4.4 - Water Pollution
1/13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Water Pollution
the contamination of bodies of water by pollutants either directly or indirectly.
Types of Water Pollution
Anthropogenic (created by human activities), Natural (eg. volcanic eruption, algal bloom), Point Source, Non-point source, Organic, Inorganic, Direct, Indirect
How to measure water pollution in Marine Ecosystems
Abiotic Factors: Salinity, pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, wave action
Biotic Factors: Kick sampling, sweep nets
How to measure water pollution in Freshwater Ecosystems
Abiotic Factors: Turbidity, flow, velocity, pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen
Biotic FactorsL Kick sampling, sweep nets
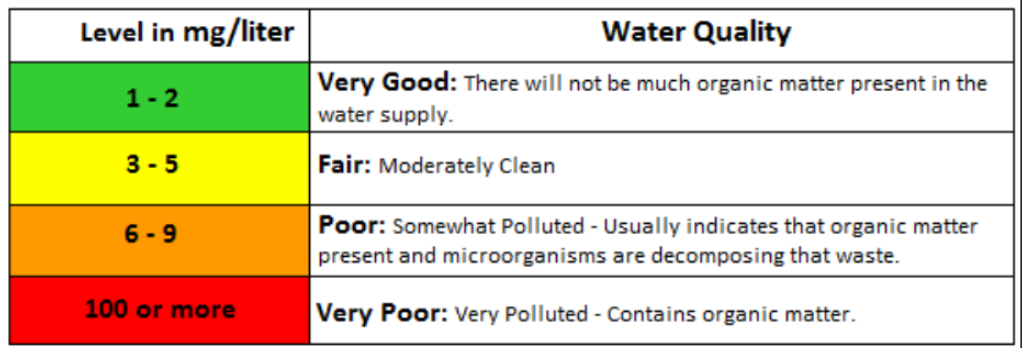
Biochemeical oxygen demand (BOD)
A measure of the amount of dissolved oxygen required to break down the organic material in a given volume of water through aerobic biological activity
Used to indirectly measure the amount of organic matter within a sample
More organic matter = less dissolved oxygen
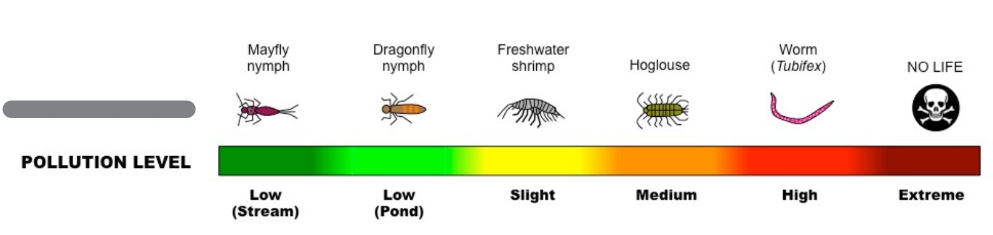
Indicator Species
Plants and animals that show something about the environment by their presence, absence, abundance & scarcity
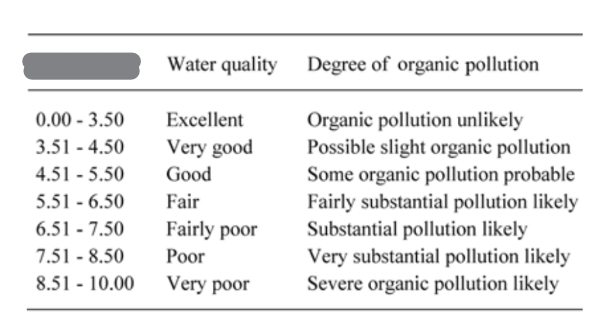
Biotic Index
Measures the impact on species within the community according to their tolerance, diversity & relative abundance
Indirect measurement
Advantages of Indicator Species & Biotic Indices
Measures the widespread effects/impacts of pollutants on the system
Impacts ar emore significant than the quantity/concentration/nature of the pollutant
Are specific to the characteristics of a given habitat
Address the combined/integrated impact of many pollutants/human activities
Cost-effective, it’s cheap
Disadvantages of Indicator Species & Biotic Indices
Does not identify the specific pollutant
Leaving the possible source of pollution unclear
The quality of a given community may vary for reasons other than pollution/initial quality may not be known
May require counting/identification of organisms which are difficult to collect/identify (eg. lichen, invertebrates, prone to human error
Impacts of Eutrophication
Oxygen deficient water
Loss of biodiversity / shortened food chains
Death of higher plants
Death of aerobic organisms (inverterbrates/fish/amphibians)
Increased turbidity
Produce toxic (smelly) gases such as methane, hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia