GEOLOGIC TIME
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Who founded modern geology and the principle of uniformitarianism?
James Hutton.
What is the fundamental principle of geology?
The present is the key to the past.
What does the principle of uniformitarianism state?
The physical, chemical, and biological processes that function today also functioned in the past.
What is relative dating in geology?
Placing rocks and events in proper sequence based on their relative ages.
What does the law of superposition state?
The oldest rocks are on the bottom of a sequence of strata.
What is the principle of original horizontality?
Sediment is deposited horizontally.
What does the principle of cross-cutting relationships state?
A younger feature cuts through an older feature.
What is an inclusion in geology?
A rock contained within another rock, where the rock containing the inclusion is younger.
What does the principle of lateral continuity say?
Strata layers can be traced or mapped out from a starting point, and they have a measurable area.
Continuous layers of strata that extends in all directions
What causes unconformities in strata records?
Erosion and/or non-deposition.
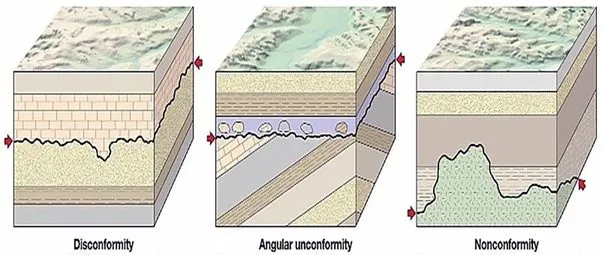
What is an angular unconformity?
Tilted rocks are overlain by flat-lying rocks.
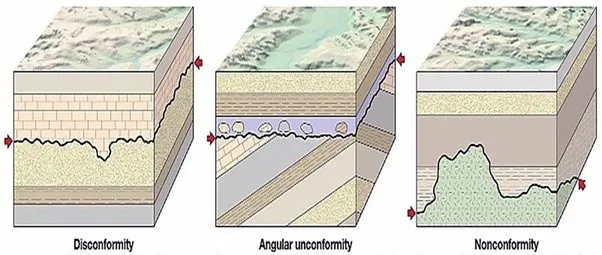
What is a disconformity?
Horizontal strata above and below an erosional surface.
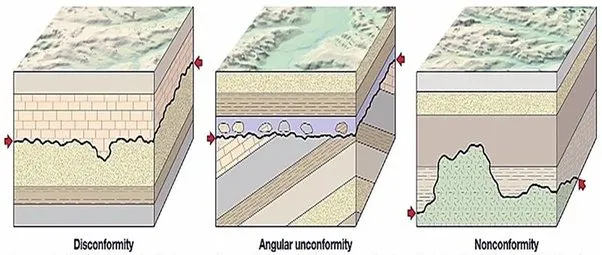
What is a nonconformity in geology?
Metamorphic or igneous rocks below erosional contact with younger sedimentary rocks above.
What is fossil preservation?
Fossils require hard parts and rapid burial for preservation.
What is petrification?
Cavities and pores of the organism are filled with precipitated mineral matter.
How are molds and casts formed?
A mold is formed when a shell or structure is buried and then dissolved by water. A cast is formed when the hollow space of a mold is filled with mineral matter.
What is carbonization in fossil preservation?
Organic matter becomes a thin residue of carbon.
What is the principle of fossil succession?
Fossils succeed one another in a definite and determinable order.
What are index fossils?
Fossils that are widespread geographically, existed for a short range of geologic time, and function as time references in strata.
What is radioactive decay?
The spontaneous breaking apart (decay) of atomic nuclei.
What are parent and daughter products in radioactive decay?
The parent is the unstable isotope, and the daughter products are the isotopes formed from the decay of the parent.
What is a half-life?
The time it takes for one-half of a sample of radioactive nuclei to decay.
What is a common error in absolute dating?
Loss of daughter products, which can give a false age.