Pedigree crosses and Pedigrees
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Types of Mendelian Inheritance
autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, and X-linked recessive.
Autosomal dominant
Only need one copy of the dominant gene for the characteristic to be present.
AA or Aa
Autosomal recessive
Need both copies of the specific gene for the characteristic to be present.
aa
X linked dominant
The dominant gene is located on the X chromosome. Only need one copy of the dominant gene for the characteristic to be present.
XA XA
XA Xa
XA Y
X linked recessive
The recessive gene is located on the X chromosome. Both copies of the gene are required in females, but only one in males for the characteristic to be present
Xa Xa
Xa Y
Autosomal meaning
meaning that is carried on chromosome pairs 1 to 22
Sex-linked meaning
meaning that is carried on the X or Y chromosome. Most cases will involve the X chromosome since it is a lot bigger and able to carry more genes, therefore X linked.
Genetic crosses meaning
A Genetic Cross is the deliberate breeding of two different individuals that results in offspring that carry part of the genetic material of each parent. Sometimes also referred to as 'crossbreeding'.
genetic crosses;
Monohybrid crosses, Dihybrid crosses
Monohybrid cross
a cross between individuals differing in one trait
Dihybrid cross
a cross between individuals different in two traits
Punnet square
Named after Reginald C. Punnett who created this approach.
The Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is used to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype.
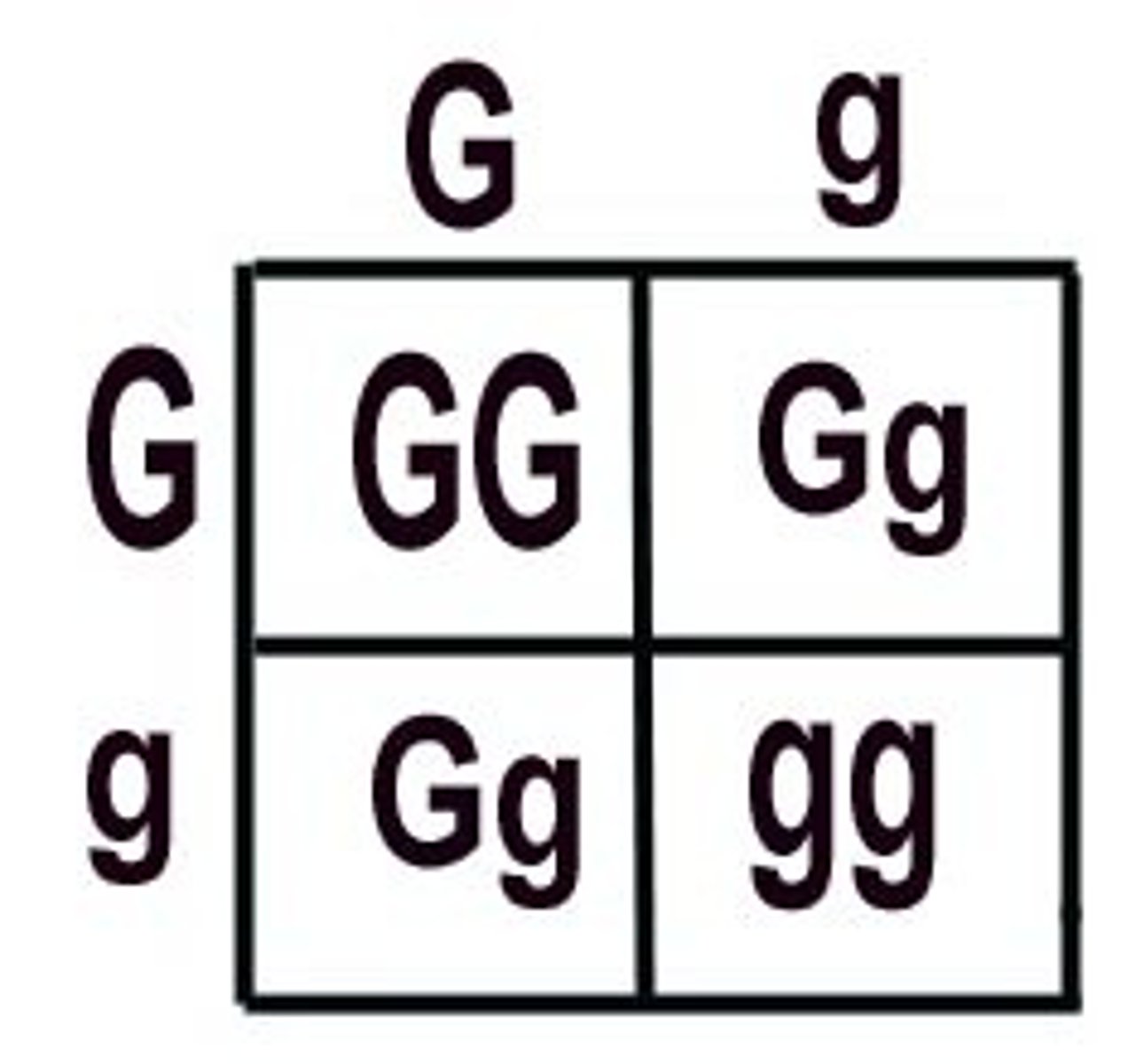
test cross
A test cross is used to determine if a group exhibiting a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous for that trait.
Test crosses determine the genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype.
A test cross involves the breeding of an individual with a phenotypically recessive individual.
Purebred = homozygous
Monohybrid cross meaning
A monohybrid cross is a mating between two individuals with different alleles of one characteristic. Used to predict a genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the offspring
Mono=one
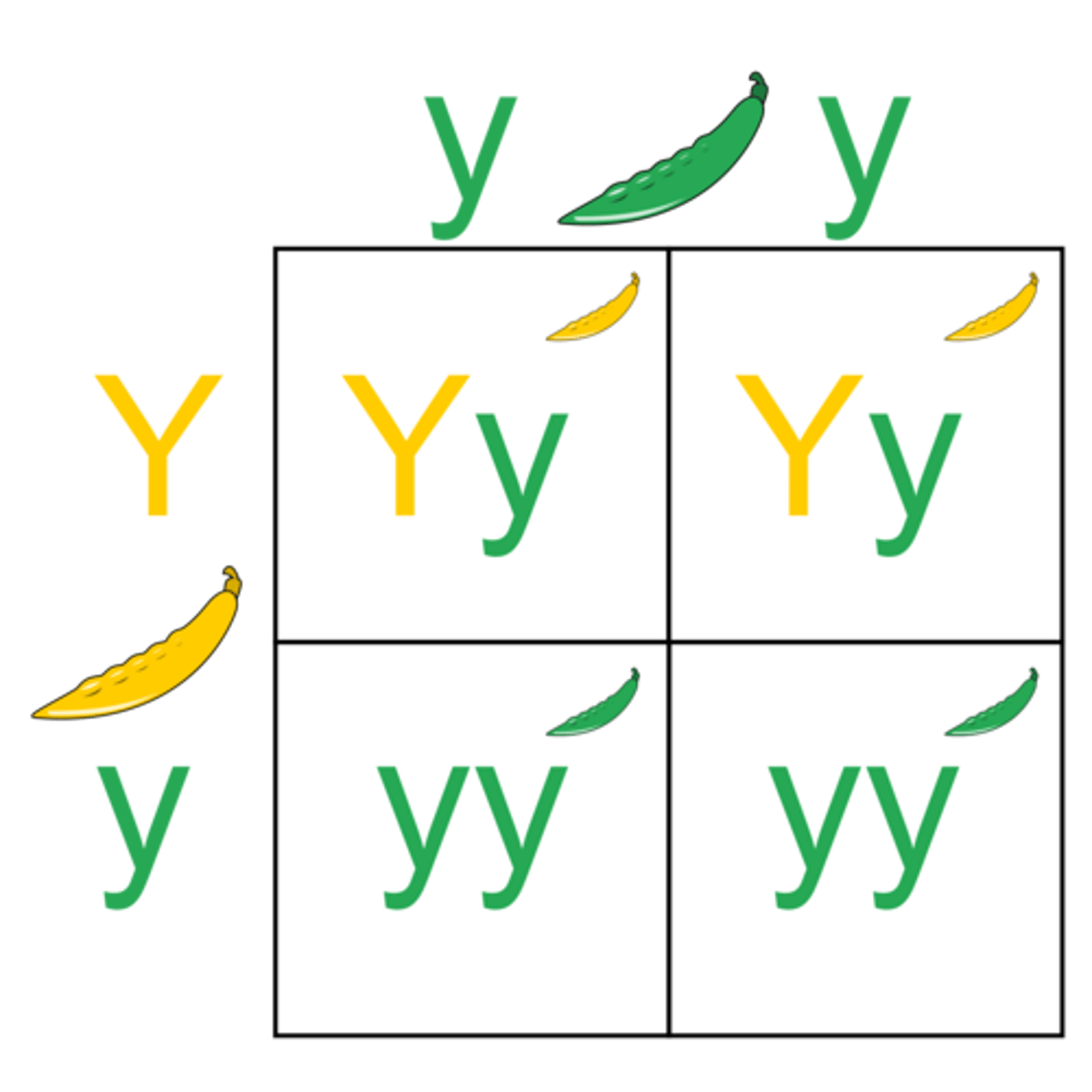
Genotypic ratio meaning
describes the number of times a genotype would appear in the offspring after a test cross
Phenotypic ratio meaning
describes the relative number of physical characteristics or combination of traits manifesting in offspring after a test cross.
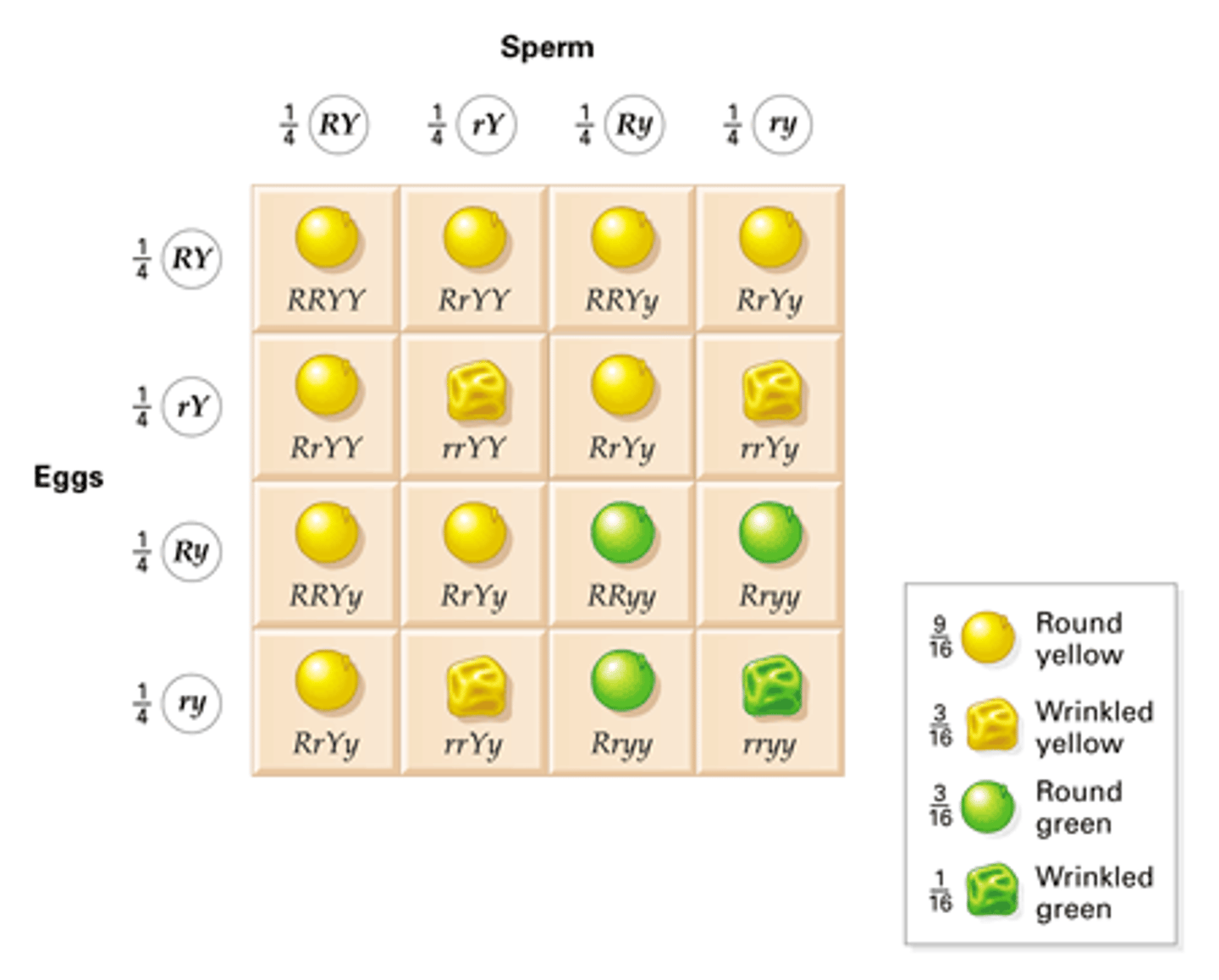
Dihybrid cross meaning
A cross between two individuals that differ in two genes/observed traits
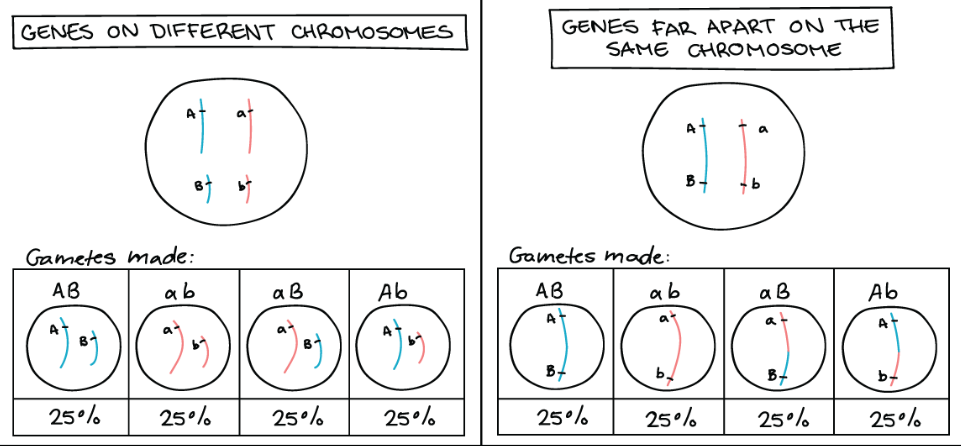
What are linked genes?
If two genes are linked,
They are found at different loci on the same chromosome.
Are more likely to be inherited together.
Examples of linked genes in humans include freckles and red hair.
What are unlinked genes
If two genes are very far apart from each other on same chromosome or are on different chromosomes they are unlinked.
When genes go into gametes, the alleles received for one gene does not affect the allele received for the other.
what is a recombinant frequency
Recombination frequency (θ) is the frequency with which a single chromosomal crossover will take place between two genes during meiosis.
What are unlinked genes recombination frequency
Genes that are unlinked have a recombinant frequency of 50%.
linked gene recombination rate
Linked genes have a recombination frequency that is less than 50%.
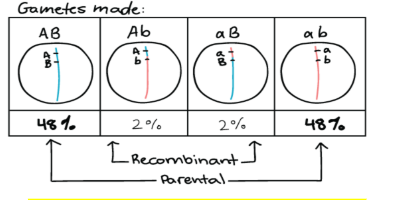
What are map units?
Map units: how far apart two genes are from each other (genetic distance). The closer together, the likelihood they are linked! Therefore have a lower % for recombination.
Map unit = % recombination
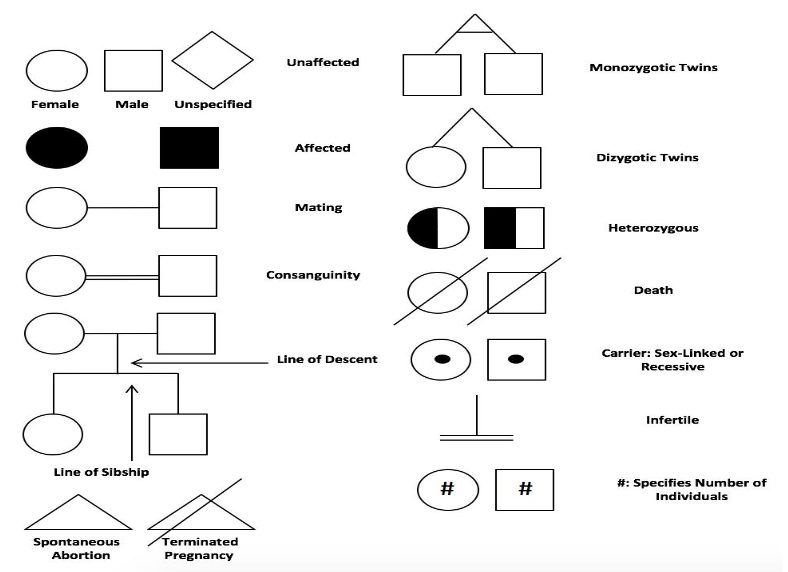
what are pedigrees
Pedigrees are family trees that show the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a particular gene and its inheritance between different members of a family through generations.
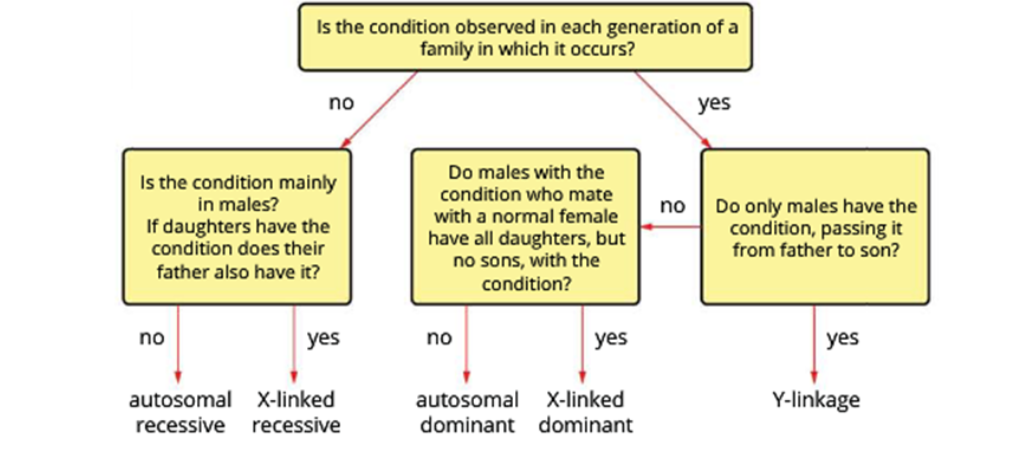
How to interpret a Pedigree Chart?
What are the patterns of inheritance
Autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, sex-linked dominant, sex-linked recessive
autosomal recessive
Heterozygotes don’t show trait so it may skip generations.
If both parents have it, all offspring will have it.
Parents don’t have to have it.
Autosomal dominant
Heterozygotes do show trait so it can’t skip generations.
Even if both parents have it, offspring don’t have to show it.
At least one parent must have it
what is sex linked pattern of inheritance
Involved with genes/traits found on the sex chromosomes - usually the X chromosome.
In sex-linkage mothers pass to sons, fathers pass to daughters
sex linked recessive (x-linked)
Mainly in males
Females can only have it if father has it and mother is at least a carrier
Affected females pass it to all their sons
sex linked dominant (x-linked)
Fathers pass to all daughters
Mothers pass to half their sons
pattern of inheritance flow chart