Biol 208: Lecture 27 - Energy flow Through Ecosystems
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Trophic Dynamics define again
Why are there usually only 3-4 trophic levels?
Trophic Dynamics = The transfer of E from one part of the ecosystem to the next
Only 3-4 trophic levels because Energy is lost every time it is transferred (Law of THERMODYNAMICS)
What are the 1st and 2nd laws of thermodynamics?
1st: Total amount of E in the universe is constant and cannot be created or destroyed only transformed
2nd: Energy transfer increases the Entropy (disorder) of the universe
Entropy - the loss of usable E from the system in this course
What is Lindeman’s law in regards to E lost
what are the 3 ways E is lost + which is the most E lost?
Lindeman’s 10% law = 10% of energy consumed by a trophic level is transferred
Loss as HEAT (most) , RESPIRATION+ DECOMP. after death
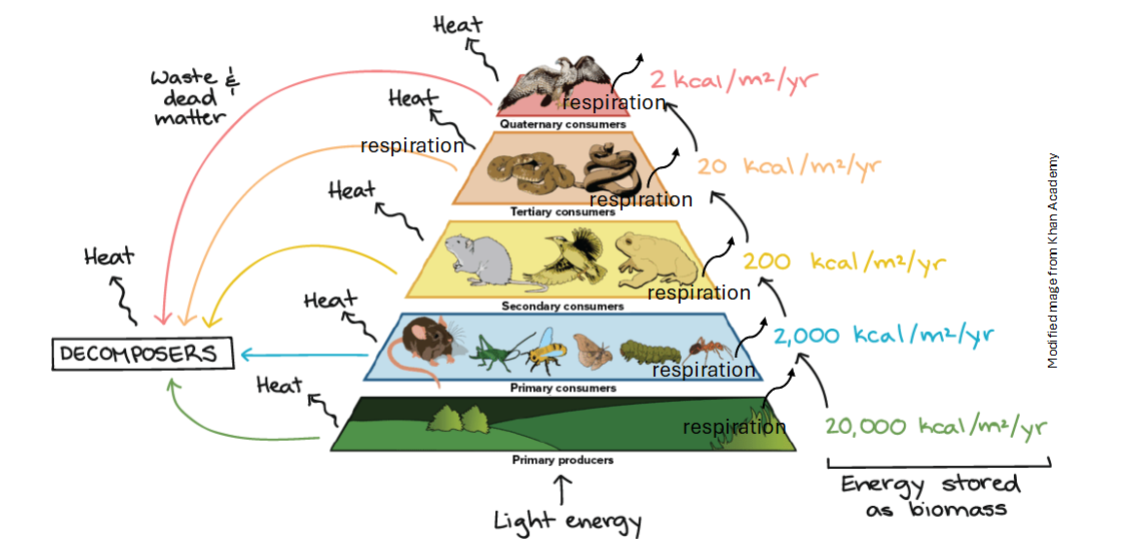
What are 2 other limits to E transfer other than E lost?
Can’t eat everything (not all biomass is edible)+ can’t find everything to eat (Not all biomass is accessible)
High trophic level individuals occur at lower abundances than lower trophic levels (= unlikely to evolve a super-predator b/c there won’t be enough food for it)
About how many percentages of the Total E input by solar radiation enters the ecosystem as NPP?
only about ONE%
Majority is lost through reflection, heat + evapotranspiration + plant respiration before it is available for consumption or decomposition
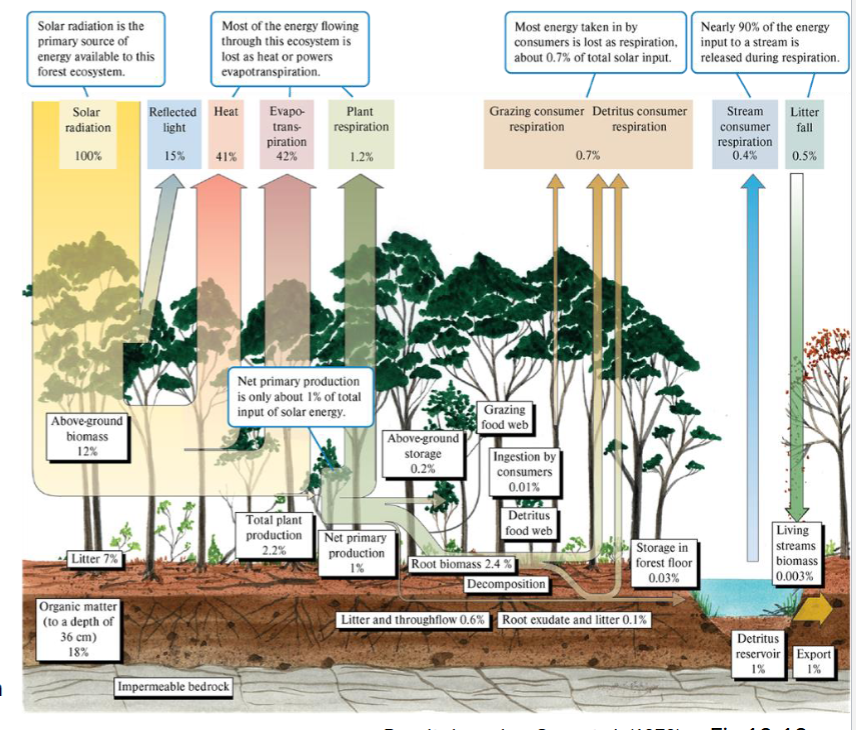
A relatively high portion of energy is captured where?
SOIL
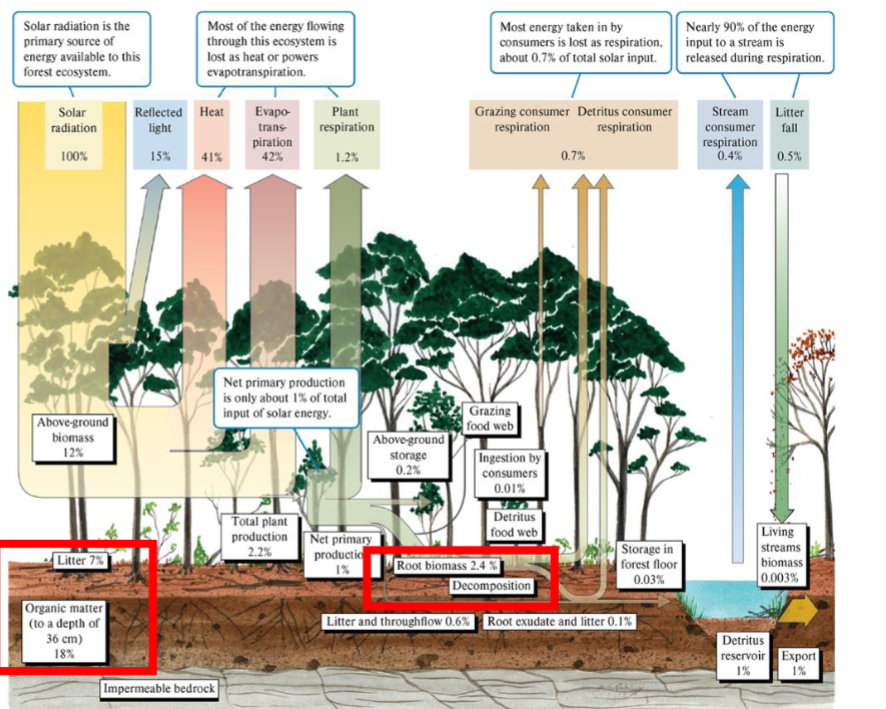

What are 4 things that we can learn from this diagram of Energy budgets?
the bottom trophic level of primary producers is relatively large
Organic belowground matter stores a lot of E
Consumers components = much smaller than Primary Prod component
Ecosystems are inefficient systems
Define Allochthonous inputs
give an example
= materials such as organic matter, nutrients, or energy that enter an ecosystem from an external source rather than being produced within the system.
eg. Salmon (aquatic) + bear (terrestrial)
eg. Leaf litter falling into a stream from surrounding forest trees
Define Trophic cascade
= when changes in the population size of a species in one trophic level alters populations in other trophic levels
Info Dump on the Trophic cascade between SEA OTTERS + KELP
Many kelp species exist along shore
Many invertebrates (herbivores) graze on kelp
Otter = Highest trophic level in the Kelp ecosystem
Sea otter + fur trade = Extirpation
Removing sea otter = reduced kelp population

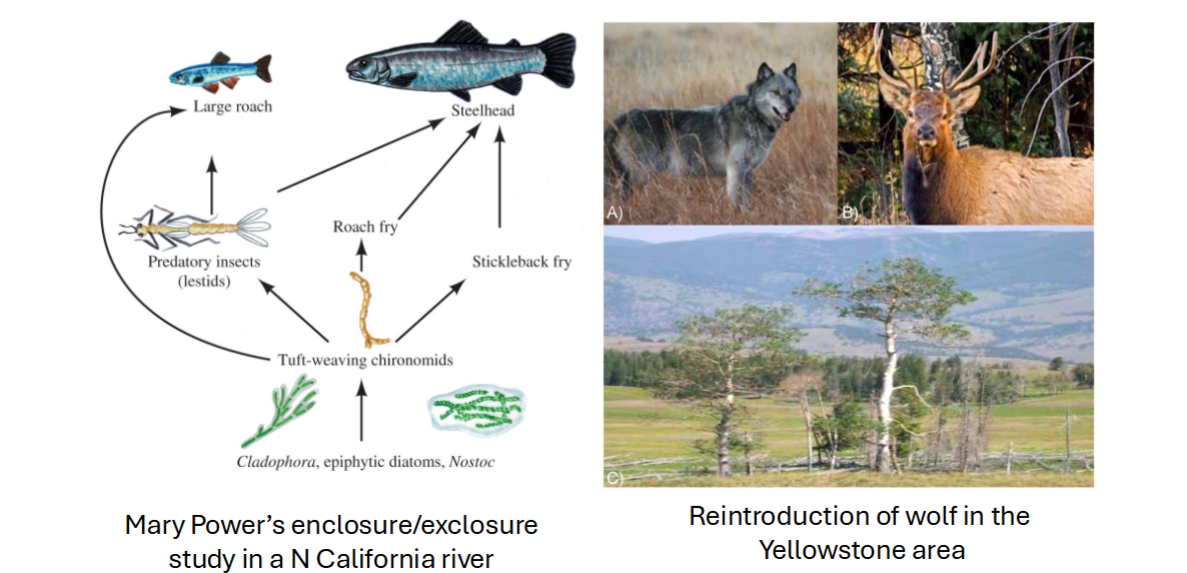
What are the 2 other trophic cascades mentioned in class?
Steelhead
Wolf + Elk