Bio: 8.1-8.2 - DNA & Replication
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
How are DNA, genes, and chromosomes related?
**DNA** makes up our **genes**, which are found on **chromosomes**
2
New cards
DNA Function
stores the genetic info of an organism as a “code” of bases
3
New cards
Gene
A segment of DNA that contains the info to make a specific protein
4
New cards
How are proteins and phenotypes related?
proteins = phenotypes, so different genes → different order of bases → different proteins → different phenotypes
5
New cards
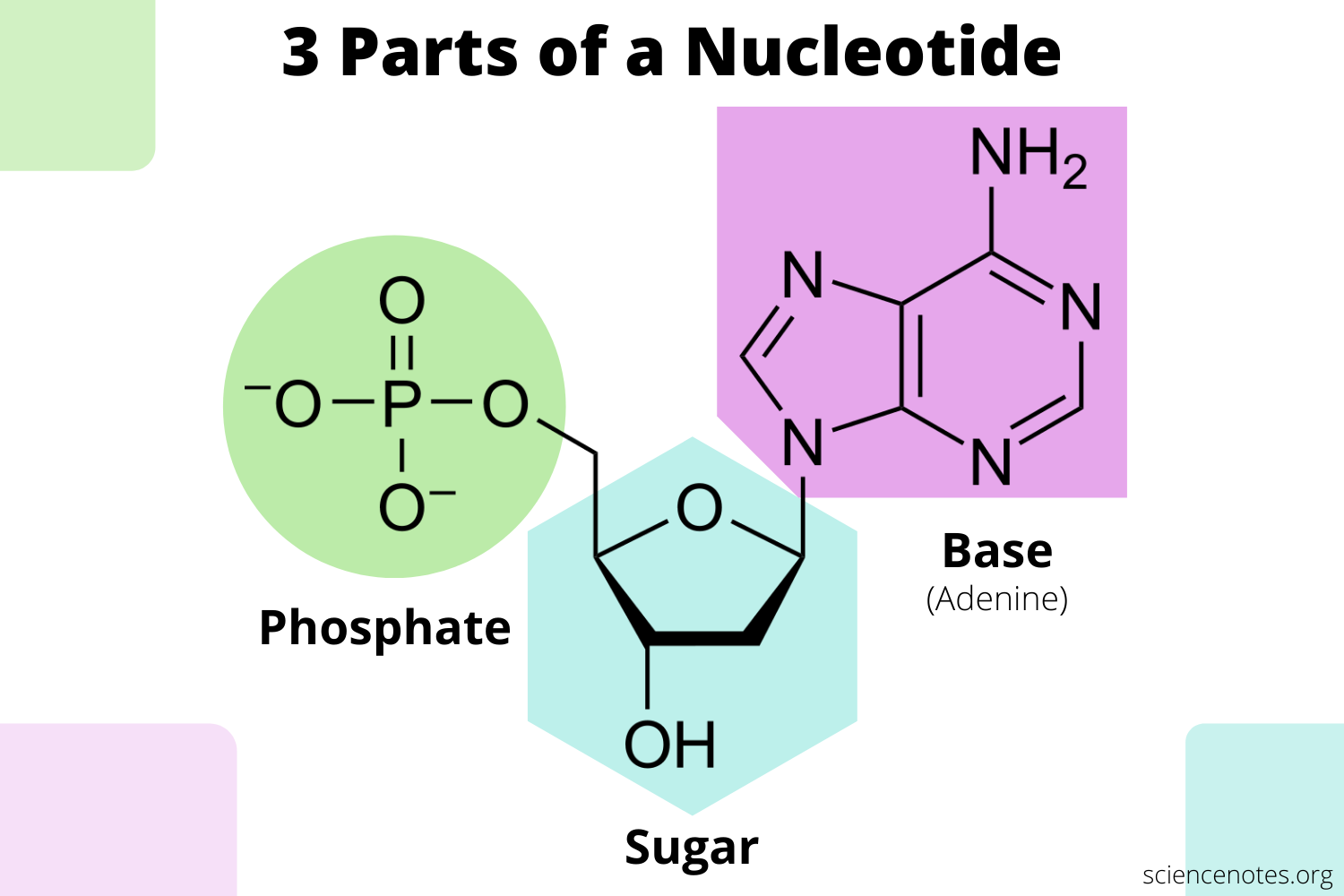
DNA Structure
made of repeating nucleotides which are made of
* 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose)
* phosphate group
* nitrogenous bases (a small organic molecule w/ a core ring made of carbon and nitrogen)
* 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose)
* phosphate group
* nitrogenous bases (a small organic molecule w/ a core ring made of carbon and nitrogen)
6
New cards
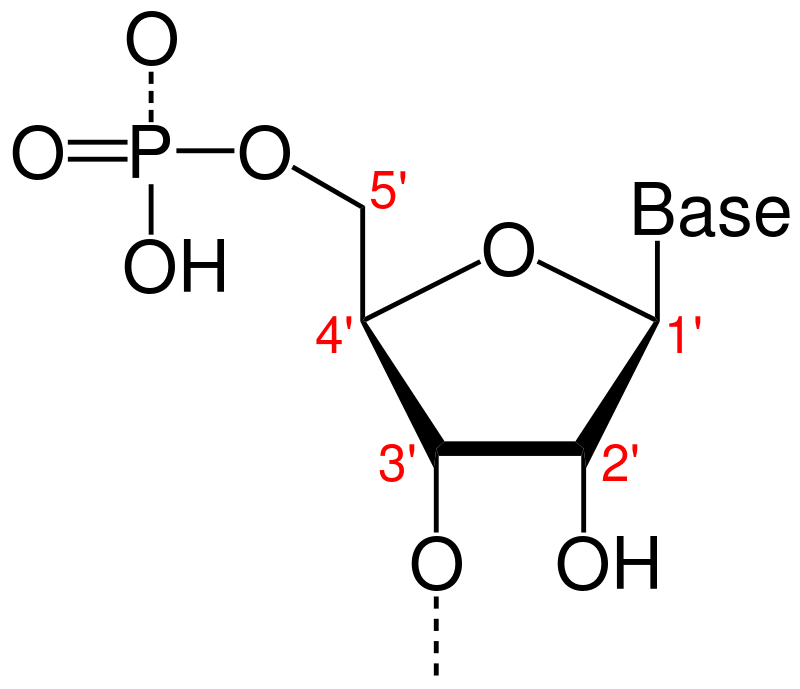
Deoxyribose
5 carbon sugar:
* 1’ carbon = nitrogenous base attaches
* 3’ carbon = -OH group
* 5’ carbon = phosphate attaches
* 1’ carbon = nitrogenous base attaches
* 3’ carbon = -OH group
* 5’ carbon = phosphate attaches
7
New cards
Nitrogenous Bases
Each nucleotide has a different one:
* Adenine
* Guanine
* Cytosine
* Thymine
* Adenine
* Guanine
* Cytosine
* Thymine
8
New cards
Purines
2 rings of C & N, larger → A & G
9
New cards
Pyrimidines
1 ring of C & N → C & T
10
New cards
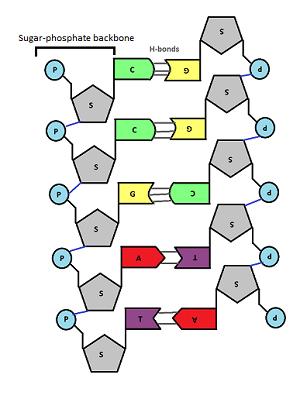
Complementary Base Pairing
chemical structures “complement” each other
* A w/ T → 2 Hydrogen bonds
* g w/ C → 3 Hydrogen bonds
a purine **must** pair w/ a pyrimidine - consistent width
* A w/ T → 2 Hydrogen bonds
* g w/ C → 3 Hydrogen bonds
a purine **must** pair w/ a pyrimidine - consistent width
11
New cards
Chargaff’s Rule
\# of A = # of T (and same w/ G & C) - small difference result from mutations
12
New cards
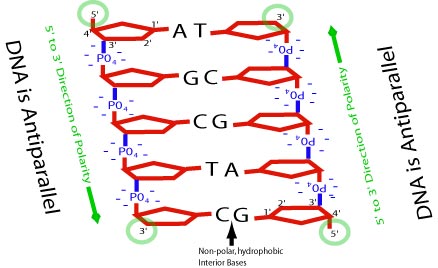
Sides of DNA
2 strands of alternating sugar & phosphates connected via covalent bonds (strong)
13
New cards
Anti-Parellel
side-by-side, but running in opposite directions
14
New cards
Ends of DNA
5’ ends = a phosphate
3’ ends = sugar w/ a “free” -OH groups at the 3’ C atom
3’ ends = sugar w/ a “free” -OH groups at the 3’ C atom
15
New cards
When does DNA Replication occur?
during interphase of the cell cycle - before mitosis
16
New cards
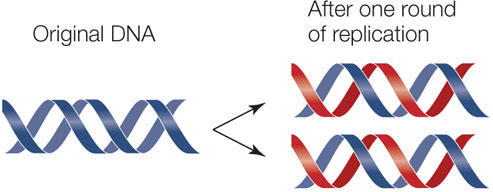
Semi-conservative
each replicated DNA is made of one “old” and one “new” strand, but identical in the genetic info they hold
17
New cards
DNA Replication Location
begins at **specific** **origins of replication** along the DNA
18
New cards
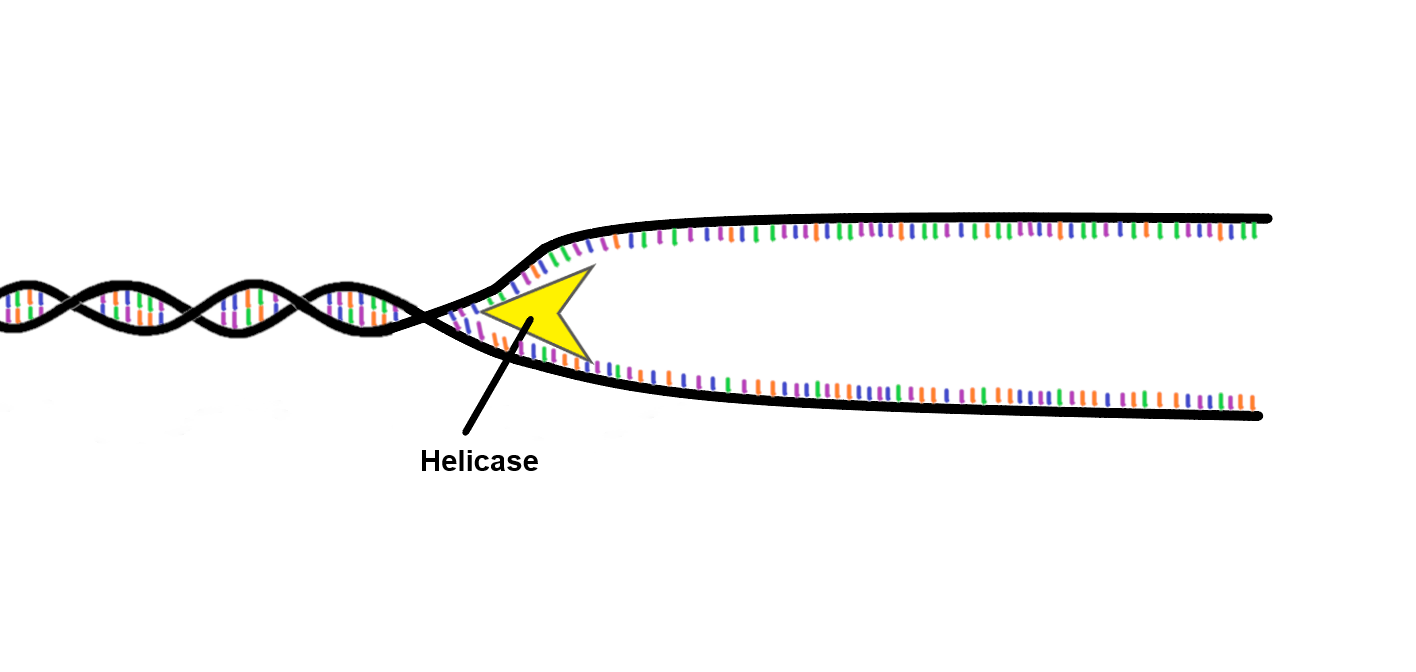
Helicase
* binds to an origin of replication - breaks H bonds between base pairs
* separates the 2 strands of DNA (like unzipping a zipper)
→ **creates replication fork**
* separates the 2 strands of DNA (like unzipping a zipper)
→ **creates replication fork**
19
New cards
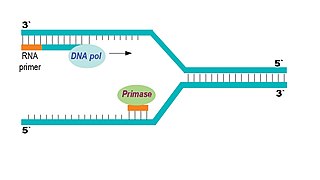
Primase
* builds **RNA Primers** - small pieces of RNA (a molecule similar to DNA
* provides a starting point for DNA to be built - has a 3’ end, so more nucleotides can attach
* provides a starting point for DNA to be built - has a 3’ end, so more nucleotides can attach
20
New cards
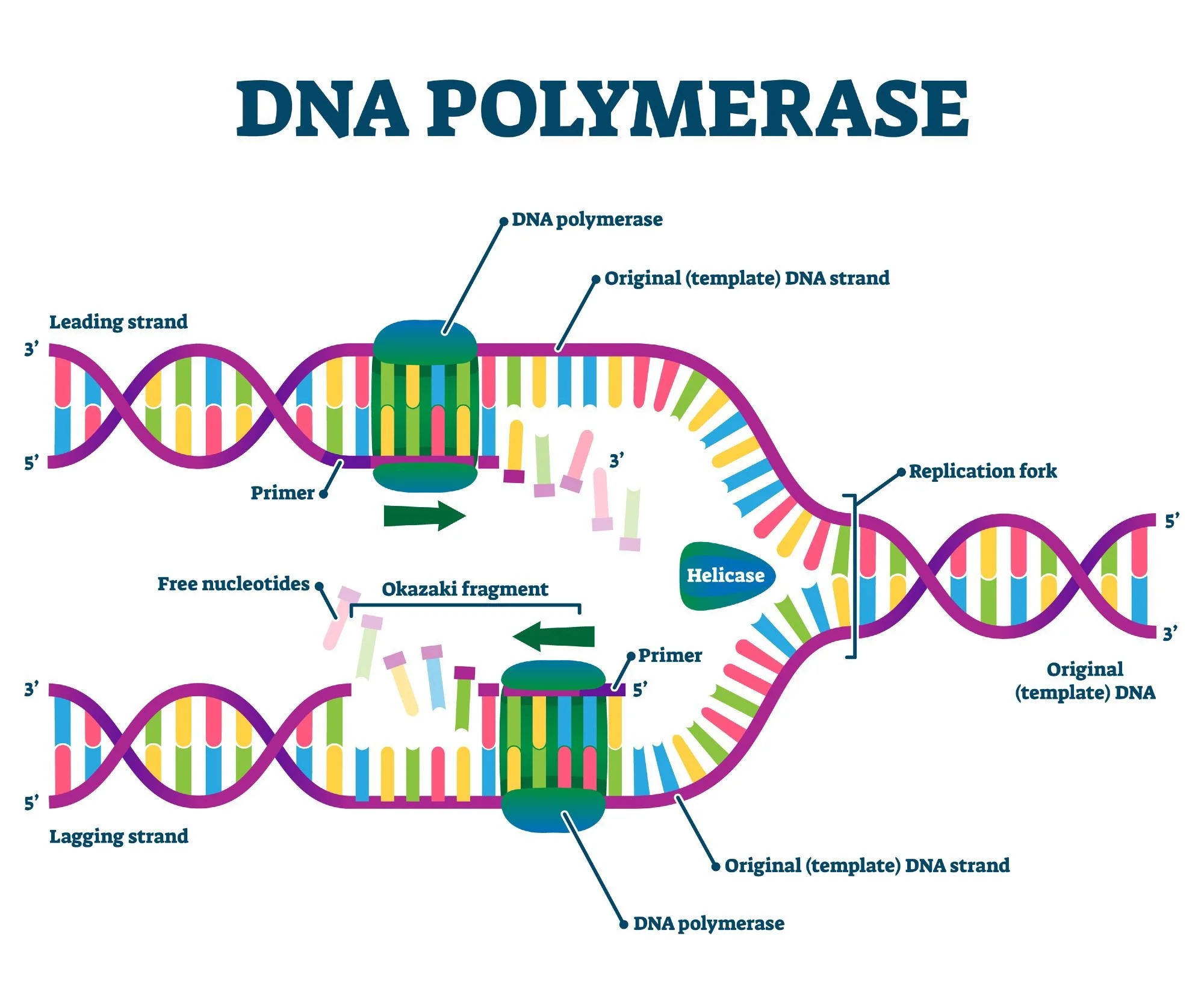
DNA Polymerase Short Definition
adds nucleotides to build new strands of DNA
21
New cards
DNA Polymerase Process
* builds new DNA off the 3’ ends of the primers - “reads” the old template DNA
* adds complementary bases in the 5’ → 3’ direction to build new DNA
* new nucleotides add to the 3’ ends via dehydration synthesis (H + OH → H2O)
* eventually removed and replaced w/ DNA
* adds complementary bases in the 5’ → 3’ direction to build new DNA
* new nucleotides add to the 3’ ends via dehydration synthesis (H + OH → H2O)
* eventually removed and replaced w/ DNA
22
New cards
Leading Strand
replicated continuously toward the fork
23
New cards
Lagging Strand
replicated in **Okazaki fragments** away from the fork - b/c original DNA molecules is antiparallel
24
New cards
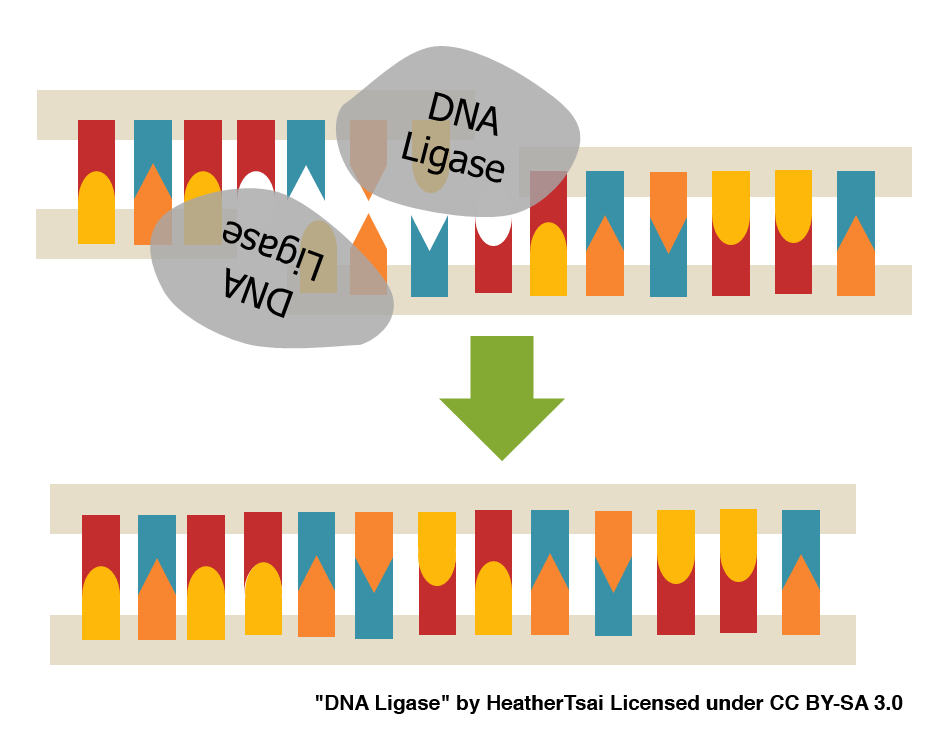
Ligase
connects the gaps in the sugar-phosphate backbone by creating covalent bonds between sugars & phosphates