General Survey of the Skull
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
How many bones are in the skull?
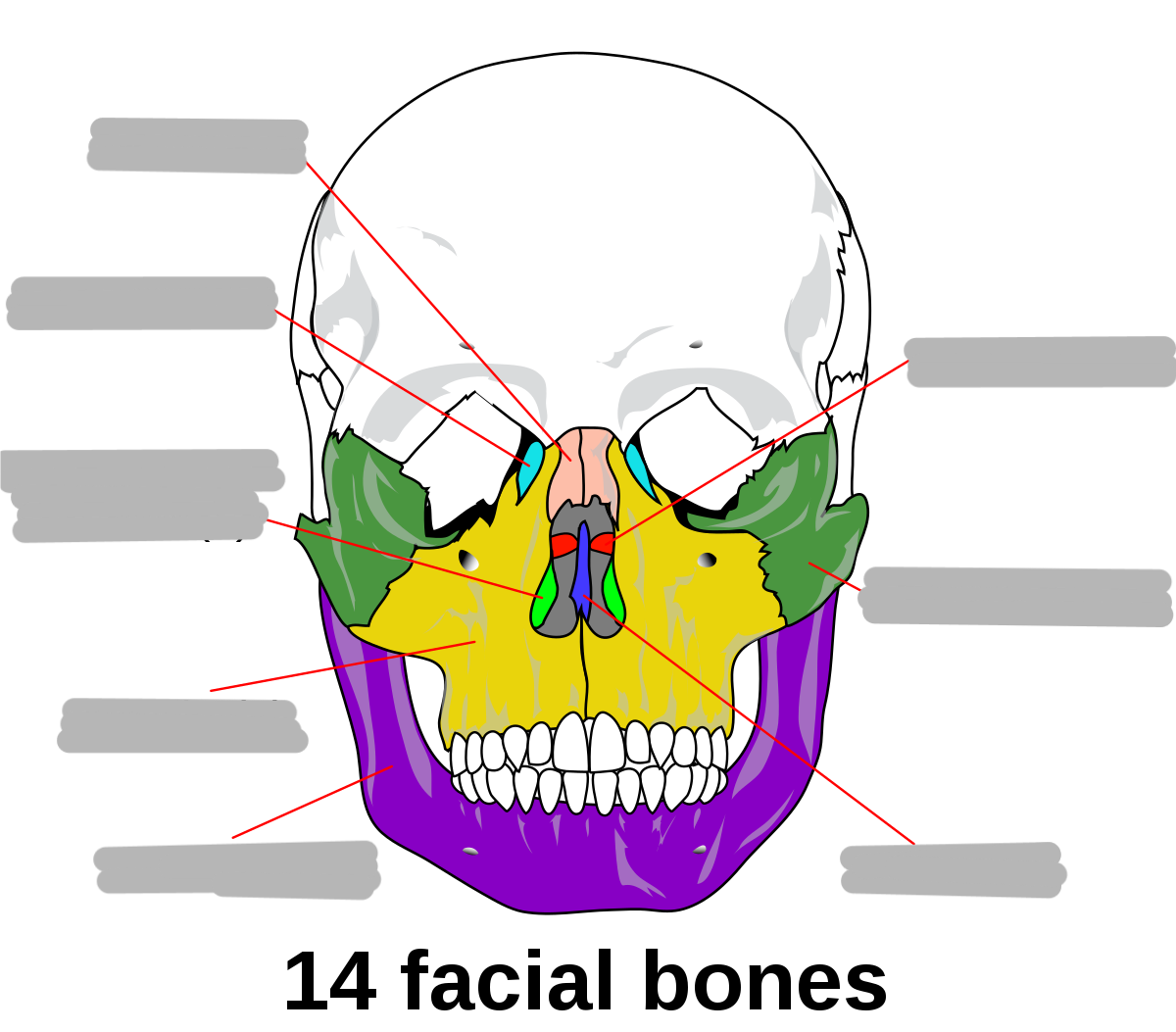
14 facial
8 cranial
22 total
How are the cranial bones classified?
flat bones
How are the facial bones classified?
irregular bones
What is the function of the cranial bones?
protect the brain
What is the function of the facial bones?
provide structure and shape to the face
List the cranial bones (and whether they are paired or individual)
frontal (1)
parietal (2)
occipital (1)
temporal (2)
sphenoid (1)
ethmoid (1)
What is the most anterior cranial bone?
frontal bone
The frontal bone makes up the ___
forehead and superior orbits
The parietal bone makes up the ___
majority of the superior aspect of the cranium
What is the most posterior cranial bone?
occipital bone
Which bone contains the foramen magnum?
occipital
The temporal bone makes up the ___
area by the ear
Where does the sphenoid bone sit?
in the middle floor of the skull
The sphenoid bone forms the ___
orbits and posterior nasal cavity
The ethmoid bone lies within the ___
frontal bone
The ethmoid bone forms the ___
orbits and nasal cavity walls
Facial bones can also be called ___
visceral cranium
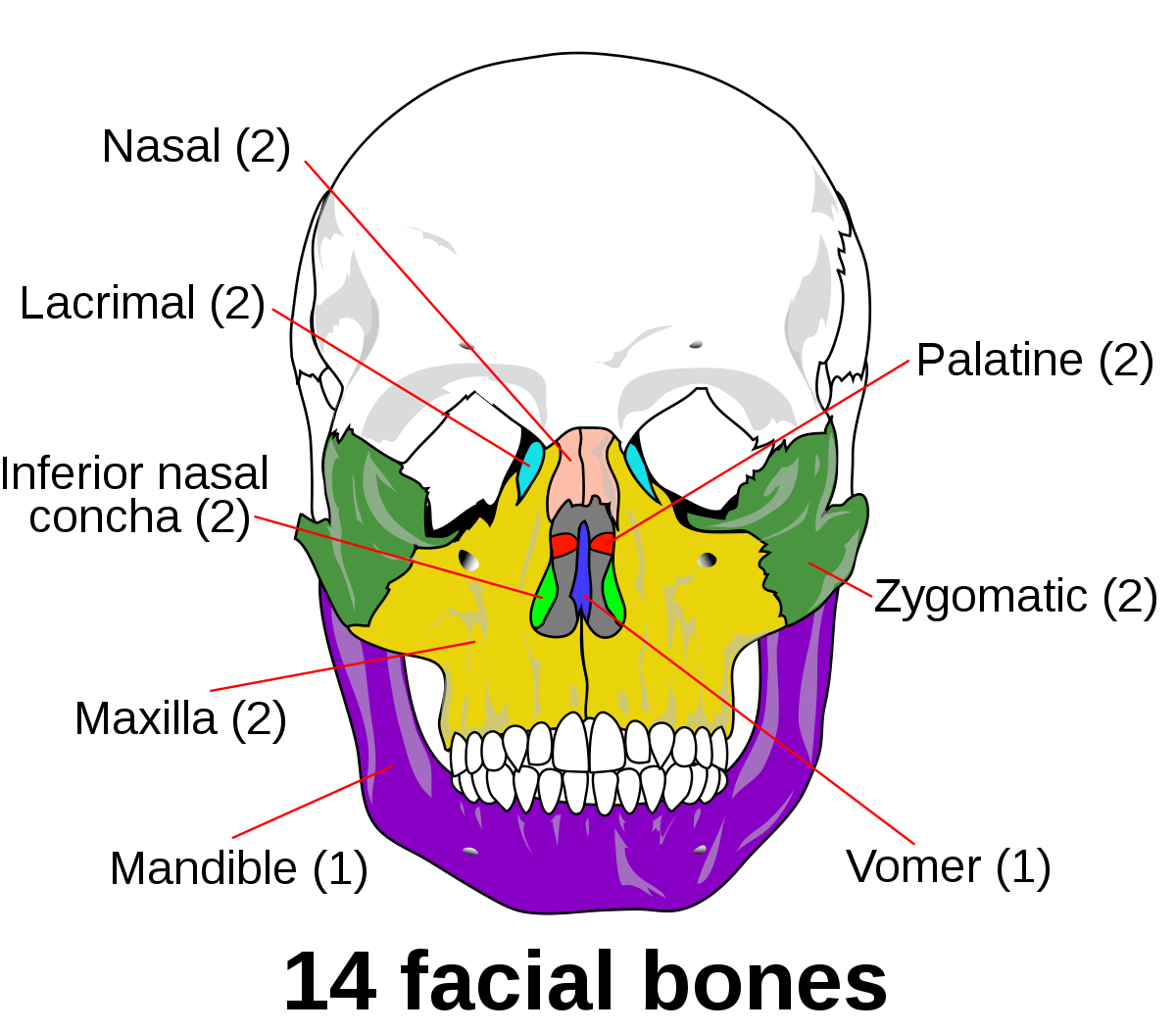
Explain the shape and location of the nasal bones
2 small oblong bones
placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face
Explain the location of the maxilla
2 bones that join at midline just above the teeth
The maxilla forms the ___
upper jaw
The maxilla houses the ___
upper teeth
The zygomatic bones form the ___
cheekbones
Explain the size and location of the lacrimal bones
2 of the smallest and most fragile bones of the face
at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit (located between the maxilla and ethmoid)
Which bone contains our tear ducts?
lacrimal bones
Explain the location of the palatine bones
2 bones situated at the back part of the nasal cavity between the maxilla and sphenoid
The palatine bones form the ___
roof of the mouth and part of the orbit
Explain the shape, location, and function of the inferior nasal conchae
2 bones
scroll-like appearance
inferior, lateral aspect of nose
cleans and filters air
Explain the location and function of the vomer
single bone
helps to form the nasal septum
located in the MSP posterior to the palatine
What is the largest moveable facial bone?
mandible
What is the articulation between the mandible and temporal bone?
TMJ joint
diarthrodial, synovial, condylar
The mandible forms the ___
lower jaw
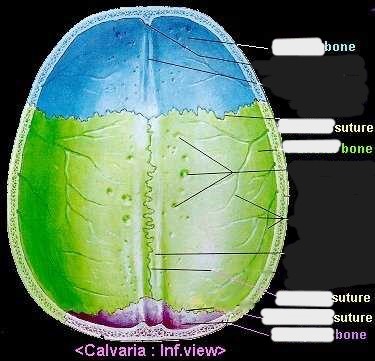
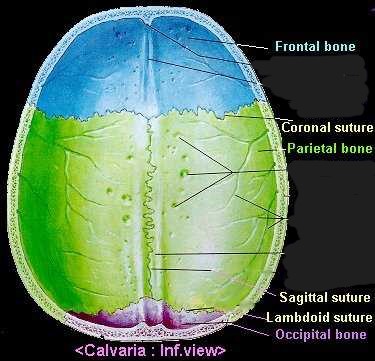
What makes up the calvaria?
frontal
occipital
parietals
What is the most superior part of the skull called?
vertex
What makes up the skull floor?
ethmoid
sphenoid
temporals
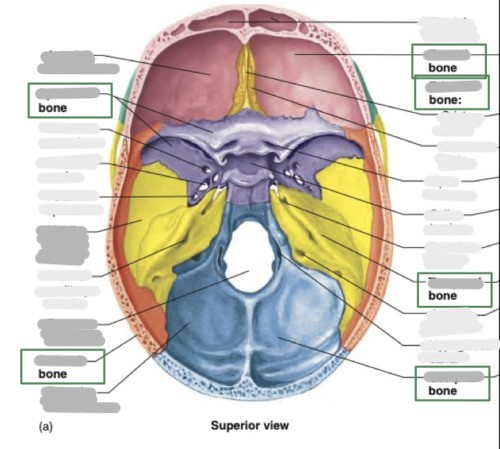
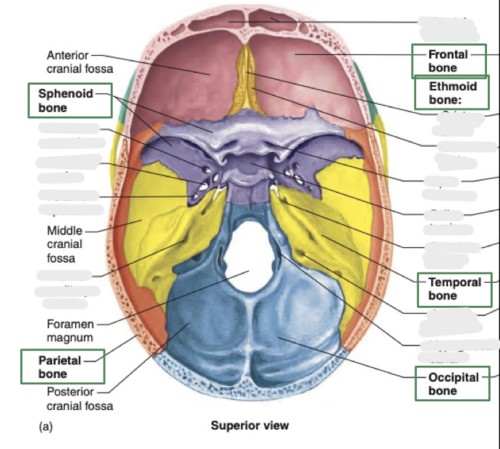
List the fossa of the cranial floor
anterior (frontal/ethmoid)
middle (sphenoid/temporal)
posterior (occipital/base of skull)
What are the measurements of the skull?
6 inches side to side
7 inches front to back
9 inches top to bottom (including mandible)
How are skull bones formed?
intramembranous ossification
formed by a thin membranes made up of embryonic connective tissue arranged in sheets like layers
flat bones have a 4 step process:
ossification center appears in fibrous connective tissue membrane
bone matrix is secreted
trabecula and periosteum form
formation of compact bone
Explain diploe
bones of the cranium are composed of 2 plates of compact bone separated by an inner layer of spongy tissue called diploe
What are the 4 sutures of the skull?
coronal (between frontal and parietal)
sagittal (between parietals)
lambdoidal (between occipital and parietal)
squamosal (between temporal and parietal)
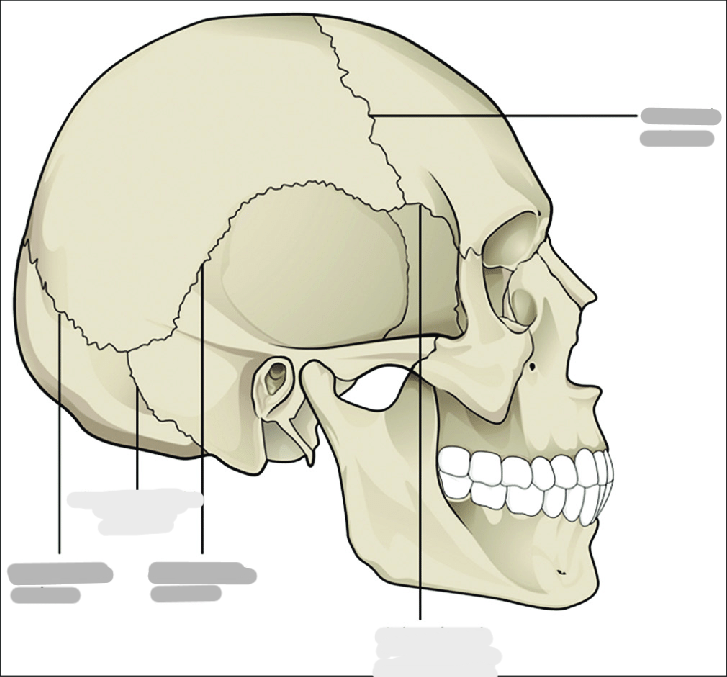
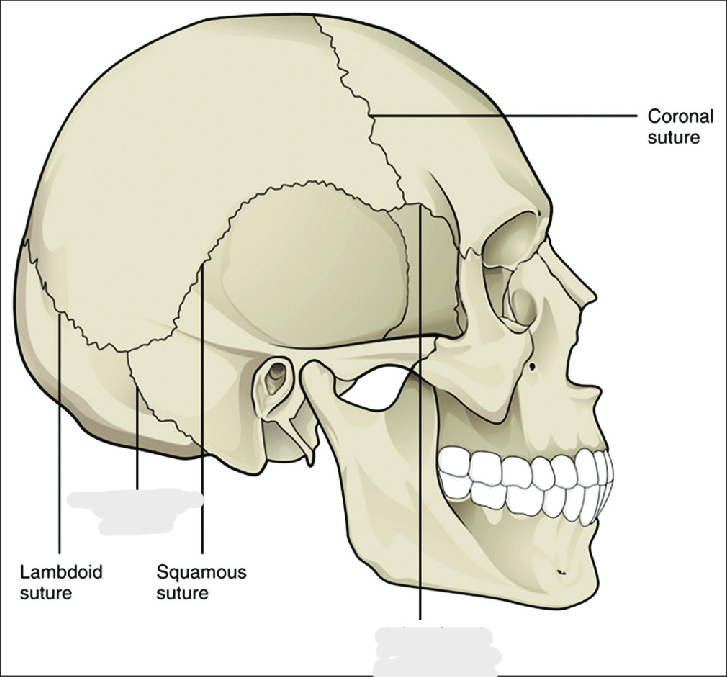
Skull sutures are classified as ___
fibrous, synarthrodial
What are the functions of fontaneles?
fetal skull can compress as it passes through birth canal
rapid growth of the brain during infancy
Explain the anterior fontanele
bregma
where parietals and frontal bone meet
at vertex
closes at 18-24 months
Explain the posterior fontanele
lambda
where parietals and occipital bone meet
closes at 2-6 months
Explain the sphenoid fontanele
pterion
parietal, sphenoid, and temporal bones
closes at 3 months
Explain the mastoid fontanele
asterion
occipital, parietal, and temporal bones
closes at 12 months
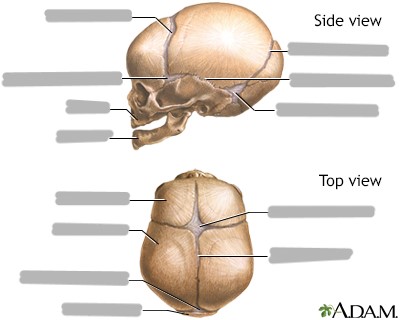
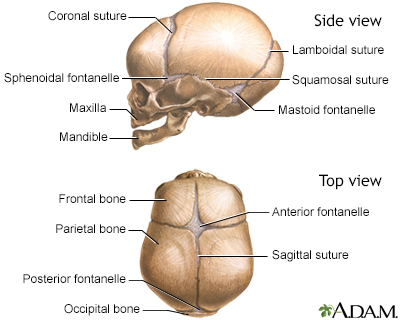
What is squamous?
the flat part of a bone
What is lateral/outer canthus?
where your eyelids unite laterally
What is medial/inner canthus?
where your eyelids unite medially
What is TEA?
Top of Ear Attachment (where top of ear attaches to skull)
What is EAM?
External Auditory Meatus (the ear hole)
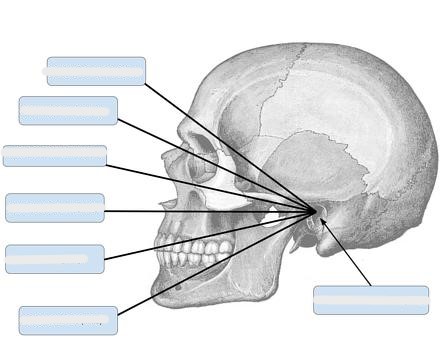
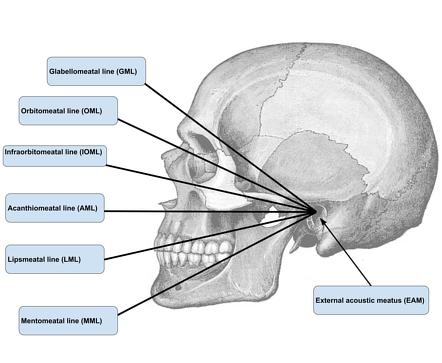
What are radiographic baselines?
lines that start at the EAM and go anterior toward the face
What is the MML?
mentomeatal line
chin to EAM
What is the LML?
lips meatal line
lips to EAM
What is the AML?
acanthiomeatal line
point just under nose to EAM
What is the IOML?
infraorbitomeatal line
below eyes to EAM
What is the OML?
outer canthus to EAM
What is the GML?
glabellomeatal line
glabella to EAM