Protein synthesis Review
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Protein Synthesis
Process that produces proteins
Need for proteins
To do all the things in our bodies
Transport oxygen through blood (hemoglobin)
Regulate blood sugar levels (insulin)
Etc
Where protein synthesis take place
Pt 1: Nucleus (transcription)
Pt 2: cytoplasm @ Ribosome (translation)
DNA-RNA
Part of the central dogma that takes place in nucleus
Nucleic acids in nucleus
DNA and mRNA
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that breaks hydrogen bonds of the original DNA molecule
Template strand
Strand enzyme reads to build mRNA molecule
Where mRNA goes after entire gene is copied
Out of nucleus and to a ribosome in the cytoplasm
Coding strand
mRNA is same as the…
Template strand
mRNA is complementary to the…
Codon
3 consecutive base pairs on an mRNA molecule
Anticodon
Found in tRNA
Nucleus
Where transcription occurs
nucleus —> ribosome
Where mRNA starts and where it ends up after transcription
3 types of RNA
mRNA tRNA rRNA
Nucleus
Where DNA is located
How RNA is different from DNA

mRNA
Function: Carries “message” and code to create protein from inside nucleus to ribosome ( copy DNA to make protein )
Location: nucleus
Made in nucleus and goes to ribosome in cytoplasm
tRNA
Function: carries and transports amino acids to site and protein synthesis/ribosome (bring amino acids to ribosome)
Location: cytoplasm
Forms ribosome (in cytoplasm)
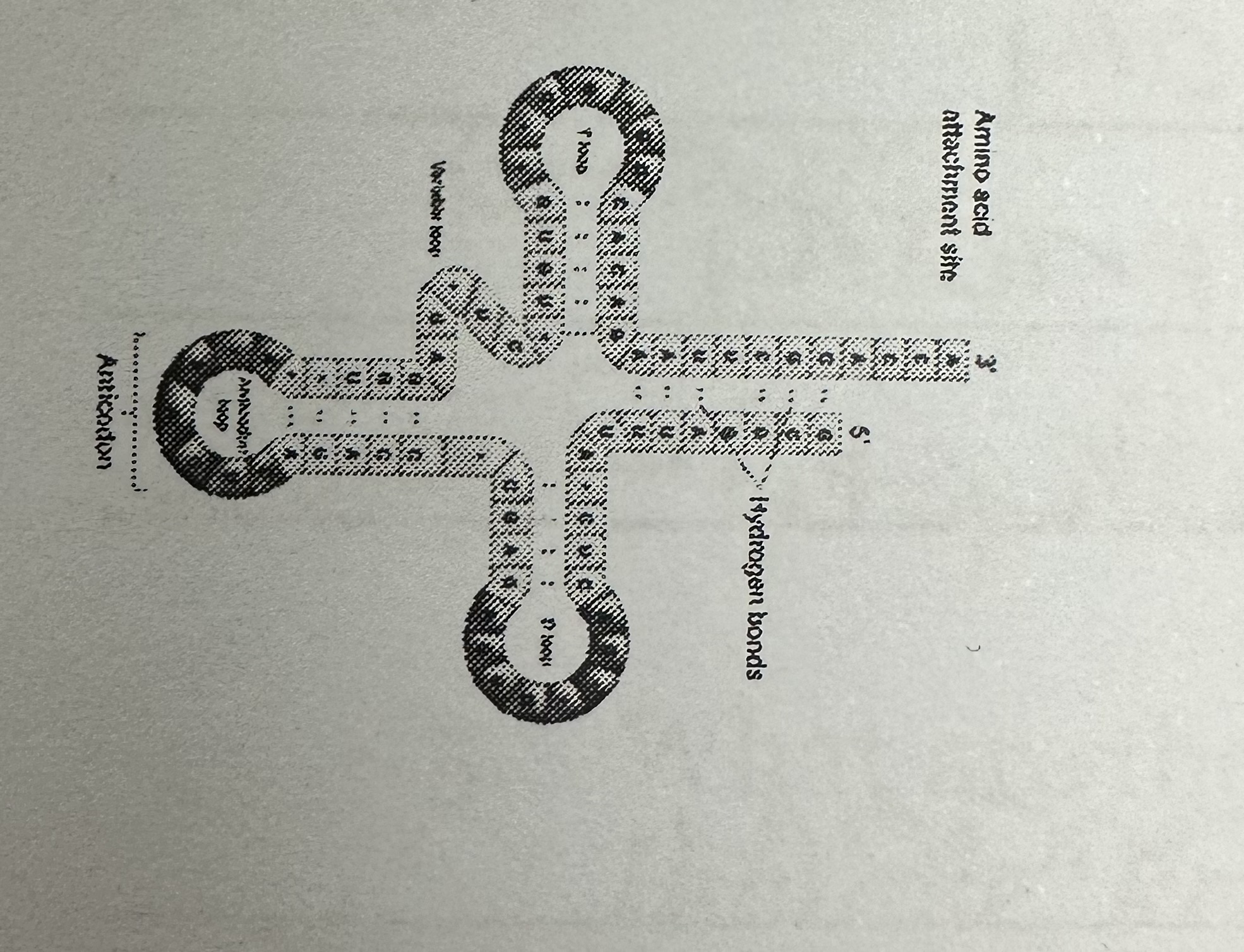
rRNA
Function: forms ribosome and site of protein synthesis (build protein / read mRNA
Location: in cytoplasm, goes to ribosome for translation
Ribosome/cytoplasm
AUG
Start codon
UGA, UAA, UAG
Stop codons
Practice translation
Use codon (mRNA) to determine amino acid
Primary structure
Peptide bonds
Holds primary structure together
Polypeptide chain
polymer of protein
Amino acid
Monomer of protein
Secondary structure
Hydrogen Bonds
Holds together secondary structure
Alpha helicase (coil)
Beta sheet (folded sheets/zig zags)
2 most common secondary structure
Tertiary structure
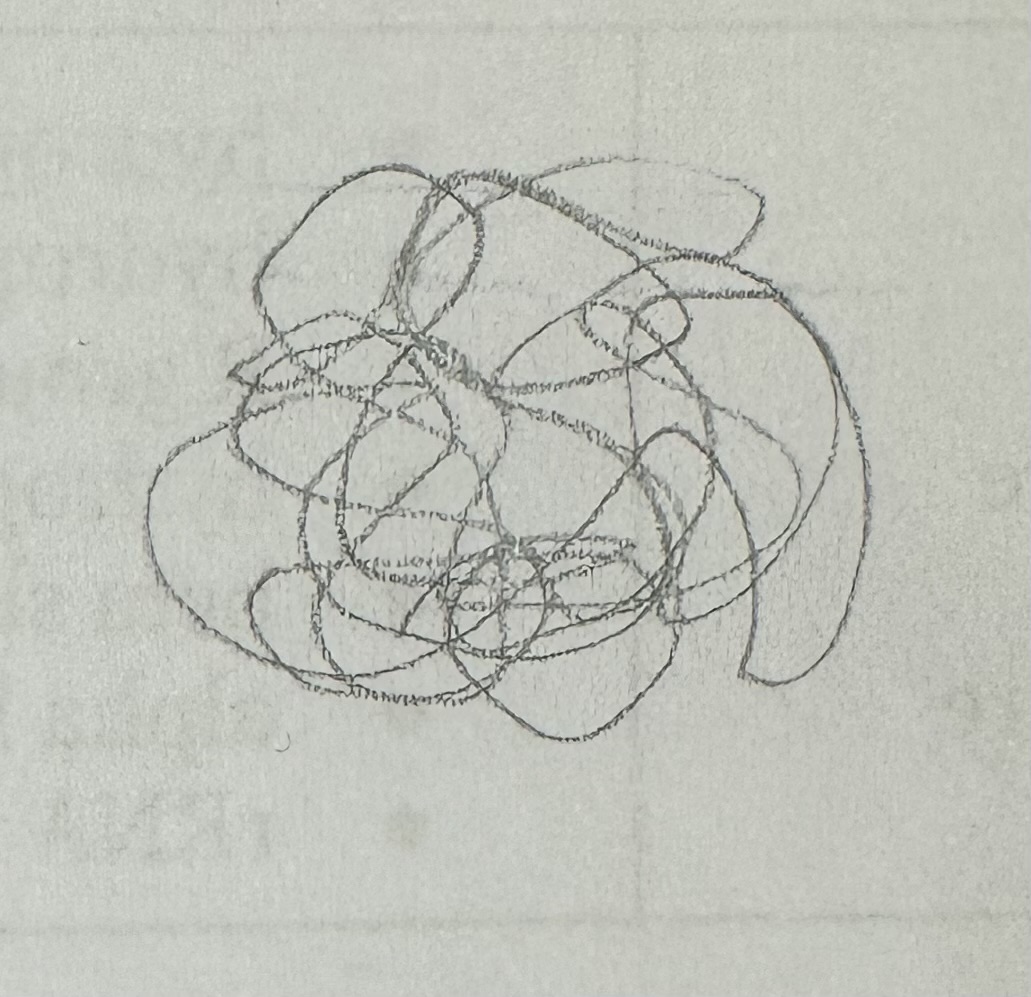

R group interactions
Holds together tertiary structure
Tertiary
One polypeptide subunit, globular structure
Quaternary structure
R group interactions
Holds together quaternary structure
Quaternary
Multiple polypeptide subunits, globular
Polar amino acids
Hydrophilic
Fold outside (like H2O)
Non polar
Hydrophobic
Fold inside (don’t like H20)
Function
The structure of a protein determines its…
Insertion and deletion
Examples of frame shift mutations
Silent, nonsense, missense
Examples of substitution mutations
Silent (substitution)
Codon sequence changes but codes for the same amino acid
(Almost no change)
Missense (substitution)
One amino acid changes
Nonsense (substitution)
One amino acid changes to stop (premature stop)
Ribosomes
rRNA forms…
Nucleotides
Monomer of DNA
DNA (double stranded)
Polymer of DNA
mRNA
messenger
RNA that carries information needed for protein production from the nucleus to other parts of the cell
tRNA
transfer
RNA that brings amino acids to a ribosome and matches their anticodon to the mRNA codon
rRNA
RNA that makes up subunits of a ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis
Transcription
Process that creates a strand of mRNA from a complementary strand of DNA
Nucleus
Where mRNA is formed
Coding
mRNA has the same sequence as the ___ strand of DNA
In cytoplasm at ribosome
Where translation takes place
Desaturation
The unfolding of a protein that occurs due to excessive temperature or pH change