HSC 101 Final Exam Review pt.2
0.0(0)Studied by 9 people
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:05 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
1
New cards
**Overview of mechanisms by which cigarette smoking causes cancer**
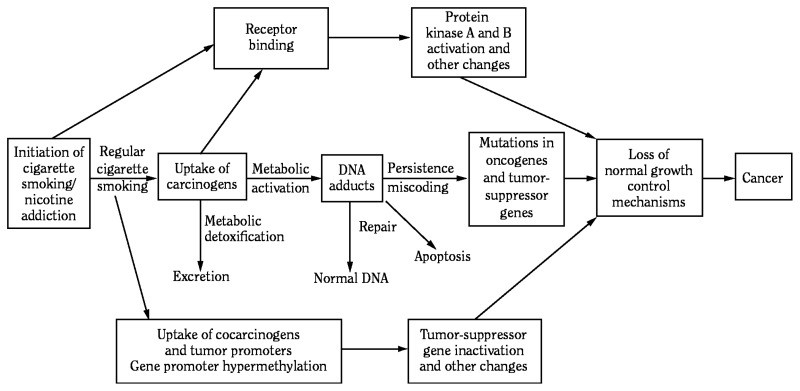
2
New cards
low energy density
contains a large volume of food with few calories
3
New cards
Energy Balance Calories In = Calories Out
* Calories In
* Fat 9 kcal/ g **(high energy density)**
* Protein 4 kcal/ g **(low energy density)**
* Carbohydrate 4 kcal/g **(low energy density)**
* Alcohol 7 kcal/ g
* Calories Out
* Resting Metabolic Rate 55-75% **(majority of total energy expenditure basically the energy you need to maintain vital body functions)**
* Thermic Effect of Exercise 10-40%
* Thermic Effect of Feeding 5-15%
* Fat 9 kcal/ g **(high energy density)**
* Protein 4 kcal/ g **(low energy density)**
* Carbohydrate 4 kcal/g **(low energy density)**
* Alcohol 7 kcal/ g
* Calories Out
* Resting Metabolic Rate 55-75% **(majority of total energy expenditure basically the energy you need to maintain vital body functions)**
* Thermic Effect of Exercise 10-40%
* Thermic Effect of Feeding 5-15%
4
New cards
How many american are overweight?
73\.6% of Americans are currently classified as overweight or obese (BMI>25 kg/ m2)
\~ CDC 2020
\~ CDC 2020
5
New cards
Adipose cells
have enabled humans to survive during periods of food shortage.
6
New cards
How much body fat do we need?
* Essential
* cell membranes, nerves, reproduction, immunity, etc.
* Non-Essential
* visceral
* surrounds the major organs (viscera). Visceral fat is more easily metabolized and increases LDL, triglycerides, blood pressure, and insulin resistance.
* higher risk for chronic disease
* subcutaneous
* is the fat that lies just underneath the skin
Lack of body fat in females may cause amenorrhea.(loss of the menstrual cycle that effects bone health)
* cell membranes, nerves, reproduction, immunity, etc.
* Non-Essential
* visceral
* surrounds the major organs (viscera). Visceral fat is more easily metabolized and increases LDL, triglycerides, blood pressure, and insulin resistance.
* higher risk for chronic disease
* subcutaneous
* is the fat that lies just underneath the skin
Lack of body fat in females may cause amenorrhea.(loss of the menstrual cycle that effects bone health)
7
New cards
Why is body fat distribution important?
* Android
* apple shape, abdominal fat
* more common in males
* Visceral fat = higher risk for chronic disease
* Gynoid
* pear shape, hips and thighs
* more common in females
* Subcutaneous fat = lower risk for chronic disease
* apple shape, abdominal fat
* more common in males
* Visceral fat = higher risk for chronic disease
* Gynoid
* pear shape, hips and thighs
* more common in females
* Subcutaneous fat = lower risk for chronic disease
8
New cards
How does weight affect health?
\*a very low body weight and a very high body weight are both associated with different effects on health.
9
New cards
How is blood glucose regulated?
* Blood Glucose is too high
* Pancreas secretes insulin
* Insulin escorts glucose into cells
* Blood glucose is decreased
* Blood Glucose is too low
* Pancreas secretes glucagon
* Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose
* Blood glucose is increased
* Pancreas secretes insulin
* Insulin escorts glucose into cells
* Blood glucose is decreased
* Blood Glucose is too low
* Pancreas secretes glucagon
* Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose
* Blood glucose is increased
10
New cards
What is Diabetes?
* Type 1
* Insulin Dependent
* Formerly “juvenile onset”
* Pancreas not secreting enough insulin
* __**Reduced insulin production**__
* Type 2
* Non-Insulin Dependent
* Formerly “adult onset”
* Cells are not responding to insulin
* __**Reduced insulin sensitivity**__
* closly related to behavior modification to reduce the risk
What contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes?
* __***Obesity and inflammation***__ increase risk
* 90% can be prevented through lifestyle changes (healthful diet, physical activity)
* Insulin Dependent
* Formerly “juvenile onset”
* Pancreas not secreting enough insulin
* __**Reduced insulin production**__
* Type 2
* Non-Insulin Dependent
* Formerly “adult onset”
* Cells are not responding to insulin
* __**Reduced insulin sensitivity**__
* closly related to behavior modification to reduce the risk
What contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes?
* __***Obesity and inflammation***__ increase risk
* 90% can be prevented through lifestyle changes (healthful diet, physical activity)
11
New cards
adiponectin
The adipose cells typically release a hormone called __*adiponectin*__ that makes cells sensitive to insulin. Obesity decreases adiponectin. This contributes to insulin resistance.
12
New cards
**Calculating** **Abdominal Circumference**
**Males Recommended**
Ab Circumference
< 40”
\
**Females Recommended**
Ab Circumference
< 35”
Ab Circumference
< 40”
\
**Females Recommended**
Ab Circumference
< 35”
13
New cards
Do Diets Work?
Most diets are not successful long term. Dieting can lead to both obesity and eating disorders.
14
New cards
Weight Management Guidelines
* 5-10% of body weight loss is associated with clinical improvements
* Healthful rate is considered ½ to 2 lb. per week
* 1 lb = 3500 cal
* Minimum Calorie Intake
* Females 1200 cal/ day
* Males 1500 cal/ day
* Healthful rate is considered ½ to 2 lb. per week
* 1 lb = 3500 cal
* Minimum Calorie Intake
* Females 1200 cal/ day
* Males 1500 cal/ day
15
New cards
Managing Hunger
* Empty Stomach Volume
* When the volume of your stomach is empty, you feel hungry.
* A healthful diet that emphasizes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes will encourage satiety.
* Low Blood Glucose
* When your blood glucose is low, you feel hungry.
* A healthful diet that includes regular, balanced meals can help stabilize blood glucose.
* When the volume of your stomach is empty, you feel hungry.
* A healthful diet that emphasizes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes will encourage satiety.
* Low Blood Glucose
* When your blood glucose is low, you feel hungry.
* A healthful diet that includes regular, balanced meals can help stabilize blood glucose.
16
New cards
Eating Disorders
* Anorexia Nervosa
* Self starvation
* Overexerciser
* Compulsive calorie counter
* Bulimia Nervosa
* Binge & purge
* Binge Eating Disorder
* Binge only
* Self starvation
* Overexerciser
* Compulsive calorie counter
* Bulimia Nervosa
* Binge & purge
* Binge Eating Disorder
* Binge only
17
New cards
Anorexia
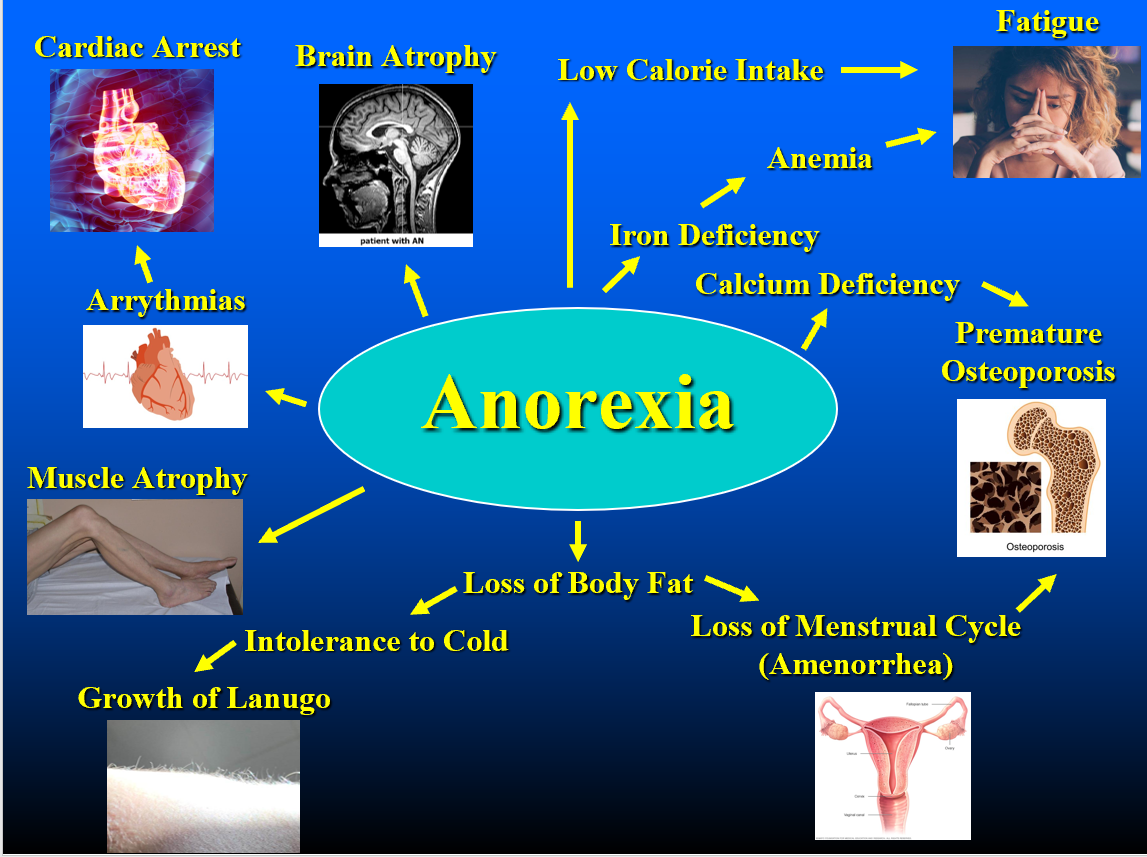
18
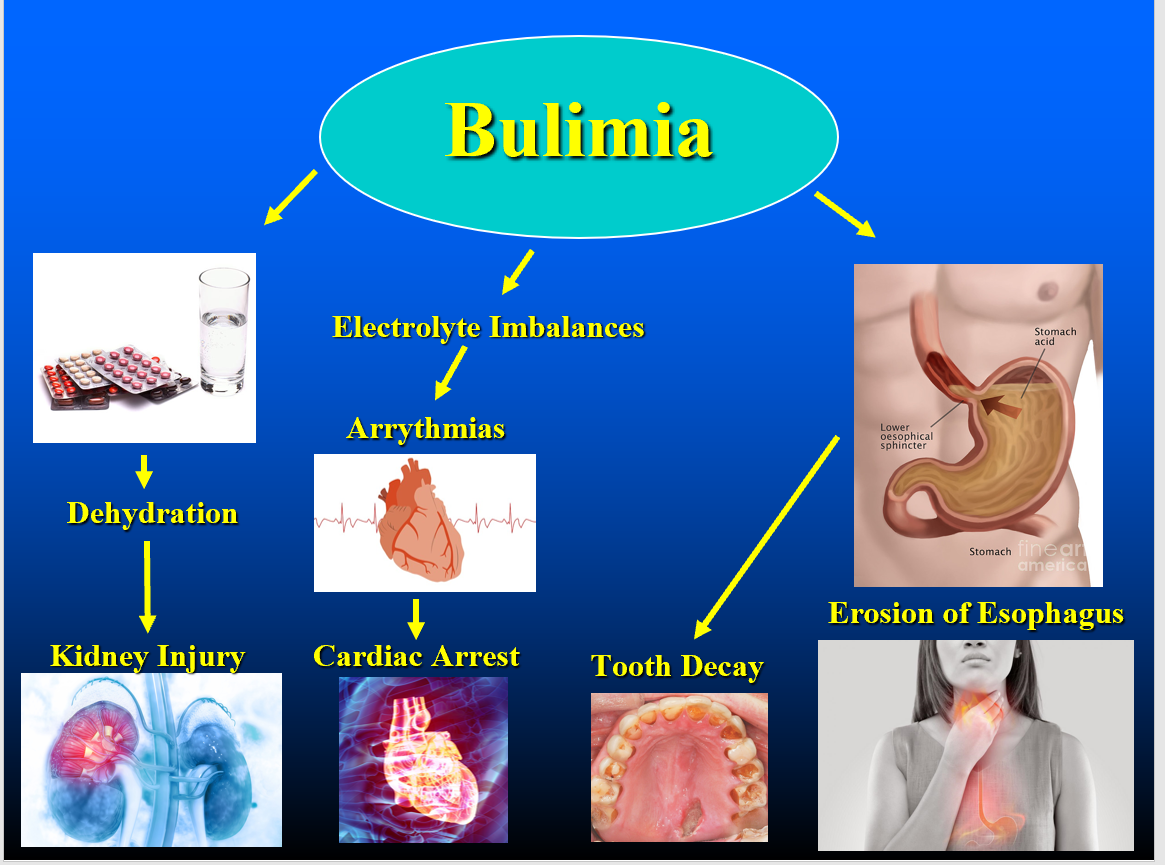
New cards
Bulimia
19
New cards
What are types of stress?
Eustress and distress are two types of stress. Eustress is a positive form of stress that can motivate and energize individuals, while distress is a negative form of stress that can lead to anxiety and health problems.
\*goes from EU to DIS when its not capable
\*know the chart
\*goes from EU to DIS when its not capable
\*know the chart
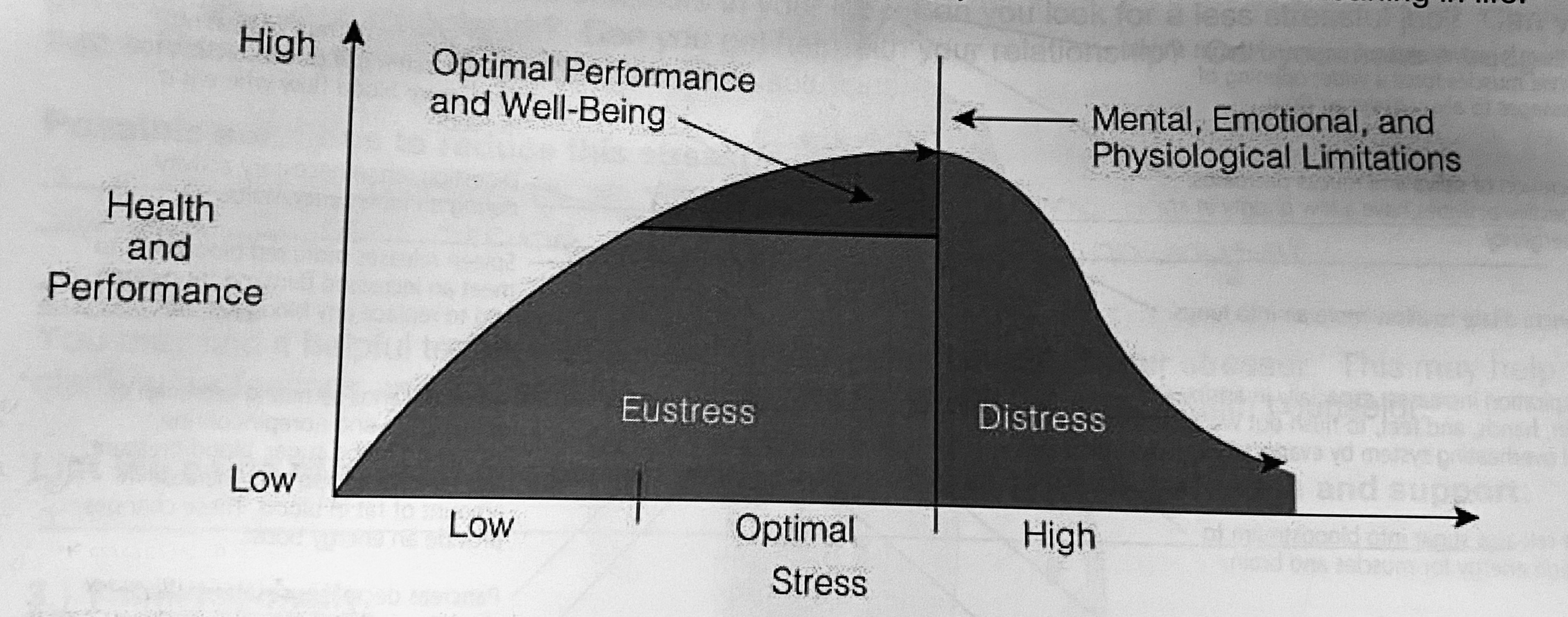
20
New cards
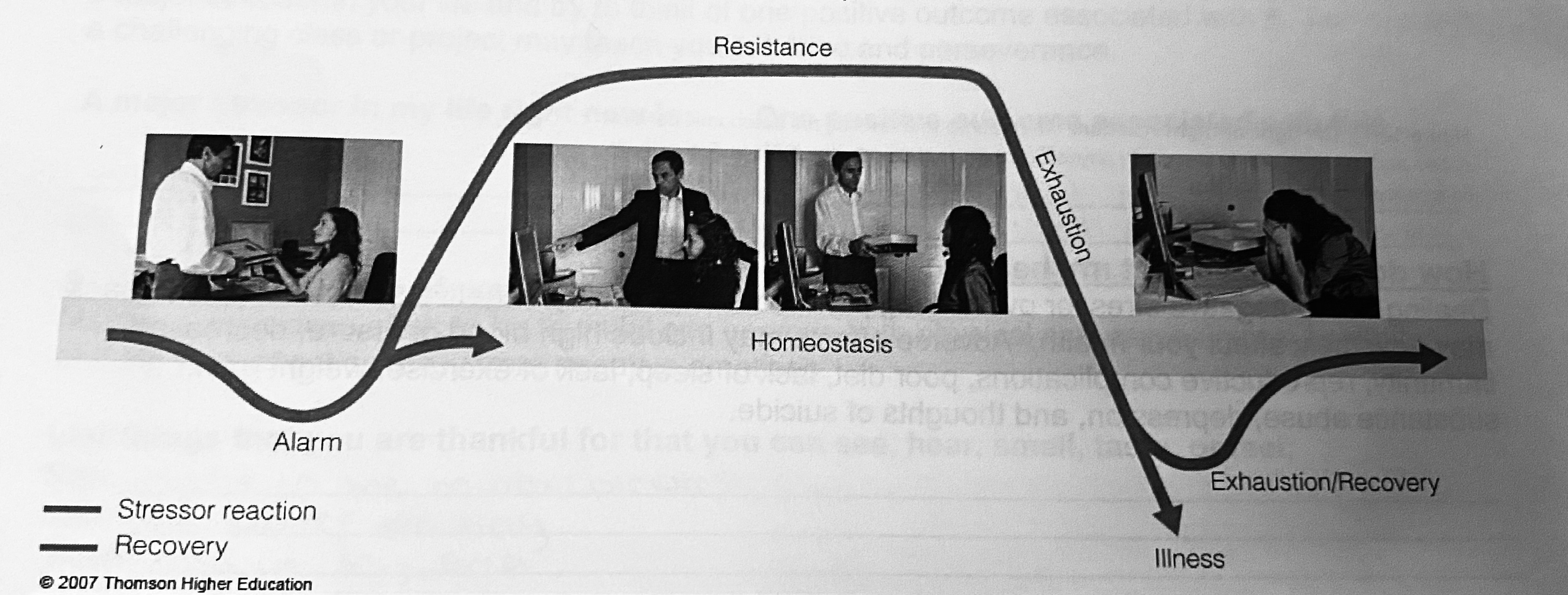
General Adaptation Syndrome
Stage 1 - Alarm: fight or flight response is initiated
Stage 2 - Resistance \*achieve a new level of homeostasis: you start to adapt and achieve a new level of homeostasis, (e.g., freshman may find a speech stressful; seniors have adapted and no longer find it as stressful). Having some stressors in your life can lead to positive adaptations.
\
Stage 3 - Exhaustion \*burnt out and decrease in performance: If you have back to back or persistent stressors you may enter the exhaustion stage. This is not the same as feeling tired at the end of the day. This is absolute burnout. It can lead to depression, suicide, extreme anxiety and mood disorders, and a distorted perception of reality. In the exhaustion stage, the body is under a constant state of stress. Health and performance are adversely affected.
\
\
\*right after the alarm in before the arrow is where fight or flight is activated
\*the pointed peak between resistance and exhaustion if where it goes form EU to DIS
\*know the diagram
Stage 2 - Resistance \*achieve a new level of homeostasis: you start to adapt and achieve a new level of homeostasis, (e.g., freshman may find a speech stressful; seniors have adapted and no longer find it as stressful). Having some stressors in your life can lead to positive adaptations.
\
Stage 3 - Exhaustion \*burnt out and decrease in performance: If you have back to back or persistent stressors you may enter the exhaustion stage. This is not the same as feeling tired at the end of the day. This is absolute burnout. It can lead to depression, suicide, extreme anxiety and mood disorders, and a distorted perception of reality. In the exhaustion stage, the body is under a constant state of stress. Health and performance are adversely affected.
\
\
\*right after the alarm in before the arrow is where fight or flight is activated
\*the pointed peak between resistance and exhaustion if where it goes form EU to DIS
\*know the diagram
21
New cards
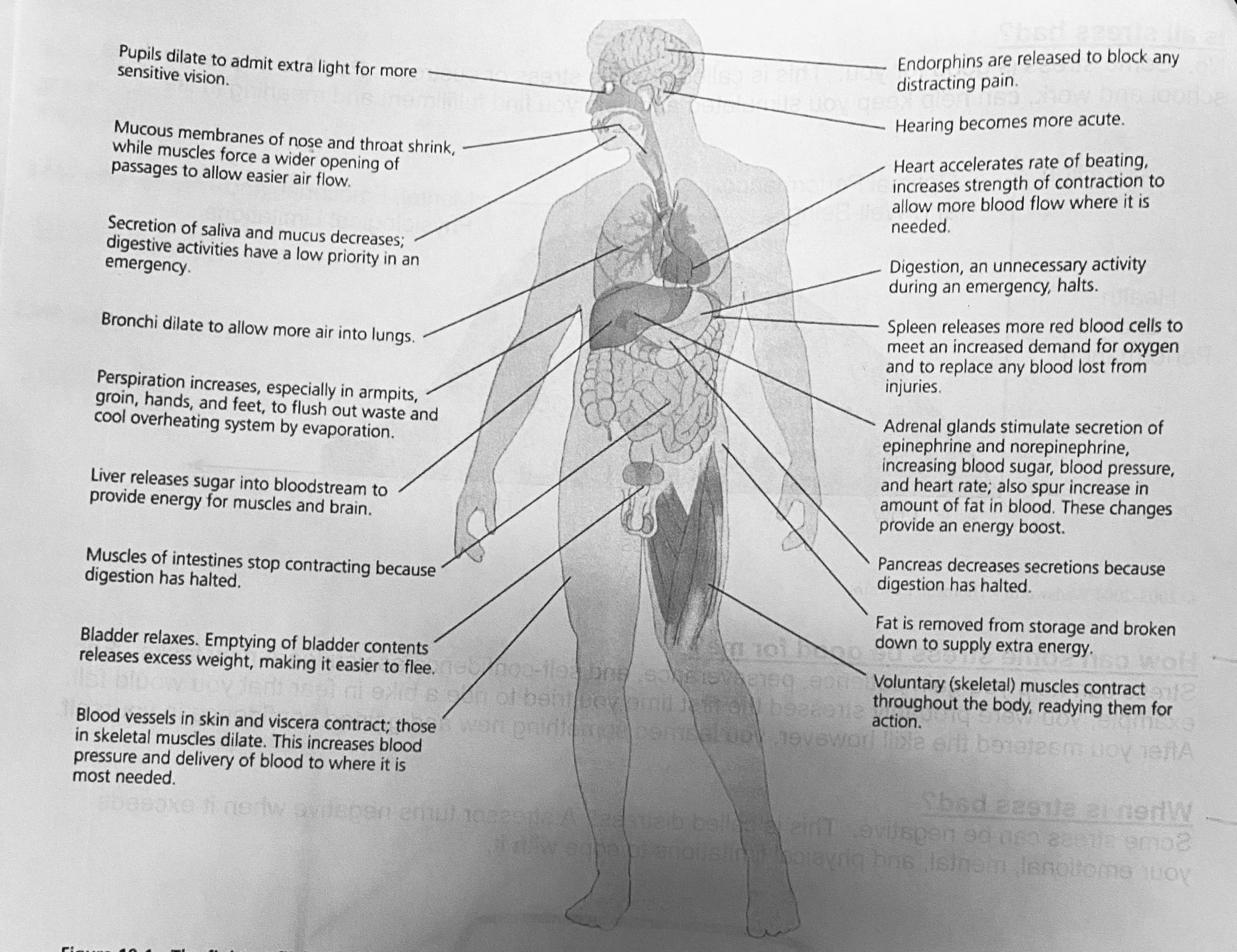
Fight or Flight
When you perceive a stressor your body prepares for danger. It sets off a series of reactions called the fight or flight response. these reaction include increased heart rate, blood pressure, rate of breathing, sweating, and muscle tension.
\
\*be familiar with all the stuff in the picture
__**The Fight or Flight Response**__
Pupils dilate
Hearing becomes more acute, (hear every little sound)
Endorphins released to block pain in case of injury
Decrease saliva and mucus in mouth, digestion low priority (dry mouth)
Bronchi dilate to let more air flow into lungs
Perspiration increases to prevent overheating (sweaty palms)
Liver breaks glycogen down into glucose for immediate energy
Digestion halt (indigestion, butterflies, nausea)
Bladder relaxes to decrease body weight, make easier to flee (wet pants)
Blood vessels dilate to increase blood flow to muscles and brain
Blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow to low priority organs, e.g., digestive system
Heart rate and blood pressure increase to get more nutrients through body
Adrenal glands increase epinephrine and norepinephrine which increase HR, BP, glucose
Muscle contract (contributes to muscle tension)
\
\*be familiar with all the stuff in the picture
__**The Fight or Flight Response**__
Pupils dilate
Hearing becomes more acute, (hear every little sound)
Endorphins released to block pain in case of injury
Decrease saliva and mucus in mouth, digestion low priority (dry mouth)
Bronchi dilate to let more air flow into lungs
Perspiration increases to prevent overheating (sweaty palms)
Liver breaks glycogen down into glucose for immediate energy
Digestion halt (indigestion, butterflies, nausea)
Bladder relaxes to decrease body weight, make easier to flee (wet pants)
Blood vessels dilate to increase blood flow to muscles and brain
Blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow to low priority organs, e.g., digestive system
Heart rate and blood pressure increase to get more nutrients through body
Adrenal glands increase epinephrine and norepinephrine which increase HR, BP, glucose
Muscle contract (contributes to muscle tension)
22
New cards
How can I manage my stress?
1. find your stressors and think of solutions
2. open up
3. think rationally
4. think positively
5. accept an attitude of gratitude
23
New cards
What is Cancer?
Uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells Caused by damage to DNA Disrupts normal bodily function May be 10+ years before detectable
24
New cards
What is a Tumor?
* Benign Tumor
* Does not typically spread
* Not cancerous
* Malignant Tumor
* Capable of metastasizing
* Cancerous
25
New cards
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis occurs when a tumor generates new blood vessels. This in creases the nutrient supply to fuel tumor growth.
26
New cards
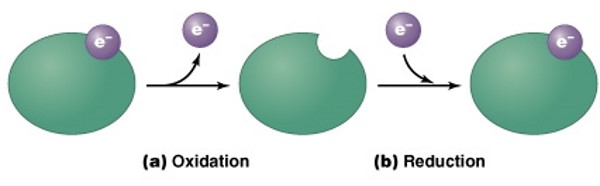
Oxidation & Reduction
During metabolic reactions, electrons can be transferred from the atoms of one molecule to the atoms of another molecule.
Oxidation is the loss of electrons from a molecule. Reduction is the gain of electrons by a molecule.
\
Oxidation and reduction usually occur together as an exchange reaction.
27
New cards
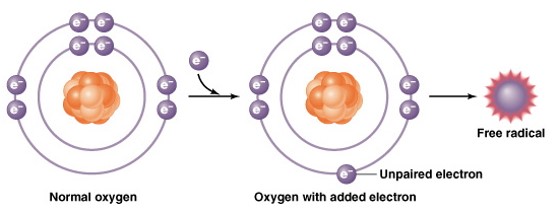
Oxidation Can Create Free Radicals
In most exchange reactions, oxidation is immediately followed by reduction making newly stabilized atoms. In rare cases, an electron on the outmost shell will remain unpaired. This creates a highly unstable atom called a free radical.
28
New cards
**Free Radicals Can Cause a Chain Reaction**
This chain reaction can damage cell membranes, LDL, cell proteins, and DNA.
29
New cards
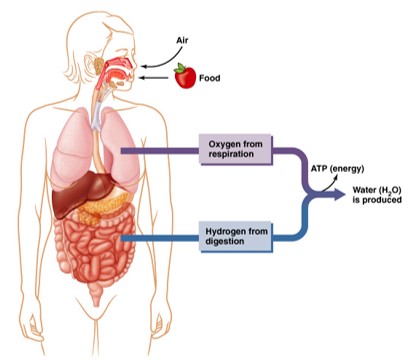
Energy Metabolism Can Create Free Radicals
Energy metabolism involves oxidation and can create free radicals. Oxygen accepts a single electron and becomes a free radical.
Regular physical activity increases the activity of antioxidant enzyme systems which disarm free radicals.
\
Regular physical activity increases the activity of antioxidant enzyme systems which disarm free radicals.
\
30
New cards
Other Factors Can Also Cause Free Radical Formation
Tobacco smoke, ultraviolet radiation, pollution, asbestos, and other toxic substances increase free radical formation.
31
New cards
**What Are Antioxidants?** \n
Antioxidants are compounds that have the ability to prevent or repair the damage caused by oxidation. For example, antioxidants can donate electrons to render free radicals harmless.
32
New cards
Antioxidants Stop the Chain Reaction
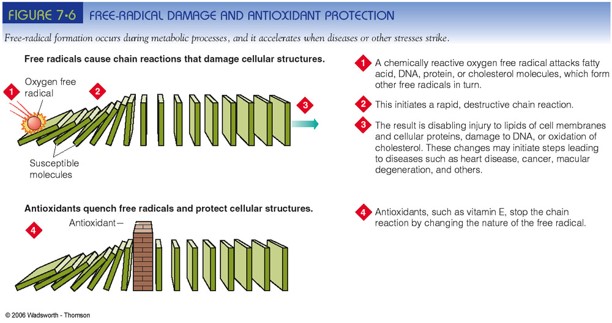
33
New cards
Metastasis
Metastasis occurs when cancer cells break off from the original site and spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic or blood vessels. Metastasis is cancer’s most destructive characteristic.
\*spreading of cancer cells
\*spreading of cancer cells
34
New cards
Oxidation
* During metabolic reactions, electrons can be transferred from the atoms of one molecule to the atoms of another molecule.
* Oxidation is the loss of electrons from a molecule. Reduction is the gain of electrons by a molecule.
* Oxidation and reduction usually occur together as an exchange reaction.
* Oxidation is the loss of electrons from a molecule. Reduction is the gain of electrons by a molecule.
* Oxidation and reduction usually occur together as an exchange reaction.
35
New cards
**How can Oxidation Can Create Free Radicals ?**
In most exchange reactions, oxidation is immediately followed by reduction making newly stabilized atoms. In rare cases, an electron on the outmost shell will remain unpaired. This creates a highly unstable atom called a free radical.
\
Free Radicals: highly reactive molecule that is missing an electron
\
Free Radicals: highly reactive molecule that is missing an electron
36
New cards
**What happens when Free Radicals Can Cause a Chain Reaction?**
**This chain reaction can damage cell membranes, LDL, cell proteins, and DNA.**
37
New cards
How can Energy Metabolism Can Create Free Radicals?
**Energy metabolism involves oxidation and can create free radicals. Oxygen accepts a single electron and becomes a free radical.**
38
New cards
How can Other Factors Can Also Cause Free Radical Formation?
Tobacco smoke, ultraviolet radiation, pollution, asbestos, and other toxic substances increase free radical formation.
39
New cards
What Are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are compounds that have the ability to prevent or repair the damage caused by oxidation. For example, antioxidants can donate electrons to render free radicals harmless.
40
New cards
What Nutrients Act as Antioxidants?
* Vitamin E (sunflower seeds/almonds)
* Vitamin C
* Beta-carotene (precursor to vitamin A)
* Selenium
* Phytochemicals
\
Fat soluble ADEK
Water soluble Bcomplex, C
* Vitamin C
* Beta-carotene (precursor to vitamin A)
* Selenium
* Phytochemicals
\
Fat soluble ADEK
Water soluble Bcomplex, C
41
New cards
Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC scale)
* ability to disarm oxygen free radicals
* Berries have the most
* Berries have the most
42
New cards
Vitamins C & E acts as Antioxidants
Vitamin C protects watery areas; Vitamin E protects fatty areas.
43
New cards
Leading Cancer with males and females
### Estimated New Cases
* Males
* Prostate
* Lung& bronchus
* colon&rectum
* Females
* Breast
* Lung& bronchus
* colon&rectum
### Estimated deaths
* Males
* Lung& bronchus
* Prostate
* colon&rectum
* Females
* Lung& bronchus
* Breast
* colon&rectum
* Males
* Prostate
* Lung& bronchus
* colon&rectum
* Females
* Breast
* Lung& bronchus
* colon&rectum
### Estimated deaths
* Males
* Lung& bronchus
* Prostate
* colon&rectum
* Females
* Lung& bronchus
* Breast
* colon&rectum
44
New cards
Lung Cancer
* Risk Factors
•#1 Smoking (80%)
•#2 Radon(ordorless gas)
•Environmental tobacco smoke
•Asbestos (Fibrous minerals
* Symptoms
•Persistent cough
•Chest pain
•Recurring bronchitis
* Reducing your risk
•Don’t use any form of tobacco or e-cig
\- Screening
•Low Dose Computed Tomography for smokers
•#1 Smoking (80%)
•#2 Radon(ordorless gas)
•Environmental tobacco smoke
•Asbestos (Fibrous minerals
* Symptoms
•Persistent cough
•Chest pain
•Recurring bronchitis
* Reducing your risk
•Don’t use any form of tobacco or e-cig
\- Screening
•Low Dose Computed Tomography for smokers
45
New cards
Prostate Cancer
* Risk Factors
* Age
* Diet
* Obesity
* Family History
* African American
* Early Detection (Age 50+) Prostate Specific Antigen test (PSA) Digital Rectal Exam
* Signs & Symptoms Urinary complications
* Age
* Diet
* Obesity
* Family History
* African American
* Early Detection (Age 50+) Prostate Specific Antigen test (PSA) Digital Rectal Exam
* Signs & Symptoms Urinary complications
46
New cards
Breast Cancer
* Risk Factors
* Gender
* Age
* Family history
* Estrogen Exposure Never had children First child after age 30 Long Menstrual history Obesity Alcohol Use Inactivity High fat diet
* Symptom (most common) Lump or mass in the breast
•Screening (Age 20-40)
•Self-breast exam monthly
•Clinical breast exam every 3 yrs
•Screening (Age >40)
•Self-breast exam monthly
•Clinical breast exam annually
•Annual mammogram
•
* Gender
* Age
* Family history
* Estrogen Exposure Never had children First child after age 30 Long Menstrual history Obesity Alcohol Use Inactivity High fat diet
* Symptom (most common) Lump or mass in the breast
•Screening (Age 20-40)
•Self-breast exam monthly
•Clinical breast exam every 3 yrs
•Screening (Age >40)
•Self-breast exam monthly
•Clinical breast exam annually
•Annual mammogram
•
47
New cards
How Does Obesity Increase Cancer Risk?
•Obesity produces chronic low level inflammation
•Can lead to DNA damage over time
•Adipose cells release estrogen
•Obesity increases insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)
•Promotes cancer development
•Adipose cells release adipokines that affect cell proliferation
•Leptin & adiponectin
•Adipose cells can affect other cell growth factors
•Obesity increases oxidative stress (free radicals)
48
New cards
Colorectal Cancer
•Risk Factors
•Age
•Family History
•Diet
•High in Red/ Processed Meat
•Low Veg, Fruit, Whole Grain, Fiber
•Smoking
•Obesity
•Inactivity
•Signs & Symptoms (late stage)
**•Blood in stool**
**•Change in bowel habits or stool shape**
**•Pain in lower abdomen**
•Age
•Family History
•Diet
•High in Red/ Processed Meat
•Low Veg, Fruit, Whole Grain, Fiber
•Smoking
•Obesity
•Inactivity
•Signs & Symptoms (late stage)
**•Blood in stool**
**•Change in bowel habits or stool shape**
**•Pain in lower abdomen**
49
New cards
Colorectal Cancer
•Risk Factors
•Age
•Family History
•Diet
•High in Red/ Processed Meat
•Low Veg, Fruit, Whole Grain, Fiber
•Smoking
•Obesity
•Inactivity
•Signs & Symptoms (late stage)
•Blood in stool
•Change in bowel habits or stool shape
•Pain in lower abdomen
50
New cards
How Food Can Block Cancer Progression
1\. Carcinogen
* DESTROY & EXCRETE CARCINOGENS
2\. Damages DNA
* ENHANCE DNA REPAIR CAPACITY
3\. Uncontrolled Cell Division
* SLOW TUMOR GROWTH
4\. Cancer Invades Nearby Tissues
* INDUCE APOPTOSIS
5\. Cancer Spreads Throughout Body
* SLOW CANCER PROGRESSION
* DESTROY & EXCRETE CARCINOGENS
2\. Damages DNA
* ENHANCE DNA REPAIR CAPACITY
3\. Uncontrolled Cell Division
* SLOW TUMOR GROWTH
4\. Cancer Invades Nearby Tissues
* INDUCE APOPTOSIS
5\. Cancer Spreads Throughout Body
* SLOW CANCER PROGRESSION
51
New cards
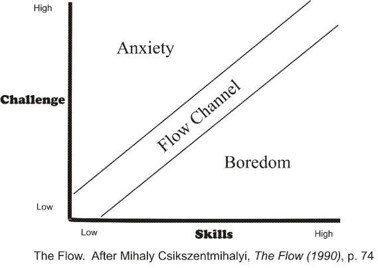
What is Flow?
a type of intrinsic motivation that involves being fully focused on the situation or task. He describes flow as "being completely involved in an activity for its own sake. The ego falls away. Time flies. Every action, movement, and thought follows inevitably from the previous one, like playing jazz. Your whole being is involved, and you're using your skills to the utmost.”
\
\*when its a little above skill level
\
\*when its a little above skill level
52
New cards
What are two nervous system response?
**Somatic Branch** (voluntary) **-** An example of the somatic branch is the motor unit (nerve connected to a group of muscle fibers.) When you want to move your muscle, the brain sends a message to the nerves. The nerves fire the muscle fibers and the muscles contract. This is a voluntary action.
\
**Autonomic Branch** (involuntary or automatic)- An example of the autonomic branch is when your heart races when you are stressed or anxious. Your body is releasing epinephrine (adrenaline) which increases the speed of your heart rate. The autonomic branch has two subdivisions– the parasympathetic and sympathetic.
\
Two types of autonomic:
**Parasympathetic-** When you are resting and calm, the parasympathetic division is largely under control. Parasympathetic control SLOWS things down. Your breathing rate and heart rate are low, digestion is working, and muscles are relaxed. involuntary, e.g,. heart beat, sweat glands, reflexes
\
**Sympathetic**- When you perceive stress, the sympathetic division takes over. Sympathetic control SPEEDS things up. Heart rate and breathing accelerate, digestion is halted, muscles tense, sweat glands start to sweat, blood is diverted away from digestion and to the muscles and brain. This is called the Fight or Flight response and is a basic survival mechanism.
\
**Autonomic Branch** (involuntary or automatic)- An example of the autonomic branch is when your heart races when you are stressed or anxious. Your body is releasing epinephrine (adrenaline) which increases the speed of your heart rate. The autonomic branch has two subdivisions– the parasympathetic and sympathetic.
\
Two types of autonomic:
**Parasympathetic-** When you are resting and calm, the parasympathetic division is largely under control. Parasympathetic control SLOWS things down. Your breathing rate and heart rate are low, digestion is working, and muscles are relaxed. involuntary, e.g,. heart beat, sweat glands, reflexes
\
**Sympathetic**- When you perceive stress, the sympathetic division takes over. Sympathetic control SPEEDS things up. Heart rate and breathing accelerate, digestion is halted, muscles tense, sweat glands start to sweat, blood is diverted away from digestion and to the muscles and brain. This is called the Fight or Flight response and is a basic survival mechanism.
53
New cards
What is the Endocrine System Response: Hormones?
**Endorphins** are released by the pituitary gland. They inhibit pain to prepare the body for injury. For example, a bungee jumper releases endorphins so it won’t hurt quite so bad if you hit the ground.
\
**Cortisol** is released by the adrenal glands used for energy. Extended exposure to cortisol decreases bone mineral density, immunity & sexual function and increases blood pressure and risk of CVD.
\
**Catecholamines** are also released by the adrenal glands. They are **epinephrine** (also called adrenaline) and **norepinephrine** (also called noradrenaline). They increase heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, blood flow to brain & muscles, and perspiration.
\
**Cortisol** is released by the adrenal glands used for energy. Extended exposure to cortisol decreases bone mineral density, immunity & sexual function and increases blood pressure and risk of CVD.
\
**Catecholamines** are also released by the adrenal glands. They are **epinephrine** (also called adrenaline) and **norepinephrine** (also called noradrenaline). They increase heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, blood flow to brain & muscles, and perspiration.
54
New cards
How does Stress and Disease: Effects on the Body
* Increase Blood Pressure
* Decrease Immunity
* Hormonal Changes
* Menstrual irregularities
* Pregnancy complications
* Impotence
__**Hypertension**__- If the body is under a constant state of stress, stress hormones elevate the blood pressure. This can lead to atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, and heart failure (all forms of heart disease.)
* Decrease Immunity
* Hormonal Changes
* Menstrual irregularities
* Pregnancy complications
* Impotence
__**Hypertension**__- If the body is under a constant state of stress, stress hormones elevate the blood pressure. This can lead to atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, and heart failure (all forms of heart disease.)
55
New cards
Stress and Disease: Effects on Behavior
* Smoking
* Substance Abuse
* Decrease Physical Activity
* Disordered Eating
* Altered Perceptions
* Altered Sleeping Patterns
* Substance Abuse
* Decrease Physical Activity
* Disordered Eating
* Altered Perceptions
* Altered Sleeping Patterns
56
New cards
What factors contribute to your perception of stress?
* Personality
* Type A
* Type B
* Past experiences
* Locus of control
* Learned coping mechanisms
* Type A
* Type B
* Past experiences
* Locus of control
* Learned coping mechanisms
57
New cards
Atherosclerosis vs. Arteriosclerosis
* Atherosclerosis:
* plaque builds up
* DECREASE vessel diameter
* DECREASE blood flow
* Arteriosclerosis:
* hardening of the arteries
* result of atherosclerosis
* plaque builds up
* DECREASE vessel diameter
* DECREASE blood flow
* Arteriosclerosis:
* hardening of the arteries
* result of atherosclerosis
58
New cards
What damages endothelial cells?
* High Blood Pressure
* Oxidized LDL
* Homocysteine ( increases plaque causes damage)
* Substances in Tobacco Smoke
* High Blood Glucose
* Bacterial/ Viral Infections
* Oxidized LDL
* Homocysteine ( increases plaque causes damage)
* Substances in Tobacco Smoke
* High Blood Glucose
* Bacterial/ Viral Infections
59
New cards
Blood vessel disorders
* Thrombus
* stationary blockage
* Embolism
* floating clot
* Aneurysm
* ballooned outward section
* plaque build up up only in outside
* Hemorrhage
* rupture
* stationary blockage
* Embolism
* floating clot
* Aneurysm
* ballooned outward section
* plaque build up up only in outside
* Hemorrhage
* rupture
60
New cards
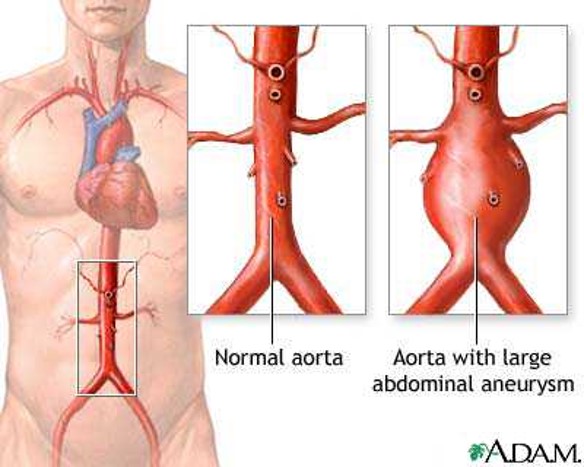
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
My grandfather had two abdominal aortic aneurysms as pictured above.
The aorta is prone to blockages because it is a high pressure vessel.
They were treated with an endovascular graft.
61
New cards
What is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
* atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries
62
New cards
What is a Myocardial Infarction? (Heart attack) \*need to know
* Blood flow through \**coronary arteries DECREASE need to know*
* O2 supply< O2 demand
* Heart tissue suffocates (Low O2)
* Heart tissue dies (No O2)
* Portions of heart can no longer function
\*pain in one or both arms, shoulders, neck
\*chest pain (squeezing burn)
\*light headedness
\*preassure in chest, short breath, vomiting
* O2 supply< O2 demand
* Heart tissue suffocates (Low O2)
* Heart tissue dies (No O2)
* Portions of heart can no longer function
\*pain in one or both arms, shoulders, neck
\*chest pain (squeezing burn)
\*light headedness
\*preassure in chest, short breath, vomiting
63
New cards
What is a Cerebrovascular Accident? (stroke) \* need to know the difference btw heart attact.
* Blood flow through **cerebral or carotid artery DECREASE**
* O2 supply < O2 demand Brain tissue suffocates (Low O2)
* Brain cells die (No O2)
* Portions of the brain can no longer function
\
Signs and Symtoms
* Sudden numbness or weakness of face, arm, or leg especially on one side of body
* Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding
* Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
* Sudden trouble walking, loss of balance, or dizziness
* Sudden severe headache with no known cause
* O2 supply < O2 demand Brain tissue suffocates (Low O2)
* Brain cells die (No O2)
* Portions of the brain can no longer function
\
Signs and Symtoms
* Sudden numbness or weakness of face, arm, or leg especially on one side of body
* Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding
* Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
* Sudden trouble walking, loss of balance, or dizziness
* Sudden severe headache with no known cause
64
New cards
Consequences of High Blood Pressure
1. **Atherosclerosis**
1. High blood pressure damages endothelial cells and leads to atherosclerosis.
1. damage to endothelial cells lead to atherosclerosis
\
1. **Arteriosclerosis**
1. High blood pressure causes the walls of the artery to remodel over time. These thicker, harder walls are not able to vasodilate efficiently.
1. push the wall all with high blood pressure
\
1. **Heart Failure**
1. When pressure in the arteries is high, this can force the heart muscle to remodel in order to adapt.
1. problem: pressure goes high to low but it has to be higher to push back so the heart models
2. \*high BP lead to congestion, if pressure is high the blood starts to back up so the heart stretches out
\*if pressure puts demand on heart it remodels
65
New cards
How is Blood Pressure classified?
45% of Americans have hypertension
>130/ 80 mmHg \*need to know
\*if blood pressure is over that then it is hypertension
>130/ 80 mmHg \*need to know
\*if blood pressure is over that then it is hypertension
66
New cards
Hypertension “the silent killer”
Hypertension has been called a “Silent killer” because there are few or no symptoms. A person may have hypertension for years without even realized it. But during this time it damages vital organs and increases the risk of heart attack, congestive heart failure, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
When a person has high blood pressure, the heart must work harder than normal to force blood through the narrowed and stiffens arteries, straining both the heart and arteries. Eventually the strained heart weakens and tends to enlarge, which weakens it even more.
\
* Sustained high blood pressure
* Complications
\- Atherosclerosis
–Heart Attack
–Stroke
–Heart Failure
* Reducing your risk
–Quit Smoking
–Limit Alcohol
–Lose Weight
–Exercise
–Manage Stress
–Limit Sodium
–Obtain adequate potassium, calcium, magnesium
When a person has high blood pressure, the heart must work harder than normal to force blood through the narrowed and stiffens arteries, straining both the heart and arteries. Eventually the strained heart weakens and tends to enlarge, which weakens it even more.
\
* Sustained high blood pressure
* Complications
\- Atherosclerosis
–Heart Attack
–Stroke
–Heart Failure
* Reducing your risk
–Quit Smoking
–Limit Alcohol
–Lose Weight
–Exercise
–Manage Stress
–Limit Sodium
–Obtain adequate potassium, calcium, magnesium
67
New cards
Tobacco & E-cigarettes
Tobacco and Electronic Nicotine Delivery Devices (E-cigarettes) contain nicotine.
Nicotine is a vasoconstrictor which increases blood pressure.
Nicotine is a vasoconstrictor which increases blood pressure.
68
New cards
Exercise
Exercise increases nitric oxide (“the great vasodilator”) which decreases blood pressure.
69
New cards
Sodium & Potassium
* Sodium
* Mineral in processed foods
* Canned soup
* Frozen meals
* Fast food
* Salt, soy sauce
* Increases blood pressure
\
* Potassium
* Mineral in unprocessed foods
* Potatoes
* Bananas
* Orange Juice
* Spinach
* Decreases blood pressure
* Mineral in processed foods
* Canned soup
* Frozen meals
* Fast food
* Salt, soy sauce
* Increases blood pressure
\
* Potassium
* Mineral in unprocessed foods
* Potatoes
* Bananas
* Orange Juice
* Spinach
* Decreases blood pressure
70
New cards
What is Congestive Heart Failure?
* Heart is failing to pump efficiently
* May cause congestion in the lungs
* Caused by:
* high blood pressure
* heart attack
* atherosclerosis
* birth defects
\
* May cause congestion in the lungs
* Caused by:
* high blood pressure
* heart attack
* atherosclerosis
* birth defects
\
71
New cards
Angiogram:
Finding the Blockage
A coronary angiogram is a special X-ray test. It’s done to find out if coronary arteries are clogged, where and by how much. A catheter is inserted from a blood vessel near the groin and guided up to the coronary arteries. A dye is injected into the coronary arteries and x-ray images are taken to evaluate atherosclerosis prognosis.
A coronary angiogram is a special X-ray test. It’s done to find out if coronary arteries are clogged, where and by how much. A catheter is inserted from a blood vessel near the groin and guided up to the coronary arteries. A dye is injected into the coronary arteries and x-ray images are taken to evaluate atherosclerosis prognosis.
72
New cards
Surgery: Coronary Bypass
Coronary artery bypass surgery reroutes the blood supply around a blocked section of the artery. During this procedure, surgeons remove healthy blood vessels from another part of the body, such as a leg or the chest wall. They then surgically attach the vessels to the diseased artery in such a way that the blood can flow around the blocked section. \n
After a bypass operation, it's especially important to watch diet and reduce the amount of fat and cholesterol you eat, since these substances cause the arteries to clog. Doctors also recommend following a routine of increased physical activity to strengthen the heart muscles.
73
New cards
**What is collateral circulation?**
Collateral circulation is a network of tiny blood vessels, and, under normal conditions, not open. When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited (coronary artery disease), collateral vessels may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to another artery nearby or to the same artery past the blockage, protecting the heart tissue from injury. (Source: Cleveland Clinic)
74
New cards
Surgery: Balloon Angioplasty
Heart failure can develop when blockages in the coronary arteries restrict the blood supply to the heart muscle. Removing these blockages can improve overall heart function, which may improve or resolve heart failure symptoms. PCI is one type of procedure to reopen blocked vessels. The procedure is usually performed in the cardiac catherization lab. A small tube – a catheter – with a tiny deflated balloon on the end is inserted through an incision in the groin area and pushed through to the diseased artery. Then the balloon is inflated to push open the artery. The balloon is removed once the artery has been fully opened. A stent may be placed during the procedure to keep the blood vessel open. Although there's a slight risk of damage to the artery during this procedure, PCI usually improves the patient's condition.
75
New cards
What is a Surgery: Stent? \*know
**What the Procedure Does**
A stent is a wire mesh tube used to prop open an artery during angioplasty. The stent stays in the artery permanently.
A stent is a wire mesh tube used to prop open an artery during angioplasty. The stent stays in the artery permanently.
76
New cards
What causes Heart Disease the 1 studies?
1. watched people and found how they related to heart disease
\
\*Our Study began in 1948 by recruiting an Original Cohort of 5,209 men and women between the ages of 30 and 62 from the town of Framingham, Massachusetts, who had not yet developed overt symptoms of cardiovascular disease or suffered a heart attack or stroke. In addition, the relationships between physical traits and **genetic patterns** are being studied.
77
New cards
Non-modifiable Risk Factors
* Heredity
* Age
* Gender
* Age
* Gender
78
New cards
Modifiable Risk Factors: Cigarette Smoking \*writing portion
* Damages endothelial cells
* Increases blood pressure
* Increases myocardial demand
* Increases LDL, decreases HDL
* Increases free radical production which leads to oxidized LDL
* Increases platelet stickiness
* Increases blood pressure
* Increases myocardial demand
* Increases LDL, decreases HDL
* Increases free radical production which leads to oxidized LDL
* Increases platelet stickiness
79
New cards
Overview of mechanisms by which cigarette smoking causes an acute cardiovascular event
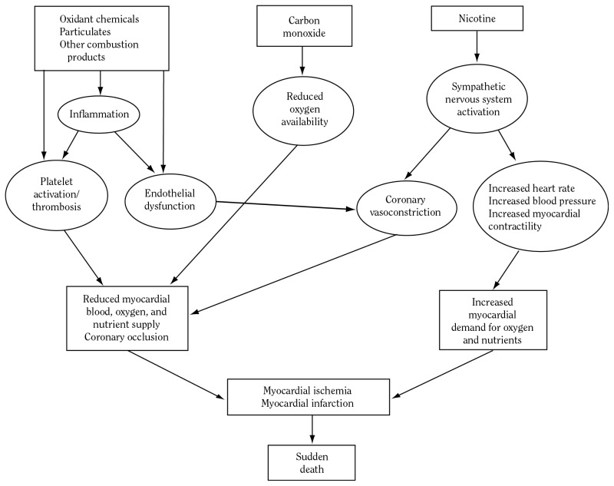
80
New cards
Modifiable Risk Factors
* Physical inactivity
* Low fruit and vegetable consumption
* High blood pressure
* High cholesterol
* Obesity Diabetes
\
Study the bus driver and conductors have few coronary events
* Low fruit and vegetable consumption
* High blood pressure
* High cholesterol
* Obesity Diabetes
\
Study the bus driver and conductors have few coronary events
81
New cards
Types of Lipoproteins
* **Very Low Density Lipoprotein**
* Carries triglycerides to cells
* **Low Density Lipoprotein**
* Carries cholesterol to cells
* Oxidized LDL leads to endothelial damage and atherosclerosis
* **High Density Lipoprotein**
* Formed in liver
* Picks up excess cholesterol and carries it back to the liver
* Carries triglycerides to cells
* **Low Density Lipoprotein**
* Carries cholesterol to cells
* Oxidized LDL leads to endothelial damage and atherosclerosis
* **High Density Lipoprotein**
* Formed in liver
* Picks up excess cholesterol and carries it back to the liver
82
New cards
What is high Cholesterol?
High risk: >240
Optimal:
Optimal:
83
New cards
New Indicators of Heart Disease
* C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
* a blood marker of inflammation
* may be better predictor of CVD risk than elevated LDL
* Exercise, a healthy diet, weight loss, and smoking cessation can lower systemic inflammation
* a blood marker of inflammation
* may be better predictor of CVD risk than elevated LDL
* Exercise, a healthy diet, weight loss, and smoking cessation can lower systemic inflammation
84
New cards
The Lifestyle Heart Trial
* Experimental
* Low fat (
* Low fat (
85
New cards
**What is Homocysteine is an amino acid.**
High levels are associated with endothelial cell damage. Vitamins B6, B9 (folate), and B12 lower homocysteine.
86
New cards
Difference between Heart Attack and Stroke?
A heart attack occurs when blood flow through a coronary artery is blocked.
A stroke occurs when blood flow through a cerebral or carotid artery is blocked.
87
New cards
**Peripheral Vascular Disease**
PAD is atherosclerosis of the peripheral arteries, usually the lower limbs
PAD also includes carotid artery disease that leads to stroke
88
New cards
ABCDE test for Melanoma
**Asymmetry**
Most early melanomas are asymmetrical: a line through the middle would not create matching halves. Common moles are round and symmetrical.
\
**Border**
The borders of early melanomas are often uneven and may have scalloped or notched edges. Common moles have smoother, more even borders.
**Color**
Common moles usually are a single shade of brown. Varied shades of brown, tan, or black are often the first sign of melanoma. As melanomas progress, the colors red, white and blue may appear.
**Diameter**
Early melanomas tend to grow larger than common moles - generally to at least the size of a pencil eraser (about 6mm, or 1/4 inch, in diameter).
\
**Evolution (most important factor when considering diagnosis of melanoma)**
Melanomas tend to change over time
89
New cards
**Dietary Intervention**
### •Decrease
* •Animal Fat
•Bile>> Secondary Bile Acids
* •Alcohol
•Ethanol is IARC Class 1 Carcinogen
•Ethanol>> Acetaldehyde
* •Processed Meats
•IARC Class 1 Carcinogen
•Nitrites>> Nitrosamines
* •Red Meats (Grilled/ Charred)
•IARC Class 2A Carcinogen
•Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
•Heterocyclic Amines
•L-Carnitine>>TMAO
•Heme iron may damage lining of colon
90
New cards
High-Fat Diets Increase Cancer Risk
Bile can be converted into carcinogenic secondary bile acids.
Since soluble fibers can bind bile, they can block this conversion.
91
New cards
Processed Meats Increase Cancer Risk
The preservative sodium nitrite can be converted into carcinogenic nitrosamines.
\
Certain nutrients, such as vitamins C and E, may block this conversion.
92
New cards
Cancer Treatment
* •Localized cancer
•Surgery
•Radiation
* •Metastasized cancer
•Chemotherapy