IB Geography Unit 6
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is Profit repatriation
A financial flow of profits from a country where a TNC has overseas operations back to the country where its headquarters are
What is Transfer pricing
A financial flow occurring when one division of a TNC based in one country charges a division of the same firm based in another country for the supply of a product or service. It can lead to less corporation tax being paid.
What is Tribalisation
The rise of “us and them” political movements which are often opposed to globalisation and westernisation
What is Populism
The idea that every political decision in a democracy should reflect what the majority of citizens believe, not what the majority of politicians believe
How are ICT systems a threat to individuals and buisnesses
WikiLeaks- Computer hacking organization which is rumoured to have hacked into Australian defense systems.
Yahoo- Suffered a major data breach where details from peoples accounts were stolen.
Tesco- Data breach where hackers stole money from peoples accounts
How has anti-globalisation protest voting occurred in developed world regions
An opposition to globalisation occurred in the form of the 2016 USA election with the election of Donald Trump. The aim is to regain control of their borders, nationalist ideology.
The vote for Brexit is also an example eg. most voters to leave were pensioners and people living in rural areas. People who voted to remain were younger and more urban.
How has anti-western movements and conflicts occurred in developing world region
Nigeria is a developing state. A violent campaign against westernisation of Nigerian society is lead by Boko Haram which is a militia group in the northeast. They kidnapped 200 girls from education and forced them into slavery as they believe western education is a sin.
What is transboundary pollution
Pollution which has damaging consequences for more that one country. Eg. Oil spills, acid rain, air and water pollution.
What contributes towards a transboundary pollution phenomena
Weather processes, emissions of greenhouses gases.
Why is transboundary pollution hard to manage
Because it covers multiple countries meaning there are many stakeholders in play.
What are the effects of Acid rain in eastern Canada
The Precambian shield (areas of hard rock) that cannot neutralise the effects of acid deposition.
The pH of lakes and groundwater may return to a normal level after the rain, however the ecosystems will be dramatically affected.
Eg. coral will lose a lot of calcium, which is required for the survival of phytoplankton.
Lakes have been reported to be more acidic, and the critical loads have been exceeded.
How has ICT been used to improve personal freedoms
CCTV cameras can help reduce crime and improve safety for the vulnerable.
Speed cameras can make sure motorists don’t pass safety limits.
National security issues can help make a case for greater online surveillance
What are geopolitical risks to global supply chains
eg. Foxconn was forced to suspend production of iPhone components in Vietnam due to political demonstrations.
Oil companies had to suspend new operations in Russia after the annexation of Crimea.
Tourism declining due to terrorist attacks eg. In Tunisia after Daesh terror attacks
What are moral/ethical risks to global supply chains
Unethical treatments of supply chain workers by outsourcing jeopardizing the reputation of TNC’s.
Eg. workers suicides and child labour allegations
Eg. Rana Plaza disaster
What is political sovereignty
The freedom of a state to govern itself fully, independent of interference by any foreign power. In theory, no UN member has complete political sovereignty.
What is economic sovereignty
The freedom of a state, from any outside intervention in its markets and trading relationships. In reality, no state has complete economic sovereignty owing to the complexities of world trade and trading agreements.
What are sovereign wealth funds (SWFs)
Money used by state governments to purchase large overseas assets such as power stations and rail infrastructure
What is corporate migration
When a TNC changes its corporate identity, relocating its headquarters to a different country.
What is an expatriate
Someone who has migrated to live in another state but remains a citizen of the state where they were born
What are disruptive technologies
A technology which brings major changes to the way people live and work instead of merely supporting and enhancing the current way things are done.
What have been the impacts of drone use
Individuals- people using it to make aerial films however the benefits must be weighed against the threat to other peoples privacy
Companies- Amazon using drones to deliver parcels. Increased use of drones may threaten the safety of passenger aircraft.
Civil societies- Used to locate victims in earthquake and hurricane zones, has already began to save lives in this context.
Military- Conflict can be waged remotely using armed drones, legality of this is questioned.
What are the impacts of 3D printing
3D printing of guns has become easier, blueprints are online
Guns can be made online
No background checks, untraceable, government are not aware of gun ownership
Blueprints are available to people who are not usually allowed to buy guns eg. felons
What are some new and emerging threats to the political and economic sovereignty of states
Economic- Tax Havens
Guernsey- No business, corporation or inheritance tax
Threat- Reduces other countries tax revenue as companies base themselves in tax havens, reduces GDP. Tax avoidance.
Profit repatriation = where profits should go to where the country is from, tax avoidance.
Corporation tax= on profits, sales revenue - costs
How has Starbucks used tax avoidance
Starbucks has to pay corporate tax in the UK, to reduce tax they increase costs
Starbucks UK can be charged by Starbucks HQ USA (in a low tax jurisdiction) to set up stores in the UK, Starbucks HQ sets the rate, reducing profits and therefore tax paid in the UK
Starbucks licence its brand- it bases it in the Netherlands (tax haven) so it pays the sub-company for licensing. This reduces profits in the UK.
Who are the winners and losers in tax avoidance
Winners in tax avoidance
Big corporations and wealthy people
9 out of 10 of the world’s top 200 companies have a presence in tax havens while corporate investment in tax havens quadrupled between 2001 and 2014.
Losers in tax avoidance
Ordinary people and poor countries
Corporate tax dodging costs poor countries at least $100 billion every year. This is enough money to provide an education for 124 million children and prevent the deaths of almost eight million mothers, babies and children a year.
How do FDI and commodity flows cause local environmental impacts
Some of world’s most polluted sites are global hubs for investment and commodity production. Eg. Nigeria’s Niger delta has had lots of oil spills, impacting people and one of the most important coastal habitats.
How do tourist flows cause local environmental impacts
Flights are more affordable, low cost airlines and the rise of the middle class. People want to visit remote regions of the world with wilderness qualities, which can disturb fragile ecosystems. Eg. Machu Piccu has been trampled by tourists as the amount of tourists has exceeded the limits
How do shipping flows cause local environmental impacts
Provides invasive species with a means of transportation. Eg. invasive species can wipe out fragile indigenous species
How do waste flows cause local environmental impacts
Most waste from the EU is sent to China. Electrical waste flows to West Africa and Asia where the waste can be dangerous or illegal.
What is a carbon footprint
The amount of carbon dioxide used by an individual, organisation or country as they go about their everyday lives/operations. It is measured in terms of the volume of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere as a result of fossil fuel consumption per unit of time.
Why has there been an accelerated growth in plastic production
Due to its use in everyday life, The cheap commodity driven by low wages in LIC/MIC fuelling throwaway attitudes where its often cheaper to bin something then to replace it. A boom in bottled water usage driven by lifestyle advertising
What are some local impacts of marine plastic pollution
Constitutes approx. 90% of all rubbish in the ocean. Areas are particularly polluted due to gyres which can cause large garbage patches. Many remote islands are being polluted with waste from other countries due to currents and gyres. Seabirds can ingest waste, causes death. Species of birds/mammals can get tangled up in the plastic. Red plastic lids mimic the shrill that albatross eat, making them inclined to eat it.
Describe the spiral of decline
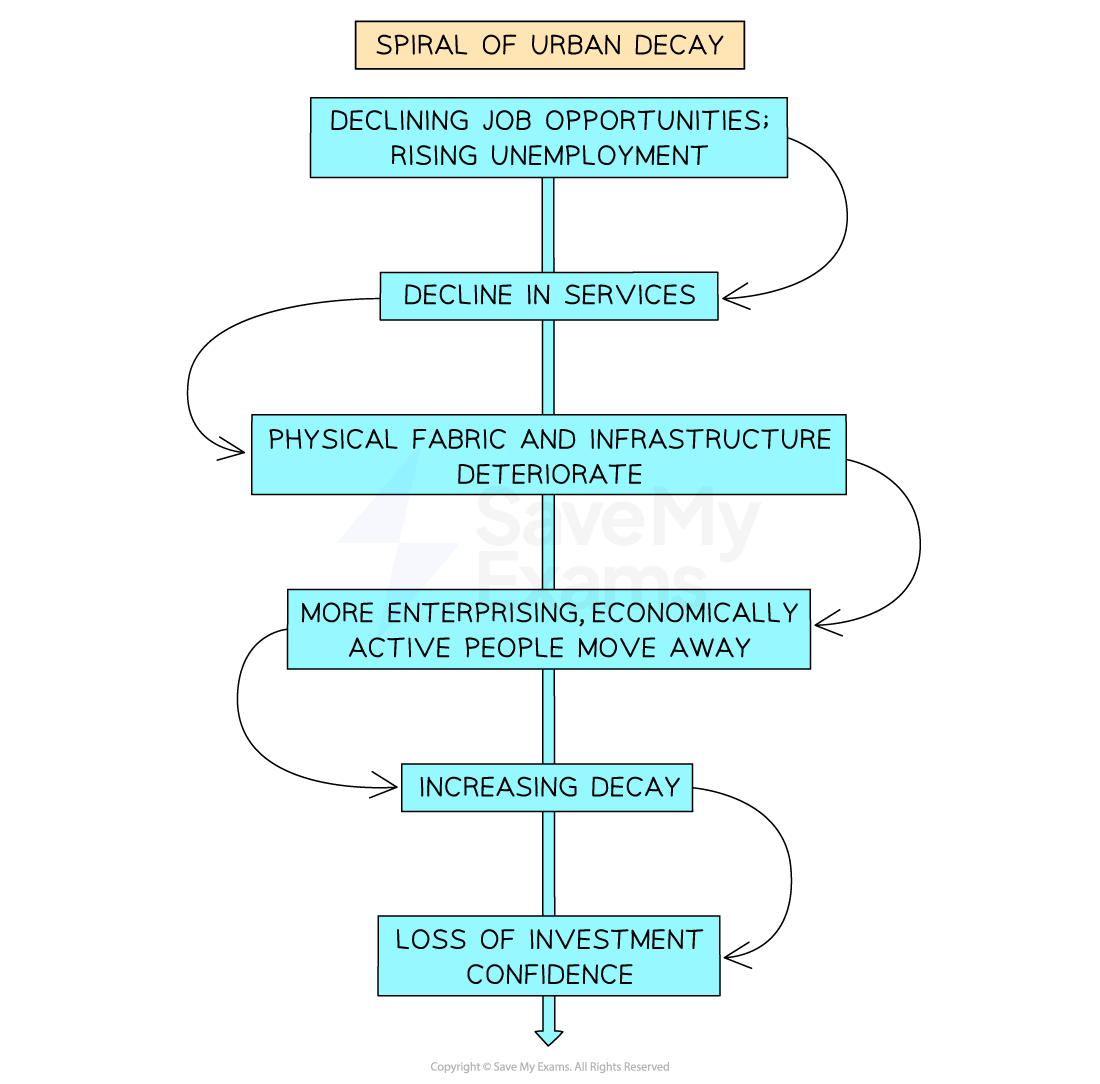
How can the spiral of decline be reversed
Investment, bringing an attractive younger workforce
What are the environmental effects associated with food production
What is global governance
Describes the steering rules, norms, codes and regulations used to regulate human activity at an international level
Case study: International civil society organizations and risks related to global interactions. World Wildlife Fund
Aims to preserve wilderness and the species which inhabit them, reducing the human impact of the environment
They do this by conserving the world’s biological diversity
Ensuring that the use of renewable natural resources is sustainable
Promoting the reduction of pollution and wasteful consumption.
They also voice opinions on development plans, to help provide advice on what would be best for the environment.
However critics argue WWF is too close to some TNC’s eg. Coca-Cola and IKEA.
They were also accused of using eco-guards who abused the rights of indigenous people in Cameroon.
Case study: International civil society organizations and risks related to global interactions OXFAM
Focuses in the alleviation of global poverty, based in the UK
They believe that poverty and powerlessness can be eliminated if there is political will and human action.
Currently they are focusing on economic justice, rights in crisis and gender justice.
There are criticisms that OXFAM is politically motivated, that some of its trustees were tax avoiders and that some of their stores have caused the closure of other charity shops.
How is a personal carbon footprint calculated
Calculated over the course of a year, estimating embedded carbon in
Goods purchased
Air flights
Home heating
Food and drink consumption
Commuting
How is a corporate carbon footprint calculated
Difficult to calculate the carbon due to questions wether it includes employees carbon, overseas operations and outsourcing
How is national carbon footprint calculated
Emerging economic have the fastest growing emissions, many of the LIC’s make a negligible contribution to the global carbon emissions.
HIC’s have high but emissions are falling.
What is the global shift
The international relocation of different types of industrial activities, especially manufacturing industries. Since the 1960s, many industries have all but vanished from Europe and America and have instead moved to Asia and South America
What is global agribusiness
A transnational farming and/or food production company. This term covers food, seed and fertiliser production as well as distribution.
What are some impacts of agriculture and food/drink TNCs
Eutrophication - Intense inputs of fertilisers in agricultural runoff over-stimulate ecosystem productivity. This results in algae bloom growth, and deoxygenation of water, causing species death
Biodiversity loss- monoculture agribusiness causes deforestation and the loss of habitats for many species
Water scarcity- Groundwater and freshwater supplies are being threatened due to water requirements in agribusiness where water is already scarce.
What are some strategies to build resilience
-Reshoring of economic activity by TNC’s, this reduces supply chain length so will minimise risk, Shorter waiting times, greater flexibility
Case Study for Reshoring: Apple
Total jobs reshored: 22,200
States benefiting: Texas,
Industry: Computers, office equipment
Headquarters: Cupertino, California
Apple is increasing its commitment to its Advanced Manufacturing Fund -- used to invest in U.S. manufacturing companies and boost the domestic manufacturing sector -- from $1 billion to $5 billion. The move is projected to create over 20,000 new jobs at Apple's existing campuses and at new office locations.
What are the pros and cons of reshoring
Reshoring is not easy or cheap, notably because many countries have lost manufacturing skills as a result of previous offshoring
Rightshoring is when things are put in the right place, eg. where taxes should be paid
Diversifies economies, creates jobs, boosts economy.
What is crowd sourcing
The act of taking a job traditionally performed by a designated employee and outsourcing it to an undefined, generally large group of people.
What is resilience
The capacity of individuals, societies, organisations and businesses to recover and assume business as usual functions and operations following a hazard event or other system shock
What is cyberespionage
When computer hackers gain illegal access to confidential government or company information