FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE PHARYNX AND LARYNX
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Functional anatomy of pharynx
Commonly known as the throat, long tube extending behind the nasal and oral cavities until larynx and oesophagus.
Generalities
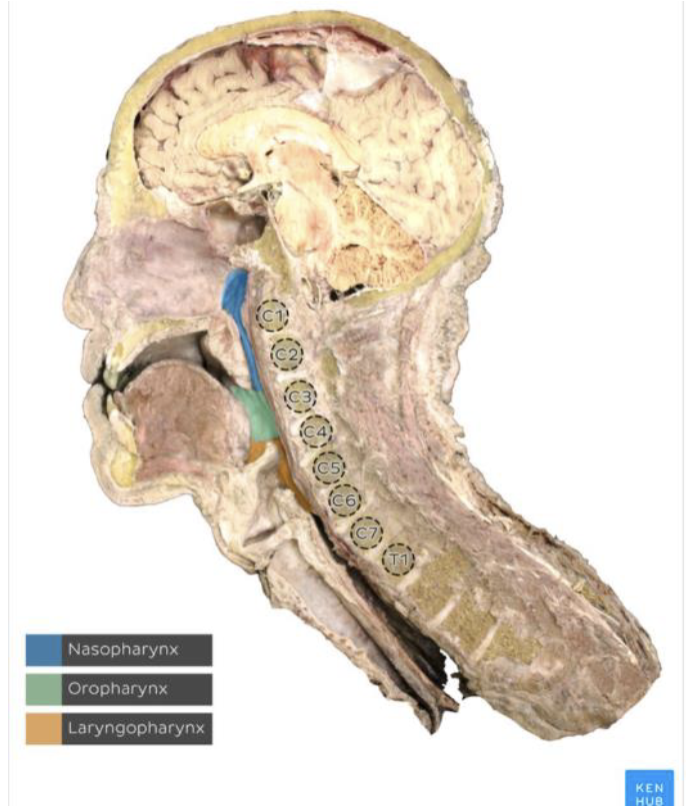
Nasopharynx- posterior to the nasal cavity
Oropharynx- posterior to the oral cavity
Laryngopharynx- posterior to the larynx
Nasopharynx
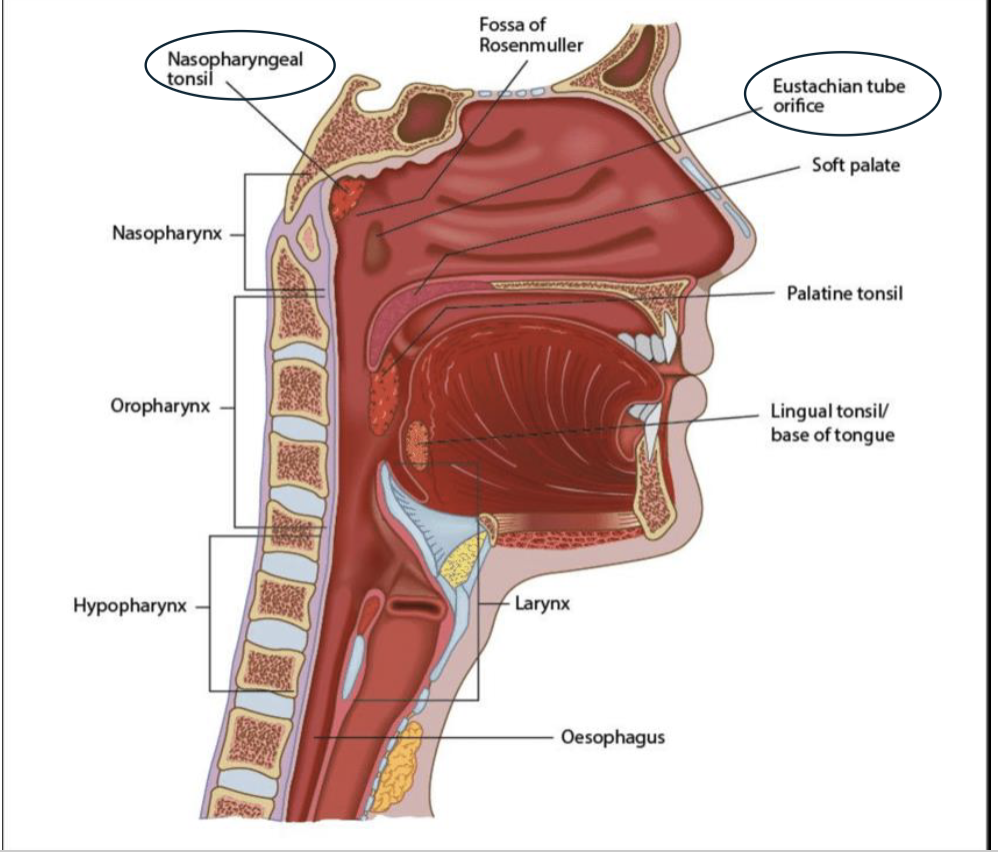
Contains the pharyngeal tonsils in posterior wall. Group of lymphoid tissues involved in immunity.
Contains opening to eustachian tube.
Oropharynx
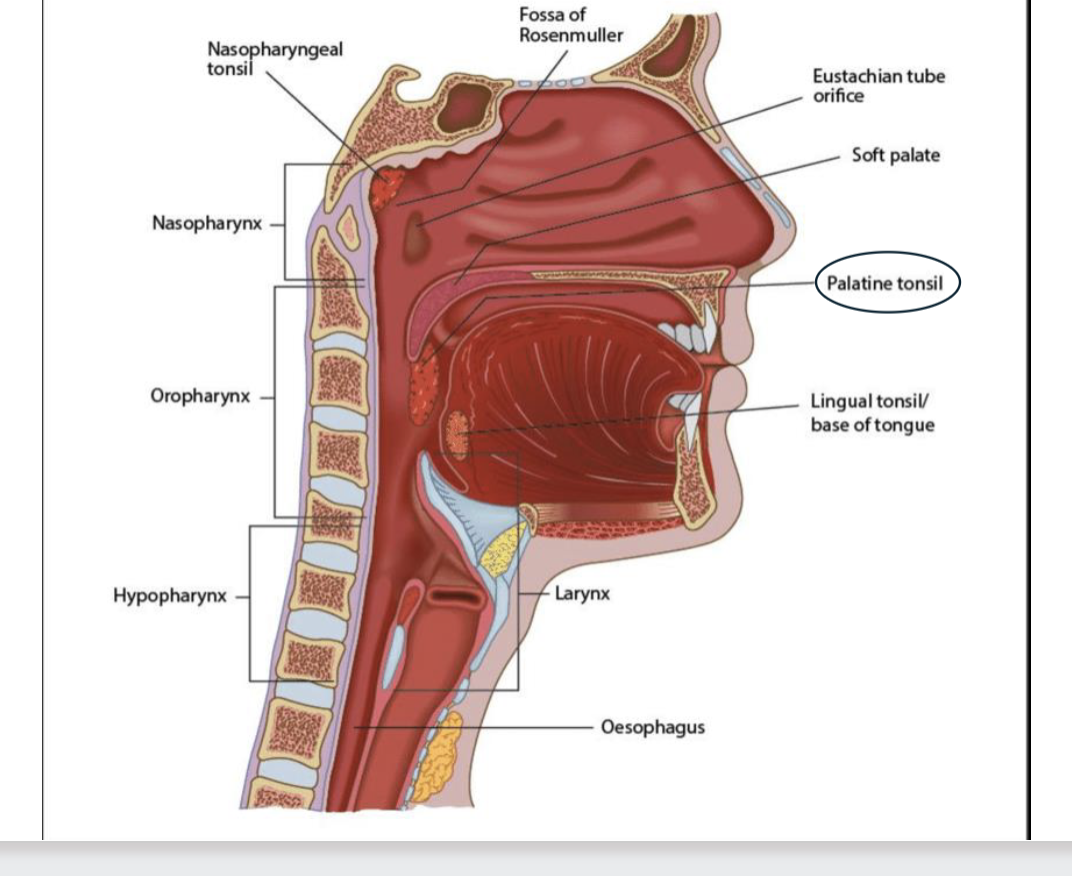
Contains palatine tonsils in posterior wall, group of lymphoid tissues involved in immunity.
Laryngopharynx
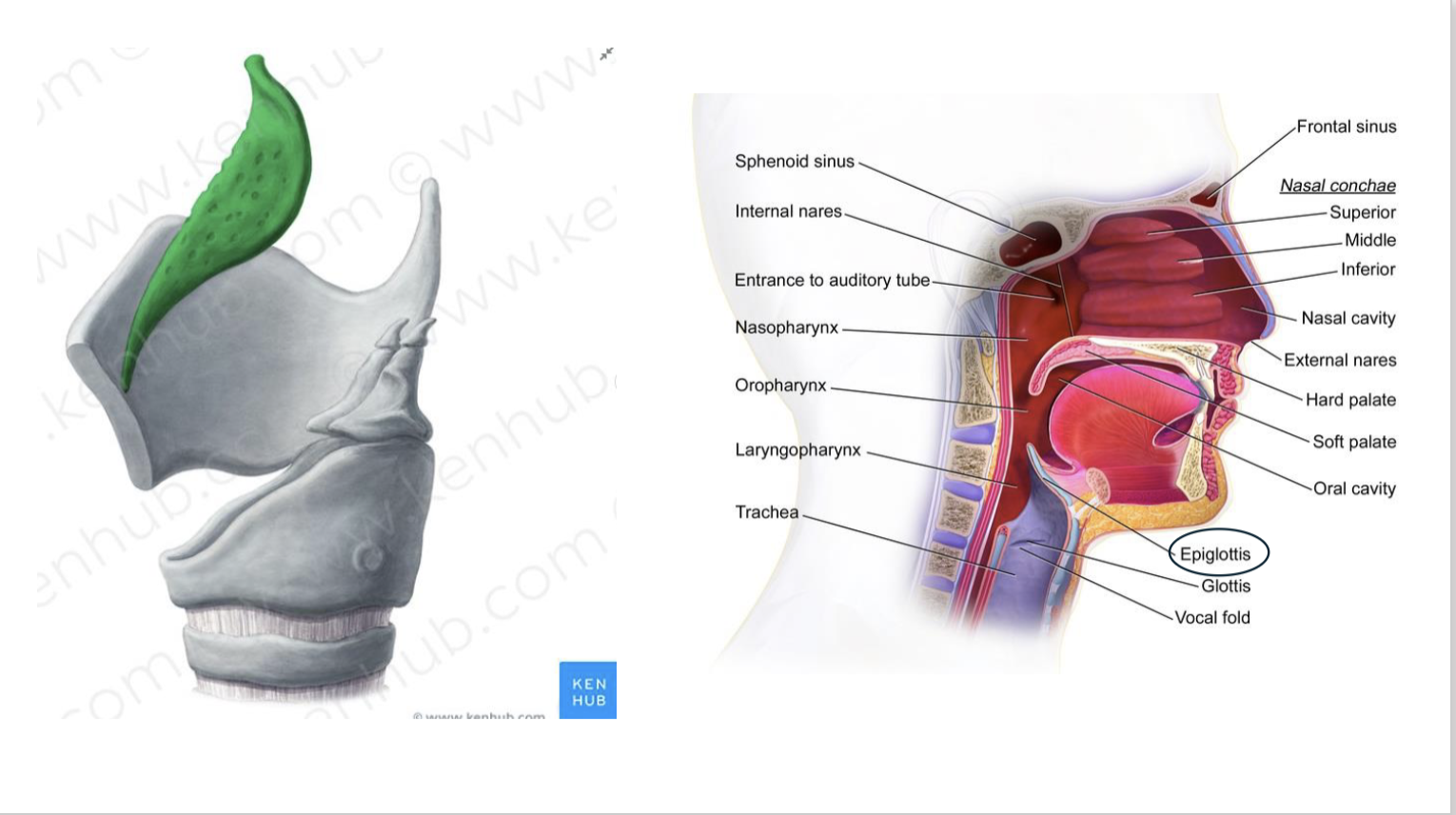
Comprises of tube between epiglottis and oesophagus.
Cartilaginous flat that closes during swelling to prevent passage of food to the respiratory tract
Nervous supply
Pharynx is primarily supplies by the vagus nerve
Functions
Passage for airway and food: Involved in respiratory and digestive systems.
Voice resonance: aids function of vocal cords in larynx
Immune defence: Through the tonsils
Equalisation of pressure through middle ear: Through the eustachian tube
Functional anatomy of Larynx
Larynx is a cartilaginous tubular structure anterior to the oesophagus
Sits above trachea
Larynx composition
Epiglottis
Throid
Cricoid
Epiglottis
Projects superiorly to the pharynx, just behind the root of the tongue.
During swallowing, epiglottis swings downward to close the superior margin of the larynx, preventing materials from entering the airway
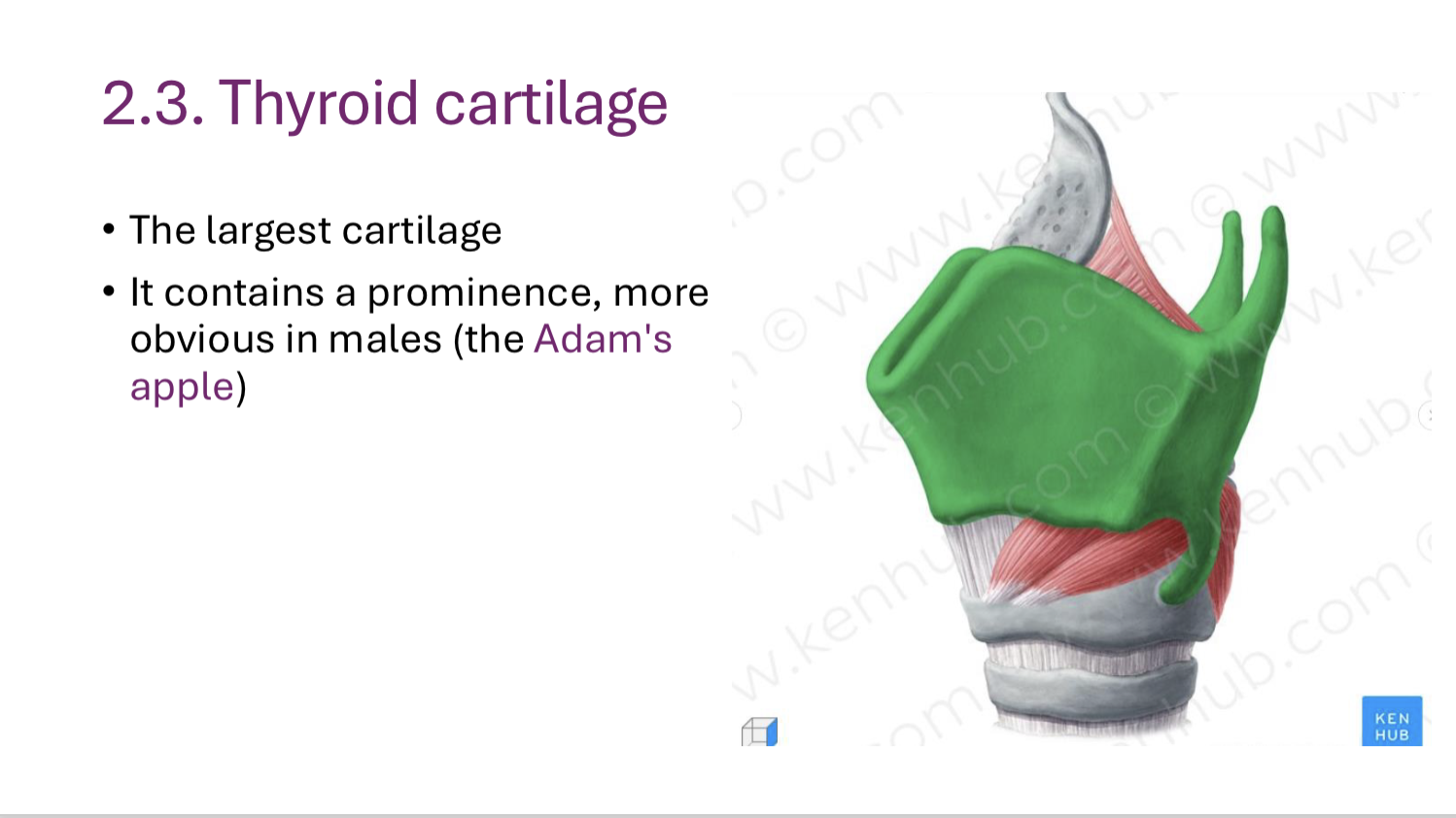
Thyroid cartilage
Largest cartilage, contains adams apple prominence
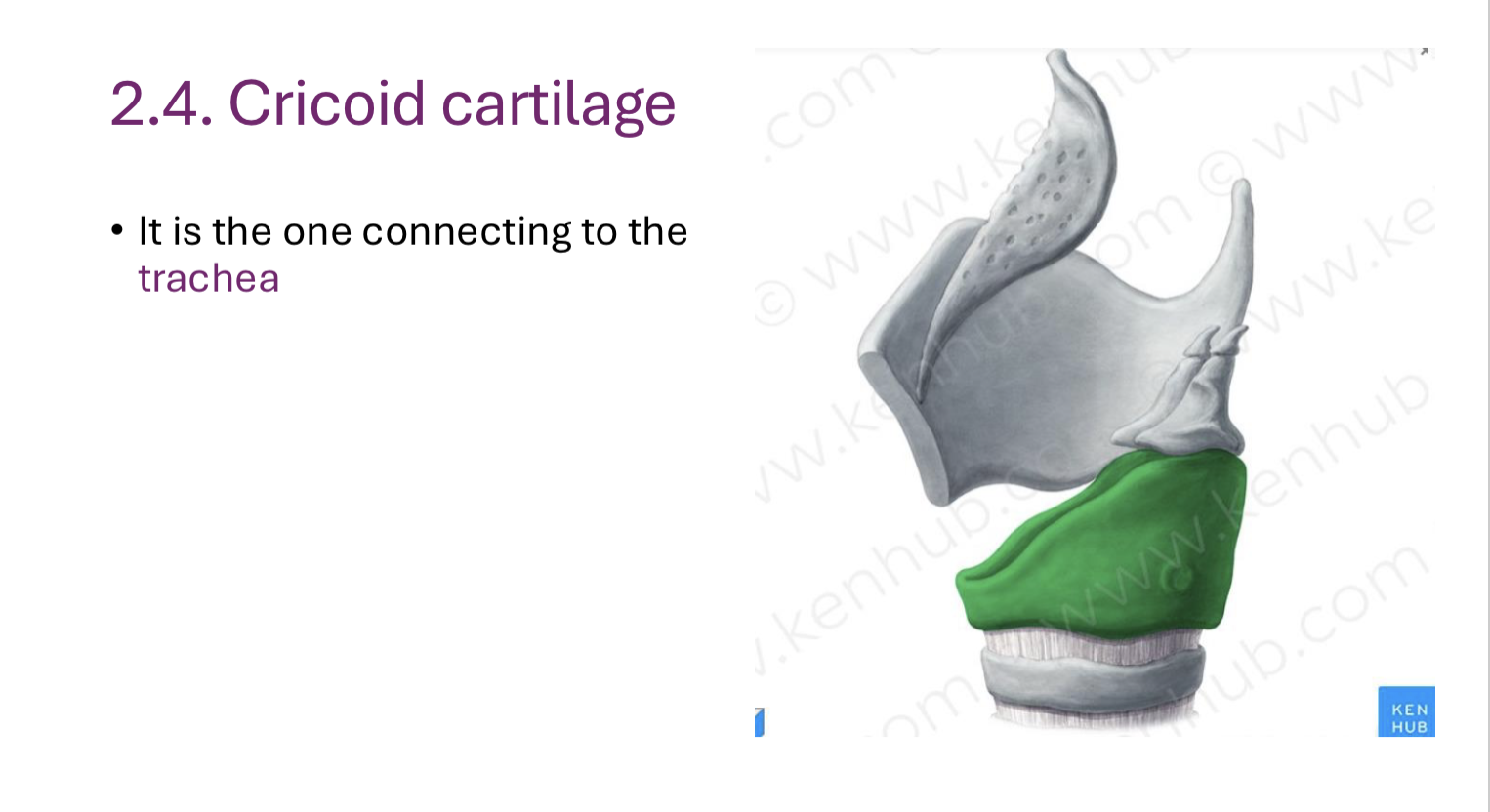
Circoid cartilage
Connects to trachea
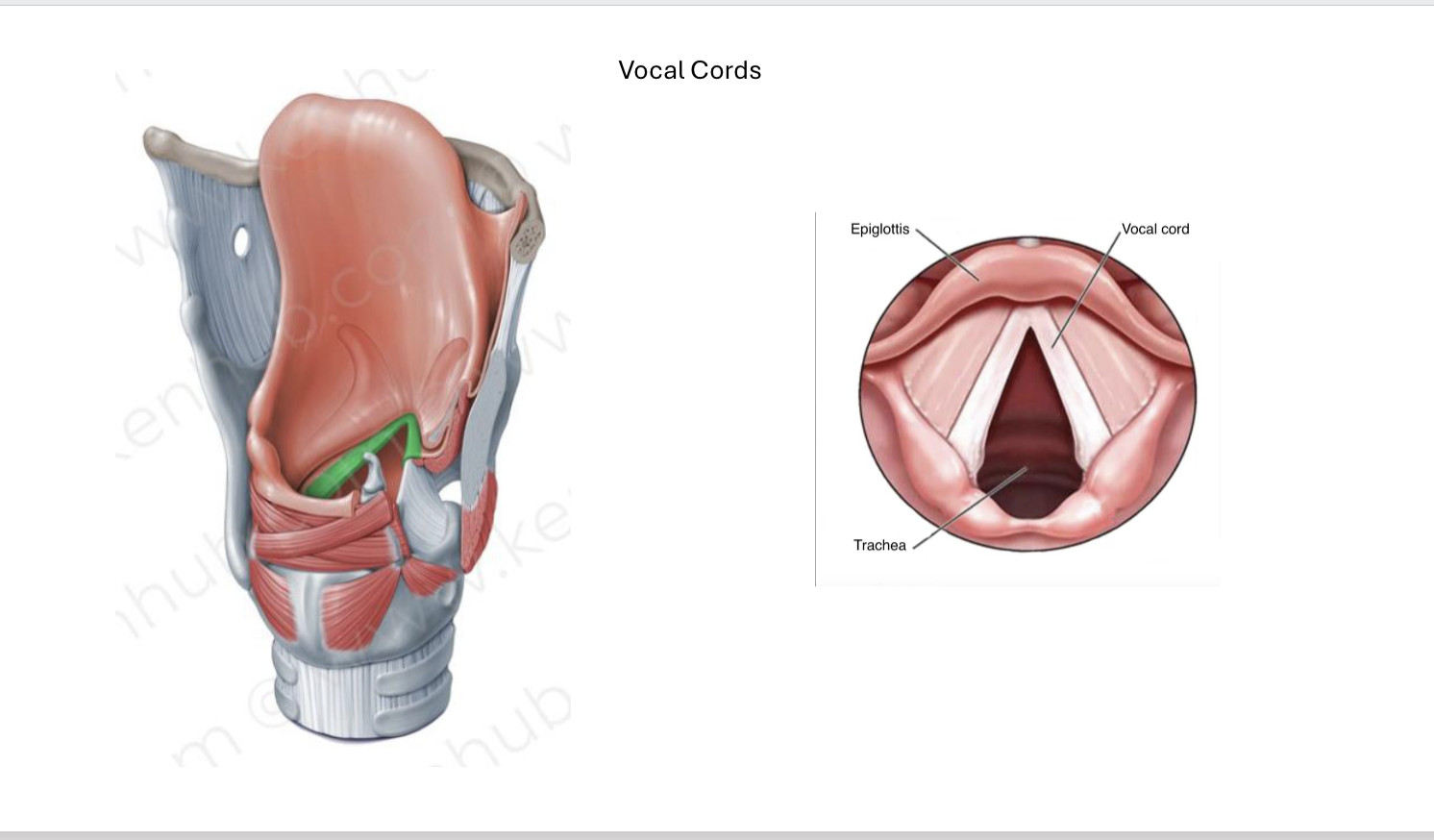
Vocal cords (folds)
Produce sound as air passes over them, extend from inner surface of thyroid cartilage.
Nerve supply
Innervated by the laryngeal nerve, branches of vagus nerve
Functions
Airway protection: through the epiglottis
• Phonation: sound production through the vocal cords
• Respiration: it acts as an air passage
• Swallowing