CVM 737B: Lecture 5 & 6
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
incision into the intestine
enterotomy
removal of a segment of intestine
enterostomy
enterostomy with reestablishment of continuity between the divided ends
intestinal resection and anastomosis
surgical fixation of one intestinal segment to another
intestinal plication (enteroenteropexy)
fixation of an intestinal segment to the body wall or another loop of intestine
enteropexy
surgical fixation of the colon
colopexy
partial or complete resection of the colon
colectomy
resection of the cecum
typhlectomy
surgical creation of an opening between the colon and the surface of the body
colostomy
straining to defecate
tenesmus
pain or discomfort on defecation
dyschezia
passage of stools that contain red blood
hematochezia
passage of tarry stools (digested blood)
melena
What is the most common indication for surgery of the small intestines?
GI obstruction
Preoperative Management of Patients Undergoing Intestinal Surgery:
obtain ________ ________
________ the ________
________ hydration, electrolyte, and acid base abnormalities
transfuse if the packed cell volume is less than ________ or if the animal is clinically weak or debilitated
withhold food from mature animals for ____-____ ________ and from pediatric patients ____-____ ________ before induction
administer ________ ________ if needed
minimum database
localize; lesion
correct
20%
12-18 hours; 4-8 hours
prophylactic antibiotics
True or false; Abdominal ultrasounds are typically done before the contract studies because it often provides the diagnosis and allows the contract study to be circumvented.
true
What is the preferred imaging modality?
ultrasonography
allows visualization and biopsy of the duodenum and sometimes the upper jejunum
gastroduodenoscopy
allows visualization and biopsy of the ileum
colonileoscopy
What can visualization of intestinal mucosa detect?
U
E
I
ulcers
erosions
infiltrated mucosa and or lymphangiectasia
allows multiple biopsies of the small intestine and allows one to direct the biopsy to obvious mucosal lesions
endoscopy
True or false: If the animal deteriorates clinically despite aggressive medical management and complete obstruction, perforation, strangulation, necrosis, or sepsis is suspected, emergency exploratory surgery is indicated without delay.
true
What part of the GI tract contains the most bacteria when compared to the rest of it? Therefore, what should be done preoperatively? Unless what?
colon; colonic emptying and cleansing to reduce bacterial load; perforation or obstruction is suspected
diet that proposes the ingestion, or in more severe cases use of a gastric feeding tube or intravenous feeding of liquid nutrients in an easily assimilated form and is usually composed of amino acids, fats, sugars, vitamins, and minerals
elemental diet
Enemas given any closer to surgery than ____ ________ pre op may liquefy intestinal content and add to the dissemination of contaminated material during surgery.
3 hours
What type of enemas should never be given to small or constipated patients?
hypertonic phosphate enemas
Enemas given to cats may be ineffective when suffering from what?
megacolon
True or false: Enemas can further deteriorate debilitated, anorectic patients and may cause colonic perforation.
true
operative wounds in which the respiratory, gastrointestinal, or genitourinary tract is entered under controlled conditions without unusual contamination or without significant spillage of contents
clean-contaminated wounds
open, fresh, accidental wounds; procedures in which gastrointestinal content or infected urine is spilled or a major break in aseptic technique occurs and should be put on antibiotics
contaminated wounds
Risk of infection after what type of surgery is high? What should be given?
colorectal; systemic perioperative antibiotics effective against anaerobes and gram negative aerobes
What type of suture for intestinal surgery?
monofilament, synthetic absorbable
What type of needle?
swaged on taper or taper cut
What does optimal healing require with intestinal surgery?
G
A
M
good blood supply
accurate mucosal apposition
minimal surgical trauma
What suture patterns should be used?
simple interrupted or simple continuous
What is the intestinal layer that provides mechanical strength? Therefore what must be done?
submucosa; it must be engaged when suturing the intestine to provide a secure closure
When it comes to intestinal surgery, how can the surgical site be covered? What needs to be done with instruments and gloves before closing the abdomen?
omentum or serosal patch; change them
For intestinal closure, how far from the edge are the simple interrupted sutures placed? How far apart?
2 mm; 2 to 3 mm apart
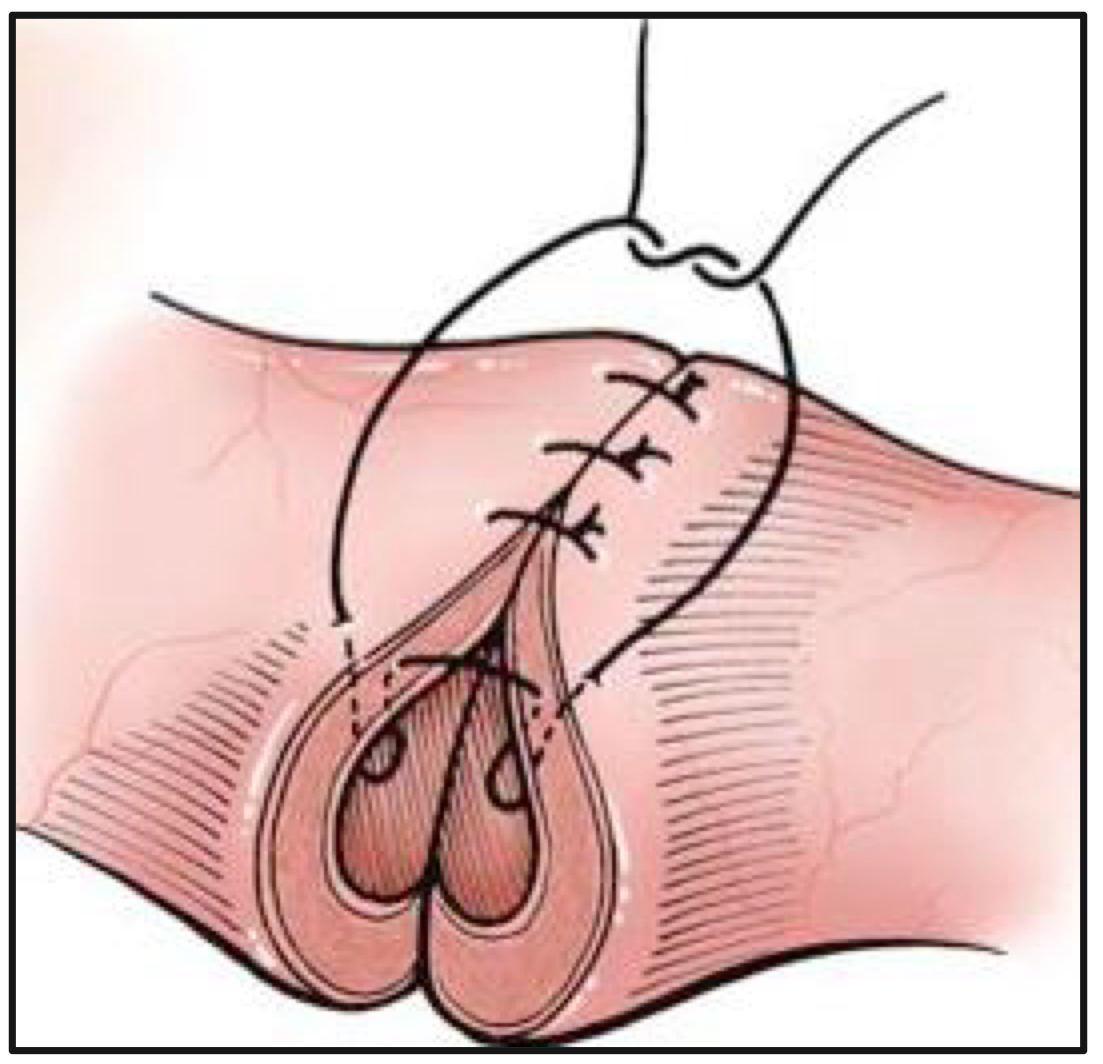
gambee suture pattern
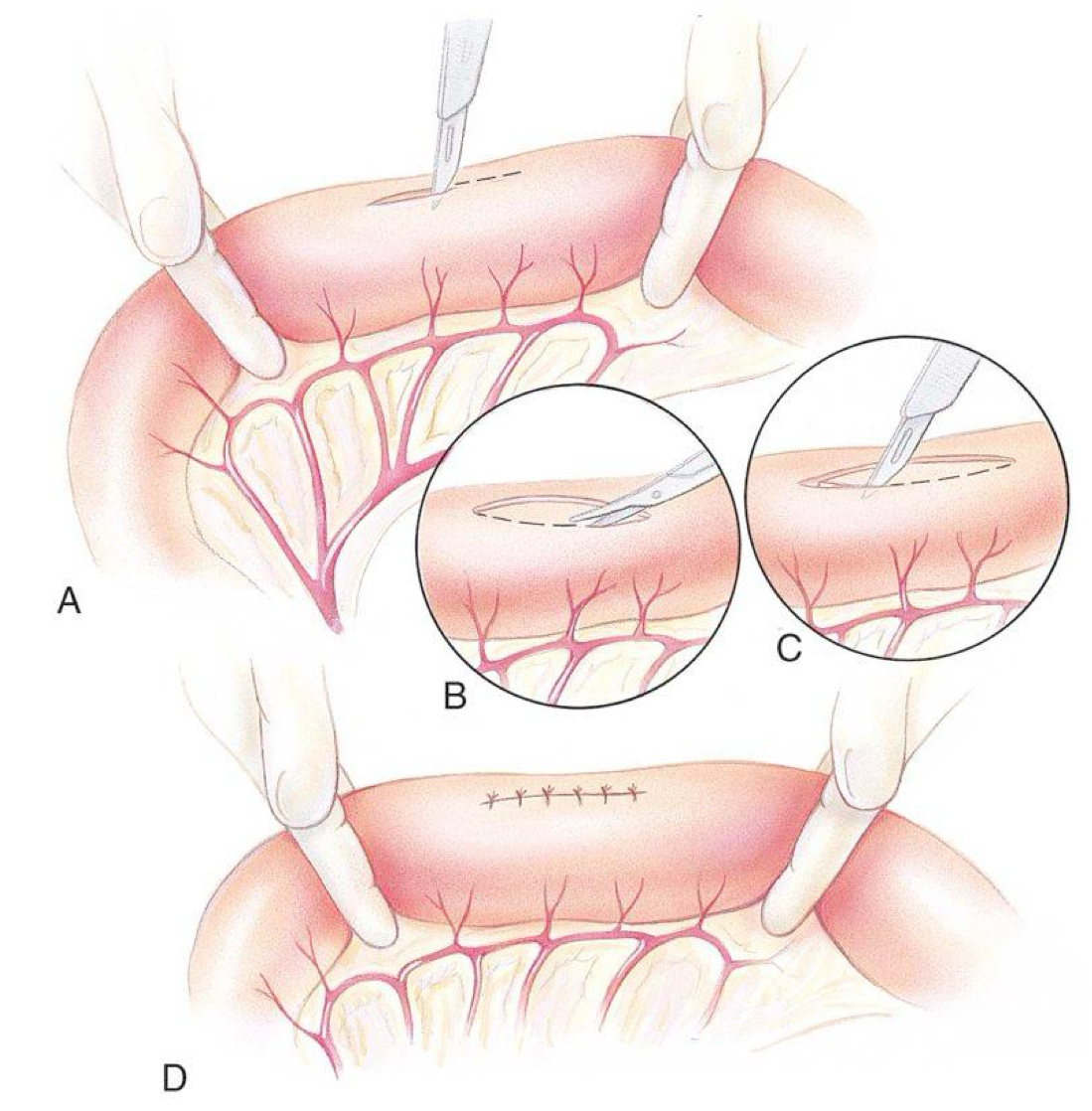
intestinal biopsy
How can an enterotomy be closed if the intestinal lumen is small?
transversely
What type of anastomosis is more expensive?
stapled anastomosis
What are the 4 stapled anastomosis techniques?
T
I
S
E
triangulating end-to-end anastomosis
inverting end-to-end
side-to-side or functional end-to-end
end-to-side anastomosis
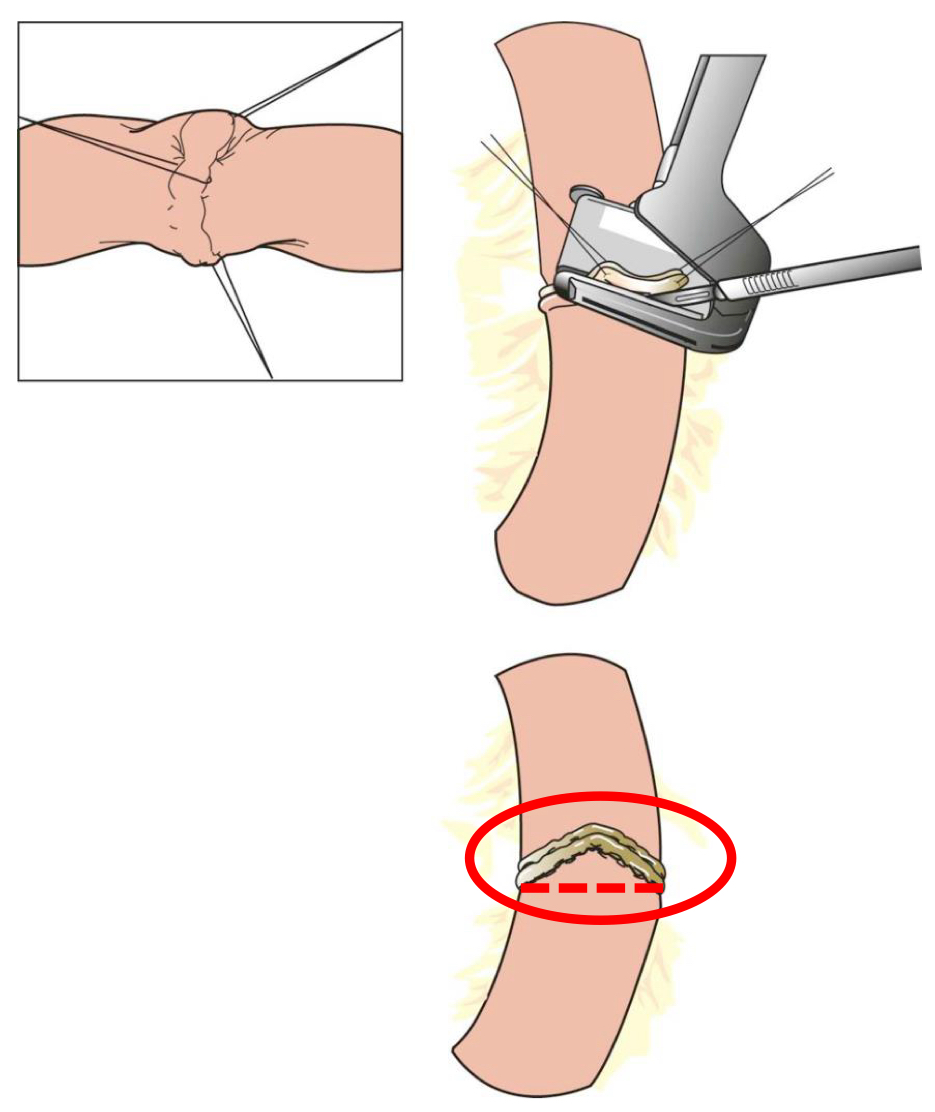
triangulating end-to-end anastomosis
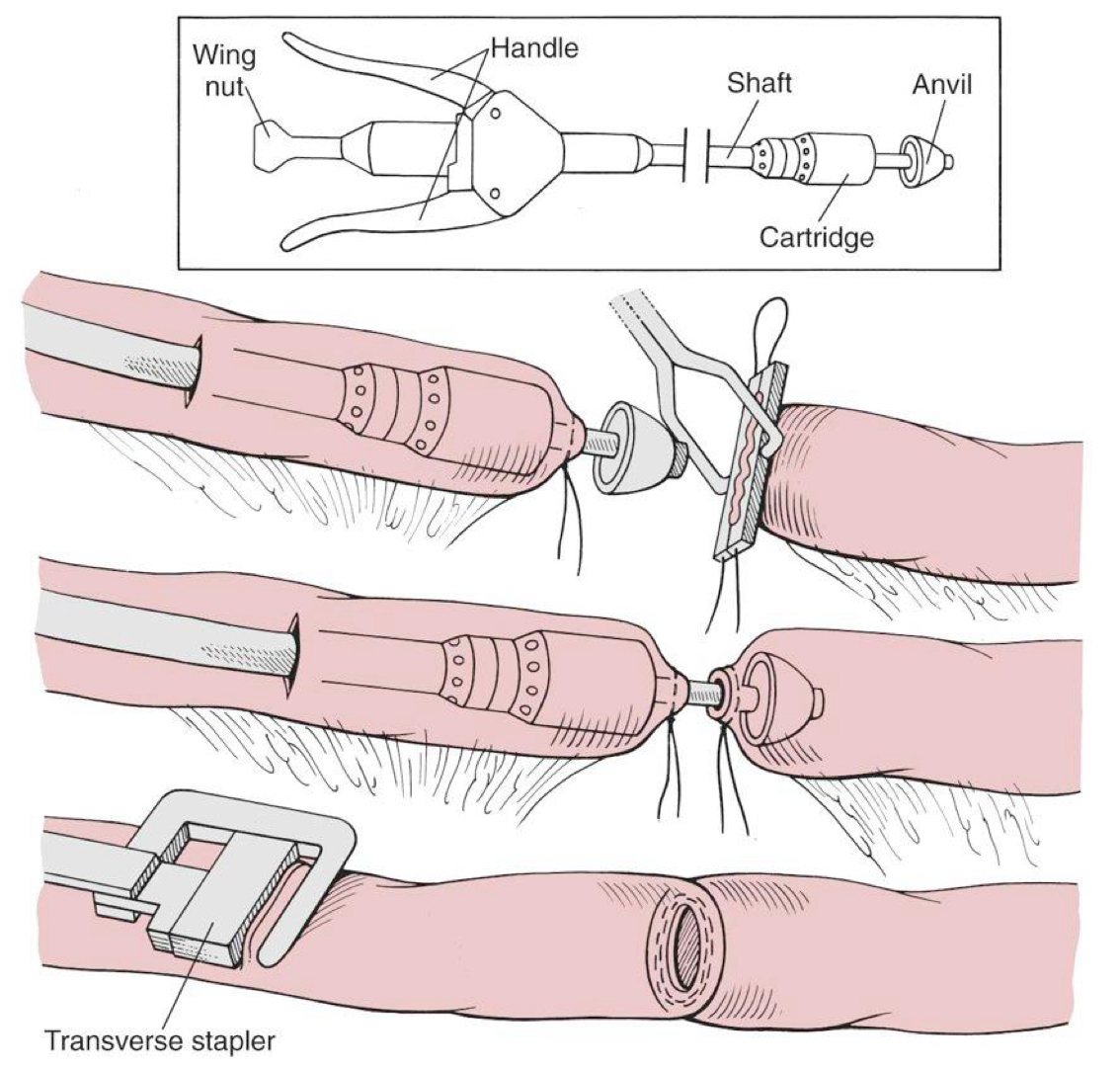
inverting end-to-end anastomosis
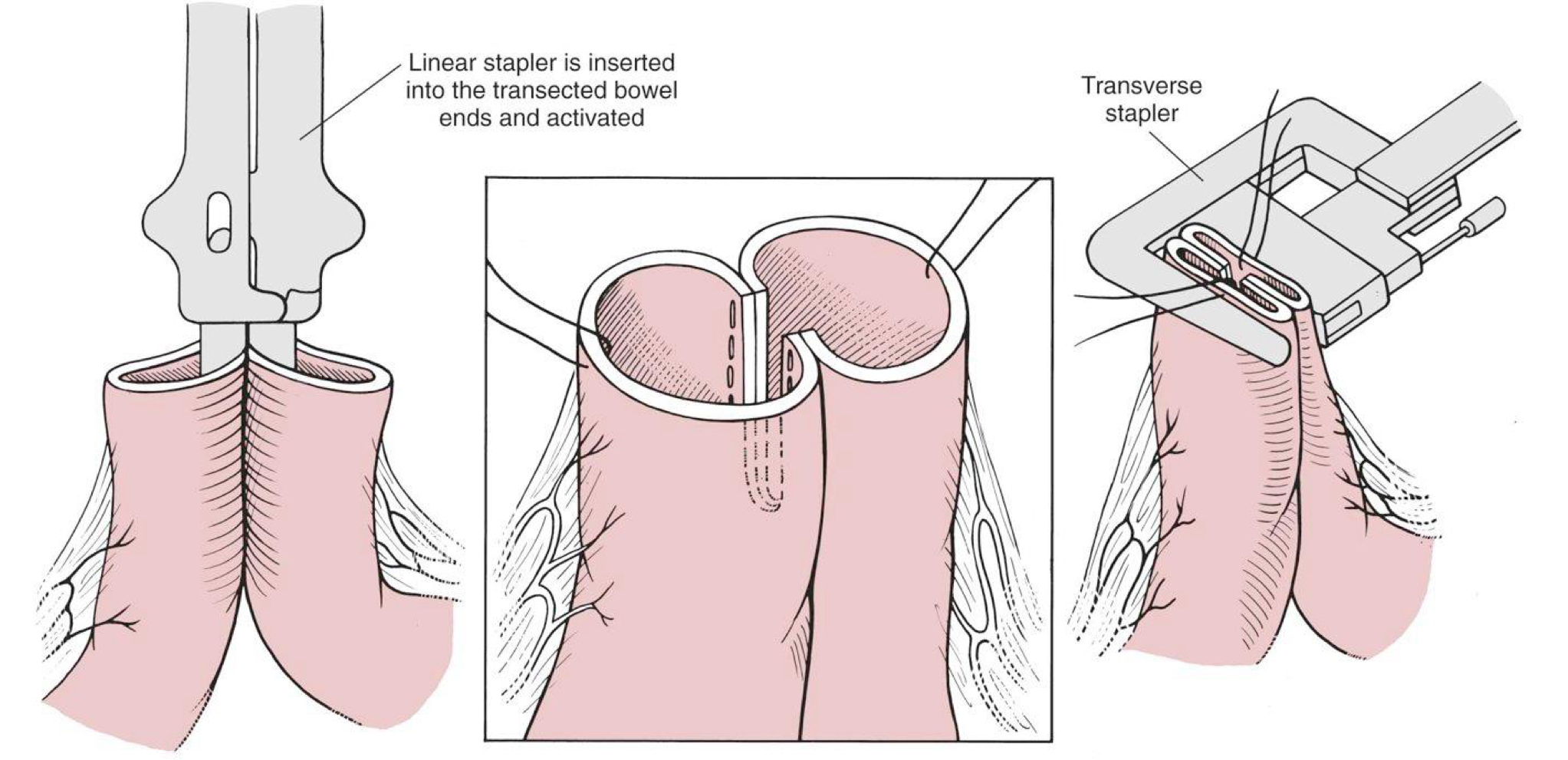
side-to-side or functional end-to-end
telescoping or invagination of one intestinal segment into the lumen of an adjacent segment
intussusception
What is the cause of most intussusceptions?
unknown
What is the presence of an intussusception in a cat more likely associated with than dogs?
neoplasia
What will an ultrasound reveal with an intussusception?
target or bull’s eye pattern
What is a major concern when performing colonic surgery?
blood supply
True or false: You need to reduce colonic bacterial numbers by eliminating oral intake, preparing the colon, and giving antibiotics.
true
With what type of bowel surgery is dehiscence more likely?
large bowel surgery
create permanent adhesions between serosal surface of the colon and abdominal wall to prevent causal movement of the colon and the rectum
colopexy
What is colopexy used to treat?
chronic recurring rectal prolapse
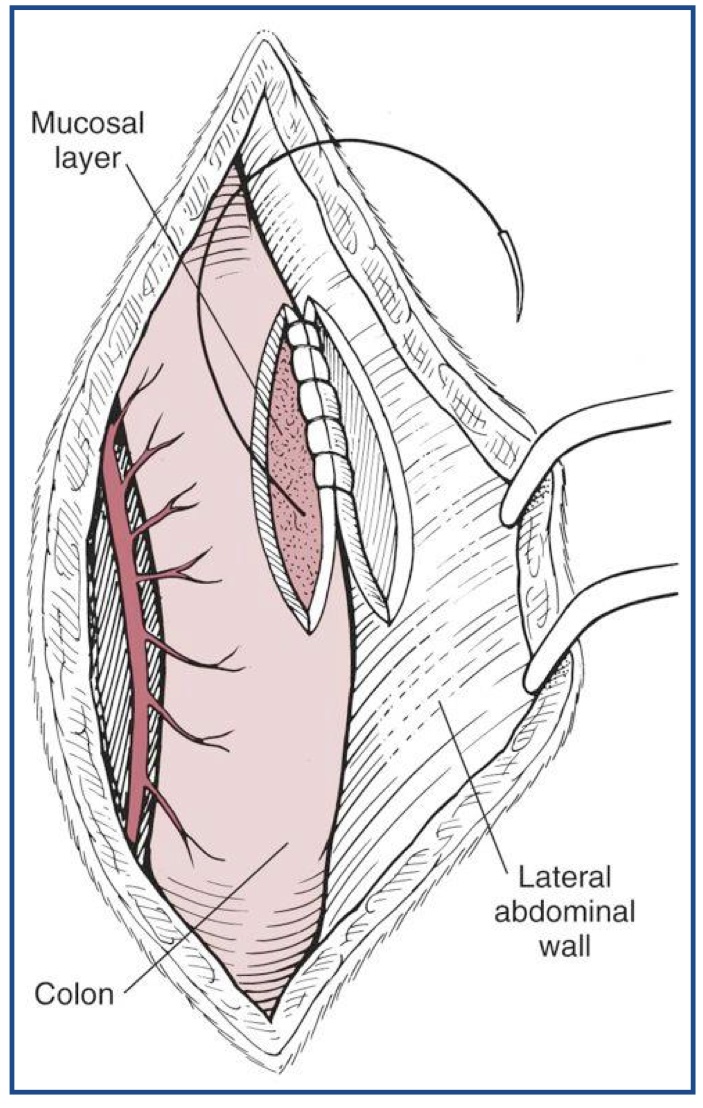
colopexy
What is colectomy and resection used primarily for?
colonic mass removal and megacolon
Up to what percent of the colon can be resected in animals without adverse side effects?
70%
Do cats or dogs tolerate colonic resection better?
cats
Subtotal colectomy is often done in ________, but should be avoided in ________.
cats; dogs
What do you need to warn owners about after subtotal colectomy in cats?
cat will probably defecate frequently and have soft stools
True or false: You can angle your needle so that slightly more serosa than mucosa is engaged to prevent mucosa from protruding between sutures.
true
True or false: Sutured anastomosis techniques are essentially like those in a small intestinal sutured anastomosis.
true
What can be done if there is a minor disparity between the lumen sizes?
space sutures around the larger lumen slight further apart than the sutures in the segment with the smaller lumen
What should you do if there is tension at the anastomotic site?
two layered anastomosis
Where is the first layer placed? Where are the knots tied?
to appose the mucosa and submucosa; within the lumen
Where is the second layer placed? Where are the knots tied?
apposed the muscularis and the serosa; extraluminally
What can the distal colon be anastomosed to?
ileum or jejunum
persistent increased large intestinal diameter and hypo-motility associated with severe constipation
megacolon
mechanical, neurologic, or endocrine cause cannot be identified
idiopathic megacolon
difficult or infrequent defecation with passage of unduly, hard dry fecal material
constipation
extreme constipation (no feces may be passed)
obstipation
Megacolon is most common in ________.
cats
What is recommended for megacolon initially?
medical management
What are the measurements for it be considered megacolon?
diameter of the colon is greater than 1.5 times the length of L7
________ often handle subtotal colectomy well but ________ tend to not handle subtotal colectomy well.
cats; dogs
removal of the entire colon except a short distal segment needed to reestablish intestinal continuity
subtotal colectomy
Healing of the LI is similar to the SI, but is ________.
delayed