Overview of the Human Digestive System
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Ingestion
the act of eating
Propulsion
movement of food through the alimentary canal
Mechanical breakdown
includes chewing, mixing food with saliva, churning food in the stomach, and segmentation
Segmentation
local constriction of intestine that mixes food with digestive juices
Digestion
series of catabolic steps that involves enzymes that break down complex food molecules into chemical building blocks
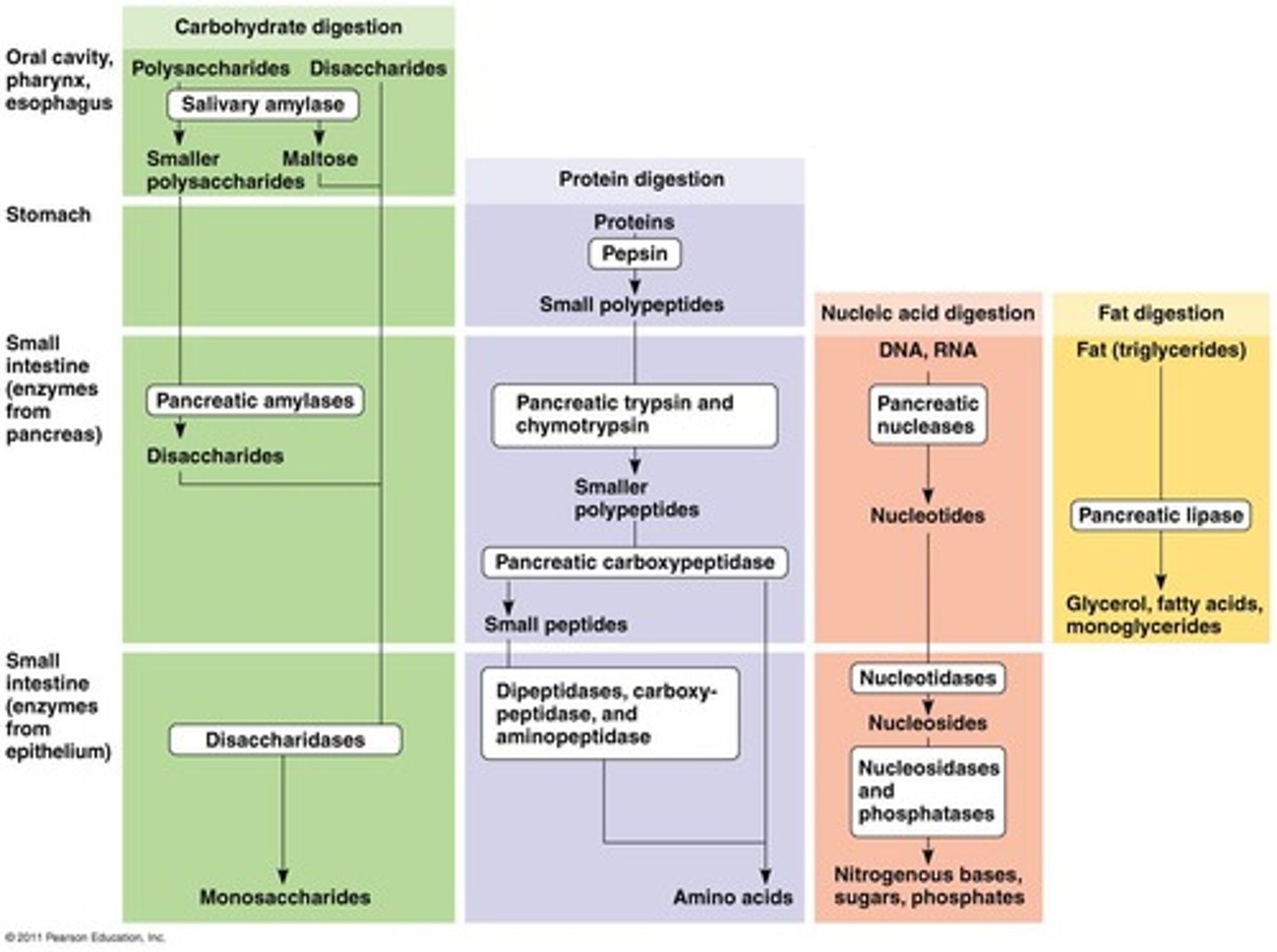
Absorption
passage of digested fragments from lumen of GI tract into blood or lymph
Defecation
elimination of indigestible substances via anus in form of feces
Hydrolytic enzymes
catalyze the digestion of each of the classes of macromolecules found in food.
What do hydrolytic enzymes break nucleotides down into?
Nucleosides, nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphates.
Extracellular digestion
the breakdown of food outside cells within compartments that are continuous with the outside of the body
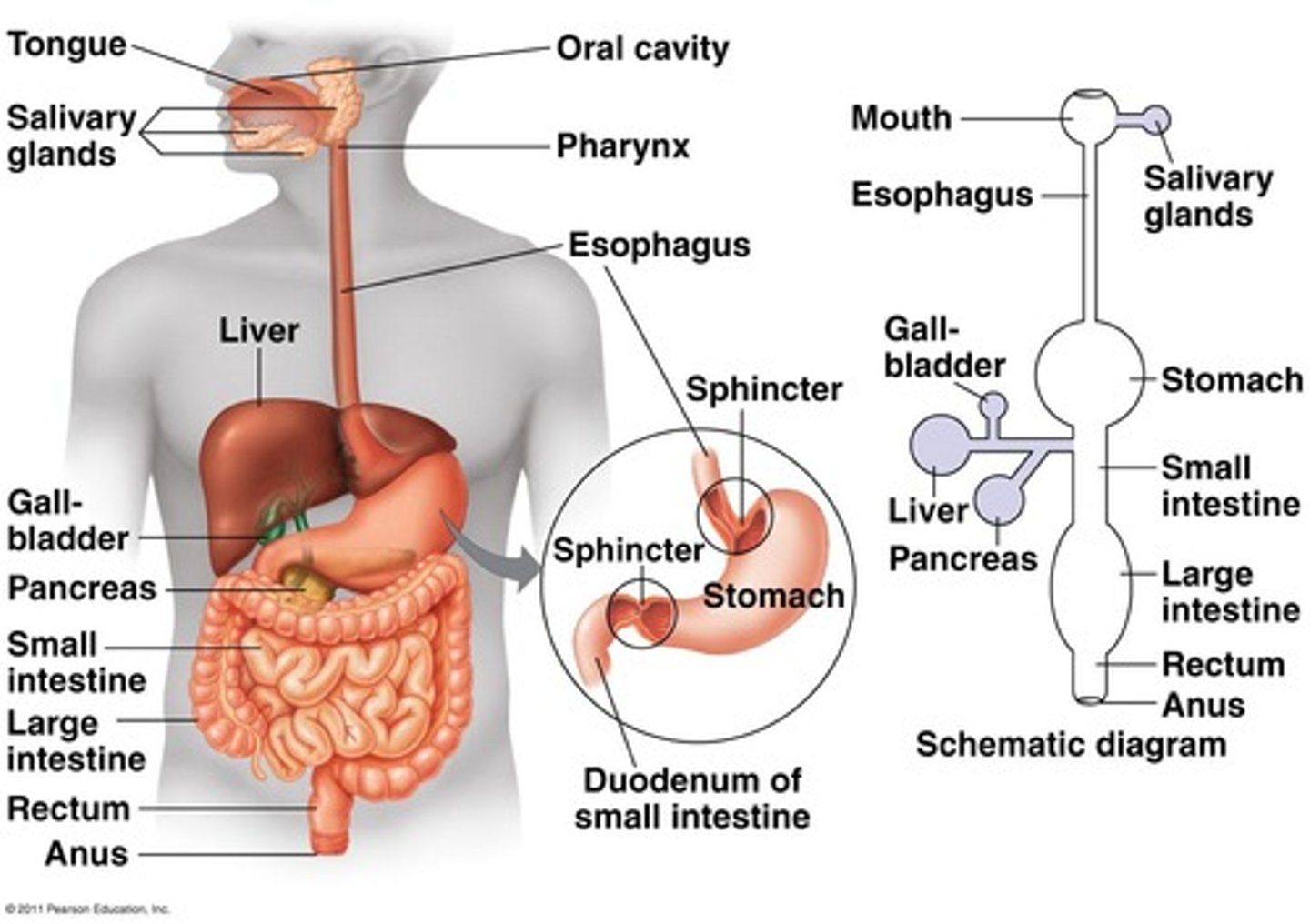
Alimentary canal
the digestive tube that food ingested through the mouth and pharynx passes through
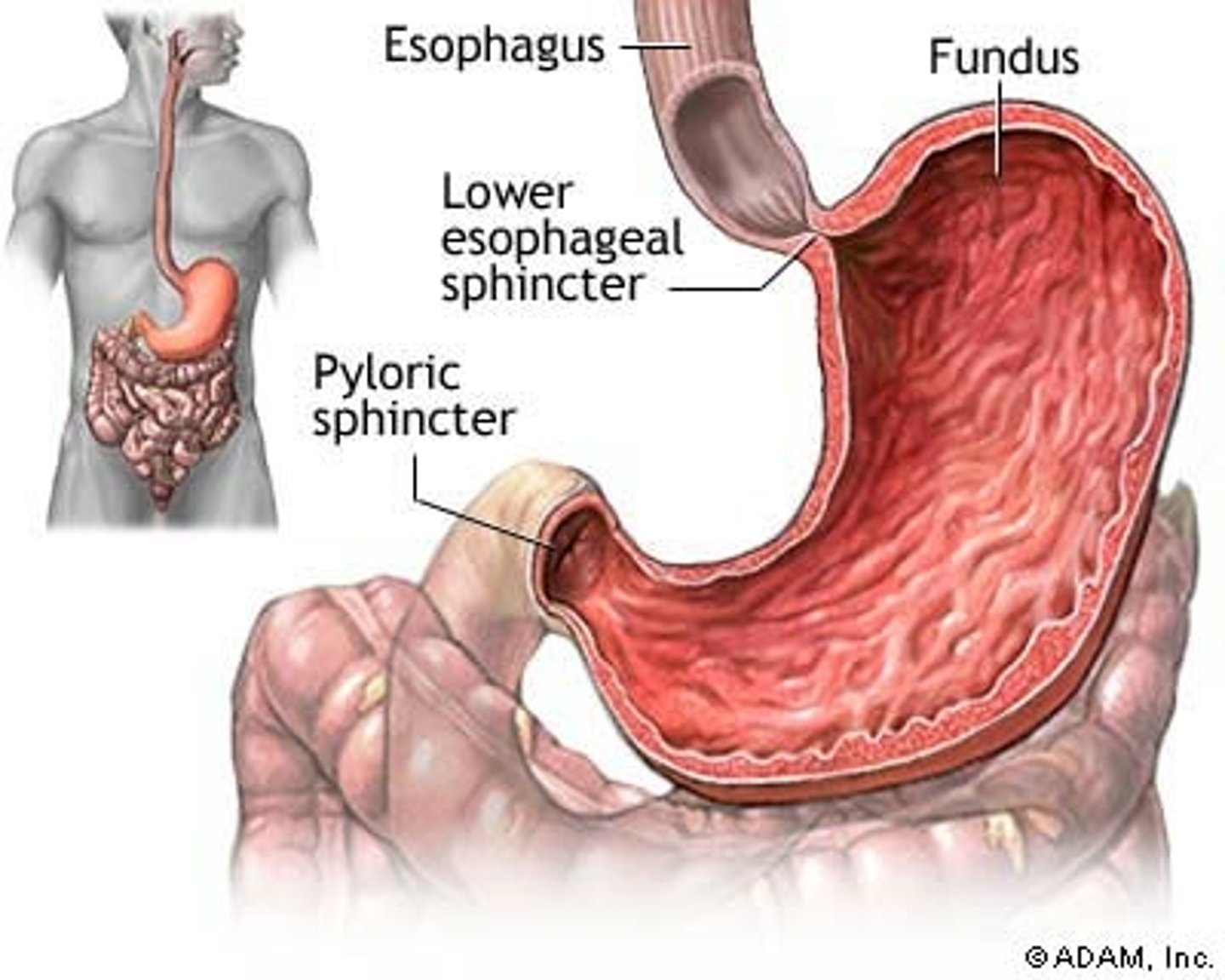
Esophagus
the tube that leads food from the mouth to the stomach
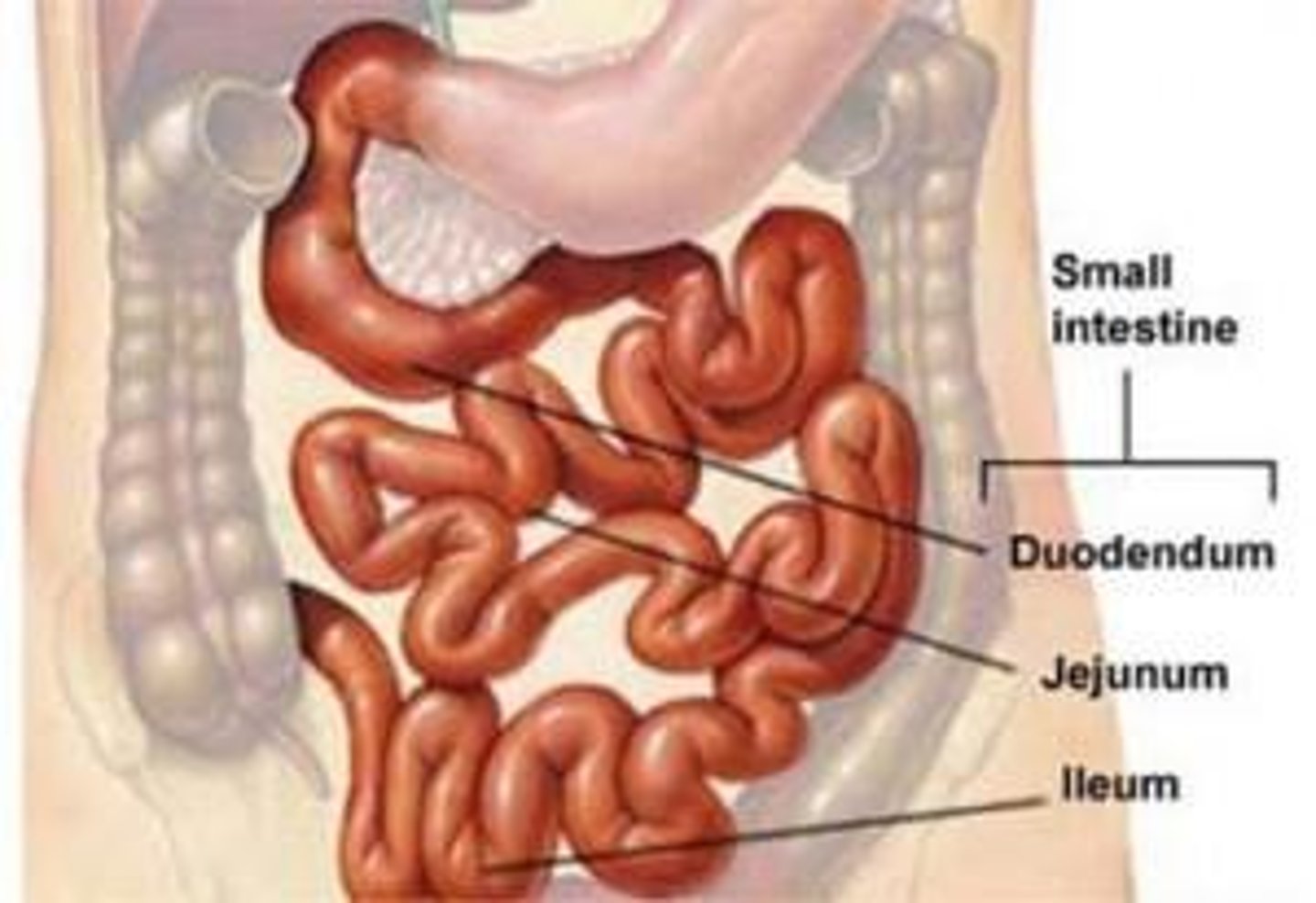
Small intestine
the site where final digestion and nutrient absorption occur over a period of 5 to 6 hours
Large intestine
the part of the digestive system where undigested material passes through in 12 to 24 hours
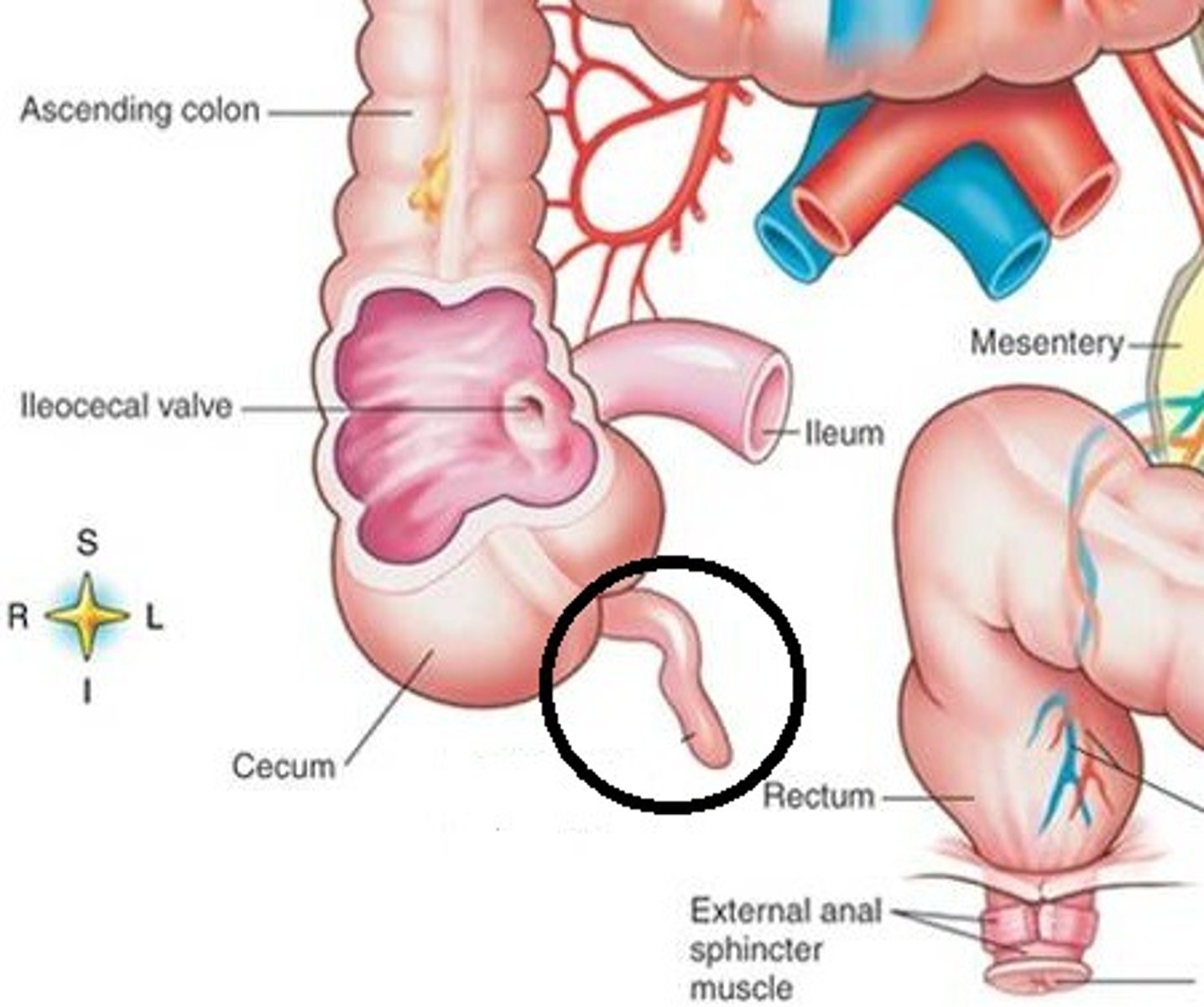
Caecum
a pouch in the lower abdominal cavity that receives undigested food material from the small intestine
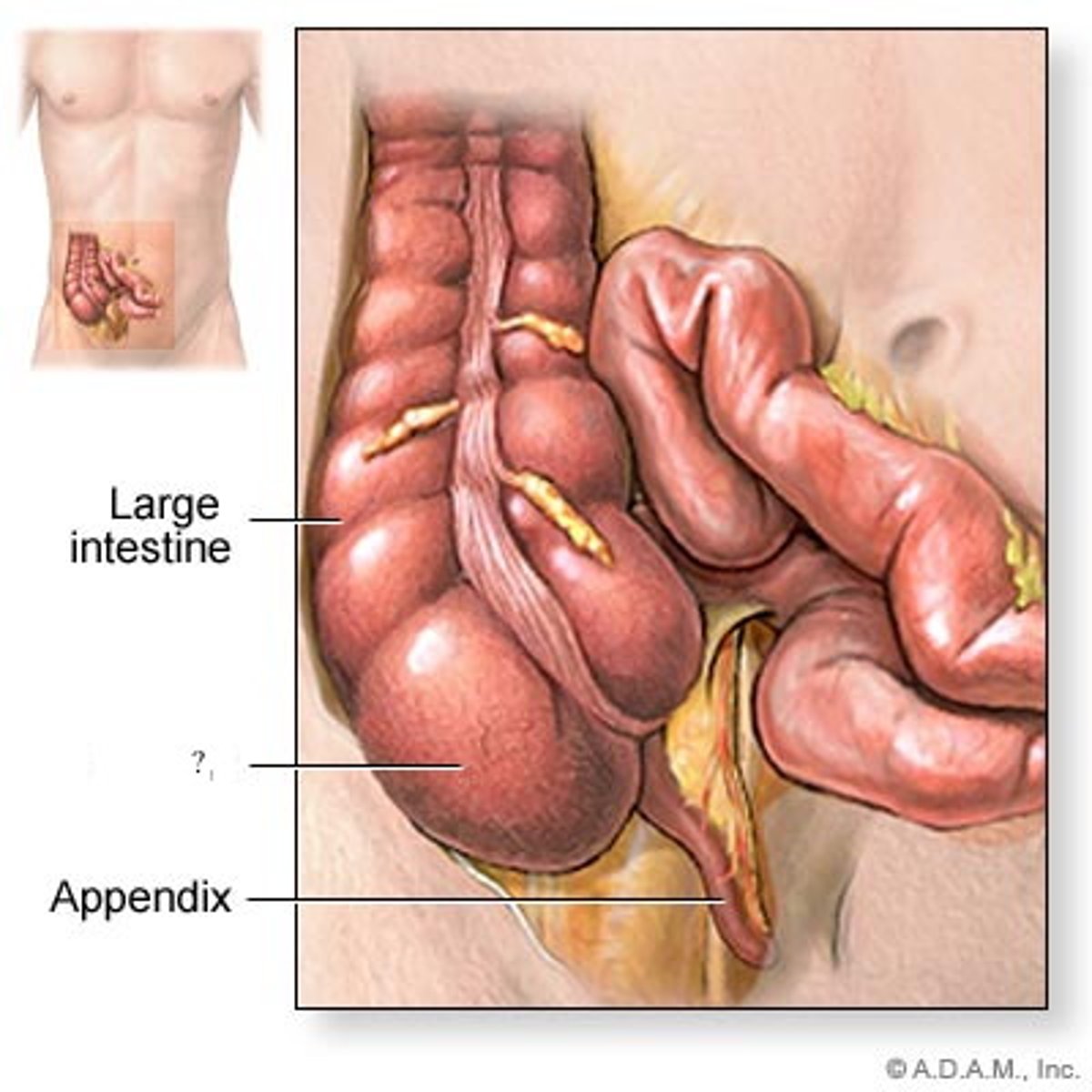
Appendix
a small structure attached to the caecum
Sphincters
- Muscular ringlike valves that regulate the passage of material between specialized chambers of the canal
- Two sphincters, one involuntary and one voluntary, are located between the rectum and the anus.
Digestive juices
secretions from accessory glands that aid in the digestion process
ATP production
the process by which the animal uses digested molecules as fuel
Polysaccharides
complex carbohydrates that are split into simple sugars during digestion
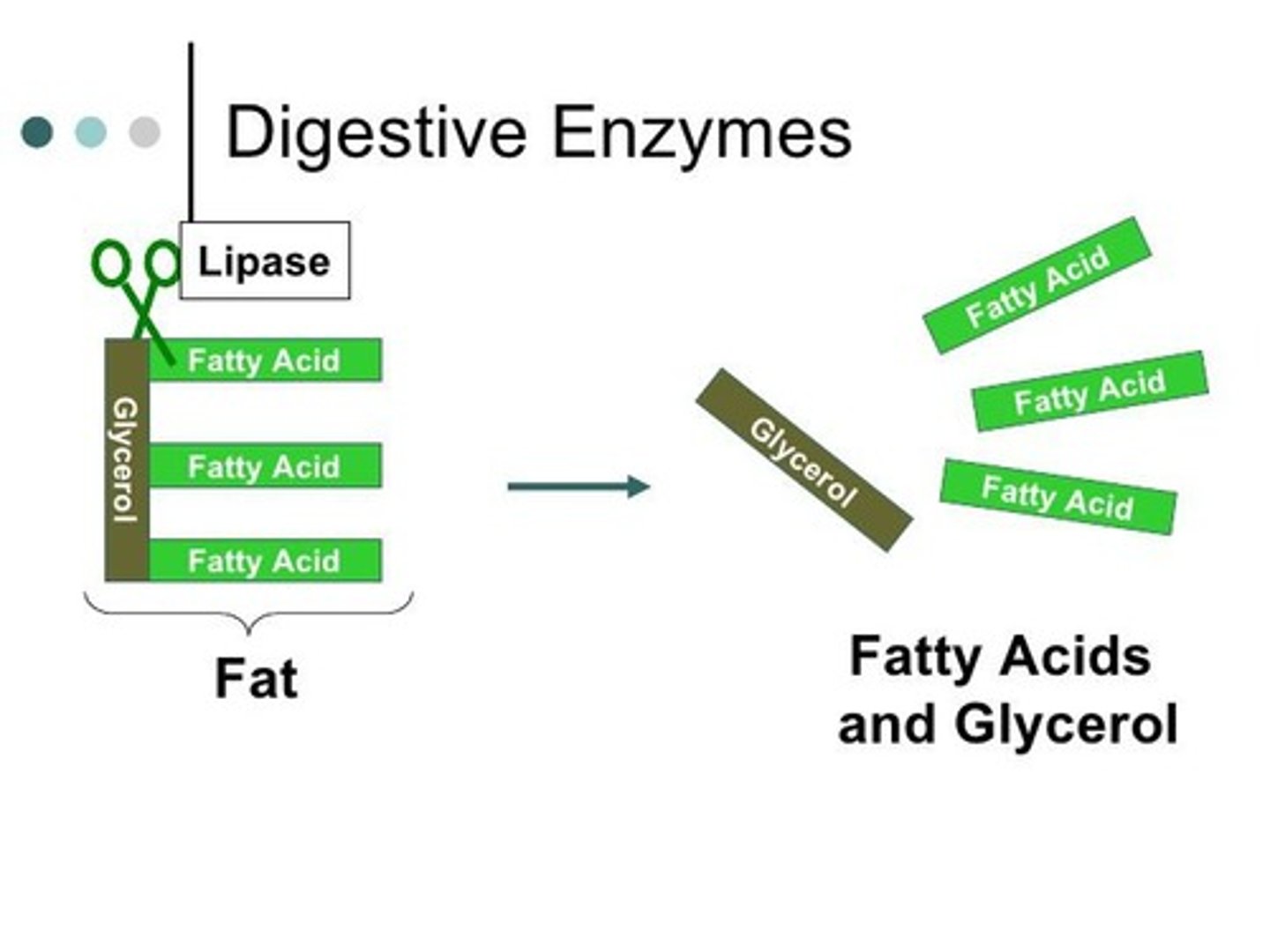
Fats
broken down into glycerol and fatty acids during digestion
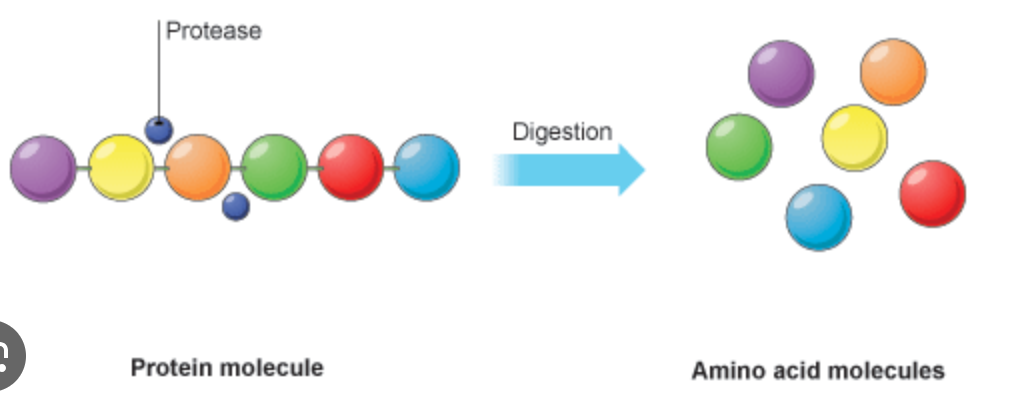
Proteins
broken down into amino acids during digestion
Nucleic acids
cleaved into nucleotides during digestion
Time for food passage
it takes 5 to 10 seconds for food to pass down the esophagus to the stomach
Time in stomach
food spends 2 to 6 hours being partially digested in the stomach
Time in large intestine
any undigested material passes through the large intestine in 12 to 24 hours
Accessory glands
Include the salivary glands, the pancreas, the liver, and the gallbladder.
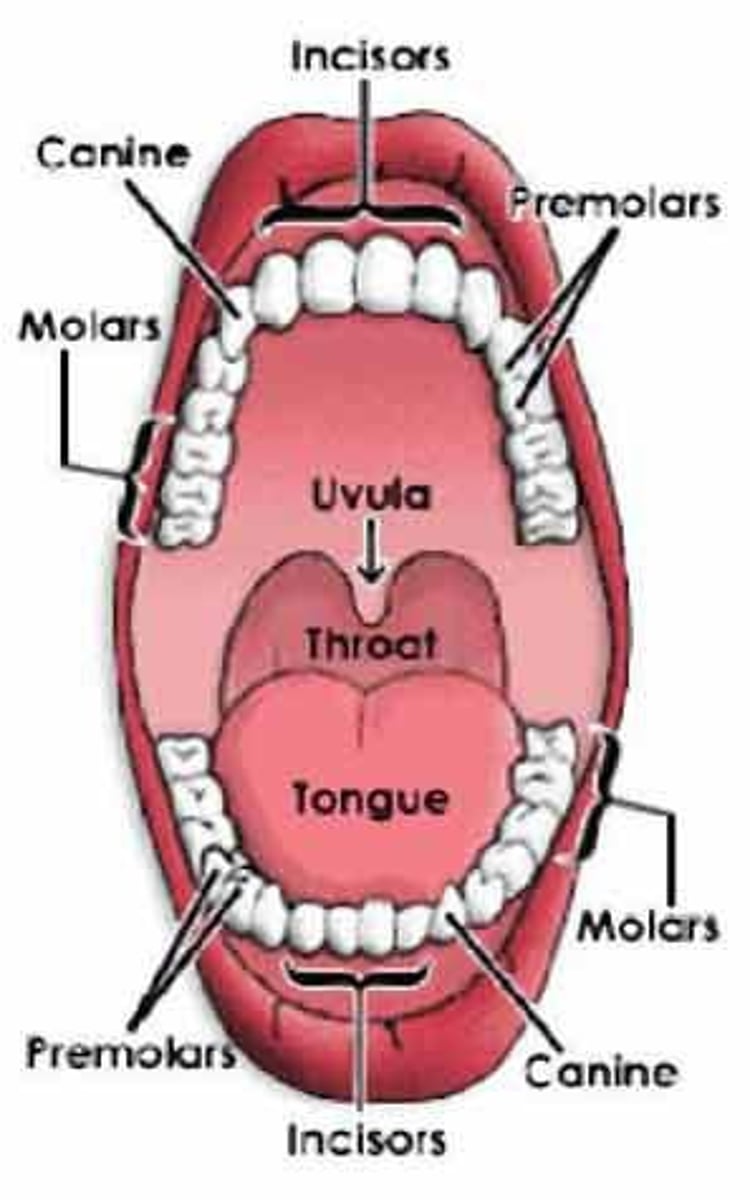
Oral cavity
Initiates food processing.
Salivation
May occur in anticipation due to learned associations between eating and stimuli.
Saliva
Contains mucin, buffers, antibacterial agents, and salivary amylase.
Mucin
A slippery glycoprotein that protects the mouth lining and lubricates food.
Salivary amylase
An enzyme that begins the digestion of starch in the oral cavity by hydrolyzing starch and glycogen into smaller polysaccharides and maltose.
Tongue
Tastes food, manipulates it during chewing, and helps shape it into a bolus.
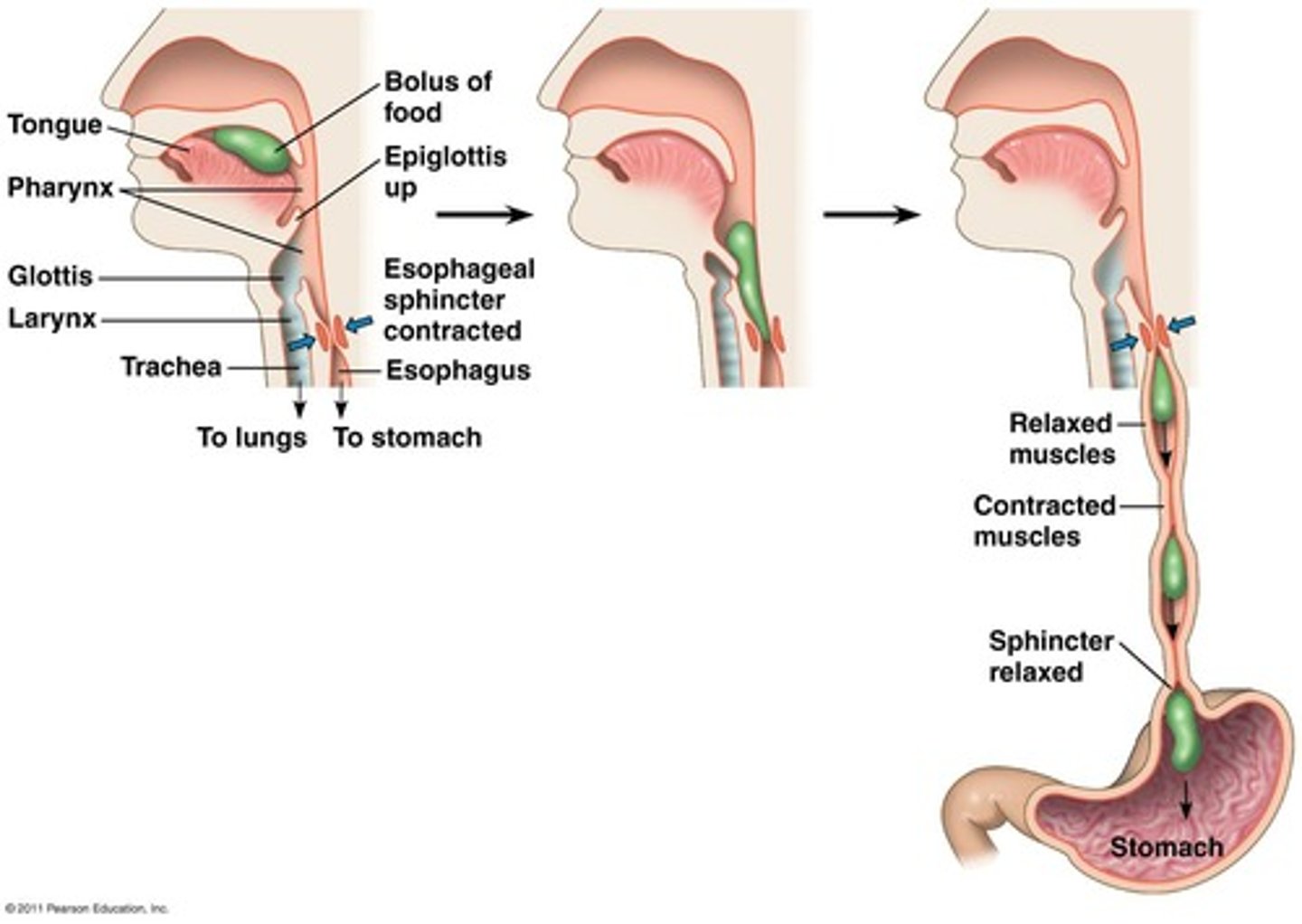
Bolus
A ball of food formed by the tongue for swallowing.
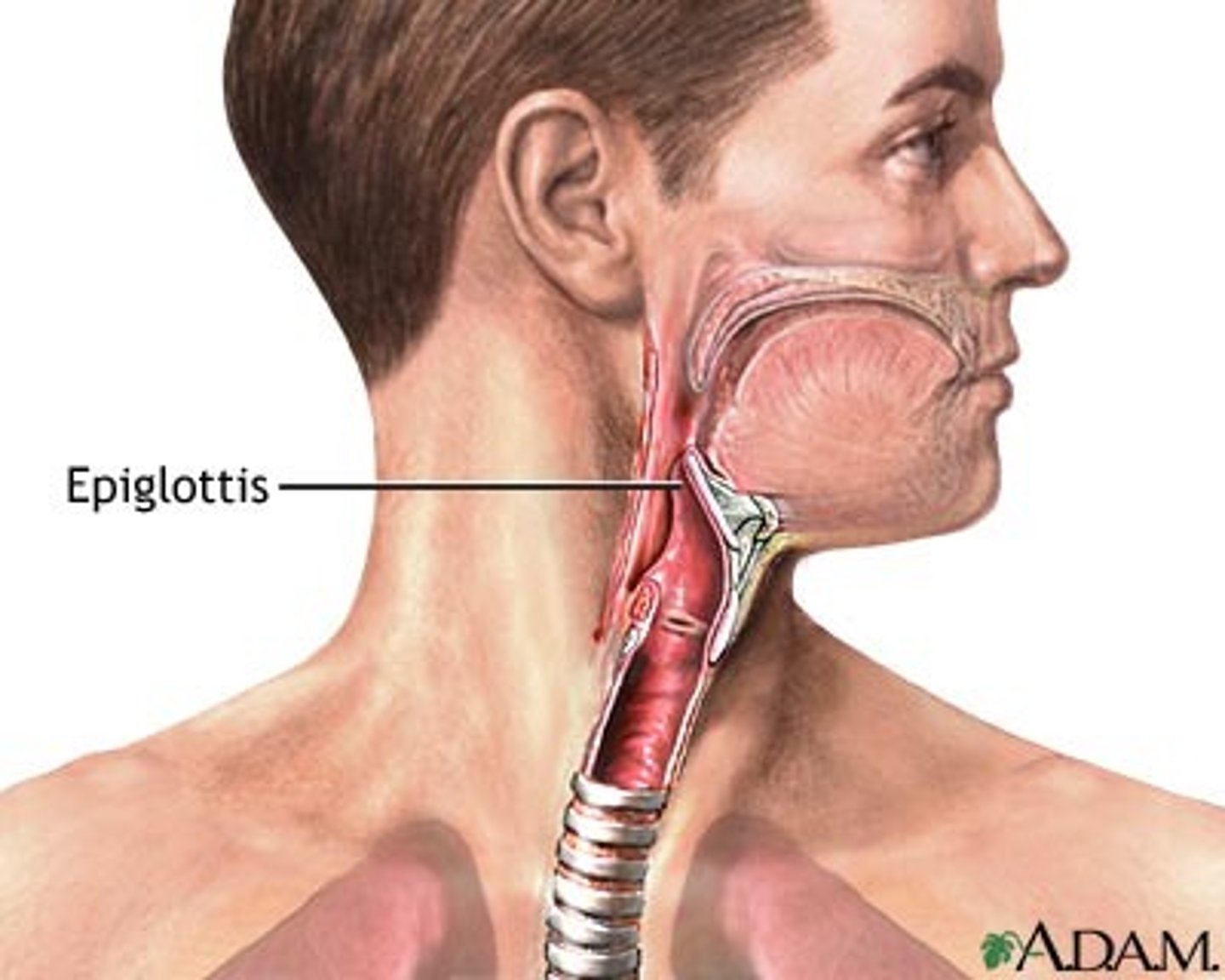
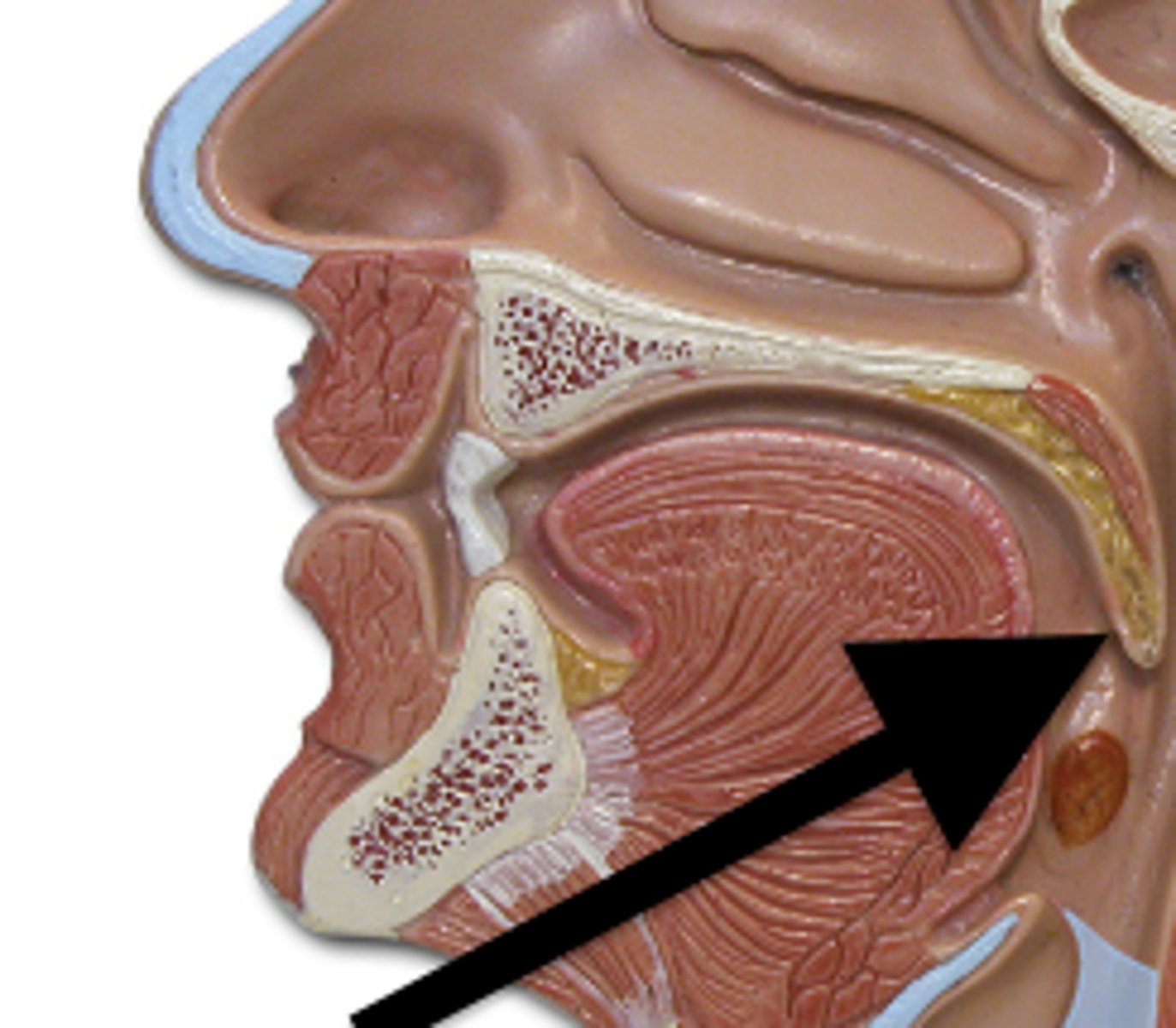
Pharynx
Also called the throat; a junction that opens to both the esophagus and the trachea.
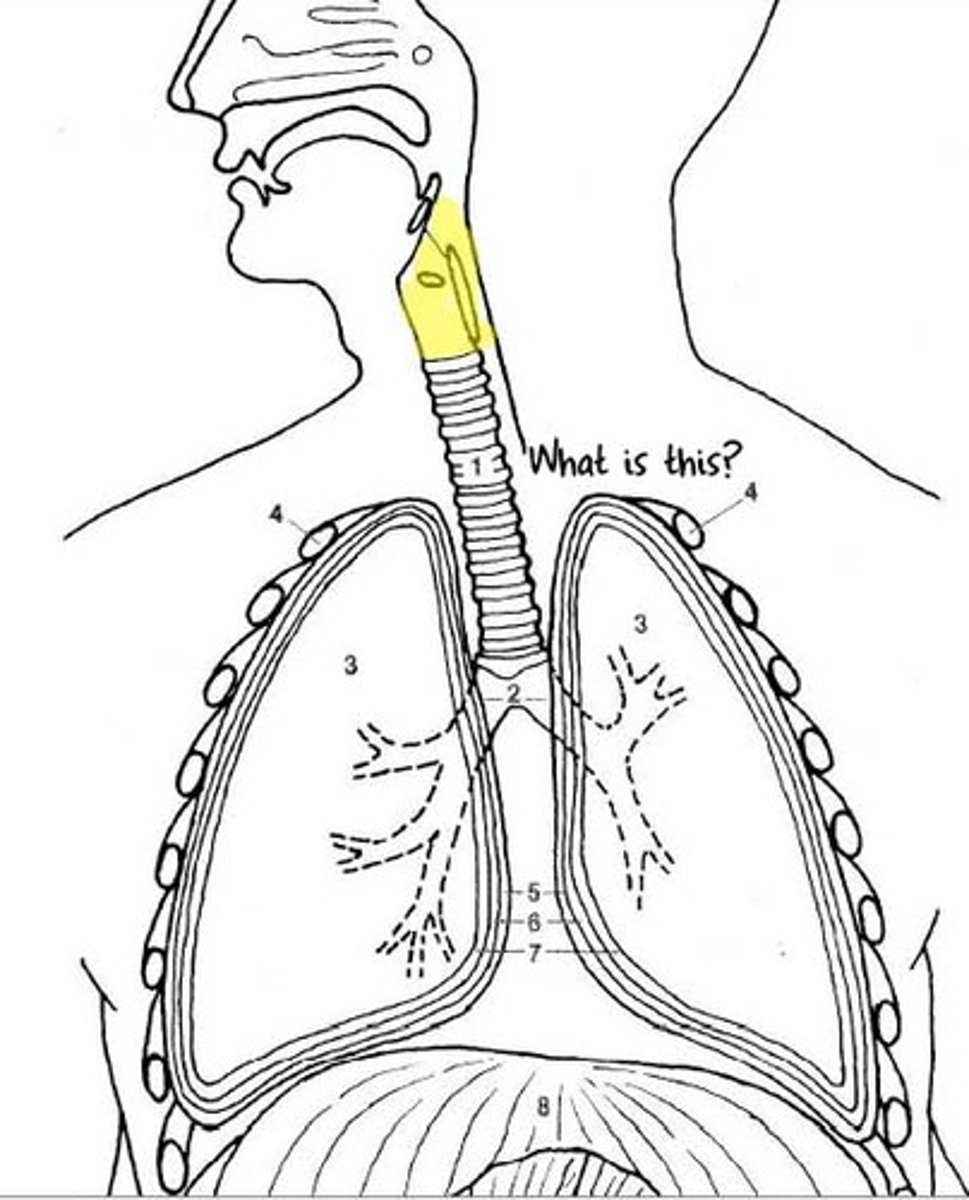
Epiglottis
A cartilaginous flap that blocks the trachea during swallowing.
Uvula
Secretes saliva, may play a role in speech, and may prevent food from entering the nasopharynx.
Esophageal sphincter
Muscle that is contracted when not swallowing, allowing airflow through the trachea.
Peristalsis
Waves of contraction that move the bolus to the stomach.
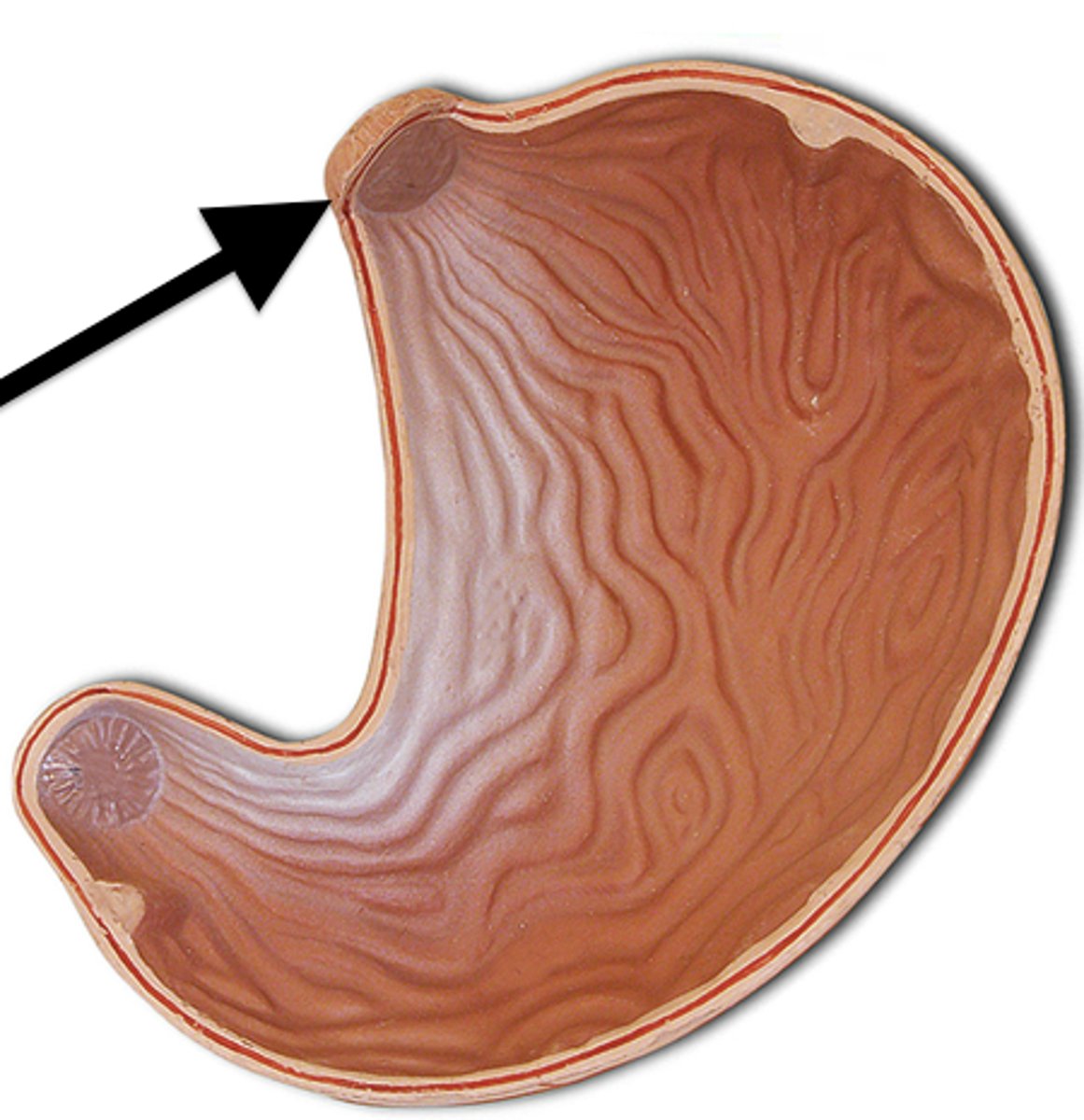
Stomach
Stores food and performs preliminary digestion with a capacity of about 2 L.
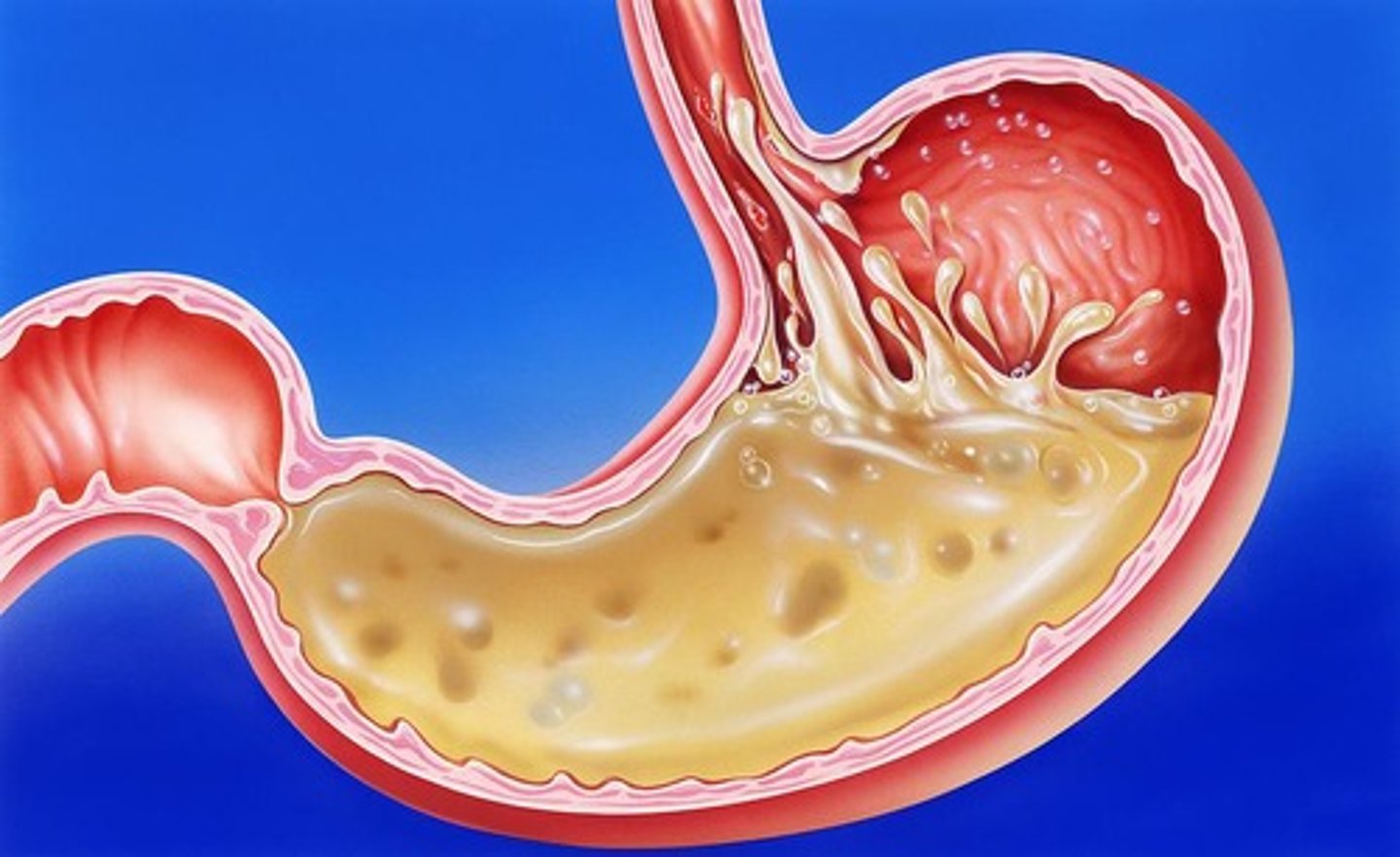
Gastric juice
Digestive fluid secreted by the stomach epithelium with a pH of about 2.
Includes enzymes, hydrochloric acid, and mucus.
Pepsin
An enzyme in gastric juice that begins the hydrolysis of proteins.
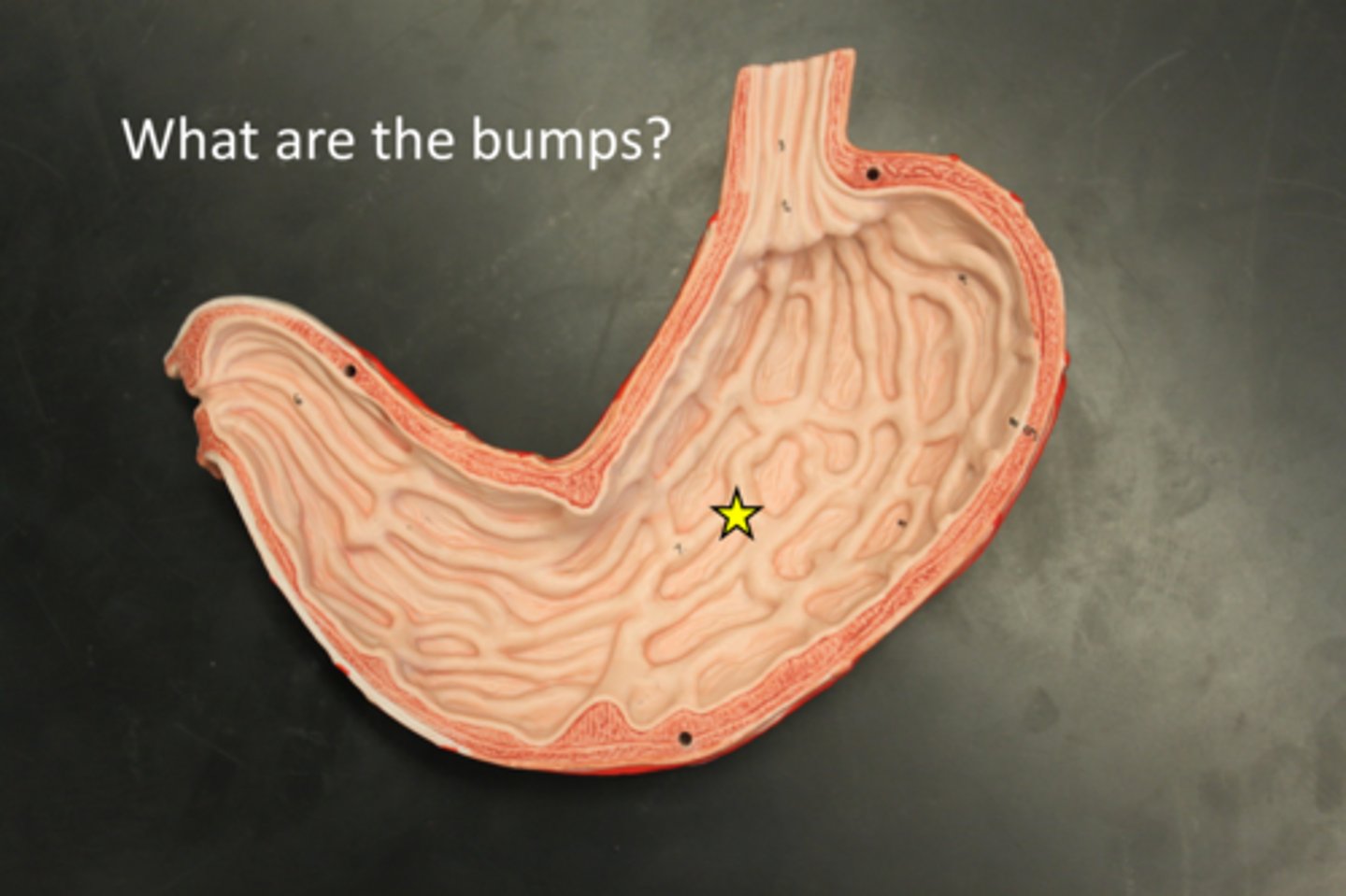
Rugae
Accordion-like folds in the stomach that allow it to stretch.
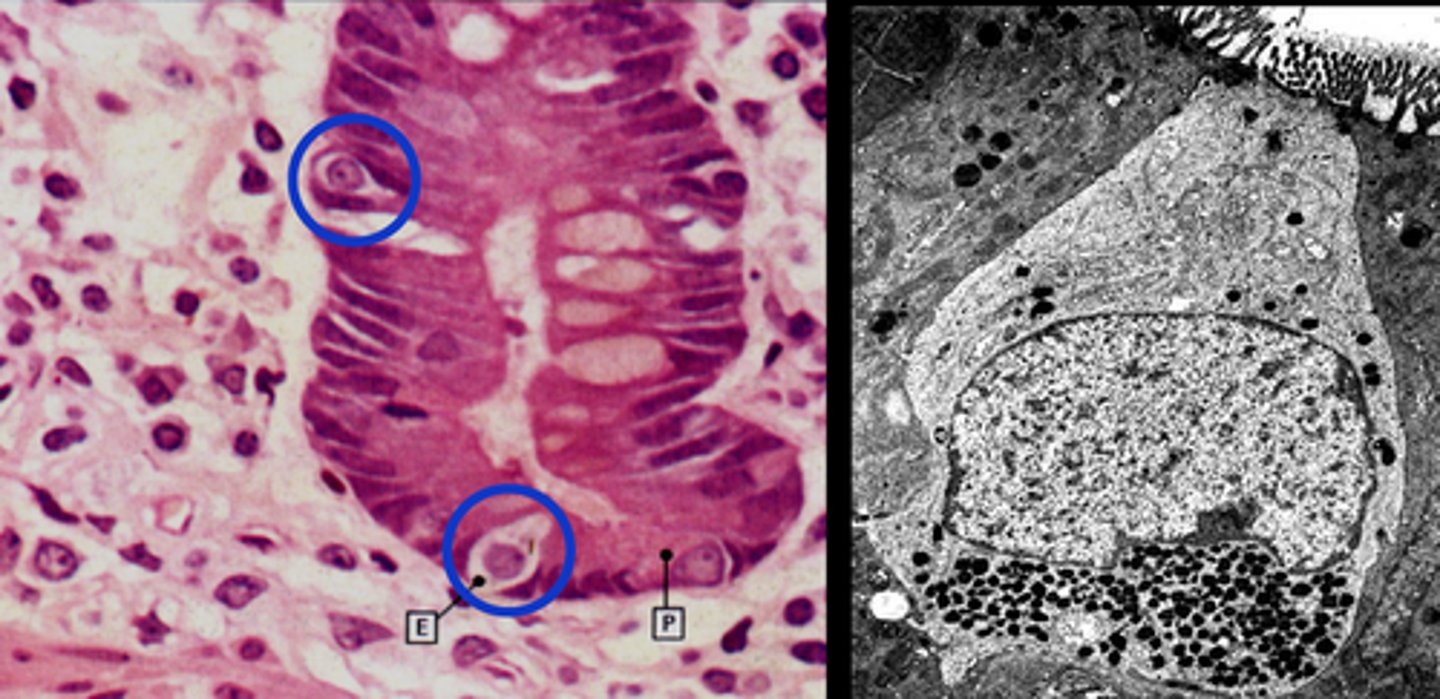
Chief cells
Cells that secrete pepsinogen, the inactive precursor of pepsin.
Parietal cells
Cells that secrete H+ and Cl- to form hydrochloric acid in gastric juice.
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Acid in gastric juice that activates pepsin and digests food.
pH of gastric juice
About 2, which is acidic enough to digest iron nails.
Extracellular matrix
Structure that is disrupted by acid in gastric juice, aiding digestion.
Pepsinogen
Inactive form of pepsin secreted by specialized chief cells in gastric pits.
HCl
Secreted by parietal cells, converts pepsinogen to active pepsin in the stomach lumen.
Positive feedback
Activated pepsin can activate more pepsinogen molecules.
Enteroendocrine cells
Cells in the stomach that secrete chemical messengers.
Serotonin
Chemical messenger that causes contraction of stomach muscle.
Histamine
Chemical messenger that activates parietal cells to release HCl.
Somatostatin
Chemical messenger with various inhibitory functions.
Gastrin
Chemical messenger with stimulating functions, including HCl secretion.
Mucus
Coating secreted by epithelial cells that protects the stomach lining.
Stomach epithelium
Continually eroded and completely replaced by mitosis every three days.
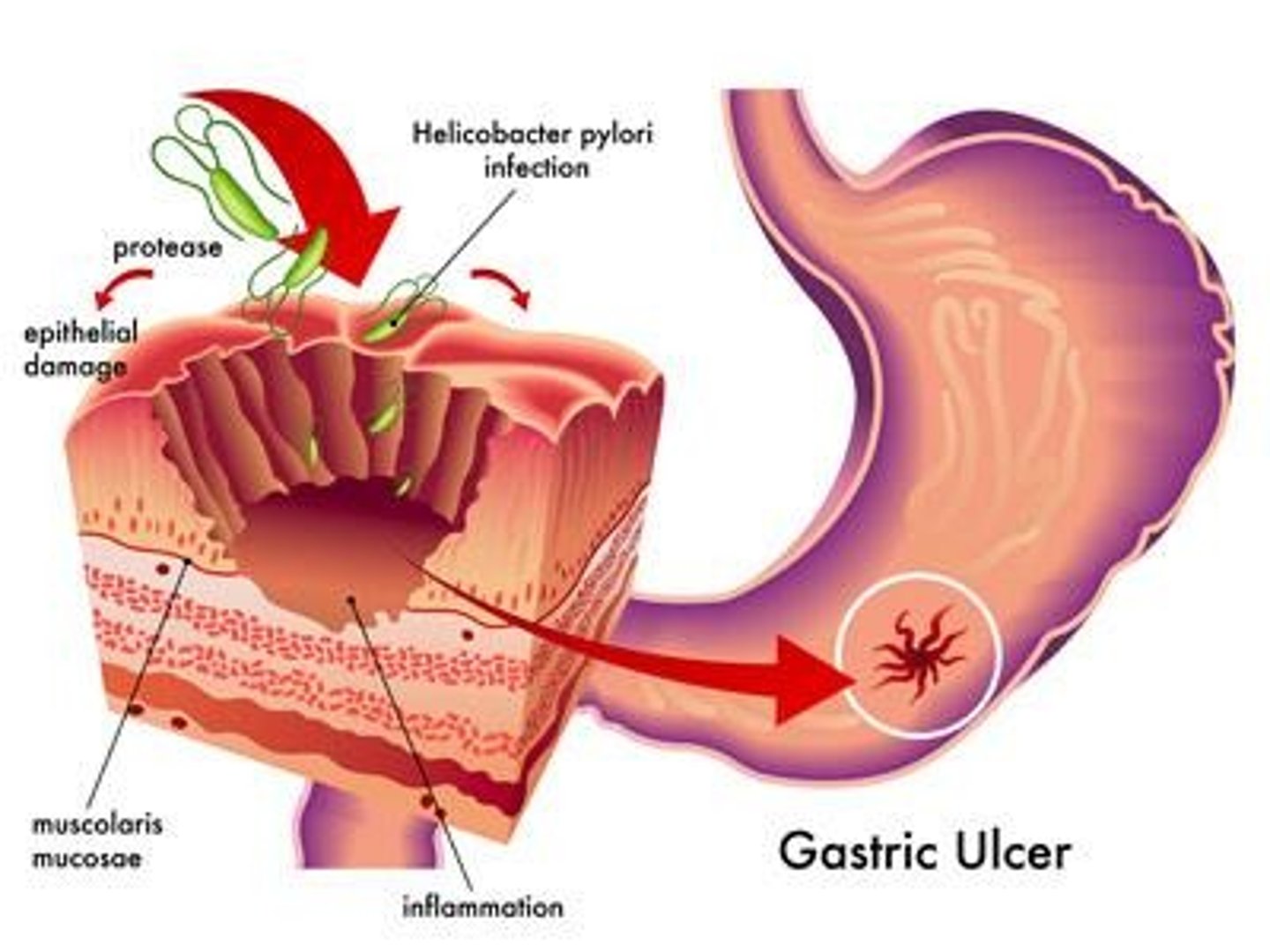
Gastric ulcers
Lesions in the stomach lining caused by the acid-tolerant bacterium Heliobacter pylori.
Acid chyme
Nutrient-rich broth formed from recently swallowed meals mixed in the stomach.
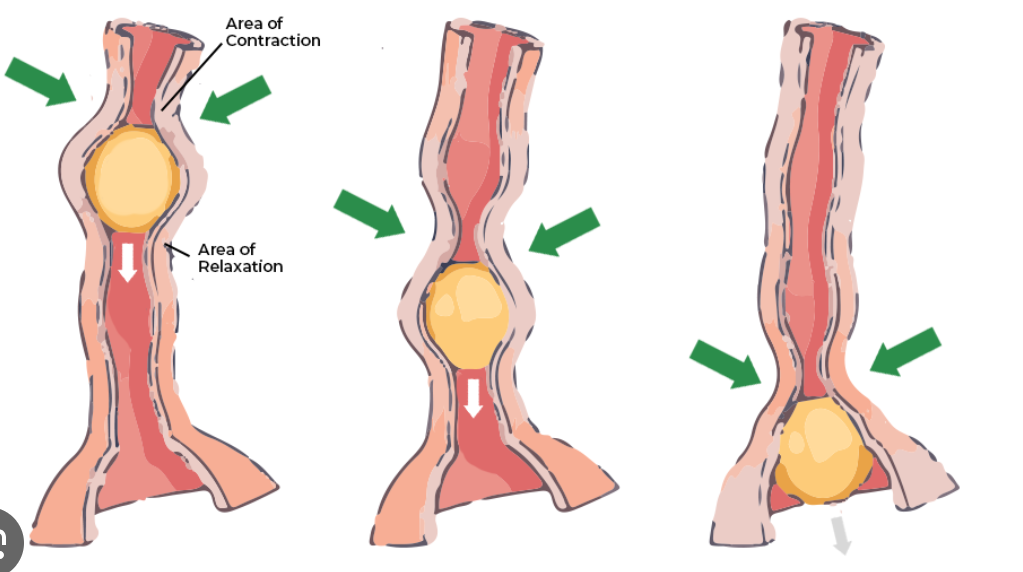
Cardiac orifice
Opening from the esophagus to the stomach that dilates when a bolus arrives.
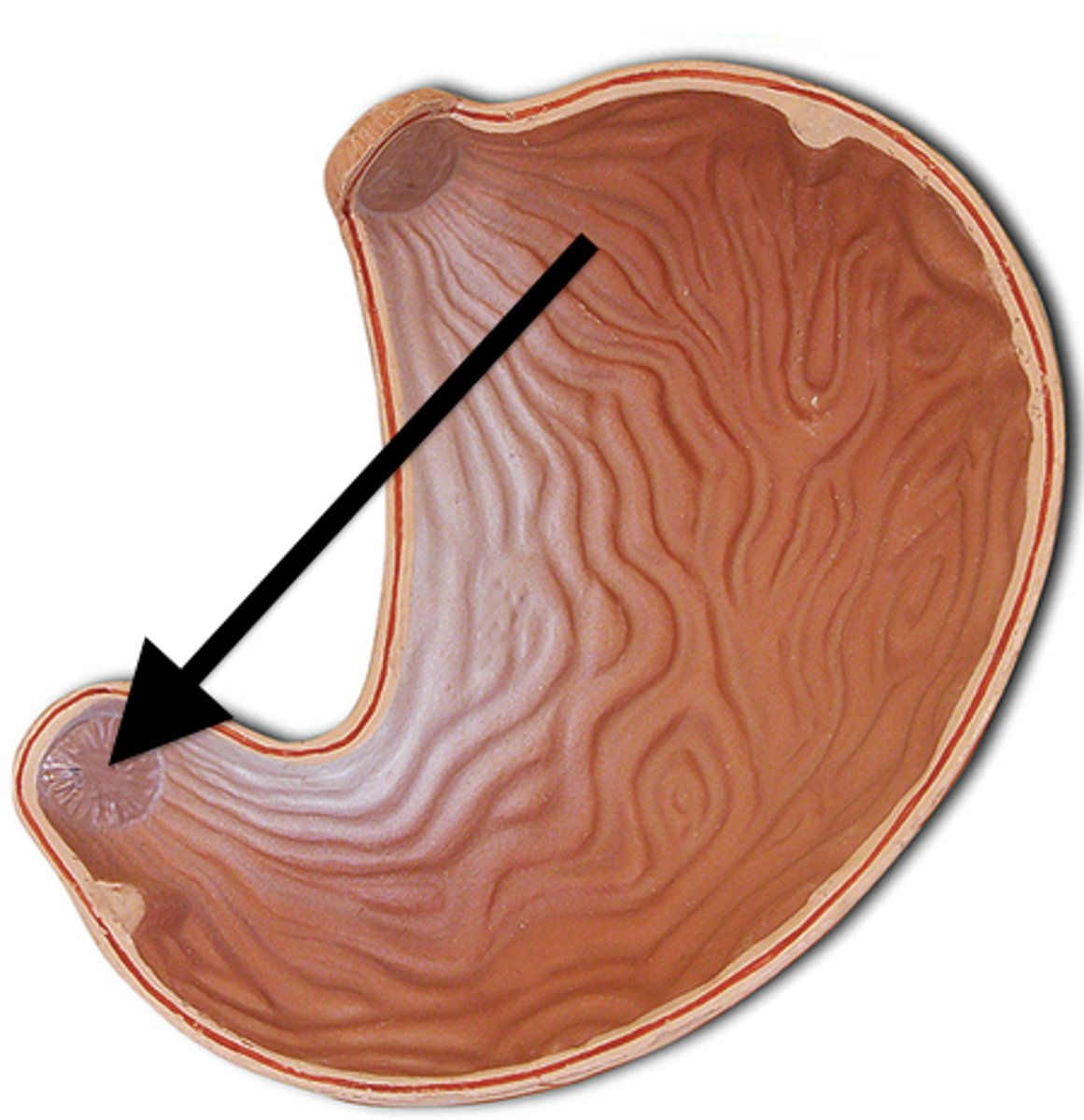
Pyloric sphincter
Regulates the passage of chyme into the small intestine.
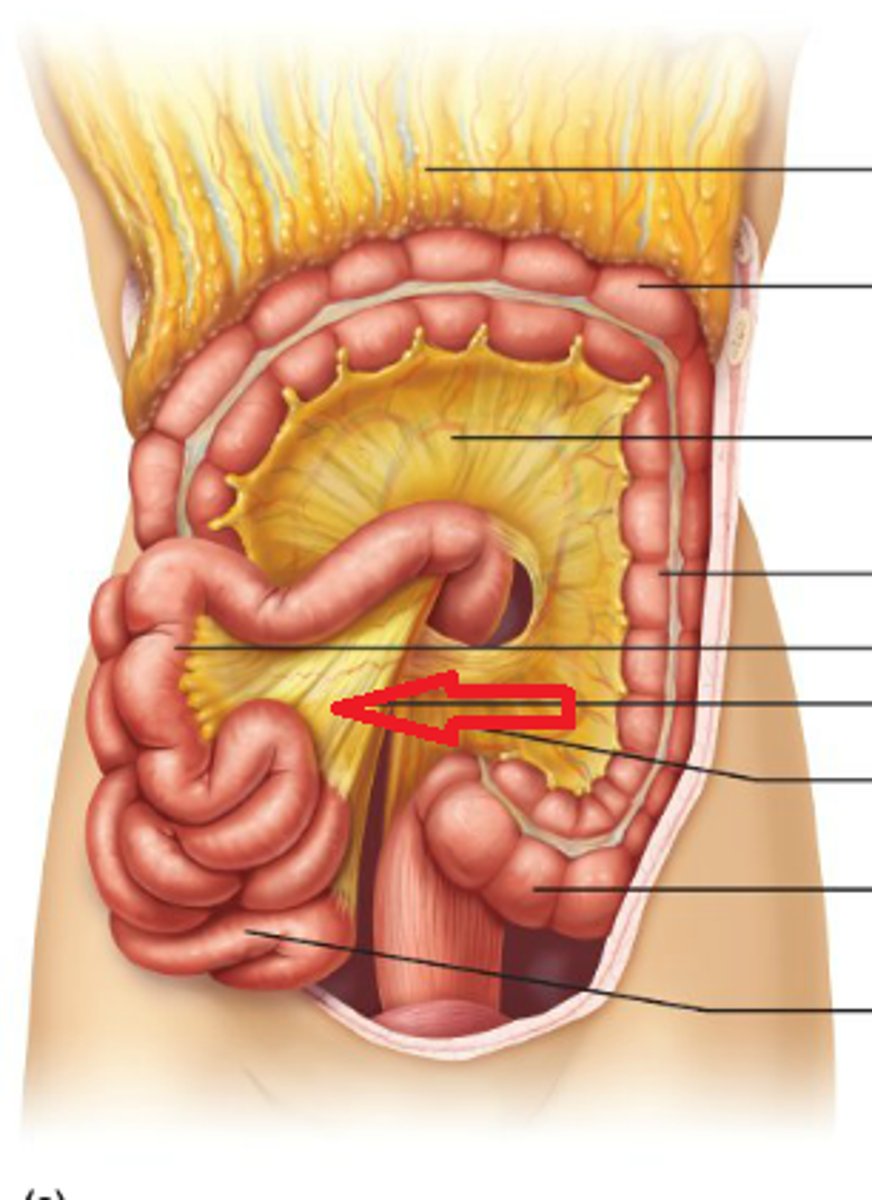
Mesentery
Fold of tissue that attaches organs to the body wall, supplying them with blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
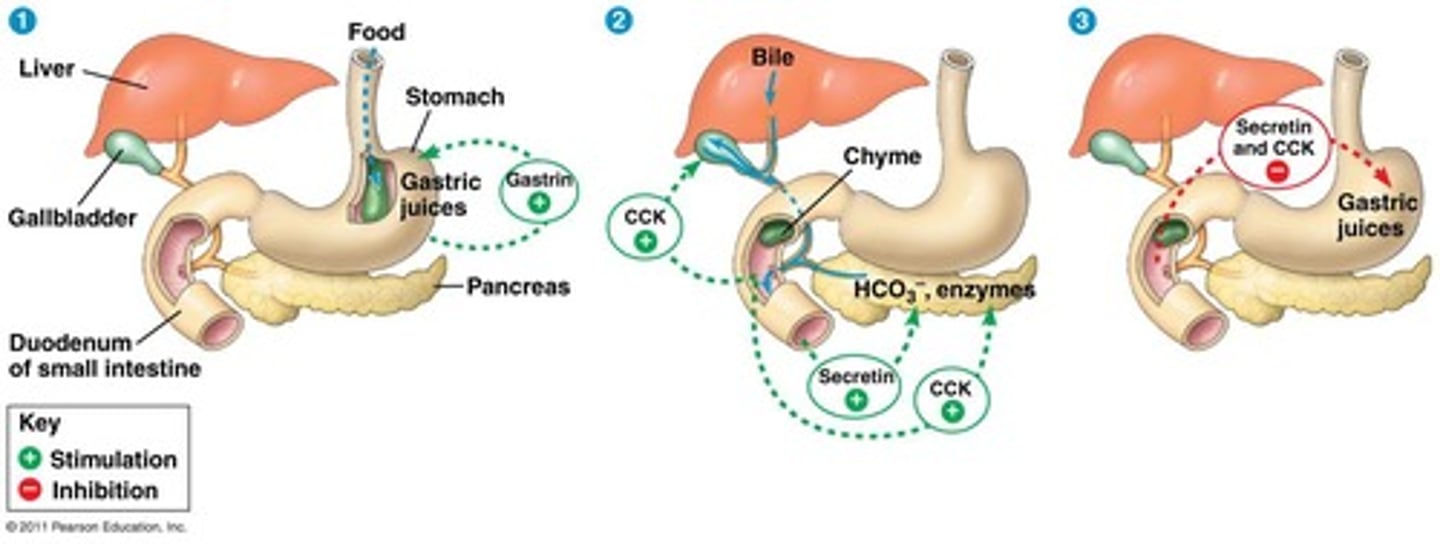
Pancreas
Produces several hydrolytic enzymes and an alkaline solution rich in bicarbonate.
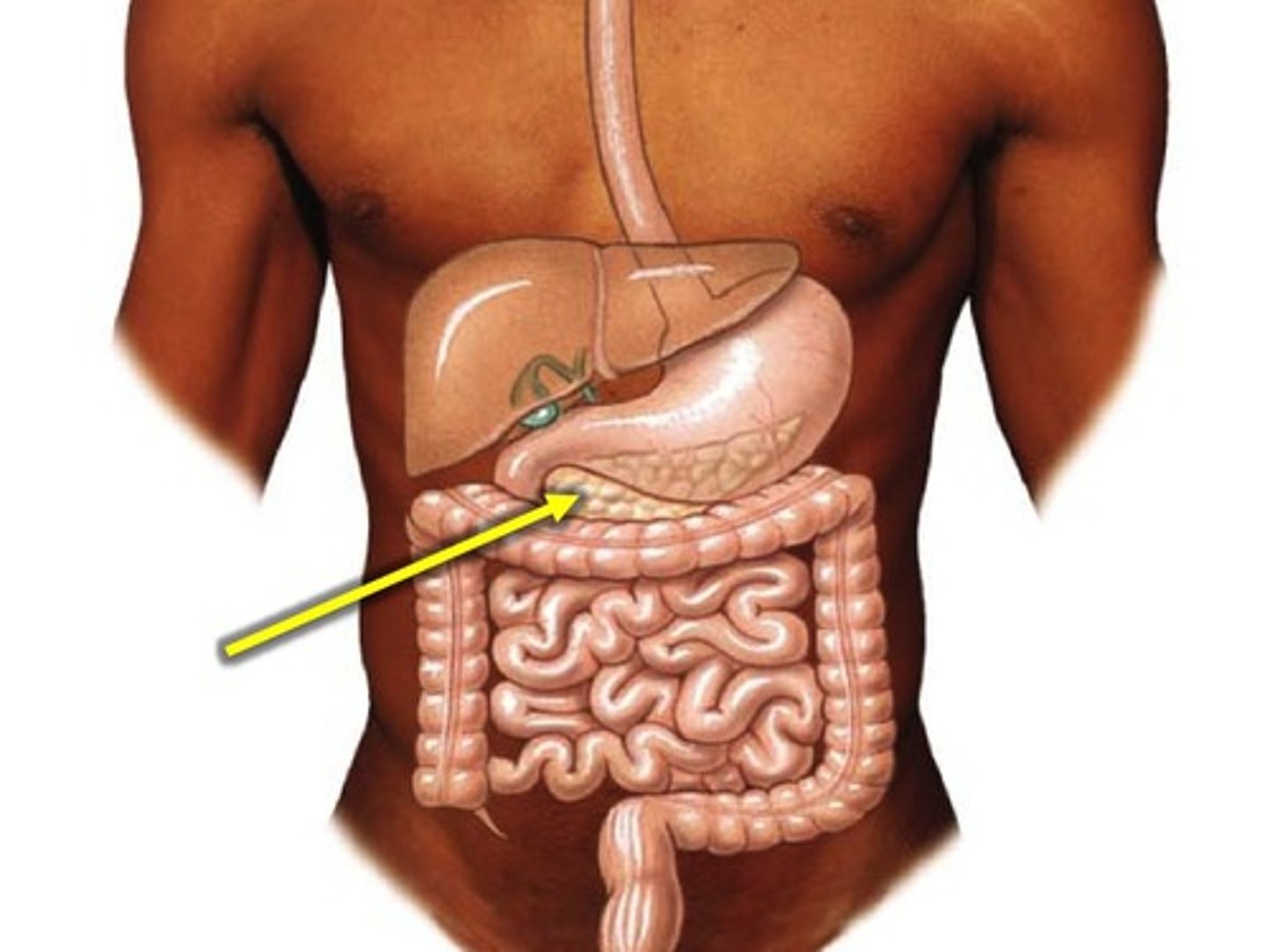
Bile
Produced by the liver, stored in the gallbladder, aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
Emulsification
Process by which bile acids break fats into small drops to increase surface area for lipase action.
Bile pigments
By-products of red blood cell destruction in the liver, eliminated from the body with feces.
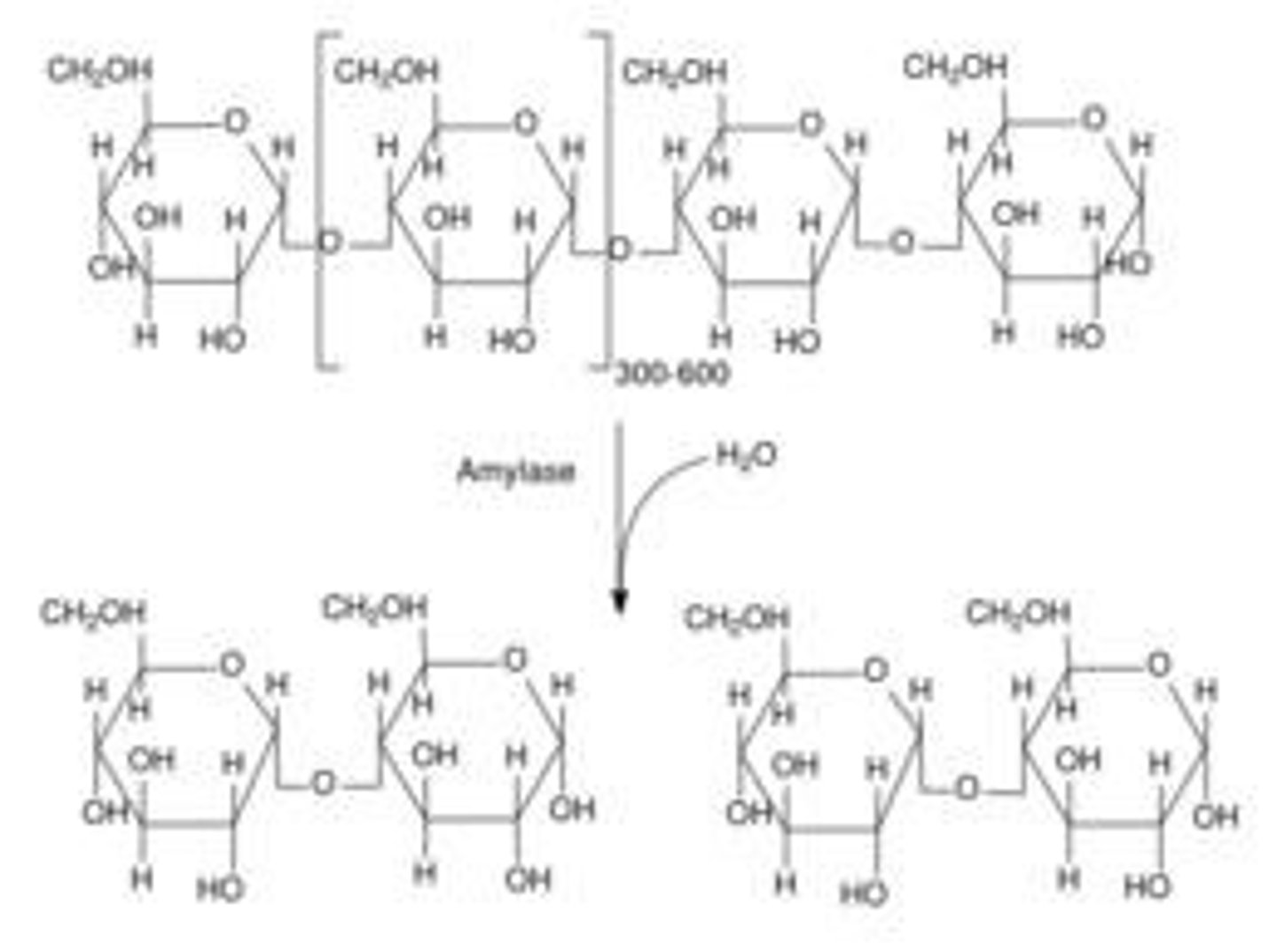
Pancreatic amylases
Hydrolyze starch, glycogen, and smaller polysaccharides into disaccharides in the small intestine.
Disaccharidases
Enzymes that hydrolyze disaccharides into monomers, built into the membranes of the intestinal epithelium.
Maltase
Enzyme that splits maltose into glucose monomers.
Sucrase
Enzyme that splits sucrose into glucose and fructose monomers.
Digestion of proteins
Completed in the small intestine, continuing the process begun by pepsin.
Enzymes in the duodenum
Dismantle polypeptides into their amino acids or into small peptides.
Trypsin and chymotrypsin
Attack peptide bonds adjacent to specific amino acids, breaking larger polypeptides into shorter chains.
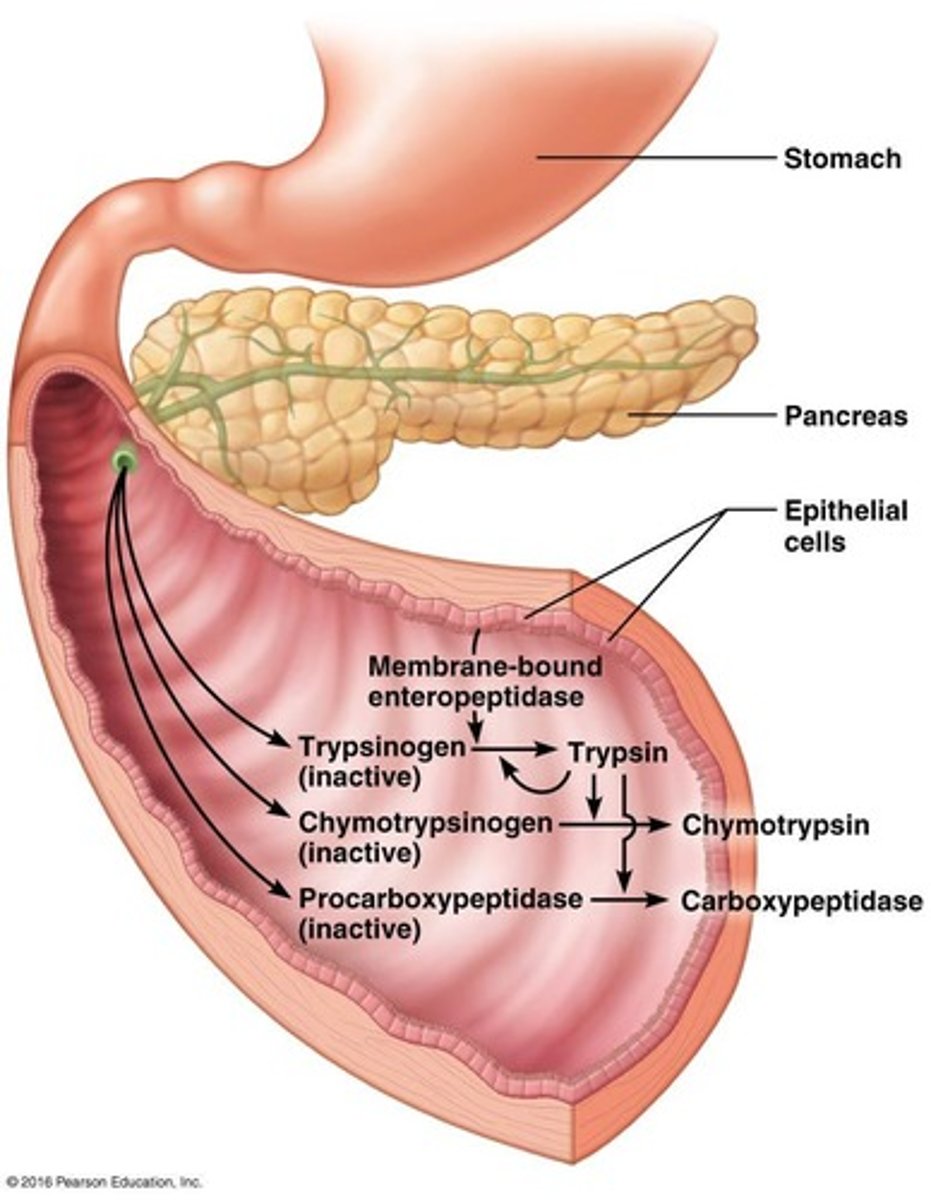
Dipeptidase
Attached to the intestinal lining, splits smaller chains.
Carboxypeptidases and aminopeptidase
Split off one amino acid from the carboxyl or amino end of a peptide, respectively.
Inactive form enzymes
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, and Carboxypeptidase are secreted in inactive form by the pancreas.
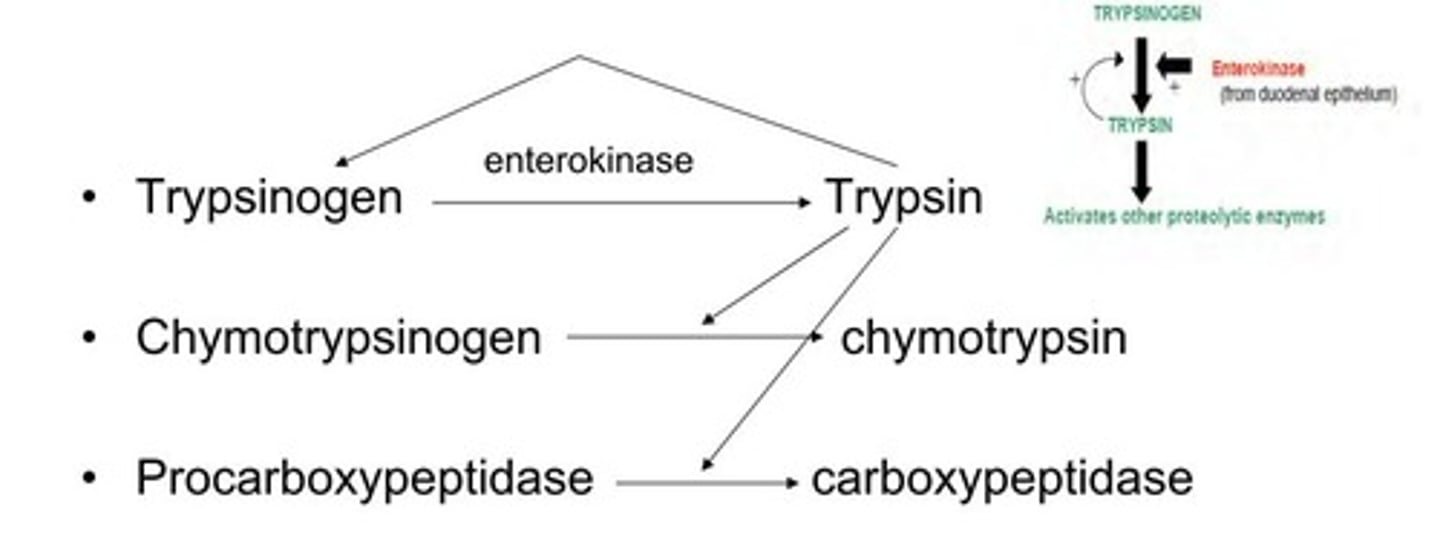
Enteropeptidase
An intestinal enzyme that converts inactive trypsinogen into active trypsin.
Active trypsin
Activates chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase and further converts trypsinogen to trypsin.
Aminopeptidase
Secreted by the intestinal epithelium.
Digestion of nucleic acids
A team of enzymes called nucleases hydrolyzes DNA and RNA into their component nucleotides.
Fat digestion
Nearly all the fat in a meal reaches the small intestine undigested.
Bile salts
Secreted by the gallbladder into the duodenum, coat tiny fat droplets and keep them from coalescing.
Lipase
An enzyme that hydrolyzes fat molecules into glycerol, fatty acids, and monoglycerides.
Chylomicrons
Water-soluble globules formed from triglycerides coated with phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins.
Lacteal
A lymphatic vessel at the core of each villus that transports chylomicrons.
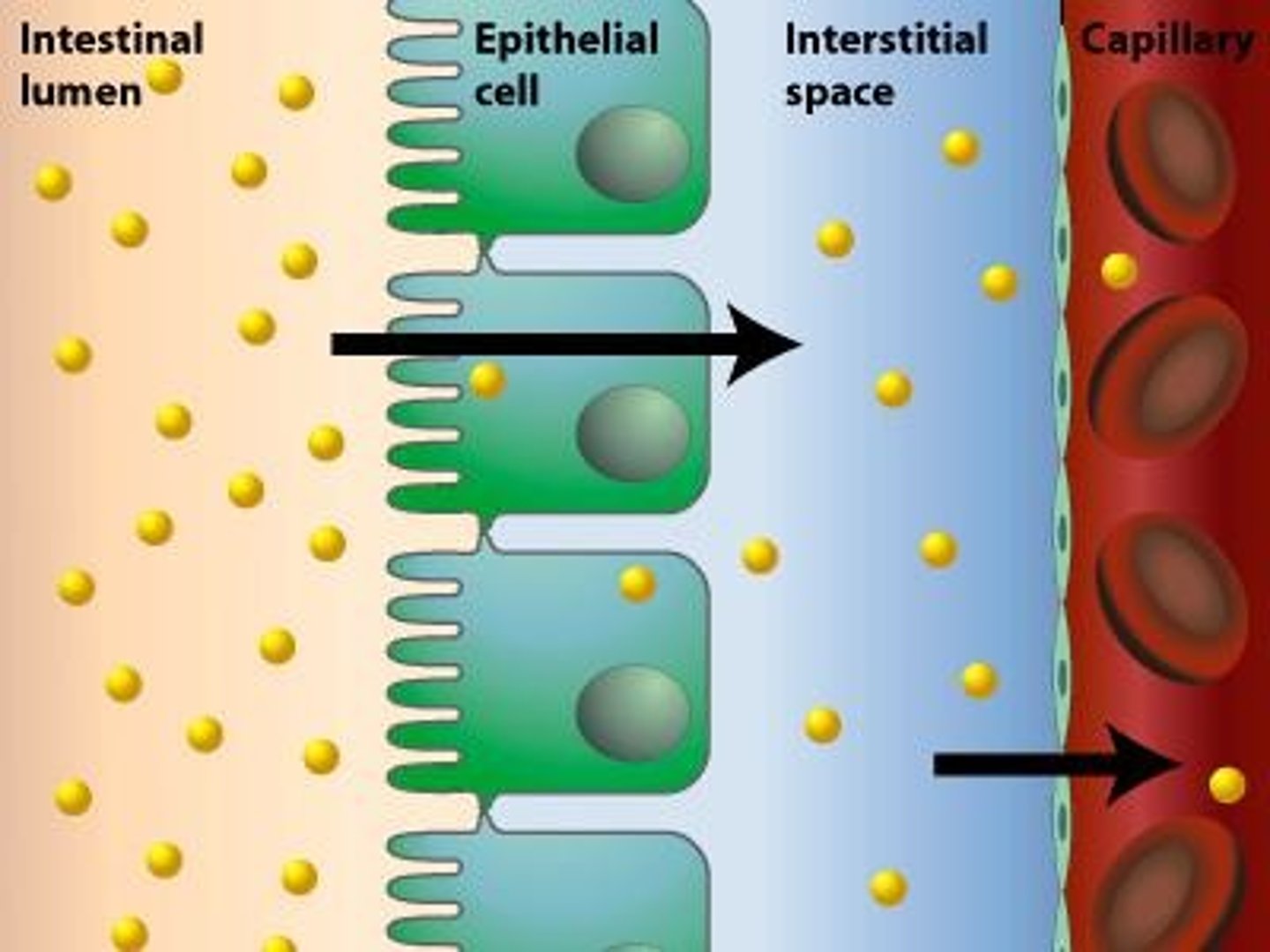
Nutrient absorption
Occurs mainly in the jejunum and ileum, where nutrients pass the lining of the digestive tract.
Surface area of small intestine
300 m2, roughly the size of a tennis court, greatly increases the rate of nutrient absorption.
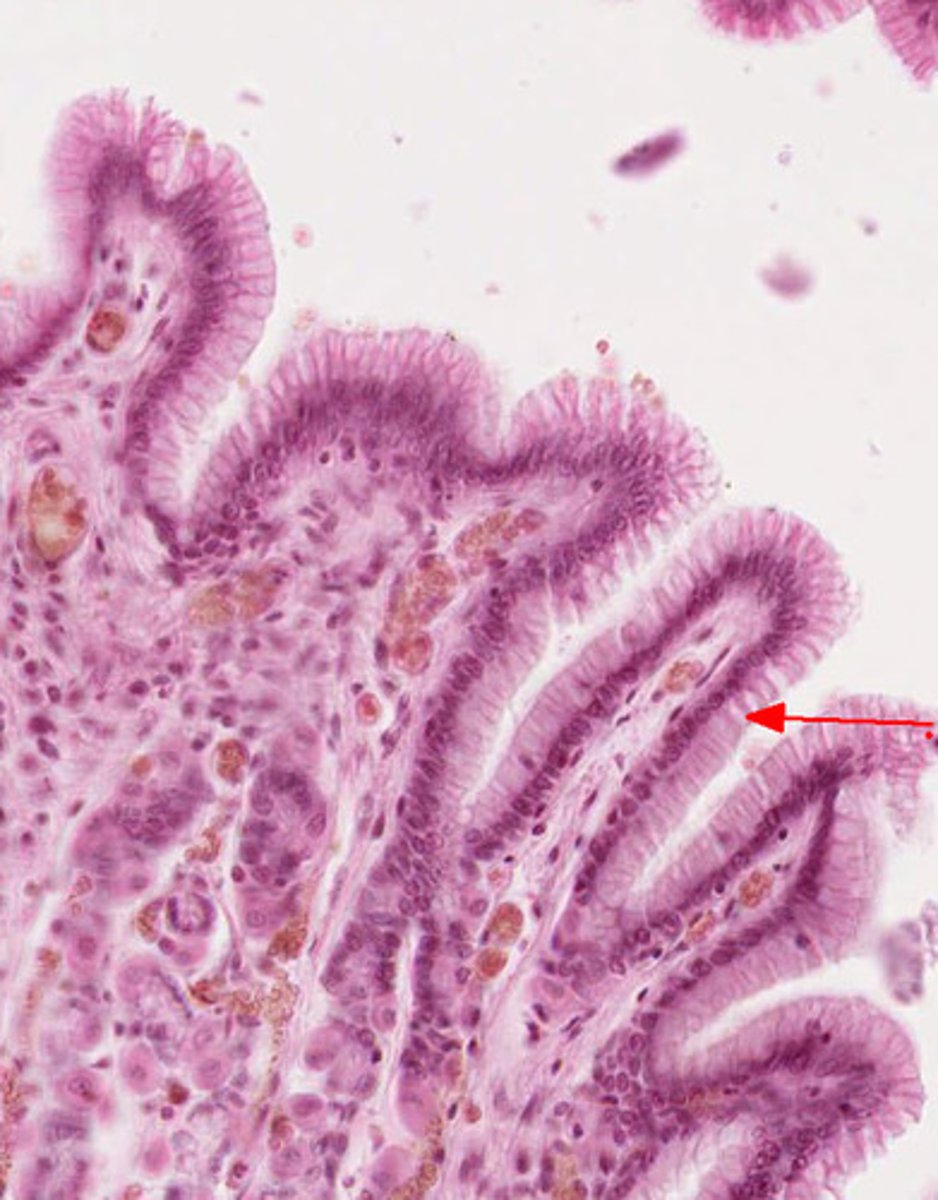
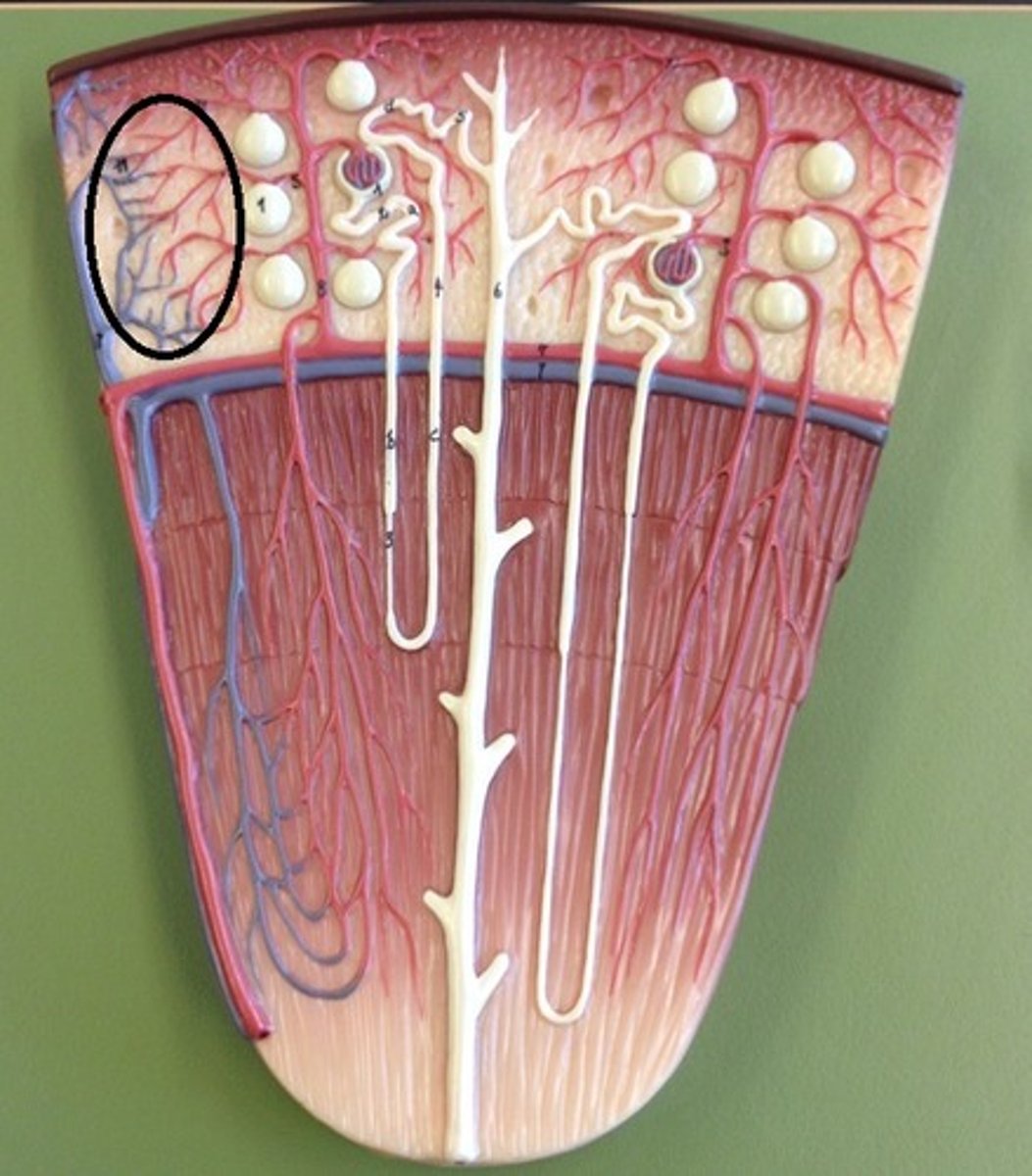
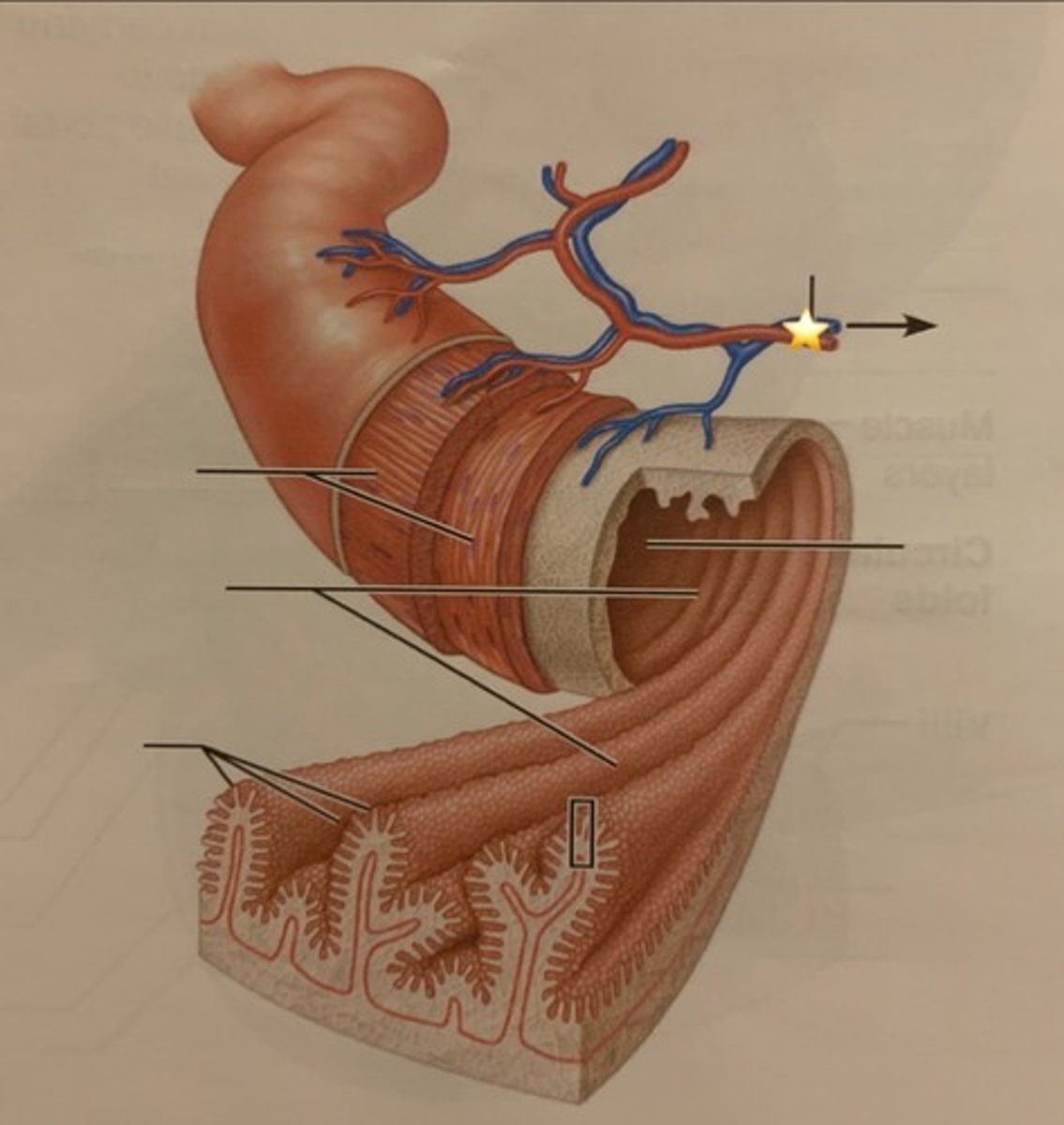
Villi
Fingerlike projections in the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption.
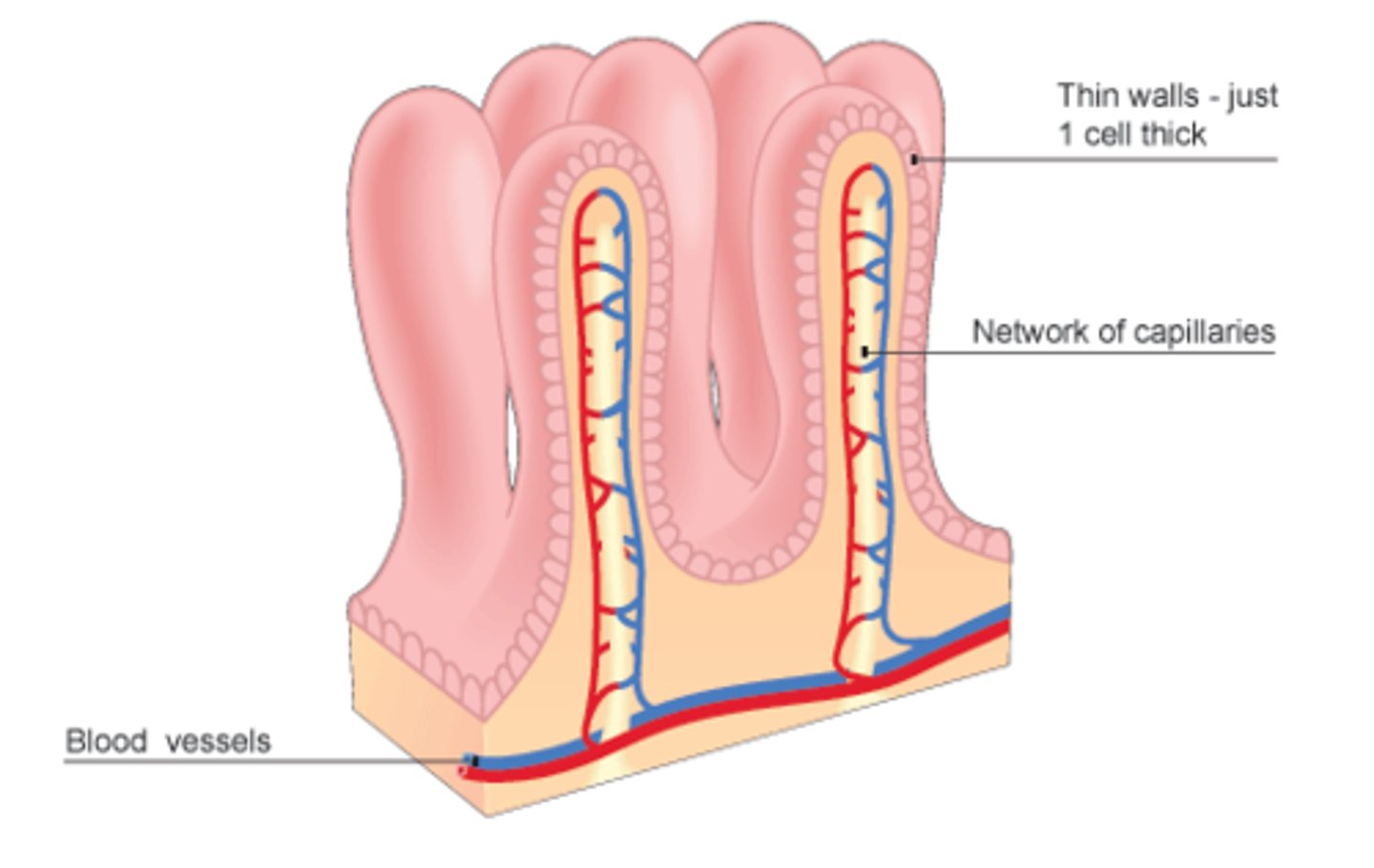
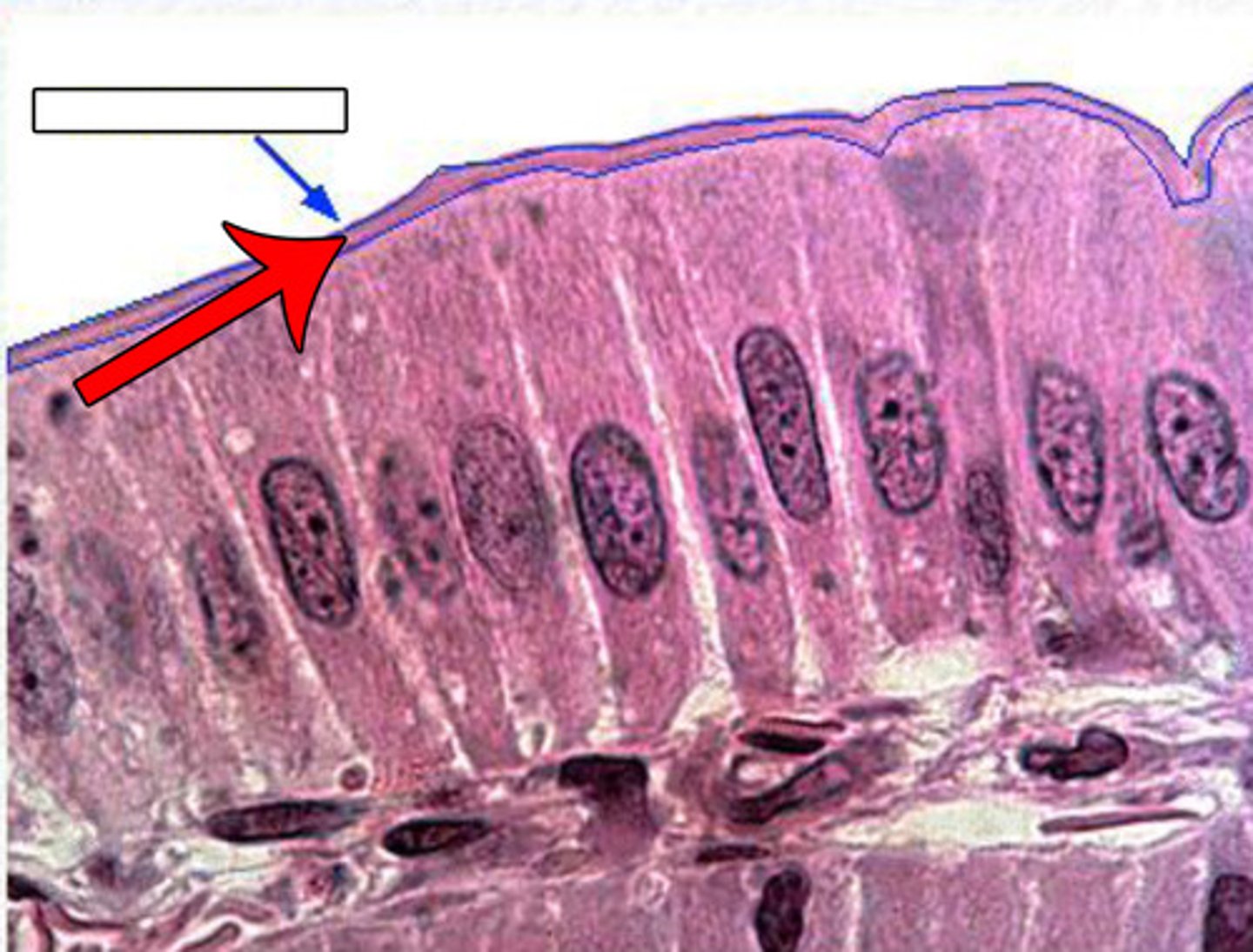
Microvilli
Many microscopic projections on each epithelial cell of a villus that are exposed to the intestinal lumen.
Capillaries
Microscopic blood vessels that penetrate the core of each villus.
Transport of nutrients
Nutrients are absorbed across the intestinal epithelium and then across the unicellular epithelium of capillaries or lacteals.
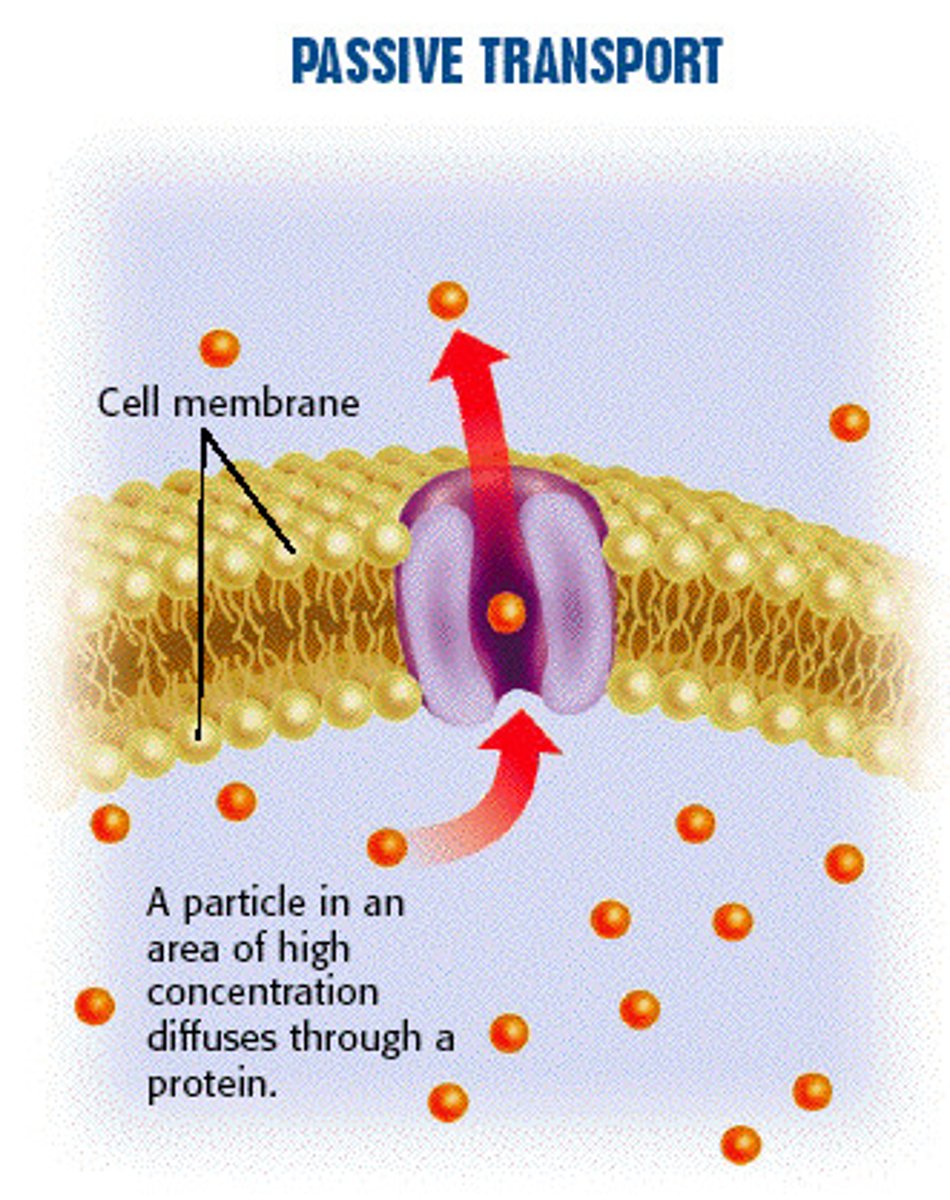
Passive transport
Nutrients move down their concentration gradients from the lumen of the intestine into the epithelial cells.
Active transport
Nutrients are pumped against concentration gradients by epithelial membranes, allowing higher absorption rates.
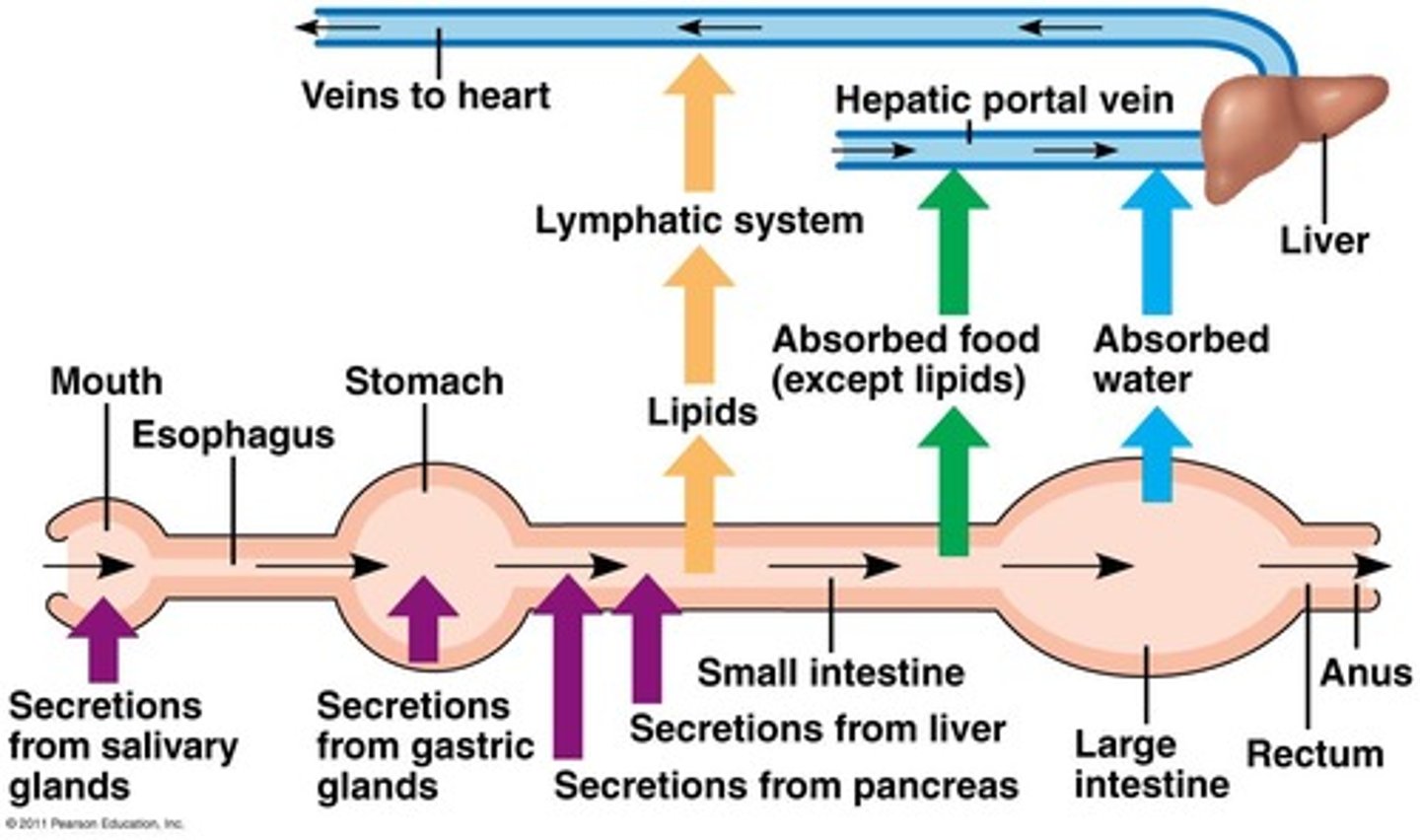
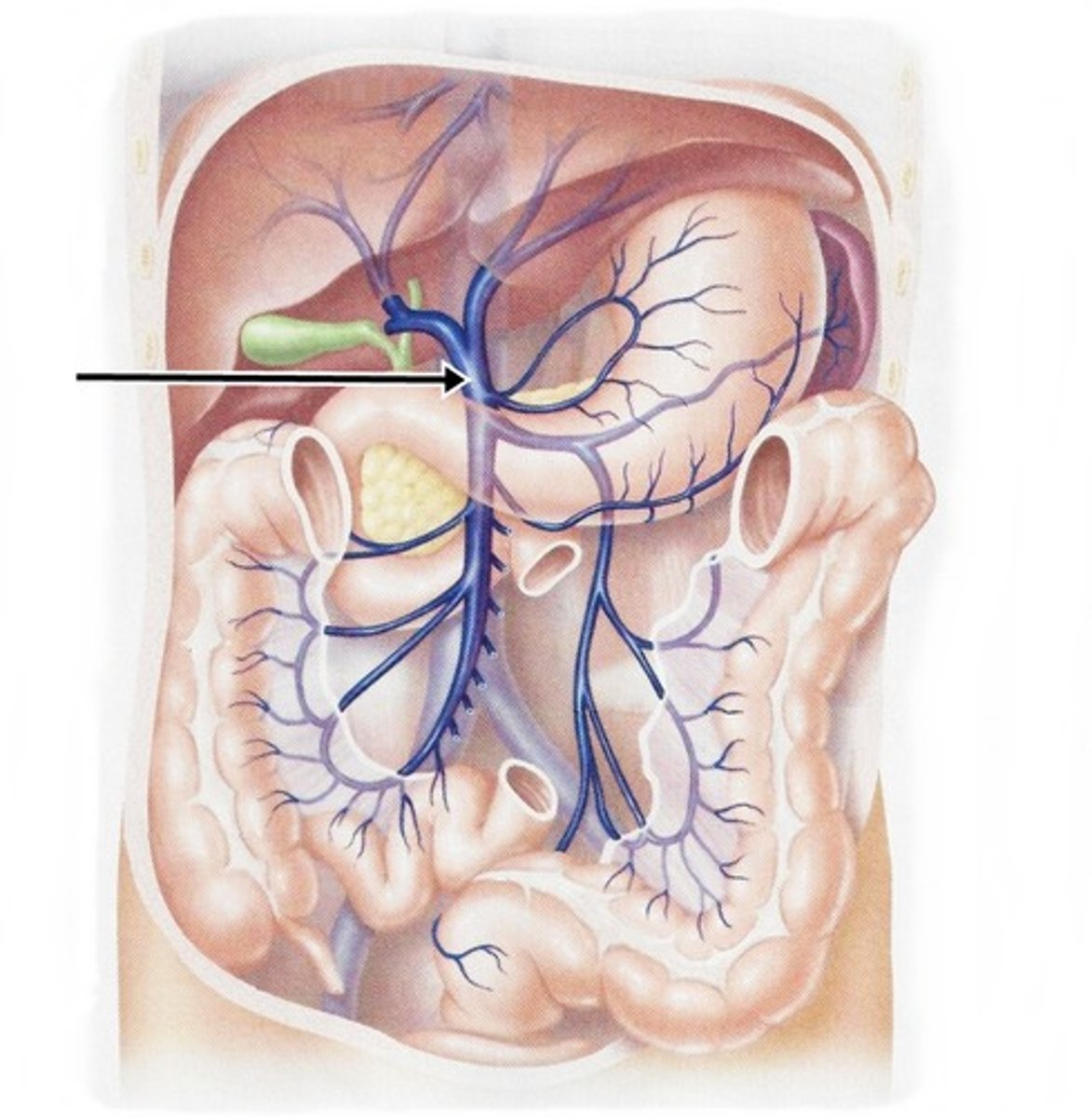
Hepatic portal vessel
The vessel that drains nutrients away from the villi and leads directly to the liver.
Hepatic portal vein
Carries nutrient-rich blood from the capillaries of the villi to the liver, then to the heart.
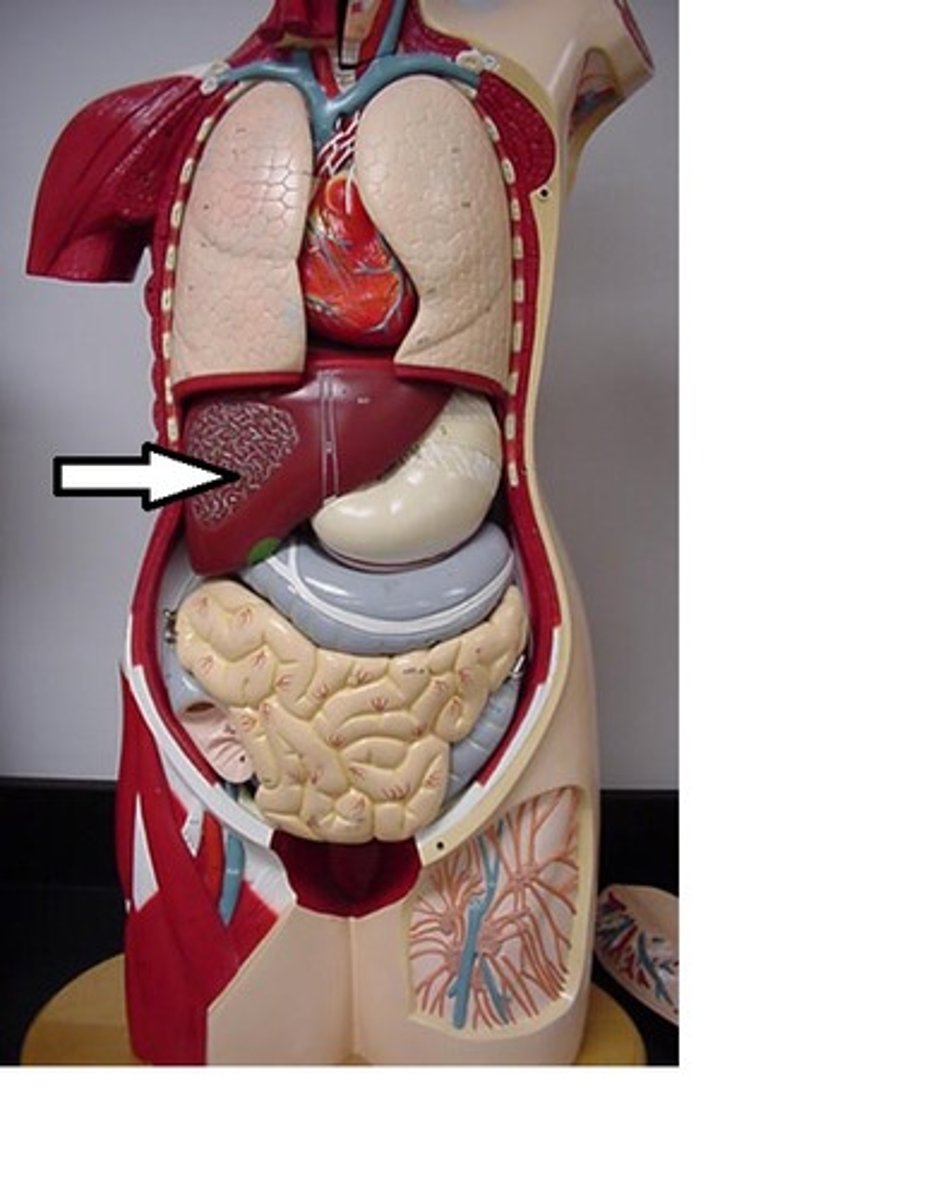
Liver
Regulates nutrient distribution, interconverts many organic molecules, and detoxifies many organic molecules.
Glucose concentration in blood
Blood exiting the liver usually has a glucose concentration very close to 0.1%, regardless of carbohydrate content of the meal.
Insulin and glucagon
Hormones that regulate glucose levels in the blood.
Absorption efficiency in developed countries
Typical diets lead to 80 to 90 percent absorption of the organic material in their food.