PHYSICS CHECK IN 2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
The mole
the amount of a substance that contains the same number atoms as 12 g of carbon
Avogadro's constant
the number of atoms in 12 g of Carbon - 12,
6.02 × 1023
Specific latent heat
the amount of energy per unit mass absorbed or released during a chaige phase at a constant temp. Energy goes into breaking or forming bonds.
Thermal energy (heat)
*Thermal Energy (Heat) (Q) - the net Energy transferred between two substances in thermal contact due a temperature difference
Capacity
the maximum amount that something can contain
Specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 Kelvin. J kg^-1 K^-1
Temperature
The property that determines the direction of thermal energy transfer between two objects.
A measure of the average random kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
.
Molar Mass
the mass of one mole of the substance (in grams the same as the mass number)
Thermal equilibrium
Objects at the same temperature so not heat energy is exchanged
Absolute zero
The temperature at which all particle movement ceases, internal energy is zero.
Pressure
Force exerted per unit area
Specitic
per unit mass
Evaporation
only takes place at the freee surface of a liquid and can happen at all temperatures.Vapor pressure<astomspheric pressure
Boiling
Takes place throughout the liquid and always at the same temperature for a given pressure. Vapor pressure= Amsopheric pressure
Principle of conservation of energy
Total energy of an isolated system remains constant. Energy can only be changed into other forms, it cannot be created nor destroyed.
Energy
The ability to exert a force causing displacement of an object (Ability to do work). Measured in Joules (J). Base units are kgm2/s2.
Work
The product of a force on an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force.. Change in kenetic energy. Unit J or Nm
Potential Energy
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its poetsition or state.
Gravatational potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is a specific form of potential energy associated with an object's position in a gravitational field.
Law of conservation of energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant over time. Energy can change forms but cannot be created or destroyed.
Efficiency
Efficiency is a measure of how well a system converts input energy into useful output energy.
Power
Power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred or transformed.
UNIT:W
Torque
The turning effect of a force.
Unit: Nm
Rotational / translational equilibrium
The sum of the resulting torques acting upon a body are zero. The body remians stationary or continues to roate at a constant velocity.
Conservation of angular momentum
If no external torque acts, then the angular momentum of a system of isolated bodies is conserved
Moment of inertia
An objects tendency to resist rotational acceleration. kg m2
Specific Latin Heat of fusion
Energy required to change the phase of 1kg of a substance from a liquid to a solid or a solid to a liquid at a constant temp.
Why is Specific Latent heat of vaporisation greater than specific latent heat of fusion.
During the change of state the Pe particles changes as bonds are weakened/ broken
The Pe Chang for vaporisation is greater than that for fusion, since more energy is required to break intermolecular forces between water molecules than to weaken them.
Heating curve
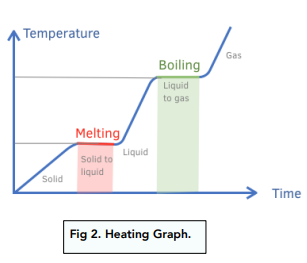
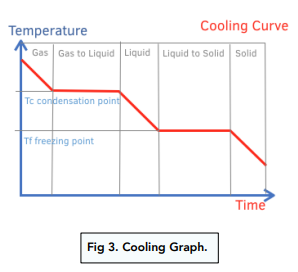
Cooling curve
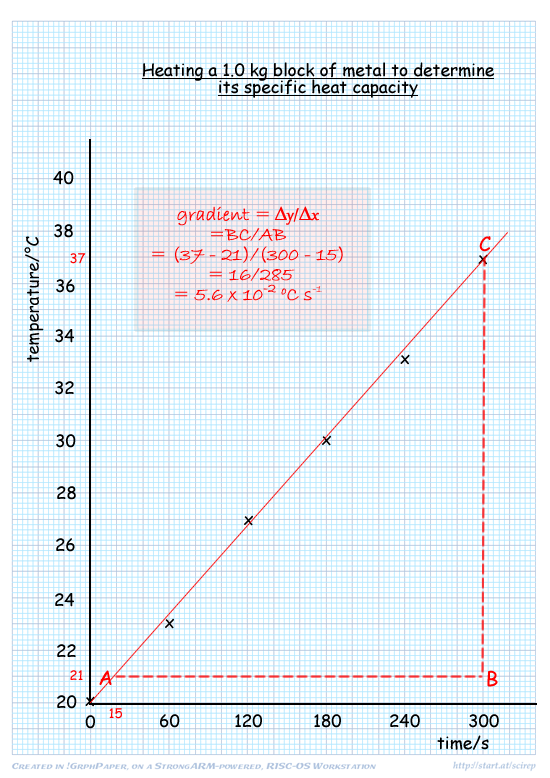
Specific Latent heat and Specific heat capacity from temp time graph.
Why does EK not change when phase changes
-When phase change eg meltingthe thermal energy supplied is used to break intermolecular forces between molecules increasing the average distance between molecules and their potential energy.
Internal energy
The sum of the total kinetic energy and the total intermolecular potential energy of the particles within the substance.
Important notes:
The above definition is for solids and liquids as they have intermolecular forces binding the particles together.
Gases have no intermolecular forces so changing their position does not require work to be done. The internal energy of a gas is therefore only the total kinetic energy.
Density
Mass per unit of volume ( g/cm3)(kg/m3) or (kg/l)
Brownian Motion
Brownian Motion is the term for random movement of particles that is suspended in a fluid (liquid or gas).
Heat
Thermal energy transfers from an object with higher temperature to another object with lower temperature. The energy transfer is called heat (the flow of energy due to temperature difference).
Solids vs liquids vs gas properties
Solids vs liquids vs gas further
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
The Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the power of radiation emitted by a black body per unit area is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature.
The total area under the graph is the total power radiated (luminosity). The power radiated by a black-body is given by:
L = σAT4
σ – Stefan-Boltzmann constant
A – surface area in m2
T - temperature
Black body
A black body which absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation is both the perfect absorber and the perfect emitter of radiation.
The radiation emitted by such a body at constant temperature is called black-body radiation.
Radiation
Energy is transferred by electro magnetic radiation.
Conduction
Energy is transferred by direct contact

Convection
Energy is transferred by the mass motion of molecules

Wien’s law
Wien’s displacement law relates the wavelength at which the intensity of the radiation is a maximum λmax to the temperature of the black body T.
This states that λmaxT = constant.
Wien’s constant is 2.9x10-3mK
Intensity
intensity is the magnitude of a quantity per unit area. In physics, intensity is usually used describe the magnitude of waves per unit area.
What is the state of thermal equilibrium
When the rate of energy absorption is equal to the rate of energy emission
Luminosity/ Brightness
Luminosity or Intrinsic Brightness - the energy emitted from a source in all directions per unit time, often measured in watts (joules per second),
Emiisivity

Colder/ warmer black bodies
— The shorter the most intense vaelemgth is the hotter the body
Inverse square law
Phase changes
The amount of heat req uired to change 1kg of a substance from liquid to gas without any change in temperature.
uired to change 1kg of a substance from liquid to gas without any change in temperature.
Specific latent heat of fusion: .
the energy needed to melt, or freeze a kilogram of substance
Specific latent heat of vaporization:
the energy needed to vaporize or condensate a kilogram of substance
Angular momentum
The property of any rotating object given by moment of inertia times angular velocity. (kg-m2/sec)
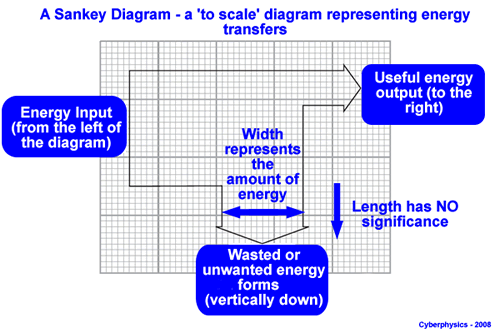
Sanky Diagram
Internal energy
The total potential energy and random kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance.