Blood banking Exam 1
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
A Caucasian patient is determined to have anti-Fya. What
is the likelihood of finding compatible blood? All you know
is that the gene frequency for Fya is 0.43 in Caucasians.
Fyb = 1-Fya =0.57 You need to find homozygous Fyb
units (aka Fya negative). Frequency of Fyb
homozygous units is 0.57x0.57 = 0.32. The likelihood
of finding a Fya negative unit is 32% assuming a
Caucasian donor base.
A patient is found to have anti-Fya and anti-K. What is the
likelihood of finding compatible blood? Gene frequency
for K is 0.04 and k is 0.96 among Caucasian donors. likely hood of finding an Fya negative unit is 32%.
The likelihood of finding a K negative unit is (k)(k) or
0.96x0.96 = 0.92 or 92%. The likelihood of finding
Fya and K antigen negative units are 0.92x0.32 =
0.29 or 29%
If a patient has anti-Fya and anti-K (29%) how many
RBCs do you have to test to find 2 compatible
units?
2/0.29= 6.89...7 RBCs
Patient MK has anti-K and anti-S and
they are preop for surgery 2 days from now. The
doctor has ordered 4 RBCs to be on hold. How
many RBCs need to be screened if the frequency
of the antigens are: K=9% and S = 55%.
Doctor wants 4 RBCs
Negative frequencies:
K = 91%
S = 45%
Number of units desired/ product of the negative frequencies=
4/ (0.91 x 0.45) =
4/ (0.4095) = 9.77 à 10 RBCs
A patient has anti-Jka, -K, -c, and –Fyb and the doctor wants to have 3 RBCs on hold for surgery. Assuming the tech is searching in ABO compatible inventory calculate the number of units he/she will have to screen to find antigen negative RBCs. The frequency of the antigens in the caucasian population is: Jka =76%, K=9%, c=80%, and Fyb=83%.
So the doctor wants 3 RBCs.
Negative frequencies: 1- (positive frequency) = negative frequency.
Jka = 24%
K = 91%
Little c = 20%
Fyb = 17%
3/ (0.24 x 0.91 c 0.2 x 0.17) =
3/ (0.007) = 428.6à 429 RBCs
very low likely hood
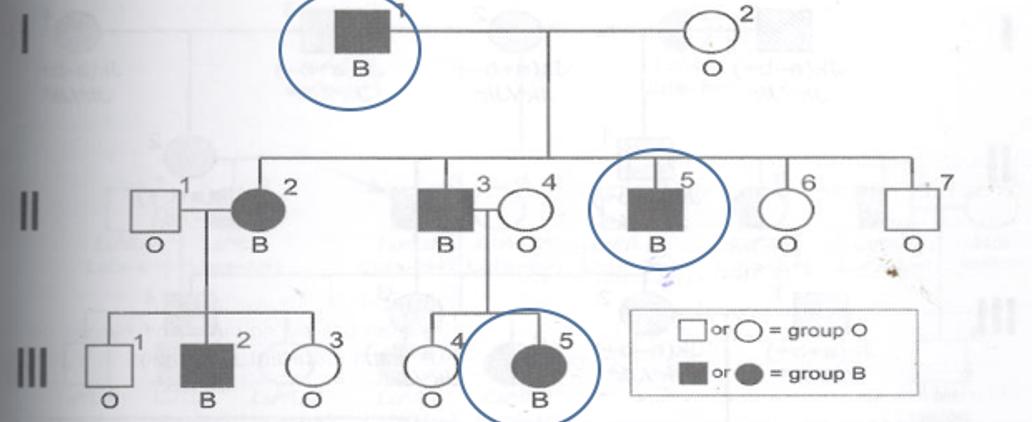
What is the inheritance pattern?
Autosomal dominant: Blood group B and O
Why: Trait appears in every generation and typically in a 3:4 ratio and sex doesn’t matter
Based on the ABO groups of the children, the father I-1 would have to be a B/O genotype since II-6 and 7 are O/O.
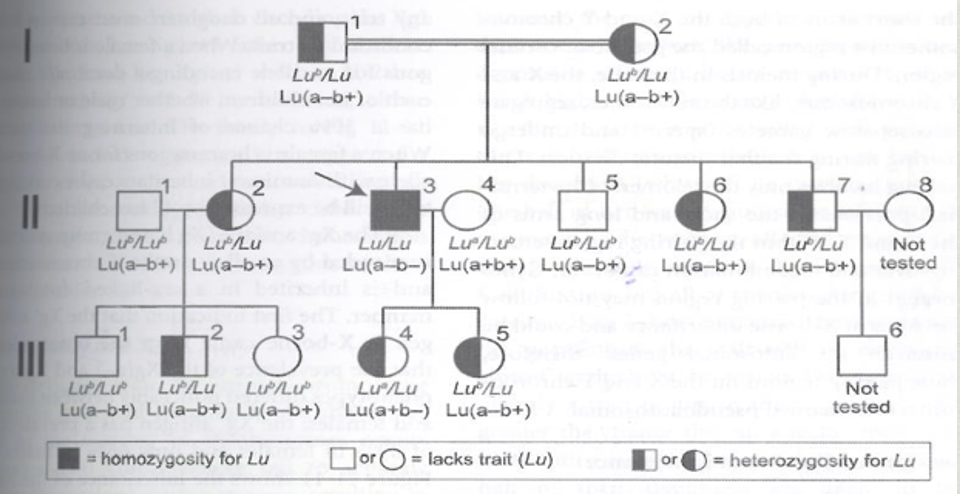
What is the inheritance pattern?
Autosomal recessive
Why: : traits appear in the 2nd generation at a 1:4 ratio and unaffected by sex.
The mating between II-3 and II-4 serves to demonstrate that Lu is recessive Lua and Lub and that the presence of the silent Lu allele is masked by the product of Lua or Lub at the phenotypic level.
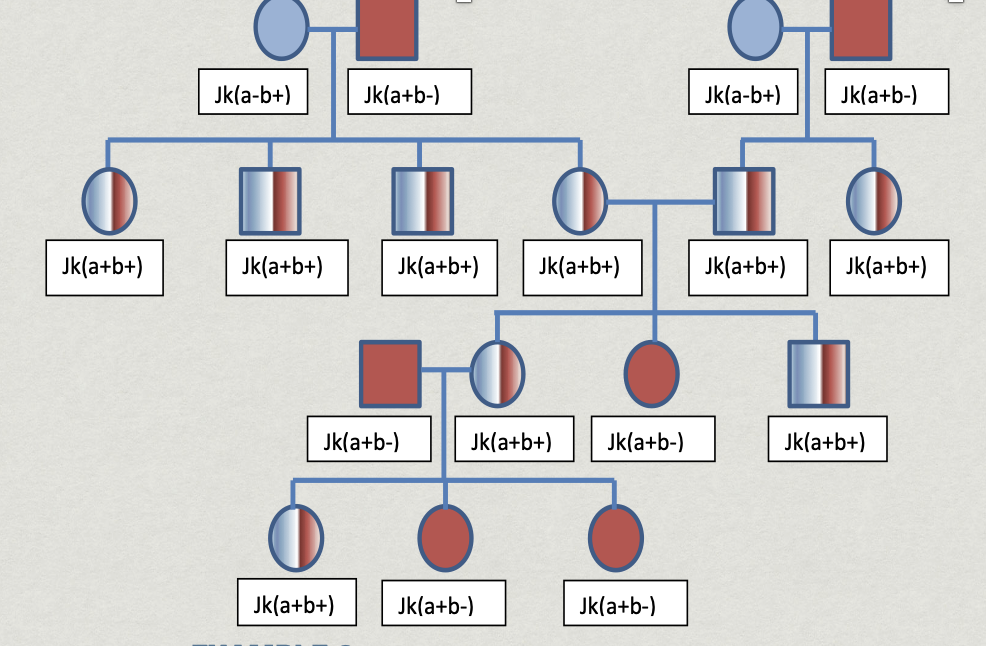
What is the inheritance pattern?
Autosomal Codominant:
Why:Sex doesn’t matter. Usually present in every generation.
An individual carrying 2 unlike alleles for any given trait may show the effects of only one of them, or of both (zygosity).
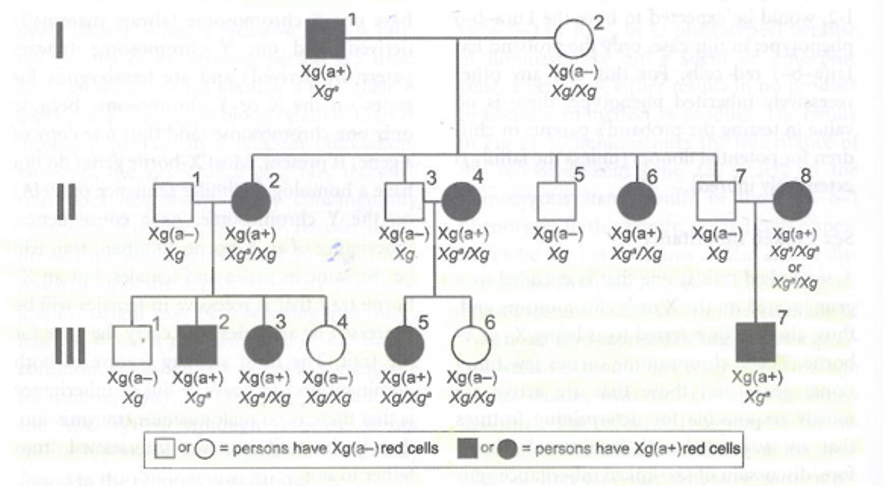
What is the inheritance pattern?
Sex-linked dominant
Why:Affected males transmit the trait to all daughters and to no son’s (no X to give to boys only Ys)
Affected females (heterozygous) transmit to half of their children either sex
Affected females (homozygous) transmit to all of their children
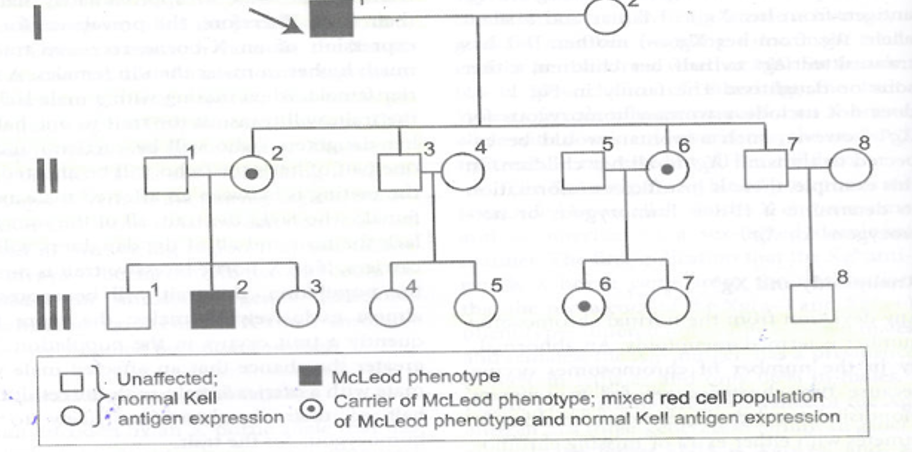
What is the inheritance pattern?
Sex linked recessive
Why: incidence of the trait is much higher in males then females. Rare to have homozygous females
Trait is passed from affected male to all daughters
All daughters who are carriers will affect half of their subsequent sons
Trait is never passed directly from father to son only through female carriers
Where does mitosis occur
everywhere but the ovaries and testicles
Where does meiosis occur?
ovaries and testicles
what is an Amorph?
An allele that does not code for a useable protein
cis
same side
trans is
opposite side
Cis orientation lends itself to a protein that puts the C antigen a bit farther away from the D antigen, meaning?
its not adding steric hindrance
Trans location results in D and C antigens being close together which results in a weaker expression of the D antigen due to…
Steric hinderance
Suppressor
affects the expression of another gene, or genes, through gene interaction by mechanisms that are not fully understood
Regulator
a gene that codes for a product that is required before another gene’s product can be expressed. This may be a precursor
first line of defense in innate and natural immunity
intact skin
mucous membranes
cilia
cough reflex
secretions
ph
second line defense in natural and innate immunity
phagocytic cells
complement-alternative pathway
cytokines
acute inflammatory reaction
Third line of defense also known as aquired and adaptive immunity
lymphocytes
B cells
antibodies
complement-classic
Cytokines
IgM
cold reacting at Room temp
Rarely causes hemolysis
IgG
React best at 37C
can cause hemolysis
IgA
allergic reactions
IgE
Hypersensitivity reactions
IgD
Antibody isotype on immature B cells
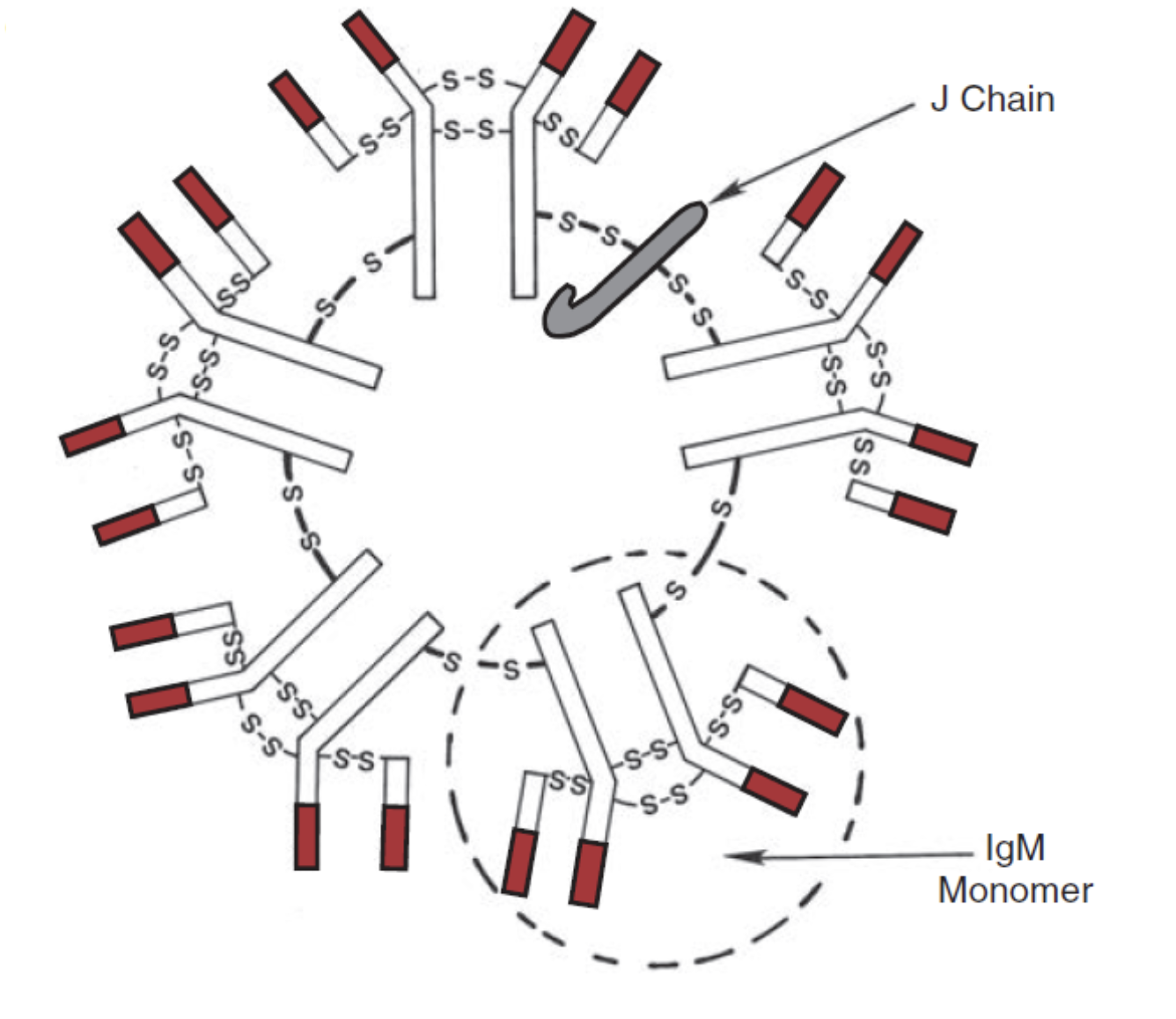
what makes IgM special
IgM is large and cant cross placenta
IgM is the first antibody detected
IgM can agglutinate red cells in saline
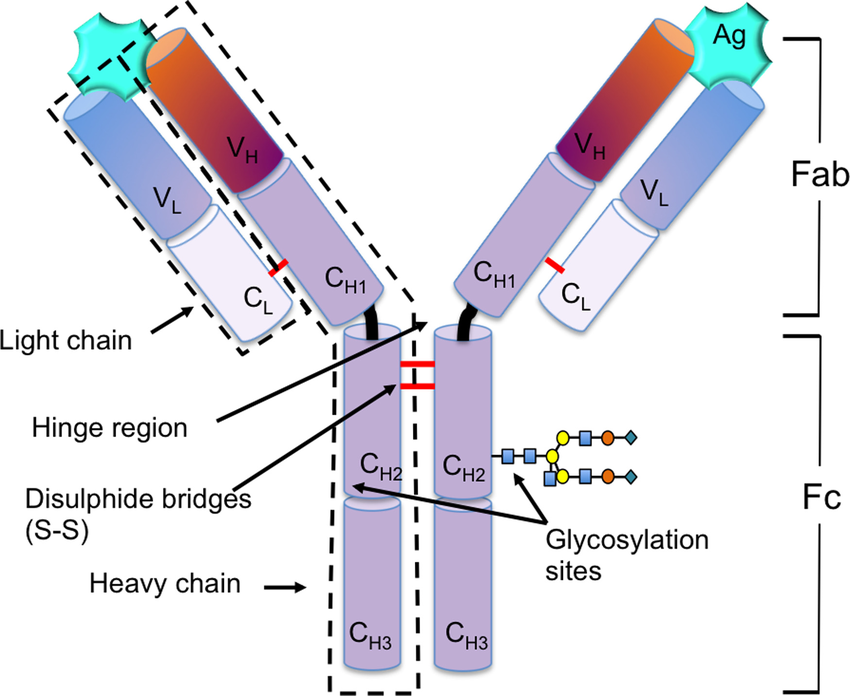
What makes IgG special
small
can cross the placentas
can bind complement and needs two igG
cannot agglutinate RBC in saline
reacts best at 37C
label a drawing of IgG
What does igM look like in vivo
Which phenotype(s) could NOT result from the mating of a Fy(a+b+) individual and Fy(a-b+) individual? Select all that apply.
Fy(a-b-) and Fy(a+b-)
T/F, Translation is the process by with DNA is copied into RNA.
False
T/F, Mitosis ends in 4 non-identical gametes each containing only 23 chromosomes.
False
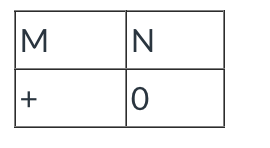
Given the following antithetical pair. Determine the most probable zygosity.
Homozygous
+0 is
homozygous
++ is
heterozygous
Given the following antithetical pair. Determine the most probable zygosity.
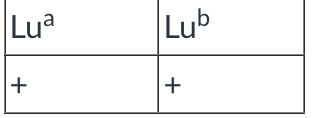
heterozygous
Given the following antithetical pairs (color coded). Determine the zygosity. for Fya, Kpa, and P

Fya=homozygous
Kpa=heterozygous
P= not applicable
Complement is activated by all of the following except?
IgG4
Sarah has a trait that neither her two brother nor parents express. Sarah's three daughters also do not express the trait. What is the inheritance pattern?
Autosomal recessive
A patient is making antibodies against K, E, and Fya antigens. If this patient is making the antibody, the most common scenario is that the patient lack the antigens and was exposed to them by either transfusion or pregnancy. Which of the following phenotypes could this patient have?
E-e+, K-k+, Fy(a-b+)
Justin expresses a trait that his brother doesn't have. Justin's father and mother also do not express it but his maternal grandfather did. What is the possible inheritance pattern?
X-linked recessive
Which of the following are found on antigen presenting cells?
Class II MHC
A patient needs 3 RBCs that are negative for the K antigen and the Fyb antigen. The frequency of the K antigen is 9% and the frequency of the Fyb antigen is 83%. How many RBCs do you have to test in order to find the 3 RBCs?
20
All of the following are involved in the acquired or adaptive immune response except?
Phagocytosis
Innate or natural immunity involves which of the following?
All answers are correct
Which of the following IgG subclasses is best at activating the complement cascade?
3
T/F, IgM is the most efficient immunoglobulin at activating the complement cascade.
True
In a primary immune response, which antibody is developed first?
IgM
Complement binds to what part of an IgG molecule?
CH2
T/F, A mature B cell or plasma cell can make antibodies against several different epitopes
False
T/F, It takes two IgG molecules to activate complement.
True
T/F, The complement cascade remains activated in an EDTA tube.
False
Which immunoglobulin(s) can activate the classic pathway of the complement cascade?
IgG1, IgG3, and IgM
All of the following are lymphocytes except _______?
PMNs
Step one of the complement cascade
Antibody (2xIgG or IgM) binds to antigen
Step 2 of the complement cascade
C1qrs binds to two Fc regions of the antibody(ies)
Step 3 of the complement cascade
C1q catalyzes C1r which activates C1s
step 4 of the complement cascade
C1s acts on C2 and C4 to form C4b2a (C3 convertase)
step 5 of the complement cascade
C3a is released and C4b2a3b (C5 convertase) is formed
step 6 of the complement cascade
C5-->C5b-->C6-->C7-->C8-->C9 = C5b6789 (MAC)
Two drops serum and one drop A1 cells, and two drops serum and one drop B cells are added to two tubes and centrifuged. The two tubes show reactivity when read macroscopically. This is an example of:
reverse type
Mixed field agglutination in ABO forward grouping may be caused by...
A3 subgroup and transfusion of the wrong blood type to someone
T/F, Antibody-antigen reactions are irreversible chemical reactions.
False
T/F, IgG antibodies can cross the placenta.
True
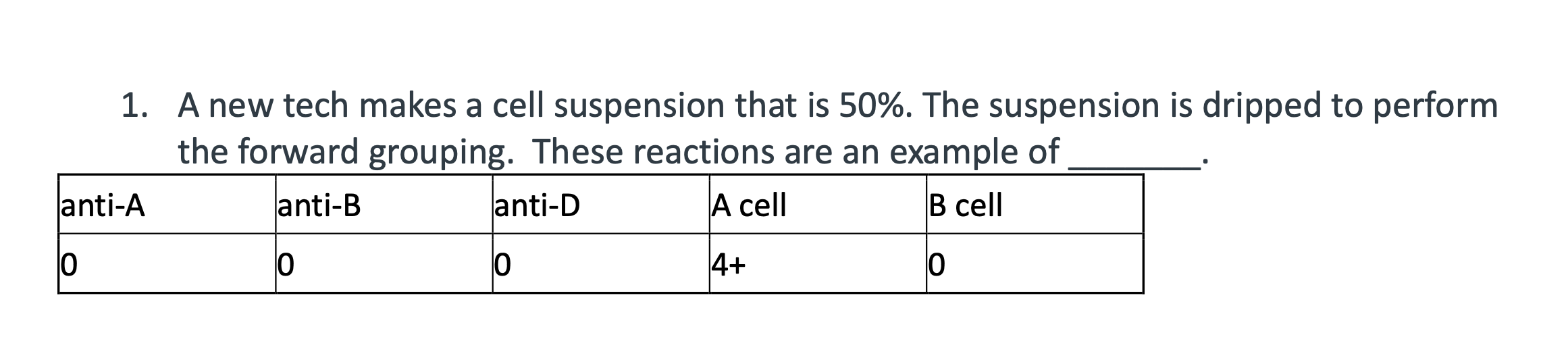
A new tech makes a cell suspension that is 50%. The suspension is dripped to perform the forward grouping. Plasma is also dripped for the back grouping along with reagent red cells. The results are as follows. This is an example of _______.

Post zone
What do LISS, PEG, Albumin, and enzymes have in common?
All answers are correct
This blood group types as an O and reacts negatively when tested with lectin Ulex europaeus. What is it?
type Oh, or Bombay
A patient has the following reactions in his front and back groupings. What terminal sugar does this patient have on his precursor substance?

N-acetylgalactosamine
If you were to describe the percentage of A1 types to A subgroups it would be....?
80% A1 and 20% A subgroup
A donor has the following genotype: A/O, Hh, and Sese. What will the donor have in his secretions?
H and A type 1 precursor substance
antigen
substance that is recognized as foreign, can cause an immune response
antibody
protein secreted by a plasma cell in response to interaction with an antigen
alloantibody
an antibody produced in one individual against the RBC antigens of anther individual
autoantibody
antibody reactive toward ones own RBC antigen
what can cause agglutination enhancements
concentration
centrifugation
pH
temperatue
antibody isotype
ionic strength
law of mass action
igm is an _____ spin phase
immediate
igG is a ______ phase (37C)
antiglobulin
least sensitive potentiators
saline
albumin
Medium sensitive potentiators
LISS
PEG
GEL/Solid phase
highest sensitivity potentiator and its issue
enzymes
issue: destroys some antigens
steps for agglutination reaction
sensitization
opsonization
lattice formation
agglutination
Prozone
antibody excess
Equivalence
optimum proportions of antigen and antibody
post zone
antigen excess
post zone
A 50% RBC suspension would cause what to be in excess?
antigen
If a patient has anti-Fya and anti-Jka how many RBCs do you have to test to find 2 compatible units? (Frequency Fya+ = 66%, Jka = 77%)
26
If a patient has anti-K and anti-Fyb and anti-s how many
RBCs do you have to test to find 2 compatible units? (Frequency K+= 9%, Fyb+ = 83%, s+ =89% )
118
H antigen sugar
L-Fucose
H antigen transferase
L-Fucosyltransferase
A antigen transferase
N-Acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
A antigen sugar
N- Aceltylgalactosamine
B antigen transferase
D-galactosyltransferase
B antigen sugar
D-galactose
List H from greatest to least…
0 > A2> B> A2B> A1> A1B
Oh, A 2, B you are meAnt 2 Be, A one and only, A1B
AB is the universal
plasma donor
O is the universal
RBC donor
Which of the following situations is most likely to cause
intravascular hemolysis when an incompatible transfusion
is given?
Group B packed cells to a group O recipient