brain ch 3-4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
1
New cards
central nervous system (CNS)
division of nervous system located within skull and spine
composed to 2 additional divisons: spinal cord and brain
composed to 2 additional divisons: spinal cord and brain
2
New cards
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
division of nevous system located outside skull and spine
composed of 2 additional divisons: domantic and autonomic nervous system
composed of 2 additional divisons: domantic and autonomic nervous system
3
New cards
somantic nervous system (SNS)
interacts with external environment
4
New cards
afferent nerves-SNS
carry sensory signals from skin, skeletal muscles, joint, eyes to central nervous system
5
New cards
efferent nerves-SNS
carry motor signals from central nervous system to skeletal mucsles
6
New cards
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
regulates the body’s internal enviornment
7
New cards
afferent nerves-ANS
carry sensory signals from internal organs to CNS
8
New cards
efferent nerves-ANS
carry motor signals from CNS to internal organs
9
New cards
sympathetic nerves
autonomic motor nerves that project from CNS in the lumbar (small of the back) and thoracic (chest area) regions of spinal cord
10
New cards
parasympathetic nerves
autonomic motor nerves that project from the brain and sacral (lower back) region of spinal cord
11
New cards
cranial nerves
most of the nerves of peripheral nervous system project from spinal cord, but there are 12 pairs of exceptions, which project from brain
12
New cards
meninges
The brain and the spinal cord (CNS) are the most protected organs in the body. They are incased in bone and are covered by three protective membranes
13
New cards
dura mater
outer meninx, tough membrane
14
New cards
arachnoid membrane
inside dura matter, fine spider-web-like membrane
15
New cards
subarachnoid space
beneath arachnoid membrane, containing many large blood vessels and cerebrospinal fluid
16
New cards
pia matter
innermost meninx, which is delicated and adheres to the surface of the CNS
17
New cards
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
protects CNS
filled in the subarachnoid space, central canal, cerebral ventricles
filled in the subarachnoid space, central canal, cerebral ventricles
18
New cards
central canal
small central chanel that runs the lenght of spinal cord
19
New cards
cerebral ventricles
four large internal chambers of the brain
two lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle
two lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle
20
New cards
choroid plexuses
cerebrospinal fluid is produced by this, which are networks of capillaries or small blood vessels that protrude into the ventricles in pia matter
21
New cards
blood-brain barrier
mechanism impedes passage of many toxis substances from blood into the brain
22
New cards
neurons
cells thar are specilized for reception, conduction, and transmission of electrochemical signals
23
New cards
neuron cell membrane
composed of a lipid bilayer (two layers of fat molecules) that contain numerous protein molecules that are the basis of many cell membrane’s functional properties
some membrane proteins are channel proteins through which certain molecules pass, while others are __*s*__ignal proteins that transfer signals to the inside of the neuron when particular molecules bind to them on the outside of the membrane
some membrane proteins are channel proteins through which certain molecules pass, while others are __*s*__ignal proteins that transfer signals to the inside of the neuron when particular molecules bind to them on the outside of the membrane
24
New cards
multipolar neuron
neuron with more than two processes extending from its cell body
25
New cards
unipolar neuron
neuron with one process extending from its cell body
26
New cards
bipolar neuron
neuron with two processes extending from its cell body
27
New cards
interneuron
neurons with either a short or no axon that integrates neural activity within single brain structure, not to conduct signals from one structure to another
28
New cards
nuclei
clusters of cell bodies in CNS
29
New cards
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in PNS
30
New cards
tracts
bundles of axons in CNS
31
New cards
nerves
bundles of axons in periheral system
32
New cards
cell membrane
semipermeable membrane that encloses neuron
33
New cards
dendrites
short processes emanating from cell body, which receive most of the snaptic contacts from other neurons
34
New cards
axon hillock
cone shaped region at the junction between axon and cell body
35
New cards
axon
long-narrow process that projects from cell body
36
New cards
myelin
fatty insulation around many axons
37
New cards
nodes of ranvier
gaps between sections of myelin
38
New cards
cell body
metabolic center of neuron
soma
soma
39
New cards
buttons
buttonlike endings of axon branches, which release chemical into stnapses
40
New cards
synapses
gaps between adjacent neurons across which chemical signals are transmitted
41
New cards
oligodendrocytes
glial cell with extensions that wrap around axons of some neurons of CNS
42
New cards
schwann cells
similar to oligodendrocytes performed in PNS
43
New cards
microglia
smaller than other glial cells and respond to injury or disease by multipyling, engulfing cellular debris or even entire cells, and triggering inflammatory responses
44
New cards
astrocytes
largest glial cells shaped like star
extensions of some astrocytes cover the outer surface of blood vessels that course through brain, and making contact with neurons
extensions of some astrocytes cover the outer surface of blood vessels that course through brain, and making contact with neurons
45
New cards
golgi stain
commonly used when the overall shape of neurons is of interest and provides a view of the silhouettes of the few nurons that make up the stain. isnt indicative of the number of neurons in the area
46
New cards
nissl stain
often used to estimate the number of cell bodies in an area, by counting the number of nissl-stained dots
47
New cards
electron microcopy
information about detaşks of neuronal structure
48
New cards
neuroanatomical tracking techniques
consist of two types: anterograde (forward) tracing method and retrograde (backwards) tracking method
49
New cards
anterograde tracking method
used when one wants to trace the path of axons projecting away from cell bodies located in particular area
50
New cards
retrograde tracking method
used when one wants to trace the path of axons projecting into a particular area
51
New cards
anterior - posterior
nose end - tail end
52
New cards
dorsal - ventral
toward the surface of the back or top of the head - toward the surface of the chest or bottom of the head
53
New cards
medial - lateral
toward the midline of the body - away from the midline toward to body’s external surface
54
New cards
superior - inferior
refer to the top and bottom of primate head
55
New cards
proximal - distal
close - far
56
New cards
midsagittal section
a section cut down the center of the brain between two hemispheres
57
New cards
cross section
a section cut at a right angle to any long- narrow structure such as spinal cord or nerve
58
New cards
gray matter
spinal cord area, H-shaped
composed largely of cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons
composed largely of cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons
59
New cards
white matter
spinal cord
composed largely of myelinated axons
glossy white sheen is a result of the myelin
composed largely of myelinated axons
glossy white sheen is a result of the myelin
60
New cards
dorsal horns
two dorsal arms of the spinal gray matter
61
New cards
ventral horns
two ventral arms of spinal gray matter
62
New cards
spinal verves
attacked to the spinal cord, on the left and on the right at 31 different levels of spine each, 62 spinal nerves divide around the chord, and its axons are joined to the cord via dorsal and ventral root
63
New cards
dorsal root
all axons, whether somantic or autonomic, are sensory (afferent) unipolar neurons with their cell bodies grouped together just outside the cord to form dorsal root ganglia
many of their synaptic terminals are in the dorsla horns of the spinal gray matter
many of their synaptic terminals are in the dorsla horns of the spinal gray matter
64
New cards
ventral root
neurons of this are motor (efferent) multipolar neurons with their cell bodies in the ventral horns
those that are part of the somatic nervous system project to skeletal muscles, while those a part of the autonomic nervous system project to ganglia, where they synapse on neurons that in turn, project to internal organs.
those that are part of the somatic nervous system project to skeletal muscles, while those a part of the autonomic nervous system project to ganglia, where they synapse on neurons that in turn, project to internal organs.
65
New cards
myelencephalon
medulla, part of brain stem
composed largely of tracts carrying signals between the rest of the brain and body
composed largely of tracts carrying signals between the rest of the brain and body
66
New cards
metencephalon
like the myelencephalon, houses may ascending and descending tracts and are part of reticular formation
two division: pons and cerebellum
two division: pons and cerebellum
67
New cards
pons
brain stem’s ventral surface
including the regulation of breathing, sleep, taste, facial movements, hearing, balance, eye movements, and facial sensation.
serves as a bridge connecting different parts of the brain, including the cerebellum, cerebral cortex, and spinal cord, and is involved in relaying sensory and motor information between these structures.
including the regulation of breathing, sleep, taste, facial movements, hearing, balance, eye movements, and facial sensation.
serves as a bridge connecting different parts of the brain, including the cerebellum, cerebral cortex, and spinal cord, and is involved in relaying sensory and motor information between these structures.
68
New cards
cerebellum
large, convoluted structure on brain stem’s dorsal surface
important sensorimotor structure; damage eliminates the ability to precisely control one’s movement and to adapt them to changing conditions
important sensorimotor structure; damage eliminates the ability to precisely control one’s movement and to adapt them to changing conditions
69
New cards
mesencephalon
two divisions: tectum and tegmentum
70
New cards
tectum
roof
dorsal surface of the midbrain
the posterior pair, the inferior colliculi, have auditory function. The anterior pair, the superior colliculi, have visual-motor function, specifically to direct the body’s orientation toward/away from a particular visual stimulus
in lower vertebrates, the function of the tectum is solely based on visual-motor functions
dorsal surface of the midbrain
the posterior pair, the inferior colliculi, have auditory function. The anterior pair, the superior colliculi, have visual-motor function, specifically to direct the body’s orientation toward/away from a particular visual stimulus
in lower vertebrates, the function of the tectum is solely based on visual-motor functions
71
New cards
tegmentum
ventral to the tectum
reticular formation and tracts of passage, also contains 3 colourful structure; periaqueductal gray, substantia nigra, and red nucleus
reticular formation and tracts of passage, also contains 3 colourful structure; periaqueductal gray, substantia nigra, and red nucleus
72
New cards
periaqueductal gray
gray matter situated around the cerebral aqueduct, the duct containing the third and fourth ventricles
73
New cards
substantia nigra and red nucleus
impoartan to the sensorimotor system
74
New cards
diencephalon
composed of two structures; thalamus and hypothalamus
75
New cards
thalamus
large, two-lobed structure that constitutes the top of the brain stem
one lobe sits on each side of the third ventricle, wich are both joined by massa intermedia which runs through the ventricle
one lobe sits on each side of the third ventricle, wich are both joined by massa intermedia which runs through the ventricle
76
New cards
hypothalamus
located below the anterior thalamus
plays important role in regulation of several motivated behaviours; sleep, eat, sexual behaviour
plays important role in regulation of several motivated behaviours; sleep, eat, sexual behaviour
77
New cards
pituitary gland
it exerts its effect in part by regulating the release of hormons from it
which dangles from ventral surface of the brain
two structures appear on inferior surface of hypothalamus; optic chiasm and mammillary bodies
which dangles from ventral surface of the brain
two structures appear on inferior surface of hypothalamus; optic chiasm and mammillary bodies
78
New cards
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerves from each eye come together
an X shape is created become some of the axons of the optic nerve **decussate** (cross over to the other side of the brain) via the optic chiasm. The decussating fibers are said to be **contralateral** (projecting from one side of the body to the other), and the nondecussating fibers are said to be **ipsilateral** (staying on the same side of the body)
an X shape is created become some of the axons of the optic nerve **decussate** (cross over to the other side of the brain) via the optic chiasm. The decussating fibers are said to be **contralateral** (projecting from one side of the body to the other), and the nondecussating fibers are said to be **ipsilateral** (staying on the same side of the body)
79
New cards
mammillar bodies
pair of spherical nuclei located on inferior surface of hypothalamus just behind the pituitary
80
New cards
telencephalon
the largest division of the human brain, mediates the brain’s most complex functions
it initiates voluntary movement, interprets sensory input, and mediates complex cognitive processes such as learning, speaking, etc.
it initiates voluntary movement, interprets sensory input, and mediates complex cognitive processes such as learning, speaking, etc.
81
New cards
82
New cards
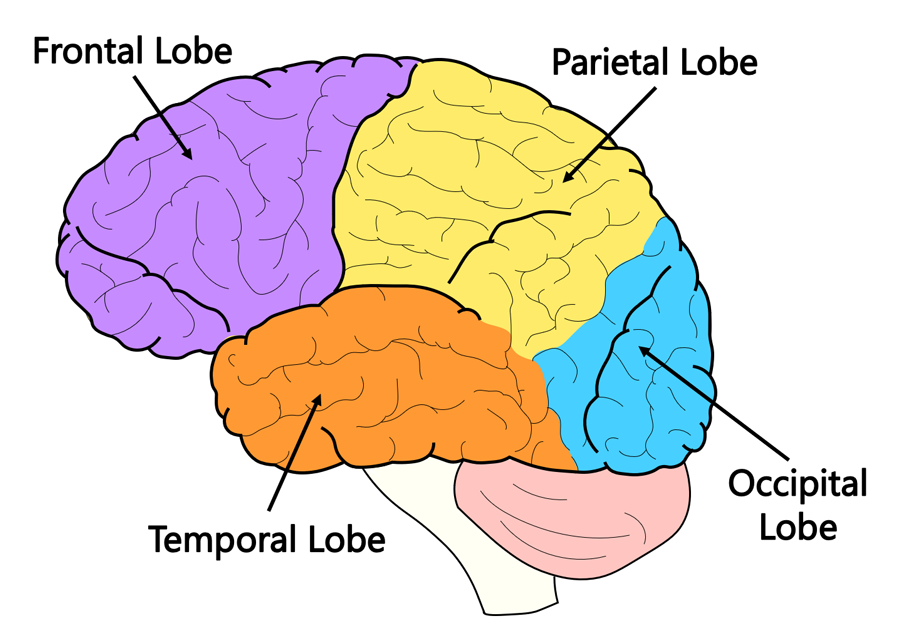
central fissure and lateral fissure
divide each hemisphere into four lobes; frontal lobe, pariental lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe
83
New cards
fissures - sulci
large furrows in convoluted cortex - small one
84
New cards
gyri
ridges between the fissures and sulci
large gyri are precentral gyri (frontal lobe), postcentral gyri (pariental lobe), superior temporal gyri (temporal lobe)
large gyri are precentral gyri (frontal lobe), postcentral gyri (pariental lobe), superior temporal gyri (temporal lobe)
85
New cards
neocortex
new cortex
six-layered cortex of relatively recent evolution
six-layered cortex of relatively recent evolution
86
New cards
longitudinal fissure
the cerebraş hemisphere are almost completed seperately by largest of the fissure
87
New cards
corpus callosum
hemisphere are connected by few tracts spanning the longitudinal fissure
88
New cards
columnar organization
neurons in a given vertical column of neocortex often form a mini-circuit that performs a single function
89
New cards
hippocampus
one important area of cortex that is not neocortex
plays a major role in some kinds of memory, particular memory for spatial location
plays a major role in some kinds of memory, particular memory for spatial location
90
New cards
limbic system
circuit of midline structure that circle the thalamus
involved in regulation of motivated behaviours, including four F’s of motivation: fleeing, feeding, fighting, and sexual behaviour
involved in regulation of motivated behaviours, including four F’s of motivation: fleeing, feeding, fighting, and sexual behaviour
91
New cards
basal ganglia
voluntary motor responses and decision making
92
New cards
amygdala
involve in emotion, particulary fear
93
New cards
membrane potential
difference in electrical charge between inside and outside of a cell
94
New cards
microelectrodes
intracellular electrodes
95
New cards
neuron’s resting potential
steady membrane potential of about -70 mV
96
New cards
polarized
in its resting state, with the -70mV charge built up across its membrane, a neuron is said to be
97
New cards
ions
salts in neural tissue sparate into positively and negatively charged particles
98
New cards
ion channels
in resting neurons, there are more Na+ ions outside the cell than isnide, and more K+ ions inside than outside
this unequal distribution is maintained throught specilised porese
this unequal distribution is maintained throught specilised porese
99
New cards
electrostatic pressure
reason for substantial pressure on Na+ ions to enter the resting neurons
resting membrane potential
opposite charges attract, -70mV charge attract the positively charged Na+ ions into resting neurons
resting membrane potential
opposite charges attract, -70mV charge attract the positively charged Na+ ions into resting neurons
100
New cards
random motion
reason for substantial pressure on Na+ ions to enter the resting neurons
Na+ ions to move down their concentration gradient
makes ions more liekly to move down their concetration gradient than up them, that is why Na+ will tend to enter
Na+ ions to move down their concentration gradient
makes ions more liekly to move down their concetration gradient than up them, that is why Na+ will tend to enter