Chemistry Reversible Reactions and Electrolysis
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Reversible reaction
Reaction where the products can react with each other and convert back to the original reactants.
Dynamic equilibrium
When the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction in a closed system (so no change in concentration of reactants or products)
Increase in temperature effect on dynamic equilibrium
Shifts equilibrium in the direction of the endothermic reaction
Decrease in temperature effect on dynamic equilibrium
Shifts equilibrium in the direction of the exothermic reaction
Increase in pressure effect on dynamic equilibrium
Shifts equilibrium to the side where there are fewer moles of gas
Decrease in pressure effect on dynamic equilibrium
Shifts equilibrium to the side where there are more moles of gas
Catalyst effect on dynamic equilibrium
No effect because it speeds up the forward and backward reaction by the same amount
Electrolysis
Using electricity to decompose aqueous or molten ionic compounds by pasing an electric current thorugh an electrolyte, causing it to decompose.
Electrolyte
Ionic compound that is molten or dissolved
Cathode
Negatively charged electrode that attracts positive ions (cations)
Anode
Positively charged electrode that attracts negative ions (anions)
What happens at the cathode?
Reduction (gain of electrons)
What happens at the anode?
Oxidation (loss of electrons)
What kind of material are electrodes made of
Inert material so that they do not take part in the reaction
How to set up an electrolysis experiment?
Get two inert electrodes and place them in a breaker filled with the electrolyte. Connect the electrodes to a power supply using crocodile clips and wires, and turn on the power supply.
What can electrodes be made of? (example)
platinum or graphite
Ions in water
H+ and OH-
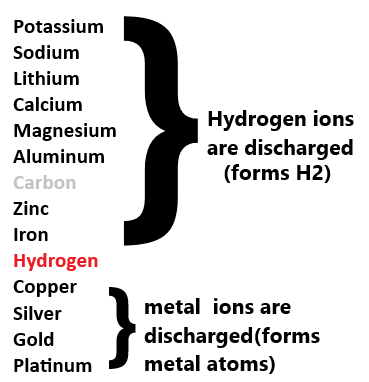
Which ion is discharged at the cathode? + state the reactivity series
The less reactive ion in the reactivity series is discharged
Which ion is discharged at the anode?
Halide ions (forms halogen gas) or otherwise hydroxide ions (forms oxygen gas)
Half equation if hydroxide ion is discharged
Se4OH- → O2 + 2H2O + 4e-
Setup for purification of copper using electrolysis
Pure copper as the cathode (negatively charged) and impure copper as the anode (positively charged)
What is the negative electrode in the purification of copper experiment? (with half equation)
Pure copper, reduction occurs Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
What is the postive electrode in the purification of copper experiment? (with half equation)
Impure copper, oxidation occurs Cu → Cu2+ + 2e-
Describe the purification of copper process (5 steps)
Negative electrode is pure copper, positive electrode is impure copper
Positive electrode gets smaller, negative electrode gets bigger
Copper ions are attracted to negative electrode and reduction occurs
Copper atoms at positive electrode lose two electronss to form copper ions which dissolve into the electrolyte
Atoms of impurities around the copper atoms have turned into ions and are released also become free, collecting as ‘mud’ beneath the electrode.
What is ‘mud’/sludge in purification of copper?
Atoms of impurities that become free when copper atoms are released into the electrolyte, containing silver and gold.
Why might a reaction not reach equilibrium?
It is not a closed system
Why might a small amount of acid be added to water before it is electrolyzed?
To increase electrical conductivity
How does catalyst affect yield?
NO EFFECT!! (in the end the amount produced is same, only sped up)
Final step of bromine ions becoming bromine gas in electrolysis
The bromine atoms join in pairs to form bromine molecules