Methods to Reduce Environmental Impacts of Fishing
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Name methods to reduce environmental impacts of fishing:
- Catch quotas.
- Net design
- Restricted fishing effort
- No-take zones
- Closed-seasons
- Minimum catch size
- Maximum catch size
- Protected individuals
- Captive rearing and release
- Biodegradable / radio tracked equipment
- Catch quotas
A catch quota sets a limit on the total weight of fish that can be landed. This quota may be divided up amongst all the fishing boats in the fleet
When do fishing quotas work best?
When the fish are found in single species shoals, where fishing will stop if the quota for that species has already been reached
When don't fishing quotas work quite so well?
In mixed fisheries.
Why don't fishing quotas work well in mixed fisheries?
Many species may be caught in the same net.
If the quota for one species has been reached, then any surplus is thrown back into the ocean, even though they are dead, while fishing for other species continues.
- Net design
• Mesh design
• Mesh size
• Escape panels
• Acoustic deterrent devices ('dolphin pingers').
• Mesh design
- Fishing nets are designed so that the mesh direction is diagonal to the direction of movement.
- This gives the net elasticity, as it is pulled through the water, but the mesh closes as it is filled with fish and drag increases, so smaller fish cannot escape through the shrinking gaps.
- Panels in the net with the mesh at right angles to the direction of movement do not not close up, so small fish can still escape
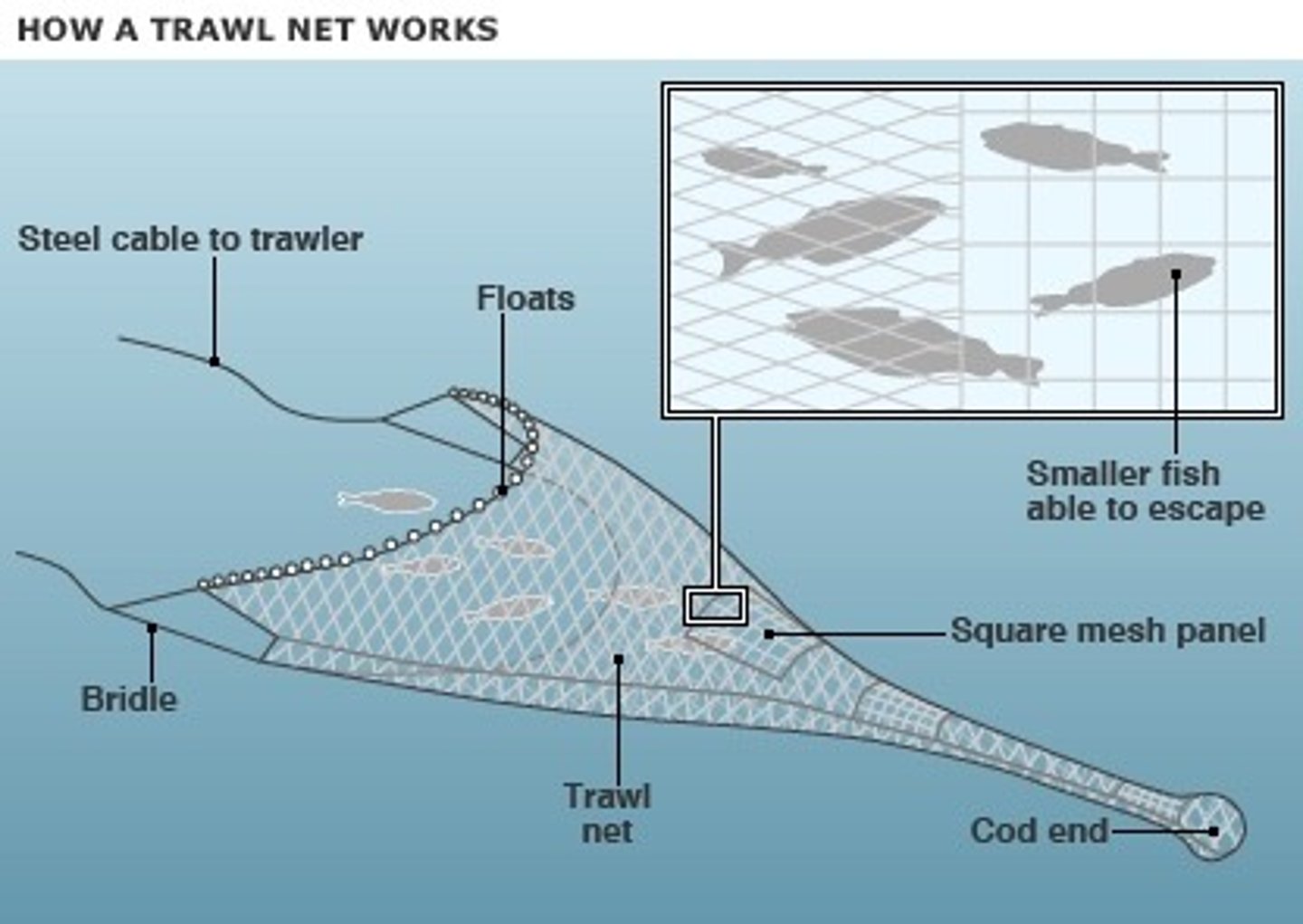
• Mesh size
Net mesh size can be set so that fish below a certain size can escape

• Escape panels
Turtle Exclusion Devices (TEDs) are large spring loaded escape panels in the nets, which allow turtles to escape

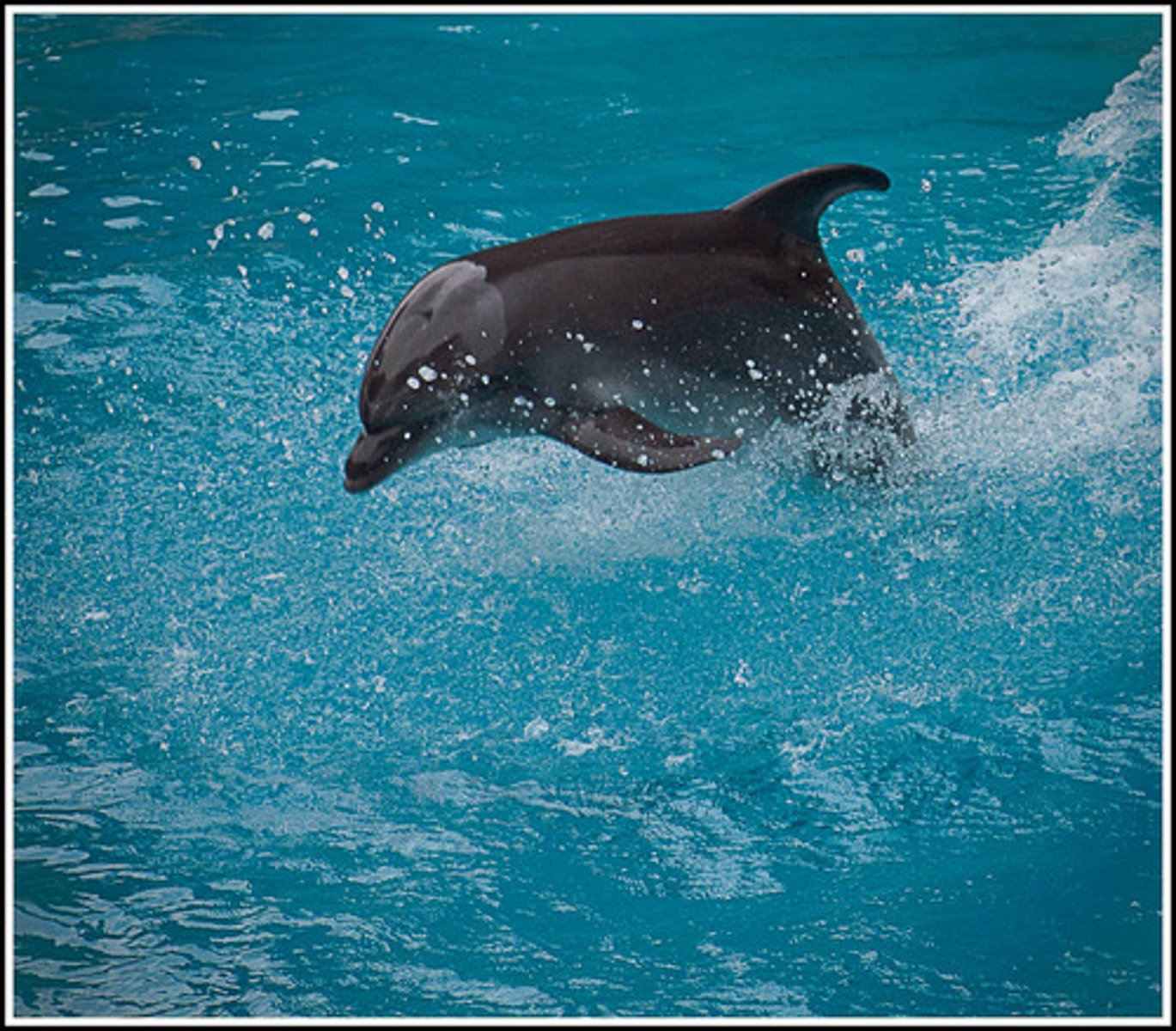
• Acoustic deterrent devices ('dolphin pingers').
These produce high frequency sounds that warn dolphins about the presence of the net

- Restricted fishing effort
- In some areas around the UK, there are limits on the size of fishing boats and the power of their engines.
- Fishing boats have limits on the number of days each year that a boat may spend fishing.
- Where the number of fishing boats is so large that overfishing is unavoidable, boat owners may receive compensation for their boats to be de-commissioned.
Describe the restricted fishing methods
- Drift nets are banned
- Demersal trawling is banned in areas of a sensitive seabed ecosystem
- No-take zones
NTZs are areas where fishing and other activities that exploit wildlife or damage the habitat are not permitted.
Why are NTZs good?
It protects the breeding populations of breeding adults, especially larger individuals.
How do NTZs help?
The breeding adults will produce a lot of offspring which can colonise surrounding areas where fishing may have reduced the populations of breeding adults. The communities of wildlife series that live within the NTZ can recover once damaging activities stop
- Closed-seasons
There is a ban on fishing for part of the year, allowing the fish to grow to a large size
When should closed season be?
Ideally, the closed season should include the breeding season (to protect future generations), however many fish species congregate in shoals to breed, making them easier to catch, so fishermen may oppose this restriction
- Minimum catch size
Banning the capture of small fish may not reduce the mass of the catch by much, but it may allow large numbers of small fish to grow to a larger size, and live long enough to breed
- Maximum catch size
Protecting large individuals may ensure there is a surviving population of breeding adults
Maximum catch size example
Large fish may produce many young
Female lobsters around the Outer Hebrides of NW Scotland may not be caught if the carapace (shell) is longer than 145mm
- Protected Individuals
The future production of young can be increased if adults that are known to be breed are protected
Protected individual example
If a female lobster that are caught and found to be carrying eggs must be released. A V-notch is cut in the tail, so if it is caught again, it will be released
- Captive rearing and release
Boosts wild populations
How does captive rearing and release work?
You raise individuals in captivity, and then release them into the wild. They are usually raised from eggs or larvae until their chances of survival in the wild are good, so they should increase the size of the adult population.
Why is captive rearing and release good?
Generally young marine species spend their first few weeks drifting in plankton before they settle to the seabed, where they may colonise a suitable habitat, and are usually eaten whilst they are in the plankton or fail to find a suitable habitat.
Population seeding increases the chances of surviving this period.
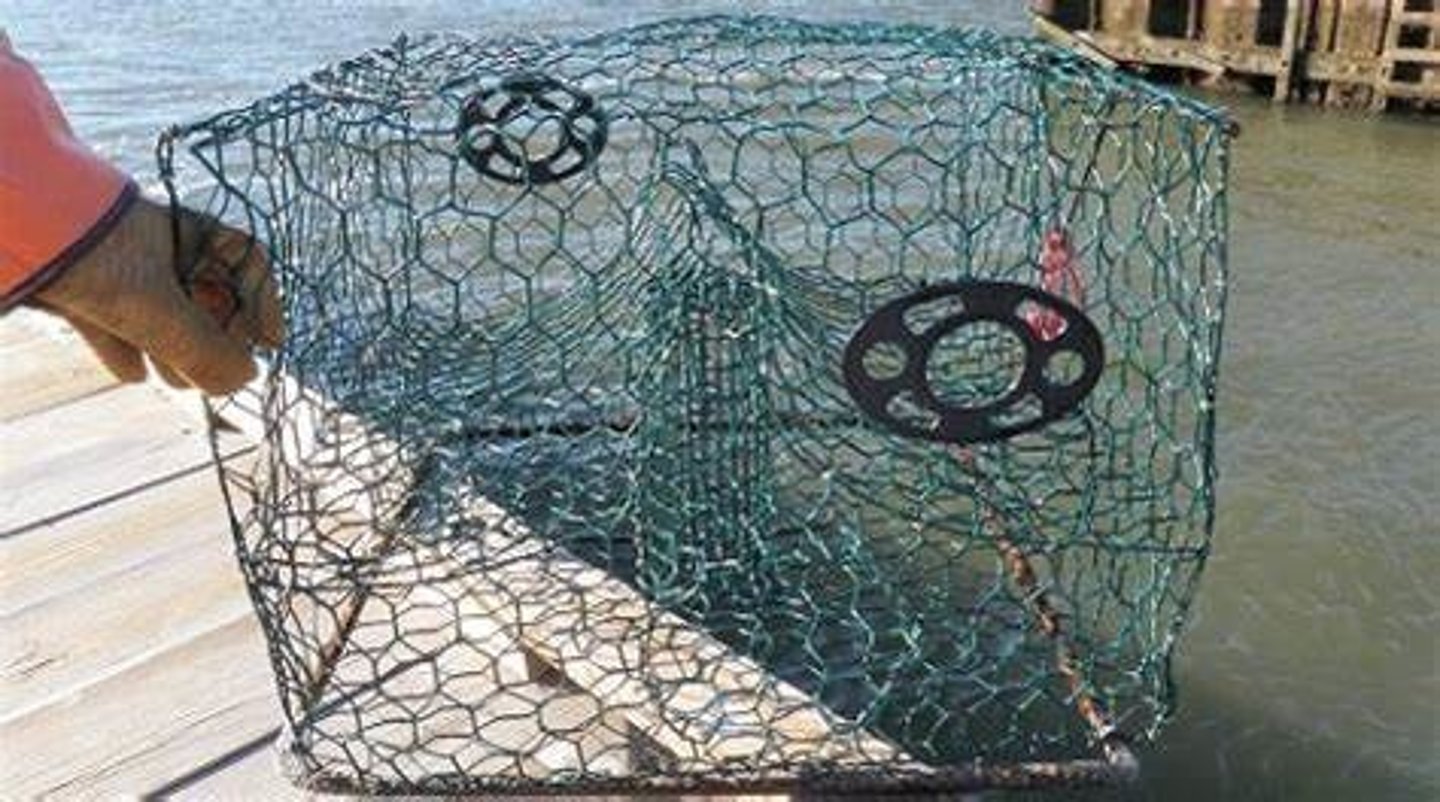
- Biodegradable / radio tracked equipment
Reduces ghost fishing
Crab traps acting as ghost traps
If traps for crabs and lobsters are lost, they may continue to catch more crabs and lobsters as the dead trapped individuals act as bait for more to be caught
How is ghost fishing reduced by biodegradable equipment?
Crab traps that are held together by biodegradable rope will fall apart if they are lost
How is ghost fishing reduced by radio tracked equipment?
In the USA, traps have radio transmitters that activate if the traps are lost, so they can be recovered