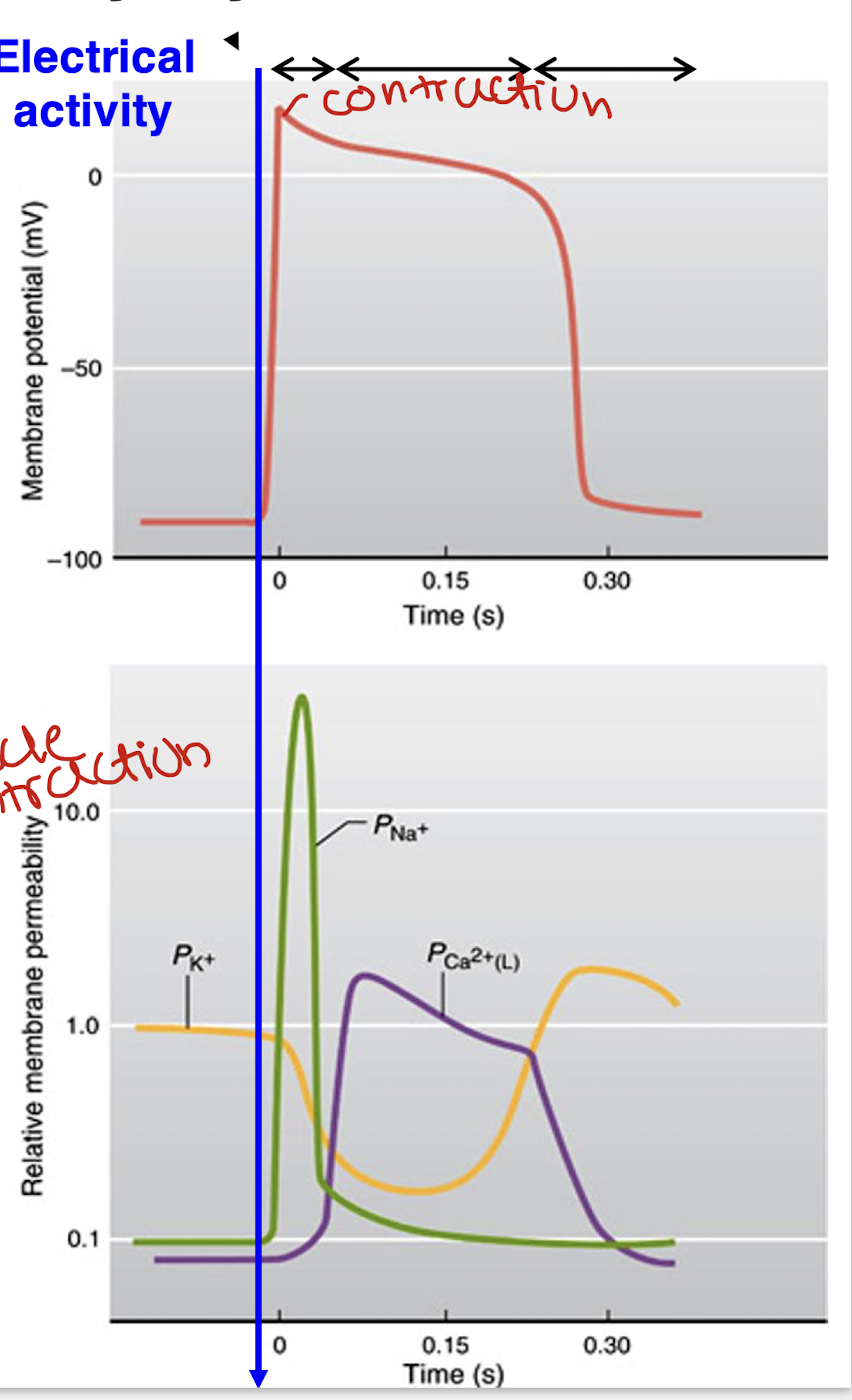
what is the mechanism of contraction of the ventricular cardiomyocytes?
electrical activity causes the rapid opening of voltage gated sodium channels which is responsible for the rapid depolarisation phase
the prolonged plateau of depolarisation is due to the slow but prolonged opening of voltage gated calcium channels(needed for muscle contraction) and closure of potassium channels
opening of potassium channels results in the repolarisation phase
contraction restarts
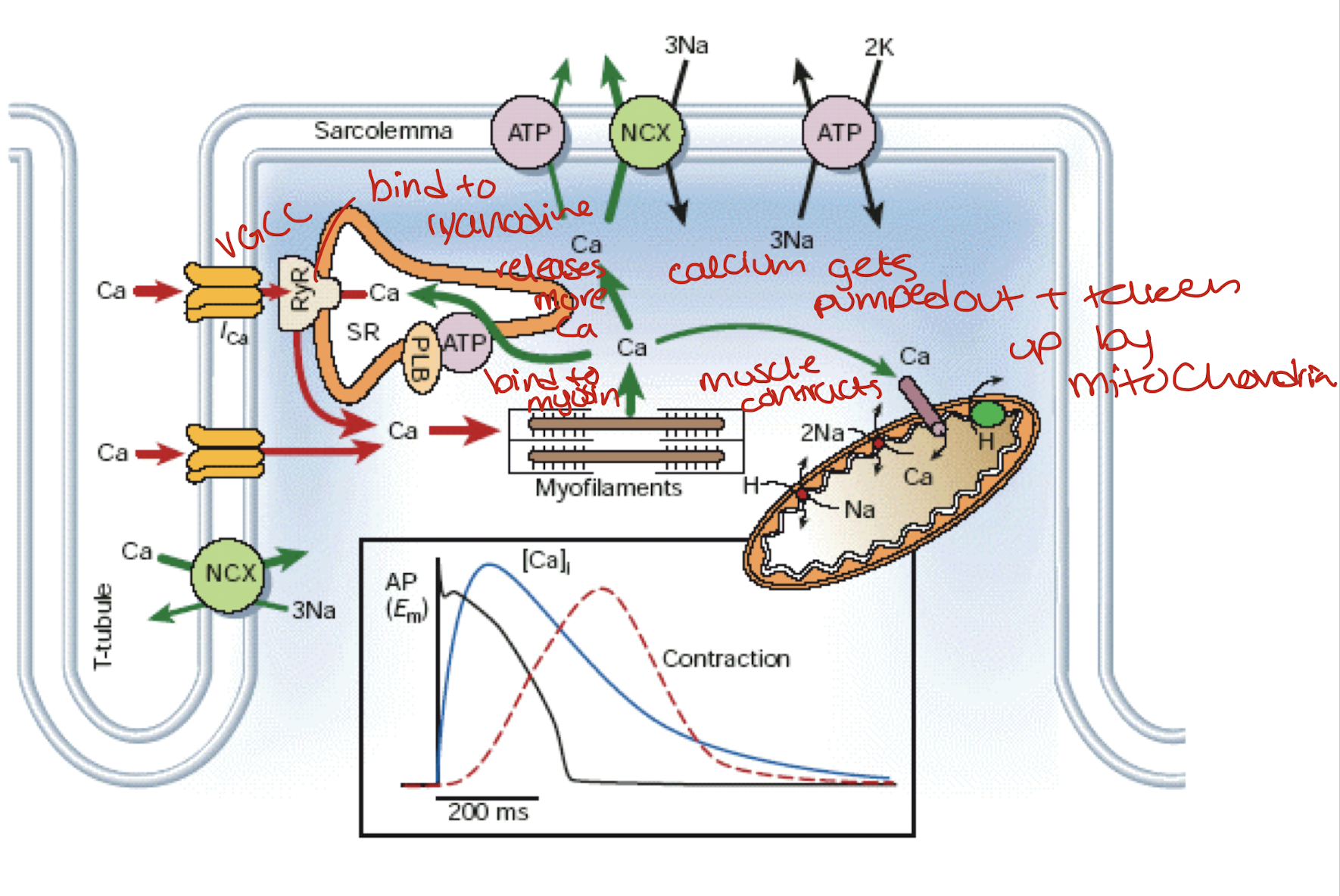
how does calcium produce contraction of the cardiac muscles?
Ca comes in through VGCC
binds to a ryanodine receptor which releases more Ca
they bind to myosin, the muscle contracts
calcium gets pumped out and is also taken up by mitochondria
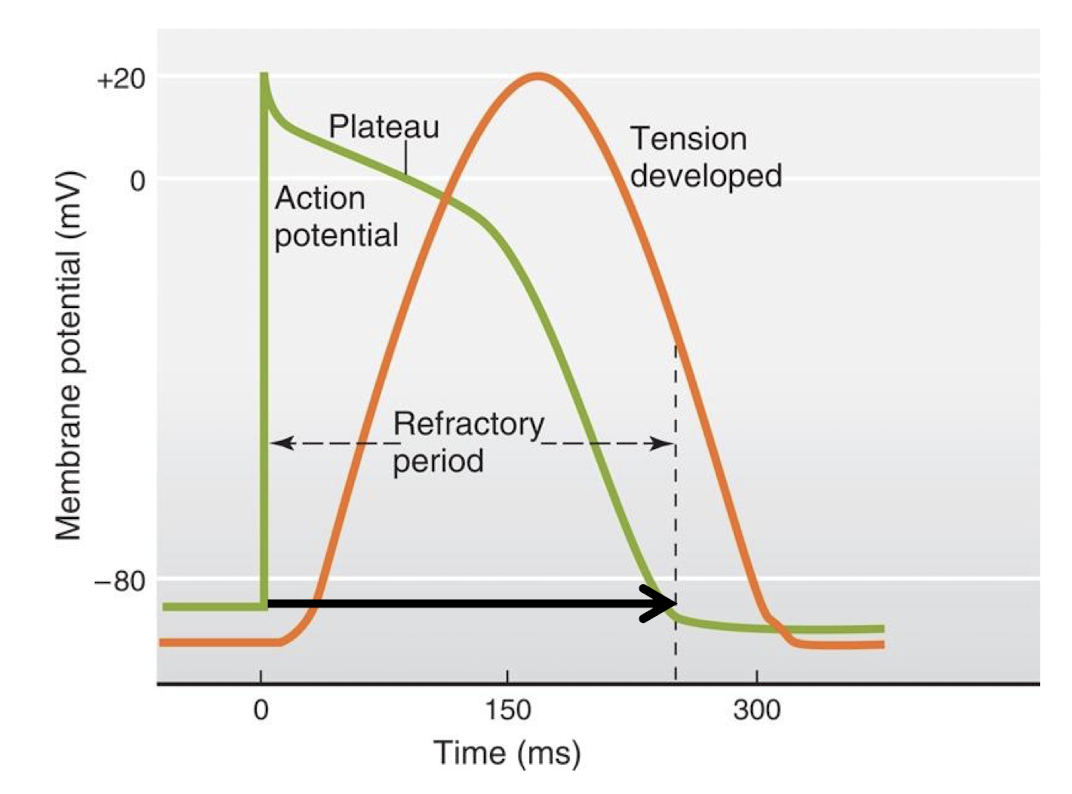
Cardiac muscle has a prolonged refractory period before restimulation which allows for ventricles to fill with blood prior to pumping
prevents heart spasms, also known as tetanus, cant pump blood out of the heart
needs a quarter of a second before restimulation
max 250 bpm
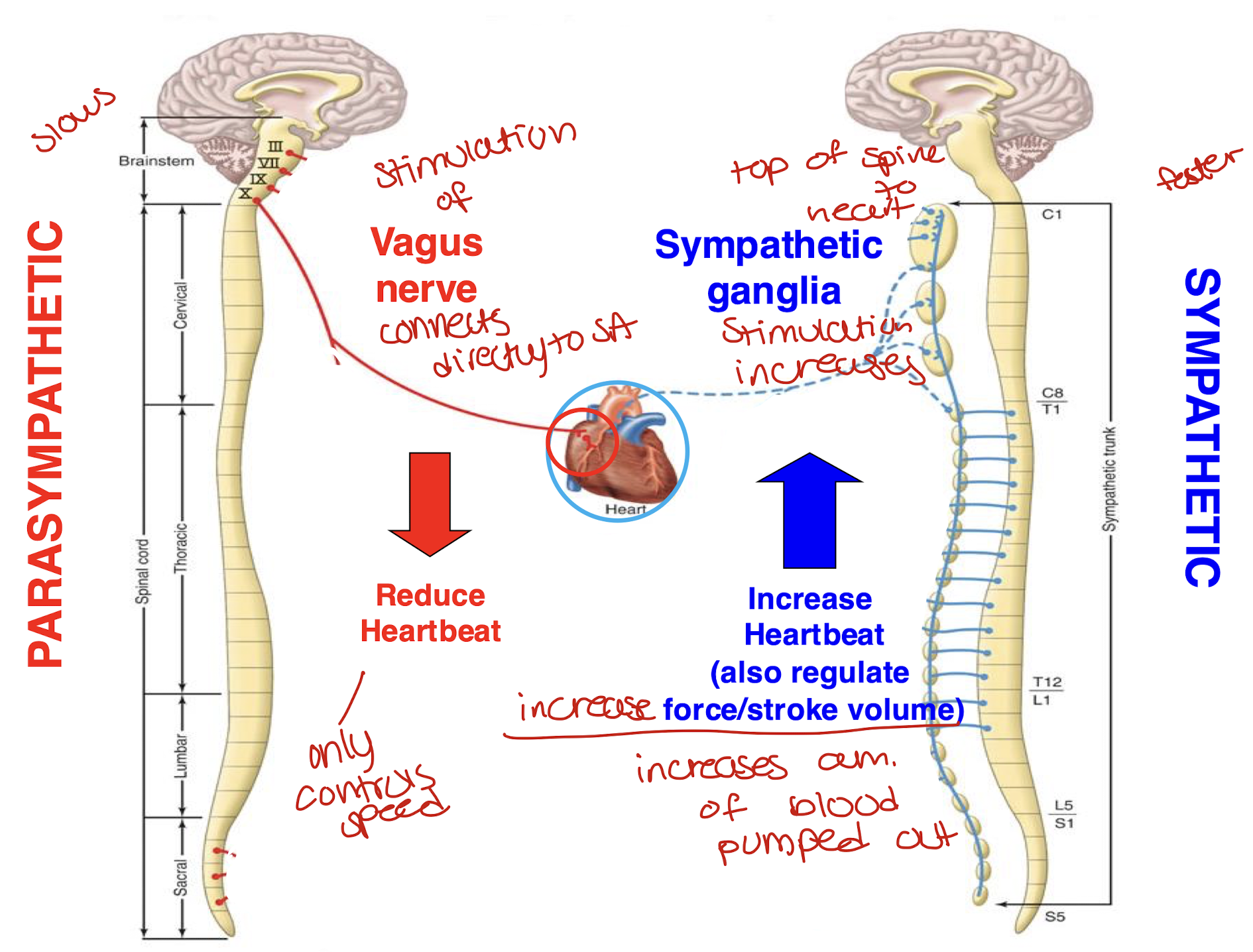
what is the role of the autonomic nervous system in the regulation of the sino-atrial node pacemaker cells?
how is the SA node regulated by the autonomic nervous system?
Parasympathetic:
stimulation of the vagus nerve connects directly to the SA node
it reduces heartbeat(slows)
ONLY controls speed
Sympathetic:
stimulation of the sympathetic ganglia which is connected to the top of the spine and the heart
increases heart beat(faster)
increases speed AND increases force/stroke volume so amount of blood pumped out
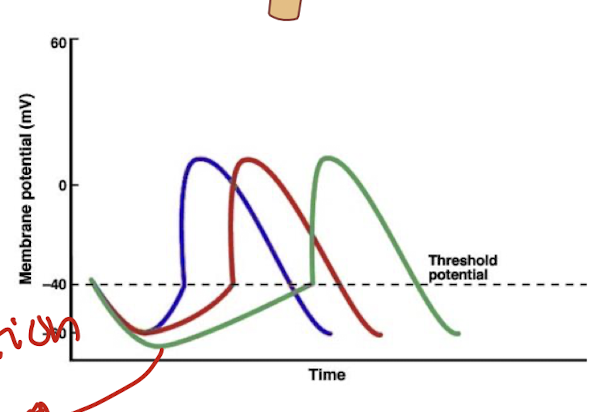
how does the parasympathetic NS reduce HR?
parasympathetic neurons release acetylcholine
they bind to m2 muscarinic receptors of SA node
this increases k+ efflux and decreases Ca2+ influx
this delays the depolarisation of SA and hyperpolarises cell(decreases rate of depolarisation)
this decreases HR
also known as Bradycardia
green
how does the sympathetic NS increase HR?
sympathetic neurons release noradrenaline
they bind to B1 adrenergic receptors of SA node
this increases Na+ and Ca2+ influx
this increases the rate of depolarisation
this increases HR
also known as tachycardia
blue
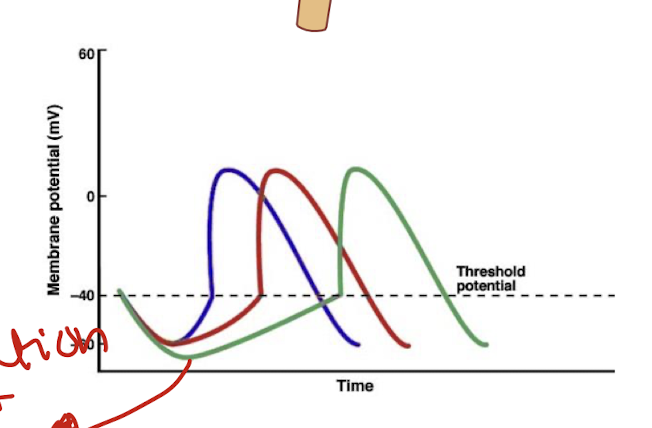
both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves are continuously active
at rest, the parasympathetic dominates and the heart rate is reduced from 100 to 70
the SA node has a natural bpm of 100 but the parasympathetic lowers that
what is an the electrocardiogram(ECG), describe the spread of excitation through the heart and how this would look on an ECG(what do PQRST stand for)?
measure electrical activity in your chest
what is an ECG?
a summation of the spread of action potentials during a heart beat through the various sections of the heart
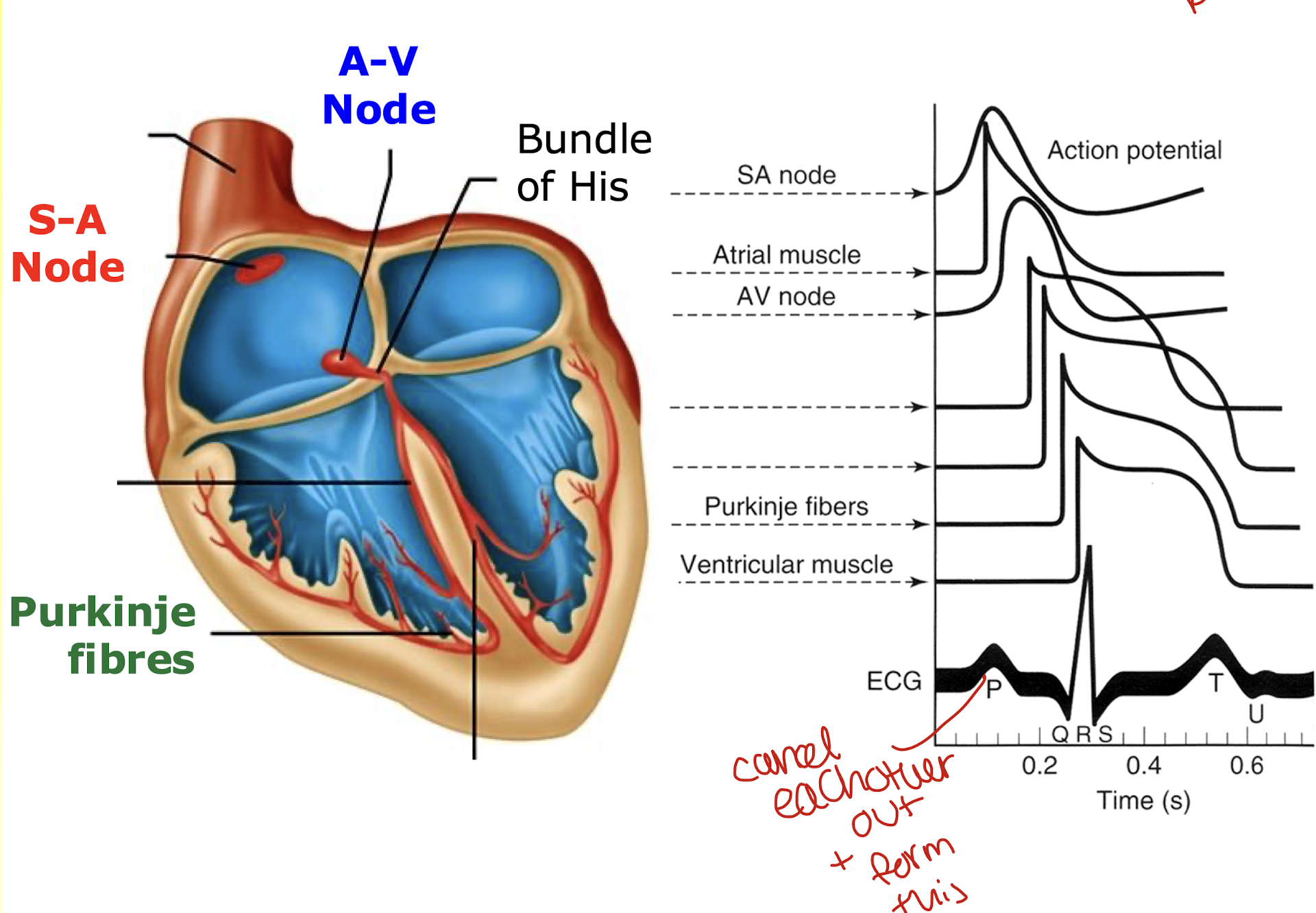
Electrical events of the cardiac cycle
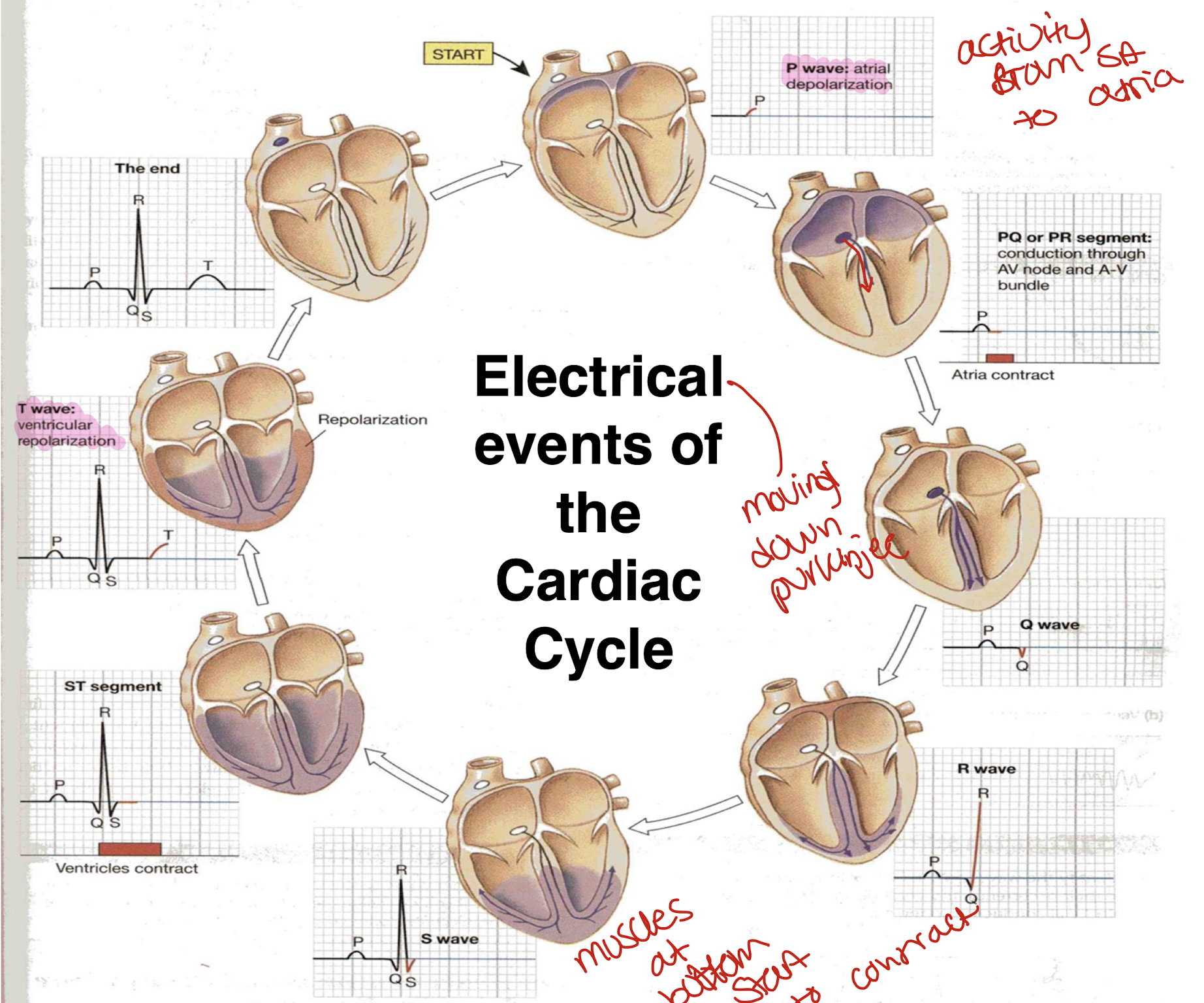
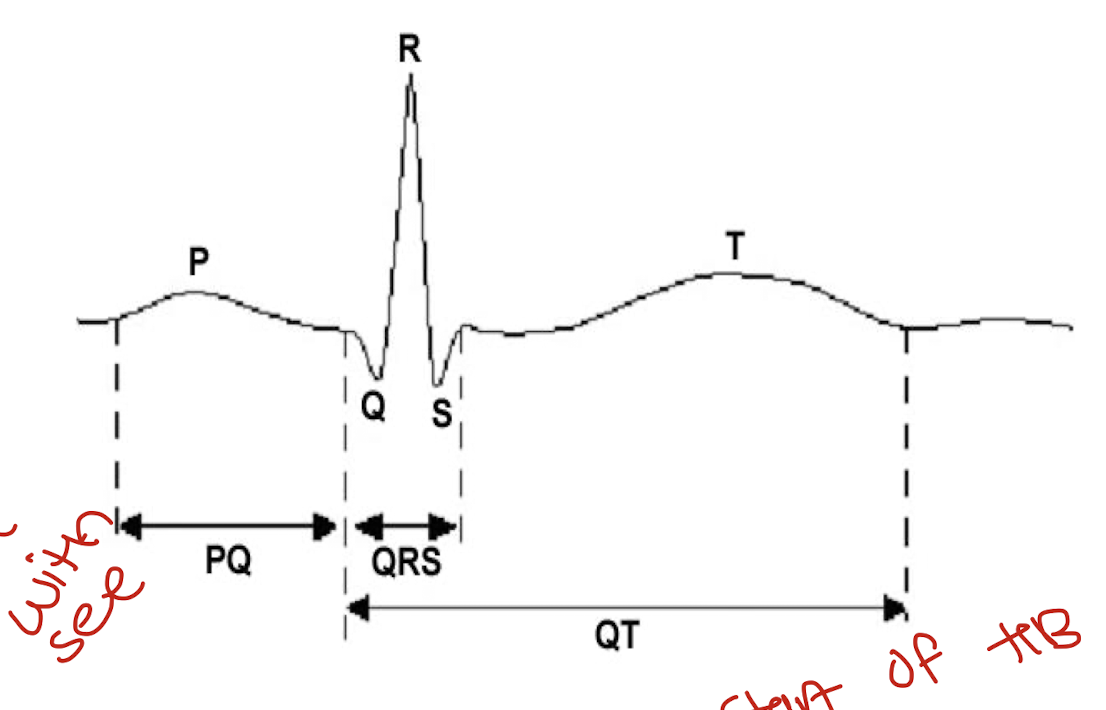
what do the deflections of the electrocardiogram mean? important
P- Atrial depolarisation: start of heart beat
QRS- Ventricular depolarisation: electrical activity to bottom of the heart starts to contract
T- Ventricular repolarisation
PQ segment- Atrial contraction(length of)
QT segment- Ventricular contraction(length of)- its used to see how length changes with drugs to see if drugs affect the heart
why is the ECG an important diagnostic tool?
provides important information concerning the electrical but not mechanical activity of the heart(mechanical is stethoscope)
used for heart rate, distrubances of rhythm and conduction, size of chambers , condition of tissues within heart, damage to heart muscles(myocardium), influence of certain drugs
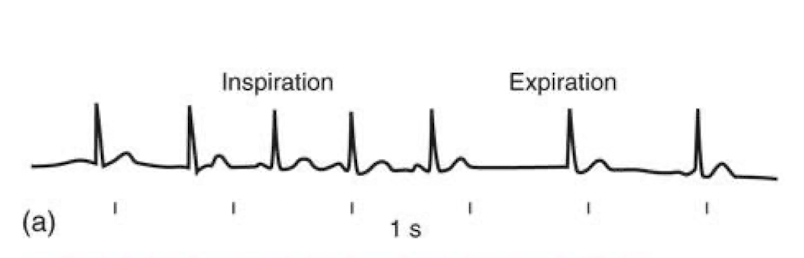
what is a sinus arrhythmia?
HR speeds up/slows down as you breathe
inspiration- decreases vagus activity so increases HR
expiration- increases vagus activity, lowers HR
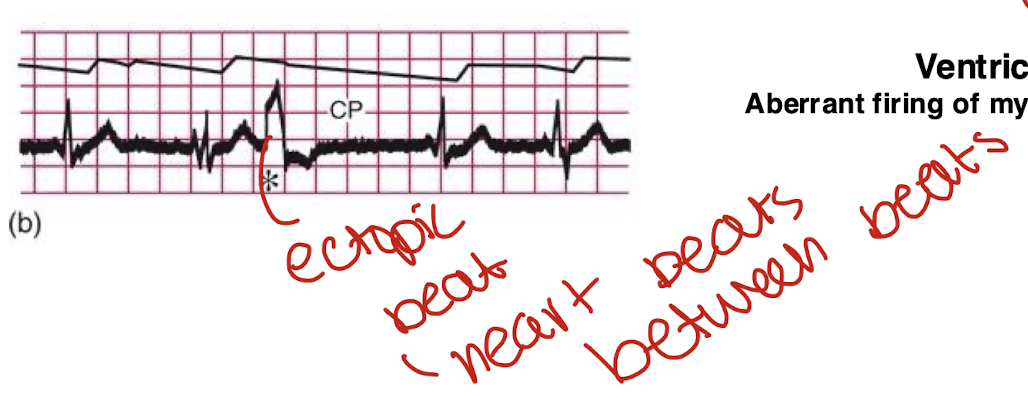
what is the ventricular ectopic beat
heart missed a beat
fails to eject blood
common after heart attacks(indicative of heart attack)
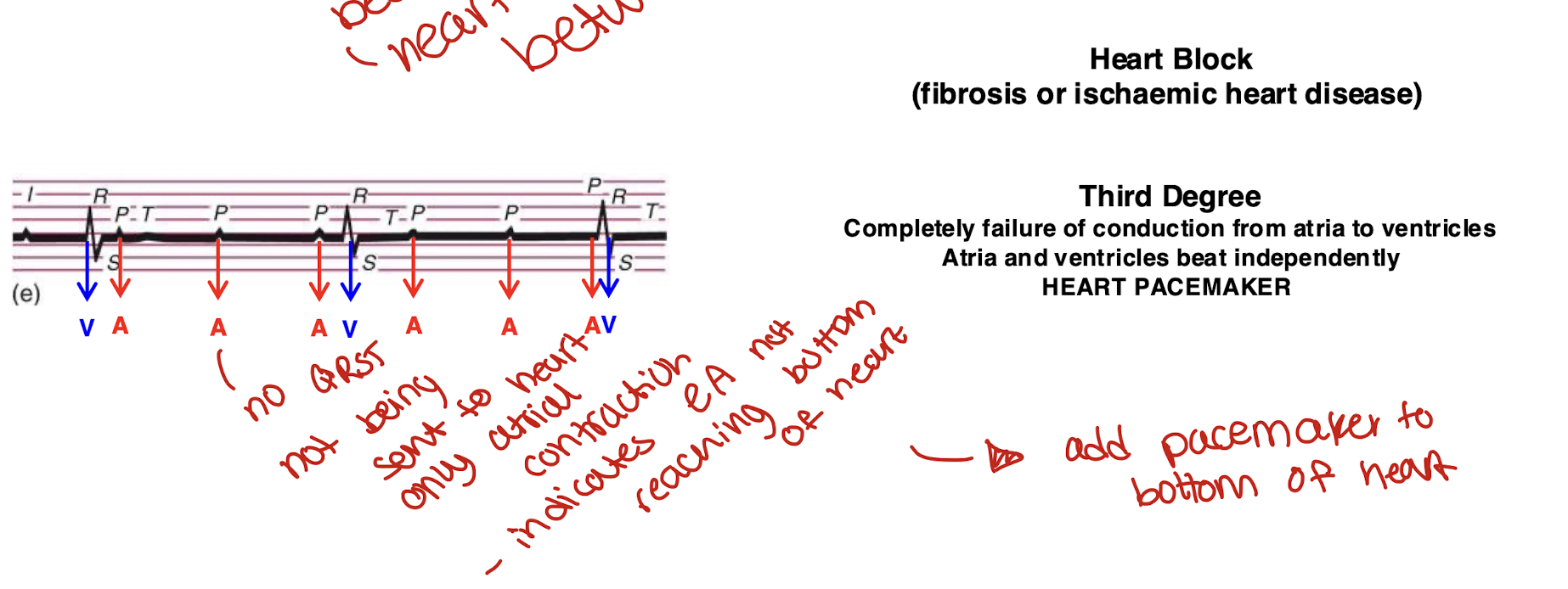
what is heart block?
due to fibrosis/ischemia heart disease
electrical stimulation doesnt pass from upper to lower region of the heart
atria and ventricles beat independently
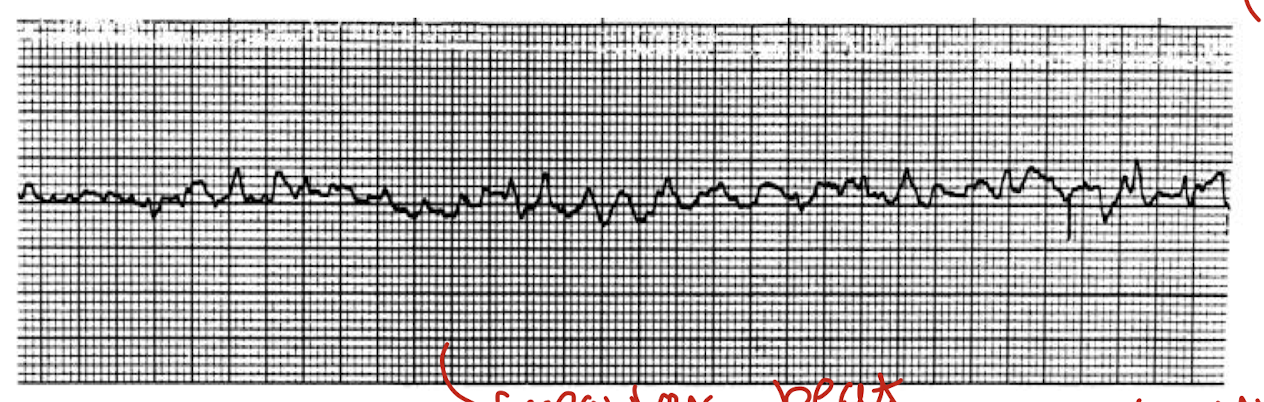
what is ventricular fibrilation?
cardiac arrest
random firing of heart beats, irregular beats
fibrillating ventricles cant pump blood
fatal after a few minutes
a heart attack is different thats when blood doesnt reach the heart
what is ventricular fibrillation caused by?
myocardial infarction (heart attack- blockage of vessels )
electrical shock
drug intoxication
impaired cardiac metabolism