Patho- Module 4: Cardiac (EXAM 2) KNACK PROOFED
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
what are congenital heart defects?
-conditions/structural defects of the heart that are present at birth
-the most common type of birth
what are the manifestations of congenital heart defects?
-heart murmurs
-dyspnea
-tachypnea
-cyanosis
-fatigue
-chest pain/discomfort
-difficulty gaining weight
-fall asleep during meals for children/babies
*can cause heart failure!
what is pericarditis? (decreased cardiac output)
-inflammation of the sac around the heart which is called the pericardium by viral infection
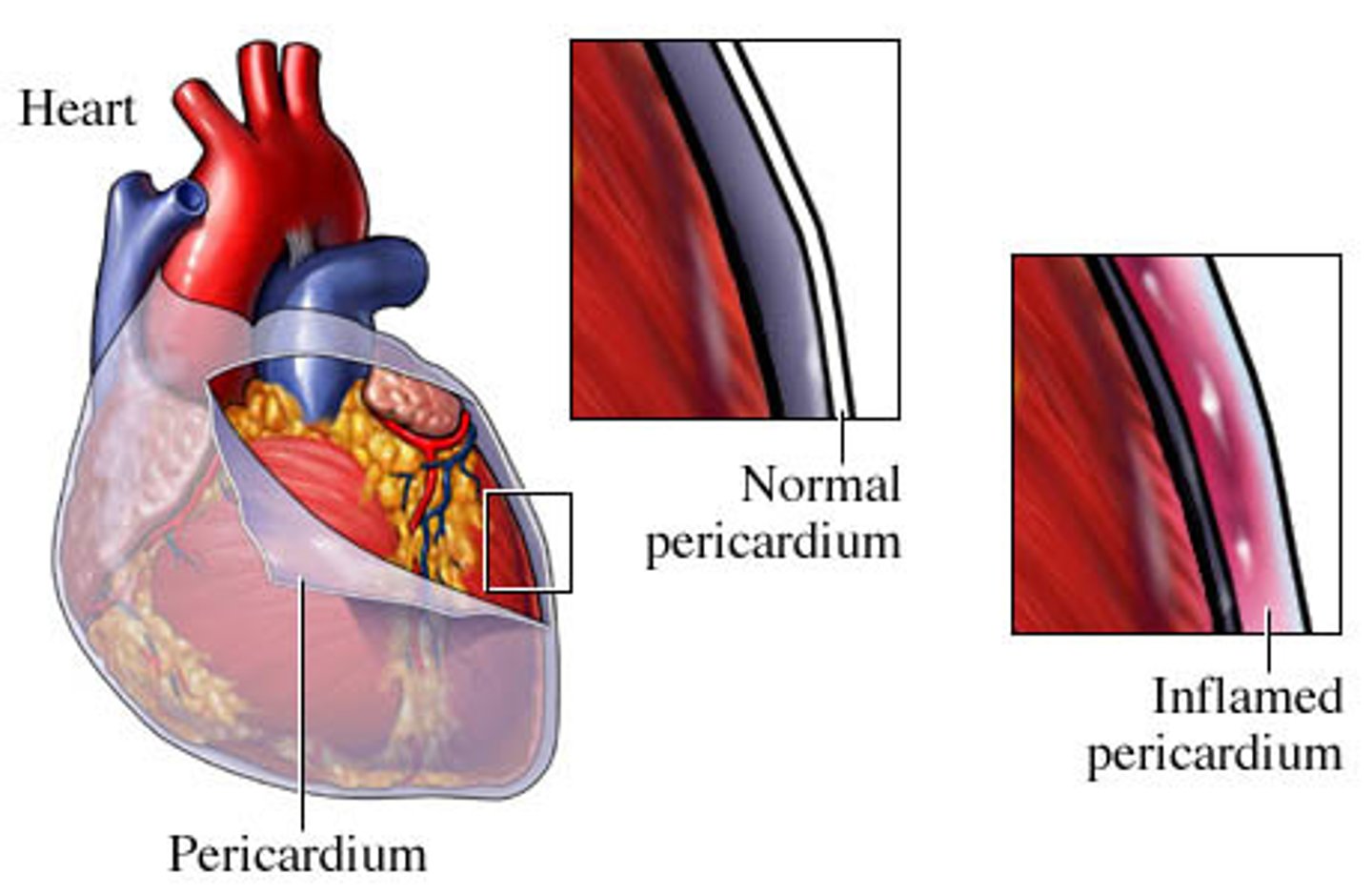
what can cause pericarditis?
-viral infection!
-chest trauma
-MI (myocardial infarction)
-cancer
-TB
-autoimmune conditions
what can pericarditis lead to?
-pericardial effusion which is when fluid accumulates in the space between the
pericardial sac and heart
-swollen tissue creates friction (swollen pericardial tissue rubbing against heart tissue)
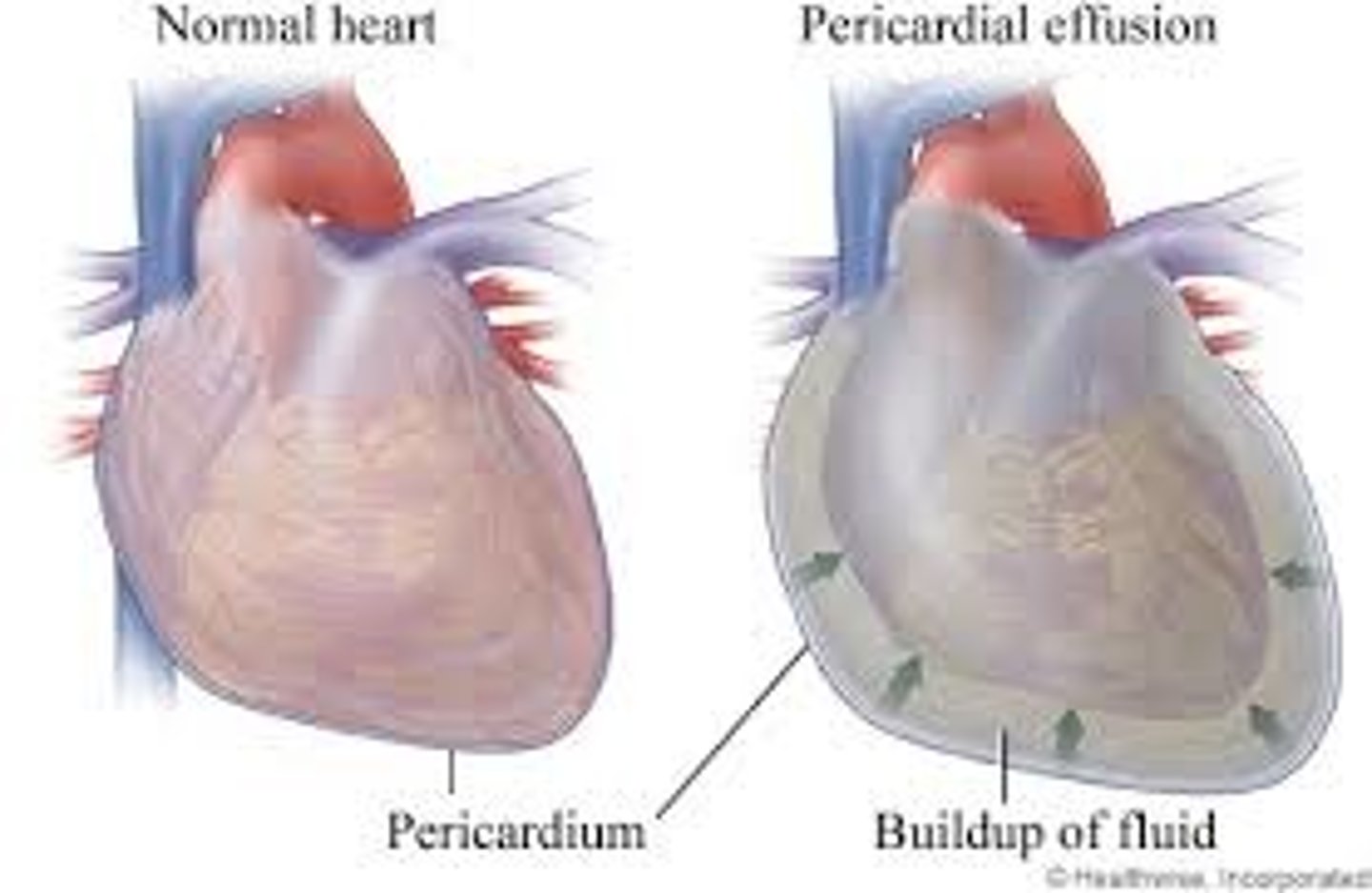
what is cardiac tamponade?
-life-threatening cardiac compression from fluid accumulation
-caused by pleural effusion
-so much fluid that the heart is compressed and it cannot pump effectively
-prevents stretching and filling during diastole leading to decreased cardiac output
-arterial pressure decreases because of decreased cardiac output
-venous pressure rises because of accumulation of blood
what are the manifestations of cardiac tamponade?
-falling arterial pressures
-rising venous pressures
-narrowing pulse pressure
-muffled heart sounds! (they are drowned out by all the fluid)
-becks triad!!! (hypotension, JVD, muffled heart sounds)
what is constrictive pericarditis?
-long-term or chronic inflammation of pericardium
-loss of elasticity from chronic inflammation
-can result in a thickened pericardium
-becomes thick and fibrous and sticky and gets stuck on the heart
-decreased cardiac output
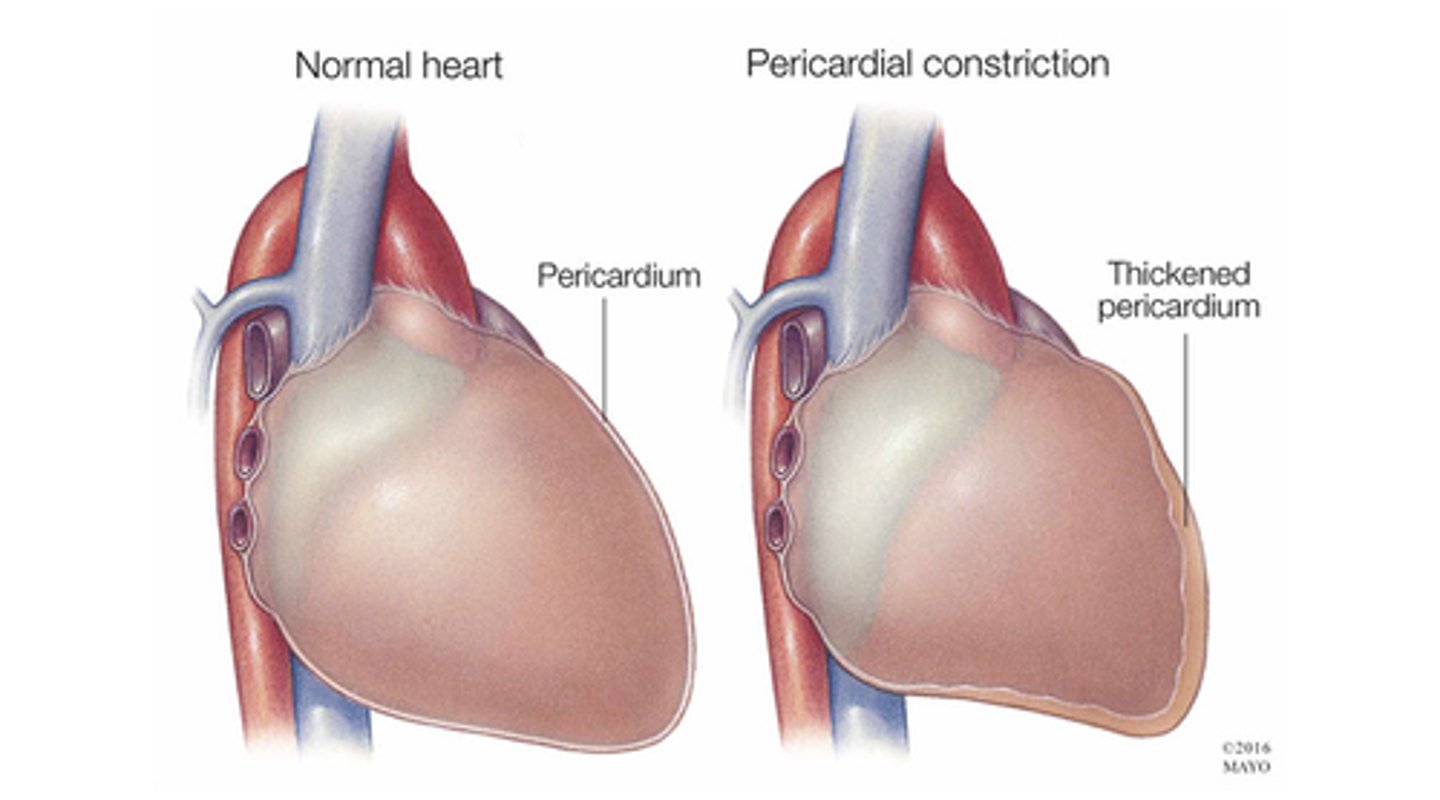
what are the manifestations of constrictive pericarditis?
-pericardial friction rub (grating sound)
-sharp and sudden severe chest pain that
increases with deep inspiration and decreases when sitting up/leaning forward
-dyspnea
-tachycardia
-palpitations
-edema
-flulike symptoms
what is infective endocarditis?
-inflammation and infection of the endocardium
-commonly caused by a bacteria such as streptococcus and staphylococcus!!
-thrombi form that travel (emboli) causing blockages
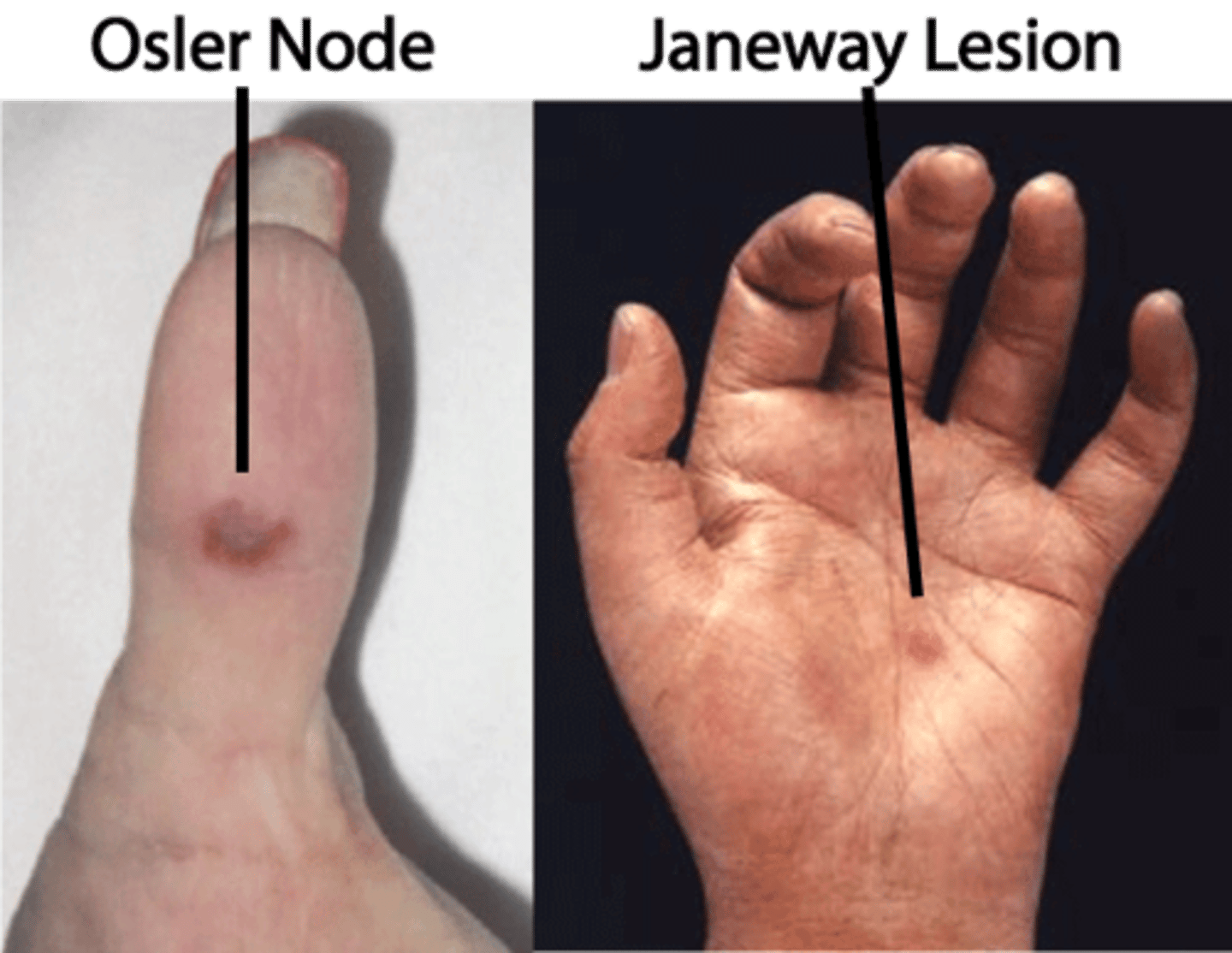
what are the manifestations of infective endocarditis?
-roth spots (retinal hemorrhages with pale/white centers)
-petichae
-osler nodes (painful, tender, red or purple nodules)
-new onset heart murmur
-janeway lesions (painless, flat, erythematous macules)
-anemia
-splinter nail-bed hemorrhages
-emboli
what are the risk factors associated with infective endocarditis?
-IV drug use!
-valvular disorder!
-prosthetic heart valves/implanted devices!
-rheumatic heart disease
-aortic coarctation
-congenital heart defect!
-Marfan Syndrome
what are the life-threatening complications associated with infective endocarditis?
-myocardial infarction
-stroke
-pulmonary embolism
*this is because of the emboli that infective endocarditis cause!
what is infective myocarditis?
-uncommon and poorly understood inflammation of myocardium
-causes the heart muscle to become thick and swollen
-penetration of an organism into the myocardium which causes muscle fiber disfunction
-organisms, blood cells, toxins, and immune substances damage the muscle
-associated with autoimmune disorders such as lupus
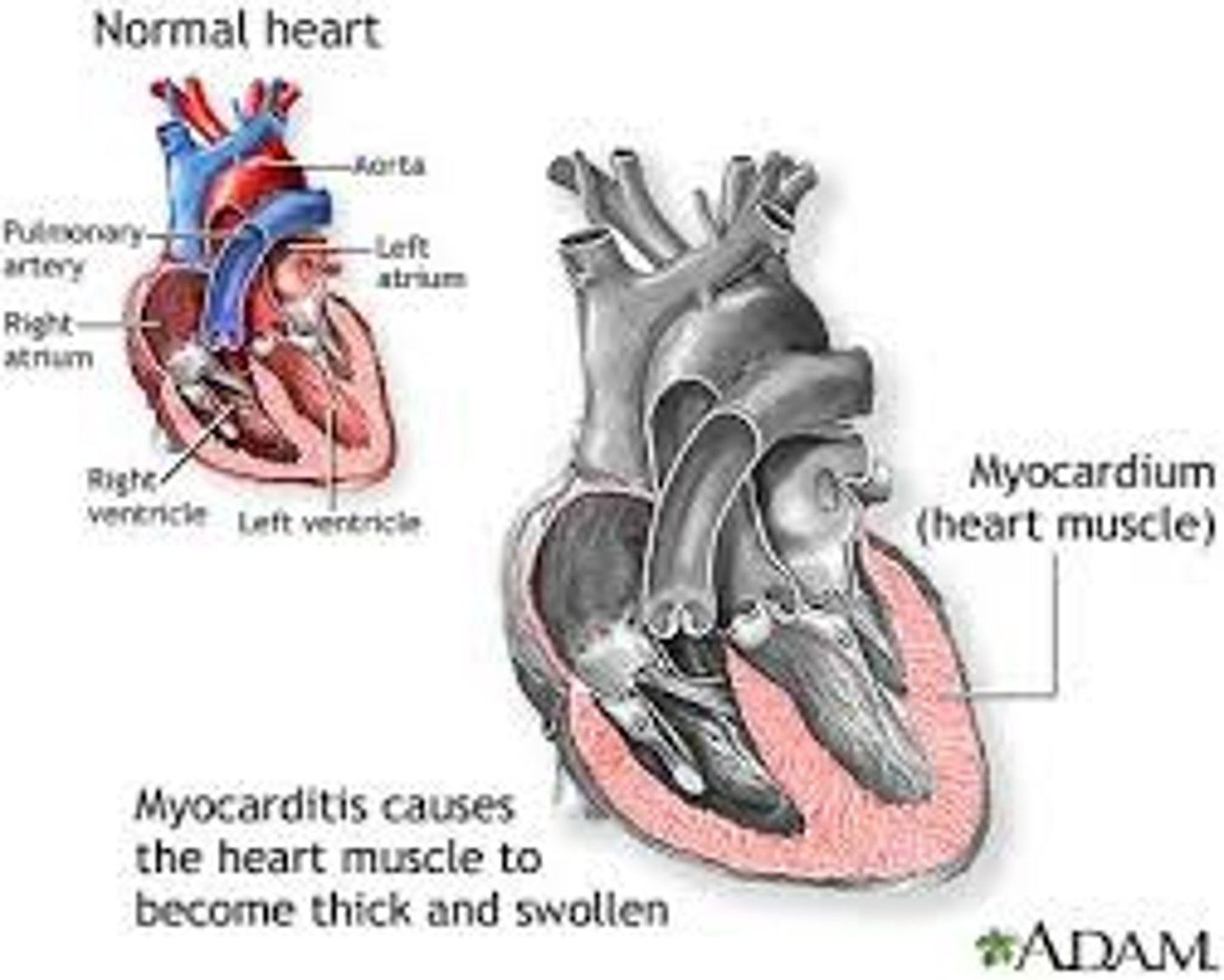
what are the complications associated with infective myocarditis?
-heart failure
-cardiomyopathy
-dysrhythmia
-thrombus formation
what are the manifestations of infective myocarditis?
-decreased urine output
-palpitations (heart beat not in regular rhythm!)
-leg swelling or fluid staying in the legs
what are valvular disorders?
-conditions where one or more of the heart valves (aortic, mitral, tricuspid, pulmonary) do not function properly, disrupting normal blood flow through the heart
what is valve stenosis?
-NARROWING of a heart valve, restricting forward blood flow
-less blood is flowing through the valve
-decreases cardiac output and increases workload which causes hypertrophy
-atresia: failure to open valve, which may
accompany stenosis
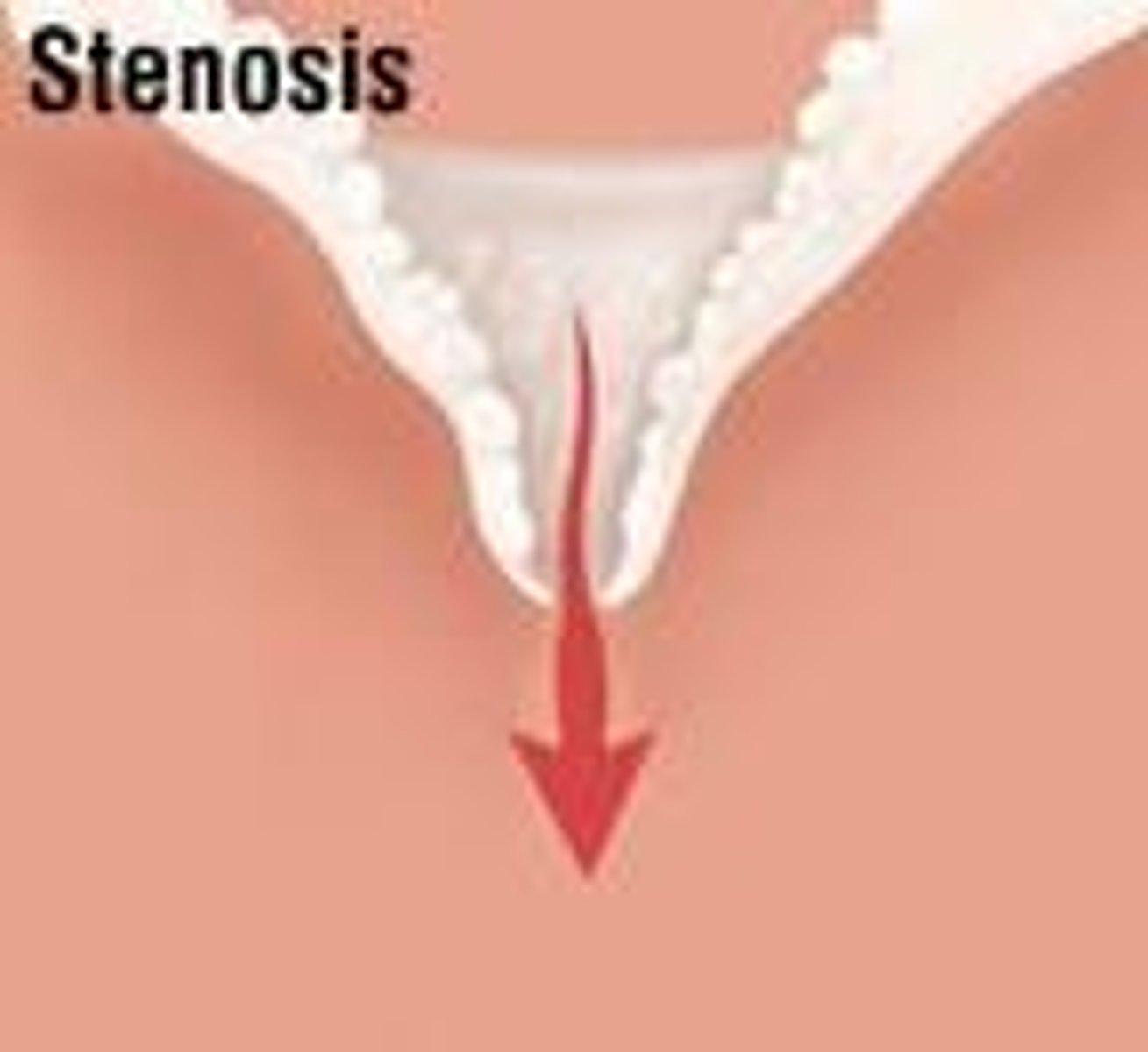
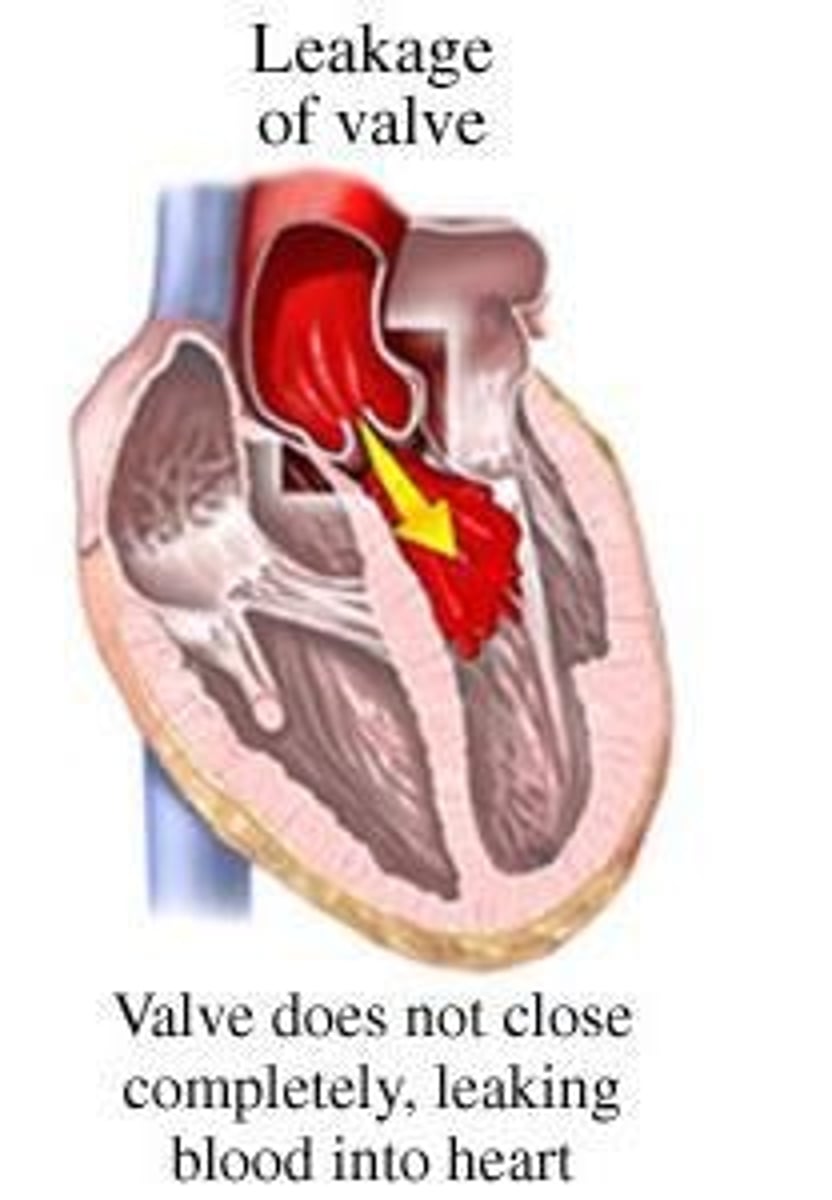
what is valve regurgitation?
-incomplete closure of a valve, allowing blood to leak backward
-bidirectional blood flow
-decreases cardiac output and increases workload on the heart which causes hypertrophy
-causes dilation of the ventricles
what causes valvular disorders?
-congenital defect
-infective endocarditis
-rheumatic fever
-myocardial infarction
-cardiomyopathy (big and sick heart/big because of hypertrophy)
-heart failure
what are the manifestations of valvular disorders?
-shortness of breath
-fatigue especially with with increase in physical activity
-chest tightness and difficulty breathing
-unable to lie down or having to get up to breath at night
-fainting
-palpitations
-swollen eyes, legs, or flatulence (the accumulation of gas in the gastrointestinal tract that is released through the rectum)
-heart failure or pulmonary embolism
what is cardiomyopathy?
-acquired or inherited conditions that weaken and enlarge myocardium
-disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body
-can cause heart failure or arrhythmias
-this is an umbrella term
what is dilated cardiomyopathy?
-most common type
-heart chambers are enlarged and weakened causing poor systolic function and decreased cardiac output and blood stagnation
-when ventricles become enlarged, baggy, and weak. they are overstretched!
-typically starts in the left ventricle and then reaches the right ventricle
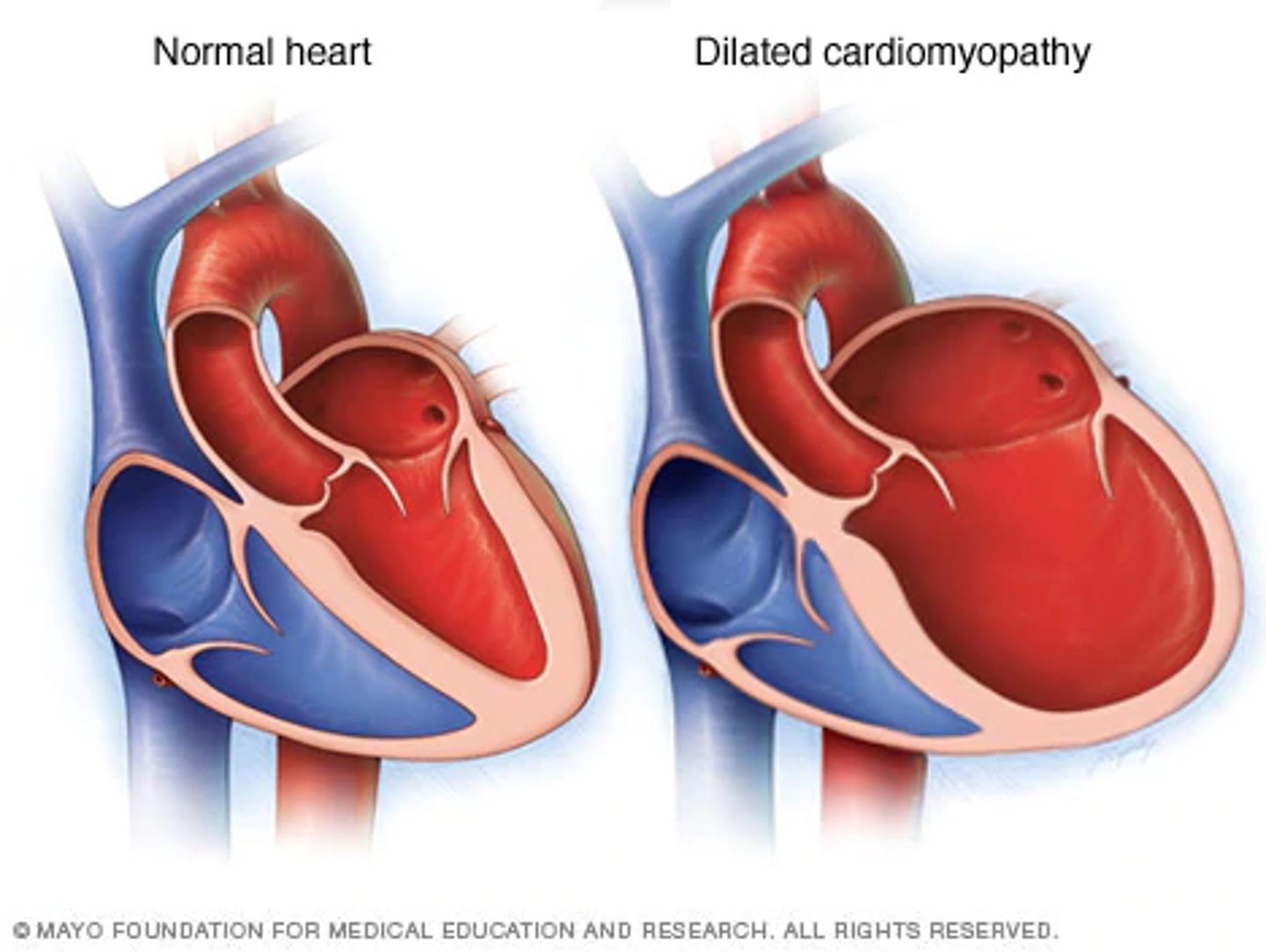
who is more as risk for developing dilated cardiomyopathy?
-african american men
-people of advancing age
what causes dilated cardiomyopathy?
-chemotherapy
-alcoholism
-cocaine abuse
-pregnancy, infection
-thyrotoxicosis
-diabetes mellitus,
-neuromuscular disease
-hypertension
-coronary artery disease
-med hypersensitivity
what are the manifestations of dilated cardiomyopathy?
-breathing changes and nonproductive
cough
-dysrhythmia(s), cardiac pain and
abnormalities
-abnormal lung sounds
-peripheral edema
-Ascites (the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal (abdominal) cavity) and hepatomegaly
-weak pedal pulse
-cool/pale extremities
-poor capillary refill
-jugular vein distension
*sympathetic nervous system and the kidneys compensate
*kidneys and heart are closely related
what is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
-thickening of the heart muscle (often the intraventricular septum) that makes filling difficult and is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death
-the ventricle wall becomes stiff and unable to relax
-hence hypertrophy! an increase in the size of the heart!
-heart becomes scarred!
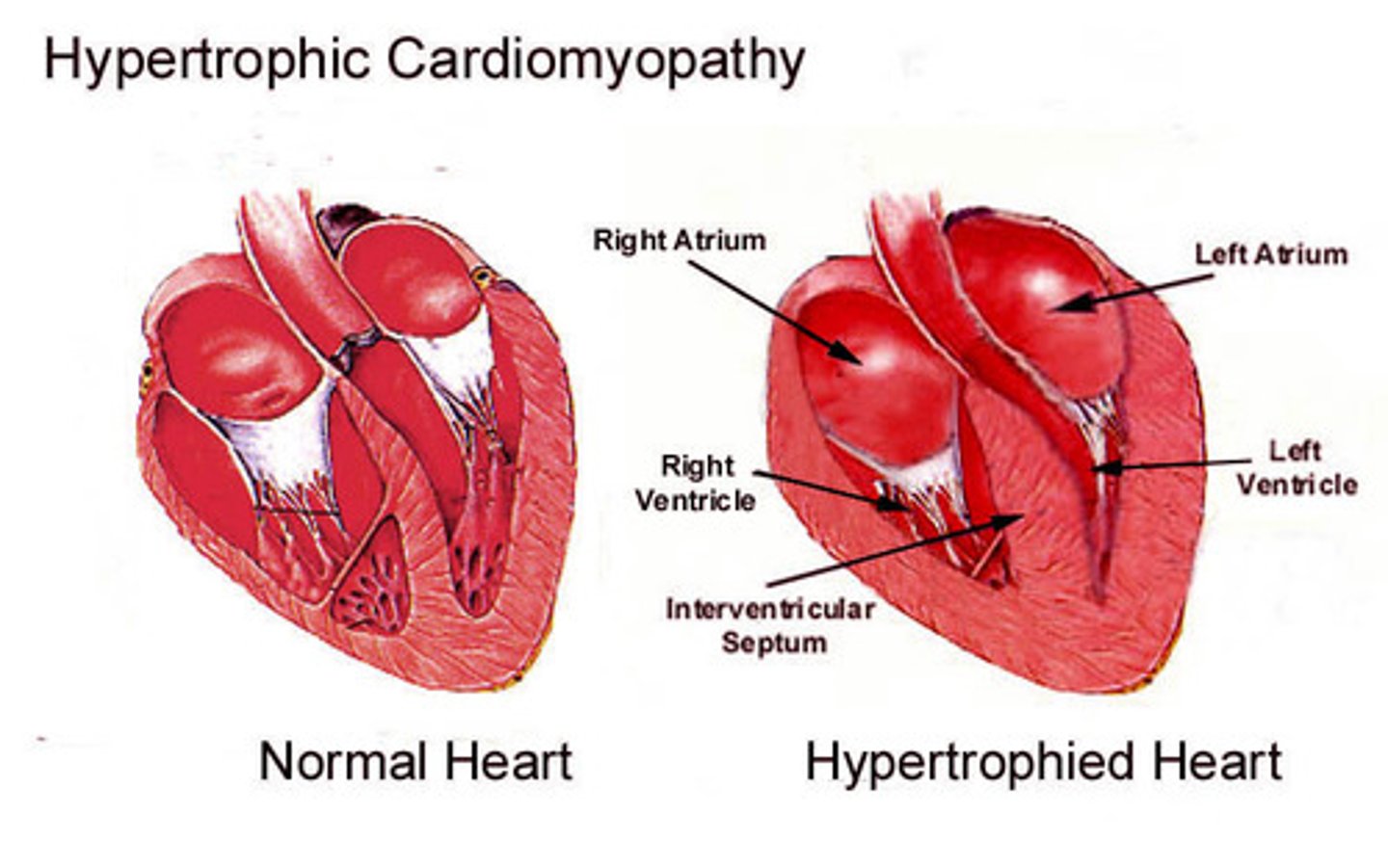
what are the risk factors associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
-hypertension
-obstructive valvular disease
-thyroid disease
-dominant genes
what are the manifestations associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
-dyspnea/intolerance on exertion (exercise should be avoided)
-syncope (a temporary loss of consciousness ("fainting") due to reduced blood flow and oxygen to the brain)
-orthopnea (difficulty breathing when lying flat)
-angina (chest pain or discomfort caused by reduced blood flow)
-dysrhythmia
-left ventricular failure
-myocardial infarction
what is restrictive cardiomyopathy?
-the ventricles are stiff and rigid and CANNOT relax
-note this is difference from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy because the walls are not thickened here!
-affects diastolic function
-poor prognosis
what are the causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy?
-amyloidosis
-hemochromatosis
-radiation
-connective tissue diseases
-myocardial infarction
-sarcoidosis
-cardiac neoplasms
what are the manifestations of restrictive cardiomyopathy?
-fatigue
-breathing and lung changes
-angina
-hepatomegaly
-jugular vein distension
-ascites
-murmurs
-peripheral cyanosis
-pallor
what are dysrhythmias?
-abnormal or irregular heartbeat (rate and
rhythm)
what is preload?
-volume of blood in ventricles at end of diastole
-ventricles are relaxed and about to contract
-the blood pressure in the left ventricle at the end of diastole right before the ventricles contract
in what situations is preload increased?
-hypervolemia
-regurgitation of cardiac valves
-heart failure
what is afterload?
-resistance LEFT ventricle must overcome to push blood out into circulation
increased after load=increased cardiac workload
in what situations is afterload increased?
-hypertension
-vasoconstriction (harder to pump)
what is heart failure?
-the inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the tissues for oxygen and nutrients!
-AKA congestive heart failure (CHF)
-leads to decreased cardiac output (CO) and increased preload/afterload!
what causes heart failure?
-congenital defect!
-myocardial infarction!
-valvular disease!
-dysrhythmia!
-thyroid disease
what are the compensatory mechanisms associated with heart failure?
-sympathetic nervous system
-renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (ultimately causes fluid retention)
-hypertrophy
*these will help at first but eventually will lead to heart failure!
what is the systolic disfunction associated with heart failure?
-decreased contractility not allowing the ventricles to pump hard enough during systole
what is the diastolic disfunction associated with heart failure?
-decreased filling which leads to not enough blood filling the ventricles during diastole
what is left side heart failure?
-left ventricle is unable to pump which results in blood backed up in lungs which causes pulmonary congestion
-causes dyspnea and activity intolerance
-associate with pulmonary circulation!!
*usually experience pulmonary dysfunction as a manifestation
what causes left sided heart failure?
-left ventricular infarction
-hypertension
-aortic or mitral valve stenosis
what is right sided heart failure?
-failure of the right ventricle to pump efficiently causing blood to be backed up
-blocks the peripheral circulation!!
what causes right sided heart failure?
-pulmonary disease (if it is not caused by left sided failure it is caused by this!)
-left-sided failure!
-pulmonic or tricuspid valve stenosis
what are the manifestations of left side heart failure?
-pulmonary congestion
-cough
-crackles
-pink-tinged sputum
-tachypnea
-tachycardia
-fatigue
-cyanosis
-exertional dyspnea
*notice how these all have to do with respiratory distress
what are the manifestations of right side heart failure?
-peripheral edema
-ascites
-enlarged spleen and liver
-JVD
-weight gain
-increased peripheral venous pressure
what are aneurysms? (a result of ineffective tissue perfusion)
-bulging blood vessels that can burst
-caused by a weakening of an artery
-commonly aortic and abdominal
* a true aneurysm affects all three vessel layers
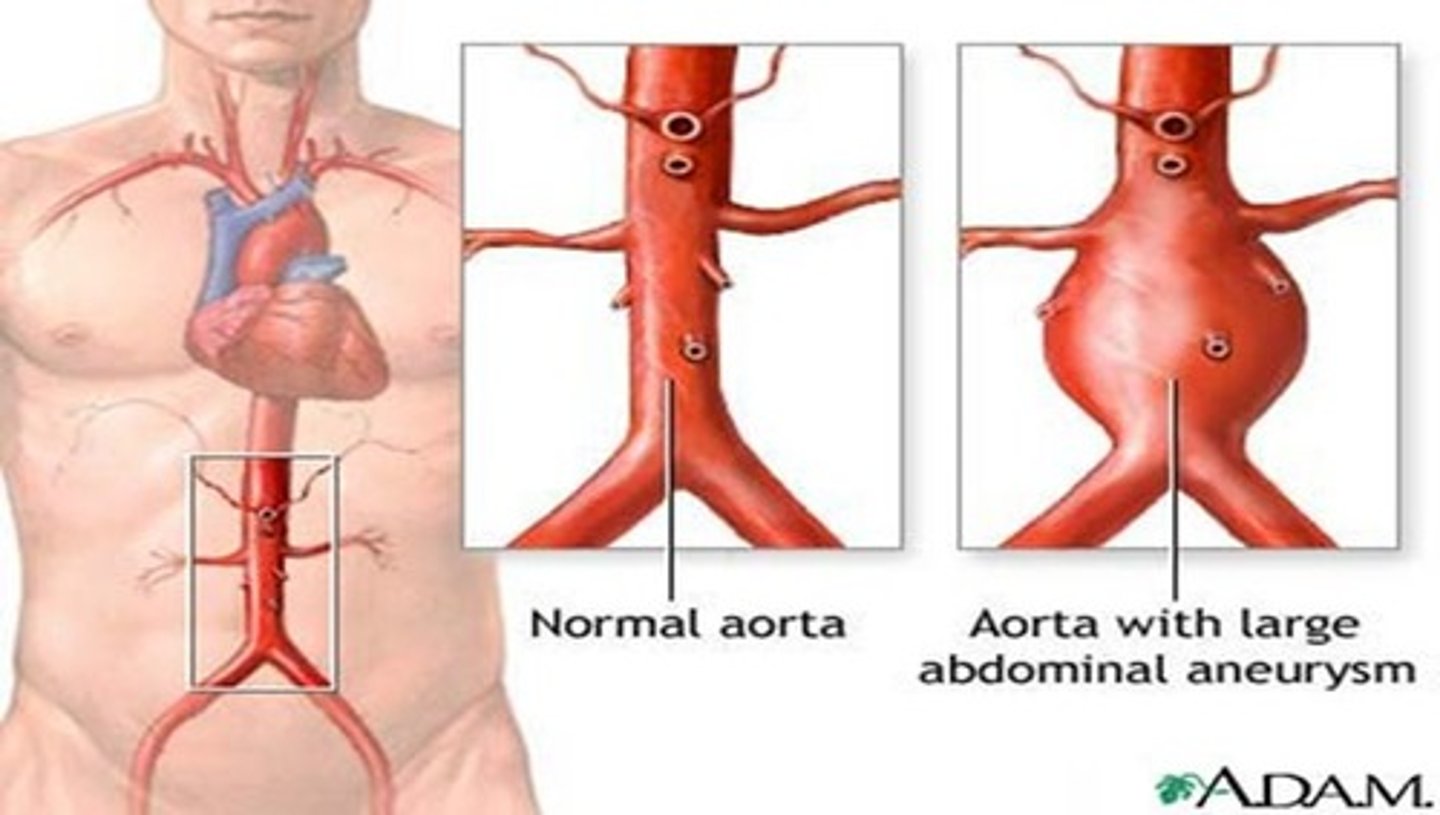
what is a possible consequence/complication to aneurysms?
-exsanguination which is severe loss of blood to the point of extreme weakness or death
what is a sacular aneurysm?
bulge on the side which is asymmetrical
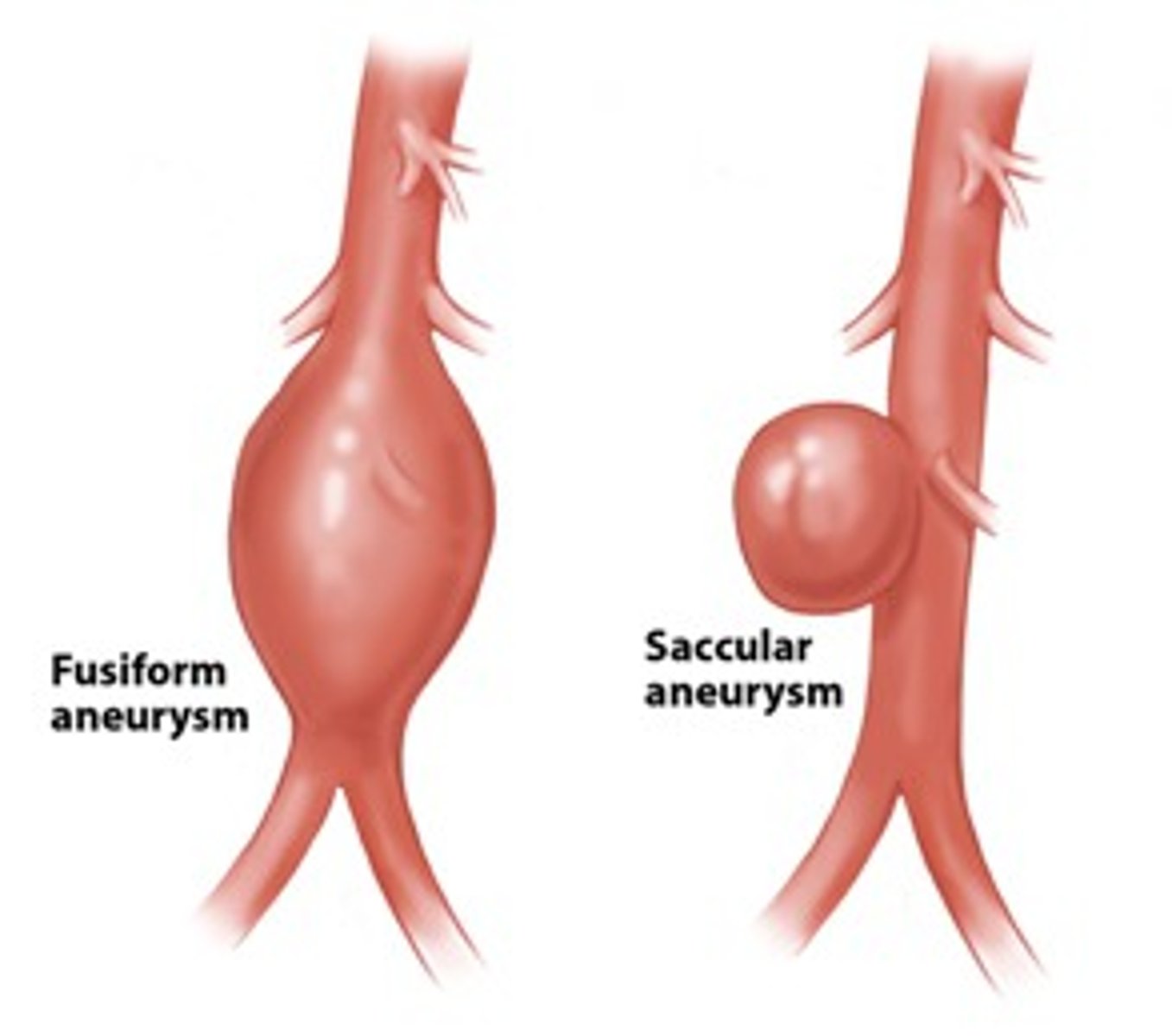
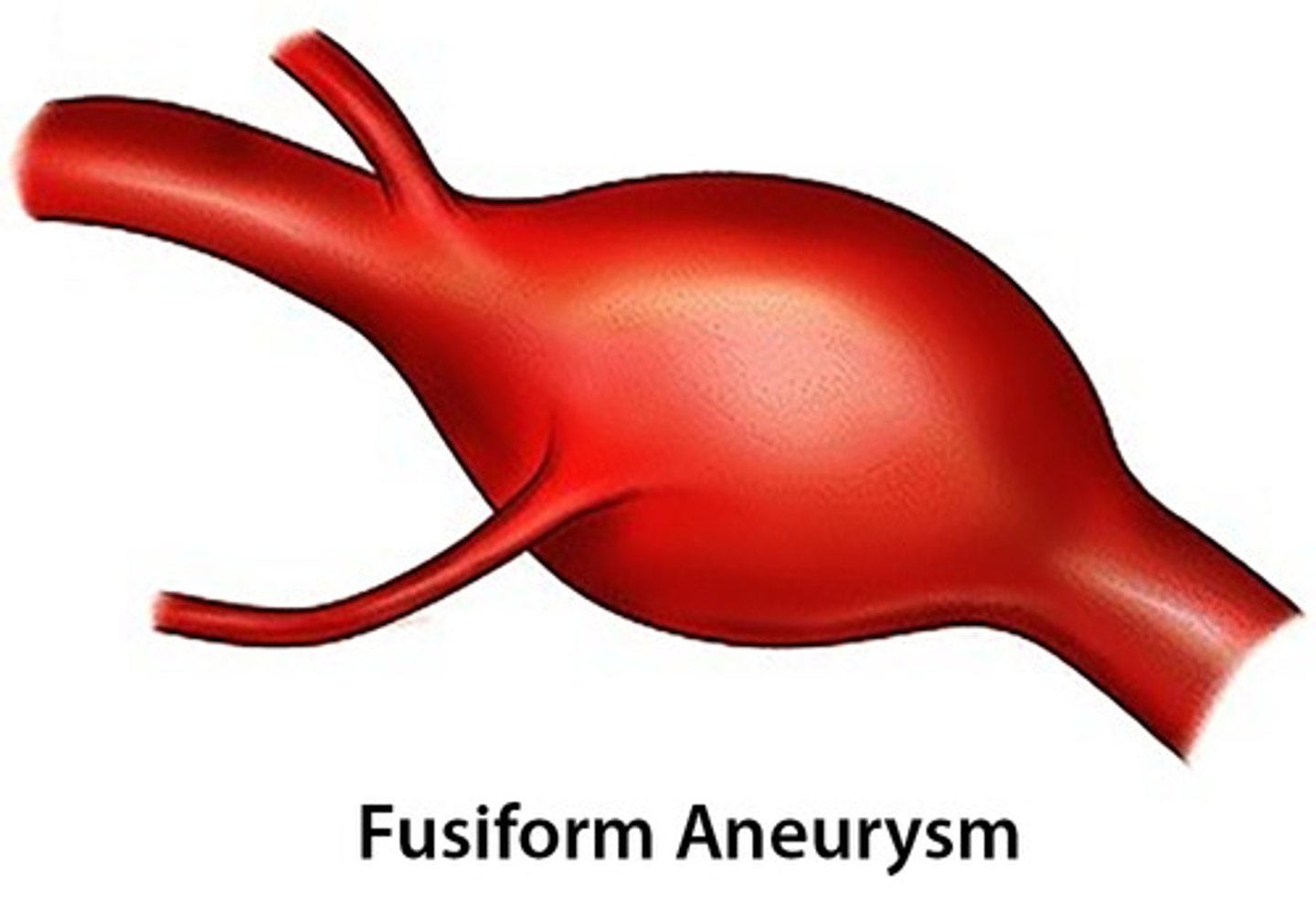
what is fusiform aneurysm?
-involves complete circumference of artery
-symmetrical
what is a dissecting aneurysm?
-not a true aneurysm because it occurs in the inner layers
what is a right sided valvular disorder?
what is a left sided valvular disorder
what is the difference between ischemia and infarction?
-ischemia can lead to death which is death
-ischemia is lack of oxygen leading to hypoxia and/or pain
what are the manifestations of aneurysms?
-depend on location and size
-may be asymptomatic
-may include: pulsating mass!
-pain
-respiratory difficulty
-neurologic decline
what is dyslipidemia?
high levels of lipids in the blood which increases risk for chronic disease
What are LDLs (low density lipoproteins)?
-"bad cholesterol"
-absorbed by cells in need of cholesterol for membrane repair or steroid synthesis
-most invasive in nature
What are HDLs (high density lipoproteins)?
-"good cholesterol"
-helps remove LDL choles
what is atherosclerosis?
-chronic inflammatory disease that is initiated by a vessel wall injury!
-leads to thickening/hardening of the arterial wall!!
-leads to platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction
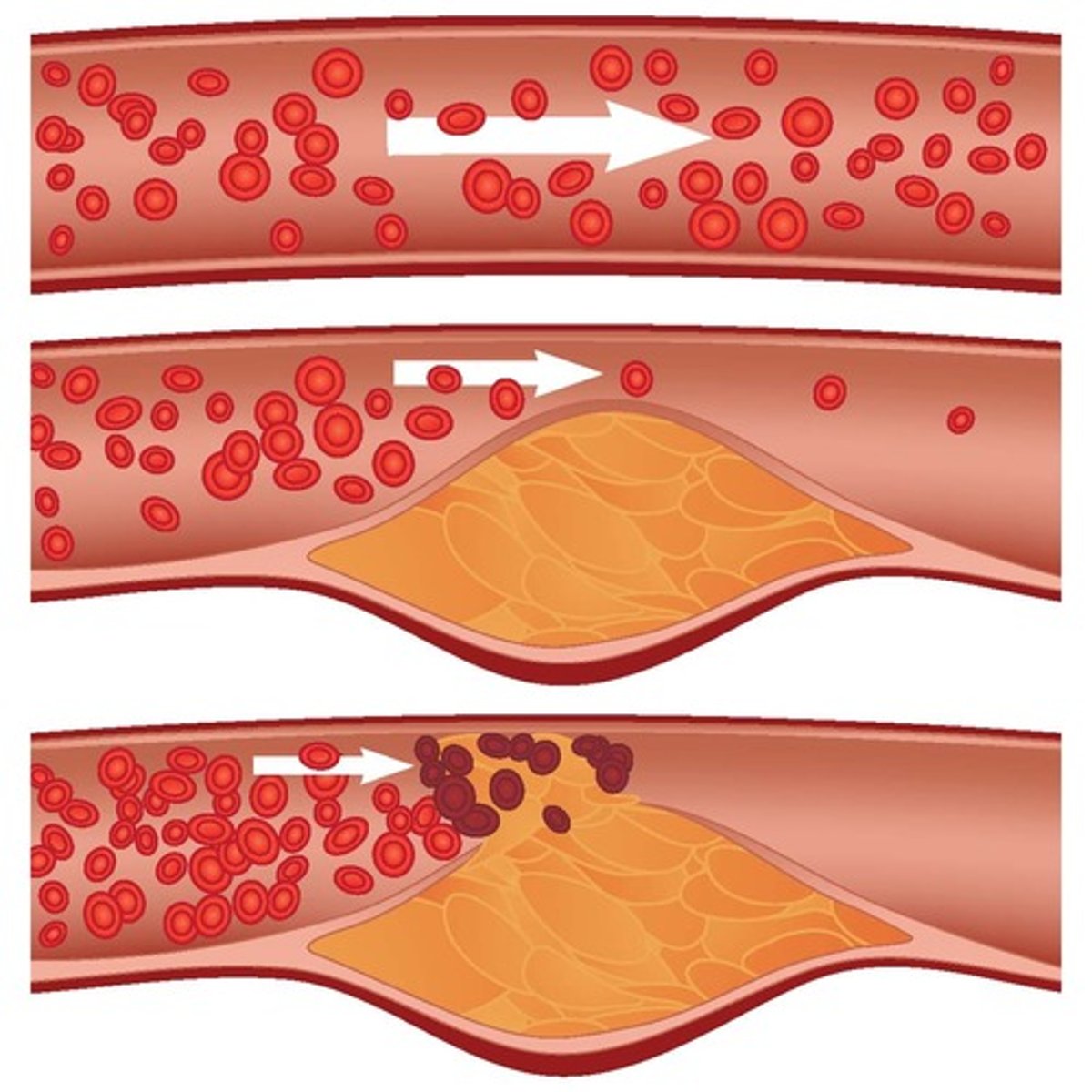
what are risk factors associated with atherosclerosis?
-diabetes
-obesity
-smoking
-hypertension
-immobile/sedentary life-style
-family history
-dyslipidemia
what are the manifestations of atherosclerosis?
-asymptomatic until complications develop
-the blockage will usually be above 70% by the time symptoms manifest
what is peripheral vascular disease?
-narrowing of the peripheral vessels (arteries and/or veins)
what is trombonists obliterans (AKA buerger disease)?
-chronic inflammatory condition of the arteries
-can lead to thrombosis
-idiopathic
-20-40 men who smoke are more susceptible!
what is raynaud's phenomenon?
-attacks of vasospasm in the small arteries and arterioles of fingers and sometimes toes
-self-resolving
-ultimately can cause ischemia
-more common in females and associated with autoimmune diseases!
what is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
-narrowing or blocking of the arteries supplies the myocardium
-the most common type of heart disease in the U.S.
-leading cause of MI/death in the world in both men and women
what is obstructive CAD?
-when plaque accumulates in the large arteries causing narrowing and decreased blood supply to the myocardium
-blood flow can be completely occluded
what is non-obstructive CAD?
-large arteries are occluded by less than 50%
-also caused by damage or injury to the lining of the coronary arteries that impact the ability to vasodilate in response to increased myocardial
what is coronary microvascular disease?
-affects smallest vessels in the myocardium
-can be a normal part of aging
what is stable angina?
-angina=chest pain
-chest pain caused by ischemia that is initiated by increased oxygen demand and relieved with decreased demand (at rest)
-exertion induced!!
what is unstable angina?
-chest pain that become unpredictable
-occurs at rest or increases in frequency
and/or intensity
-considered a preinfarction (aka a warning sign!)
-unpredictable and it hurts!
what are the manifestations of angina's?
-angina that may radiate into the neck, jaw, arm, or back
-indigestion-like sensation
-nausea and vomiting
-extremely sweaty
-fatigue
-weakness
-dyspnea
which populations do not openly exhibit symptoms of anginas?
-women
-diabetics
what is a thrombus?
stationary blood clot that forms anywhere in the circulatory system
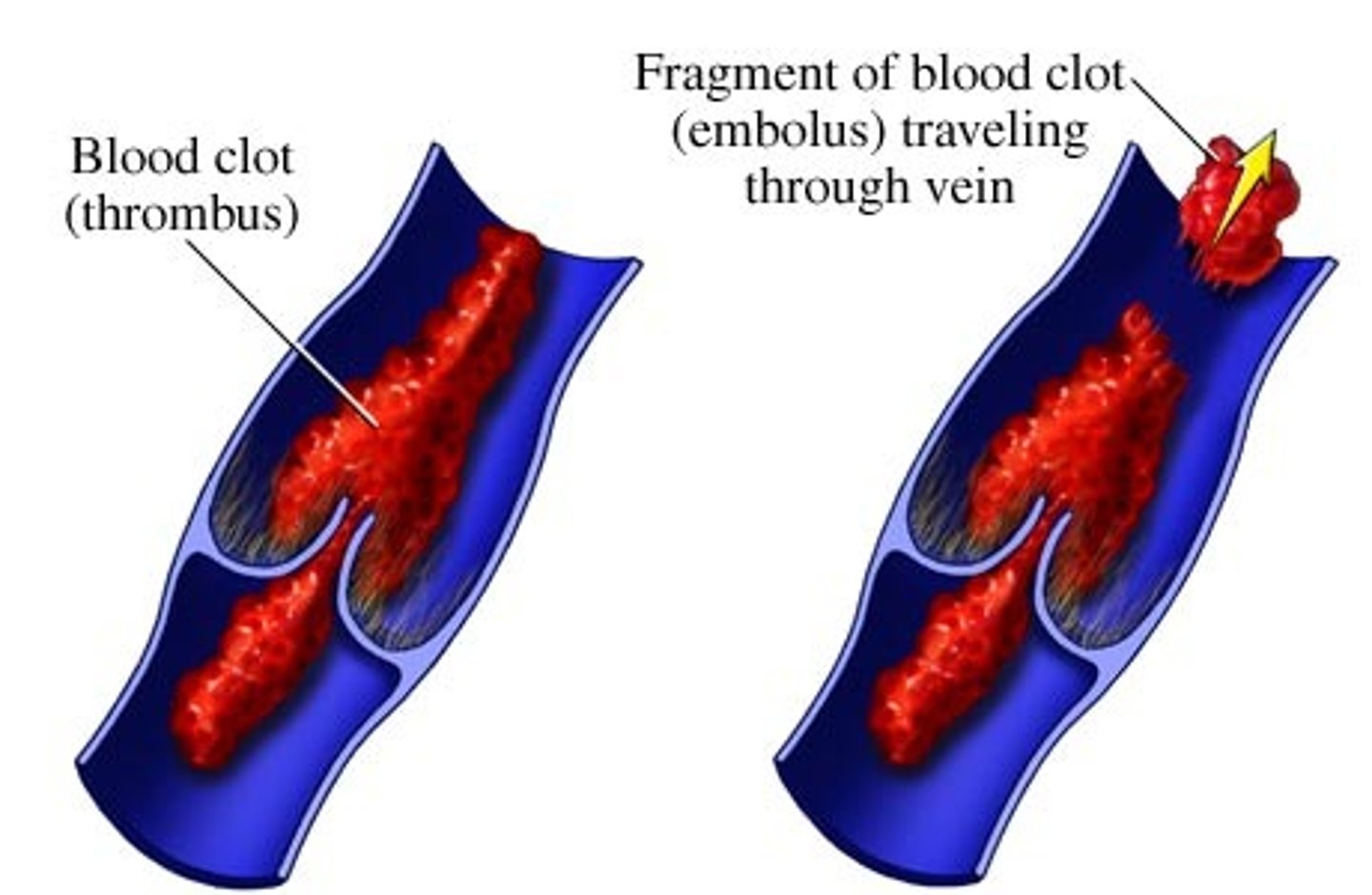
what are the three conditions that promote thrombus formation?
-endothelial injury
-sluggish blood flow
-hypercoagulability
which is the most common type of thrombi?
-venous thrombi more common that arterial due to lower pressure against gravity
what is an emboli?
-a traveling clot
-this is a portion of a thrombus that breaks loose
what is the relationship amongst emboli's and the right side of the heart origin?
-venous circulation that travels first to pulmonary circulation, creating a pulmonary embolism
what is the relationship amongst emboli's and the left side of the heart origin?
-arterial circulation and travel to other organs such as brain and heart, causing an infarction
what are the manifestations of pulmonary embolisms?
-sudden chest pain
-cough
-hemoptysis
what are the manifestations of a deep vein thrombosis?
-unilateral calf or groin pain
-swelling
-hot
-rednesss/erythema
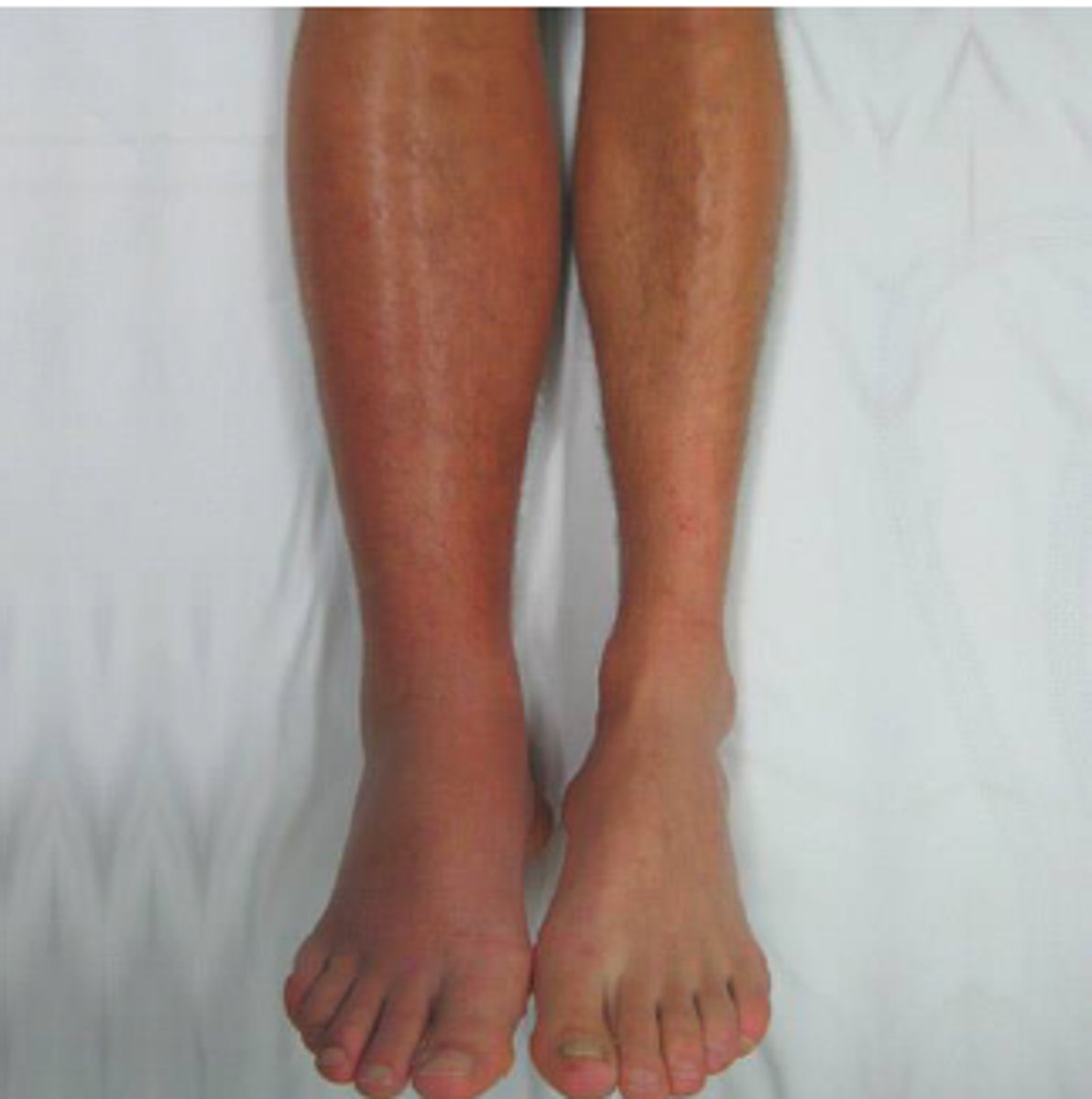
what is a pulmonary embolism?
-when thrombus originates elsewhere
and disrupts blood flow in the pulmonary
artery or its branches
what are varicose veins?
-dilated, tortuous superficial veins
-improper venous formation
-most commonly in the legs
-increased venous pressure and blood pooling causes venous enlargement
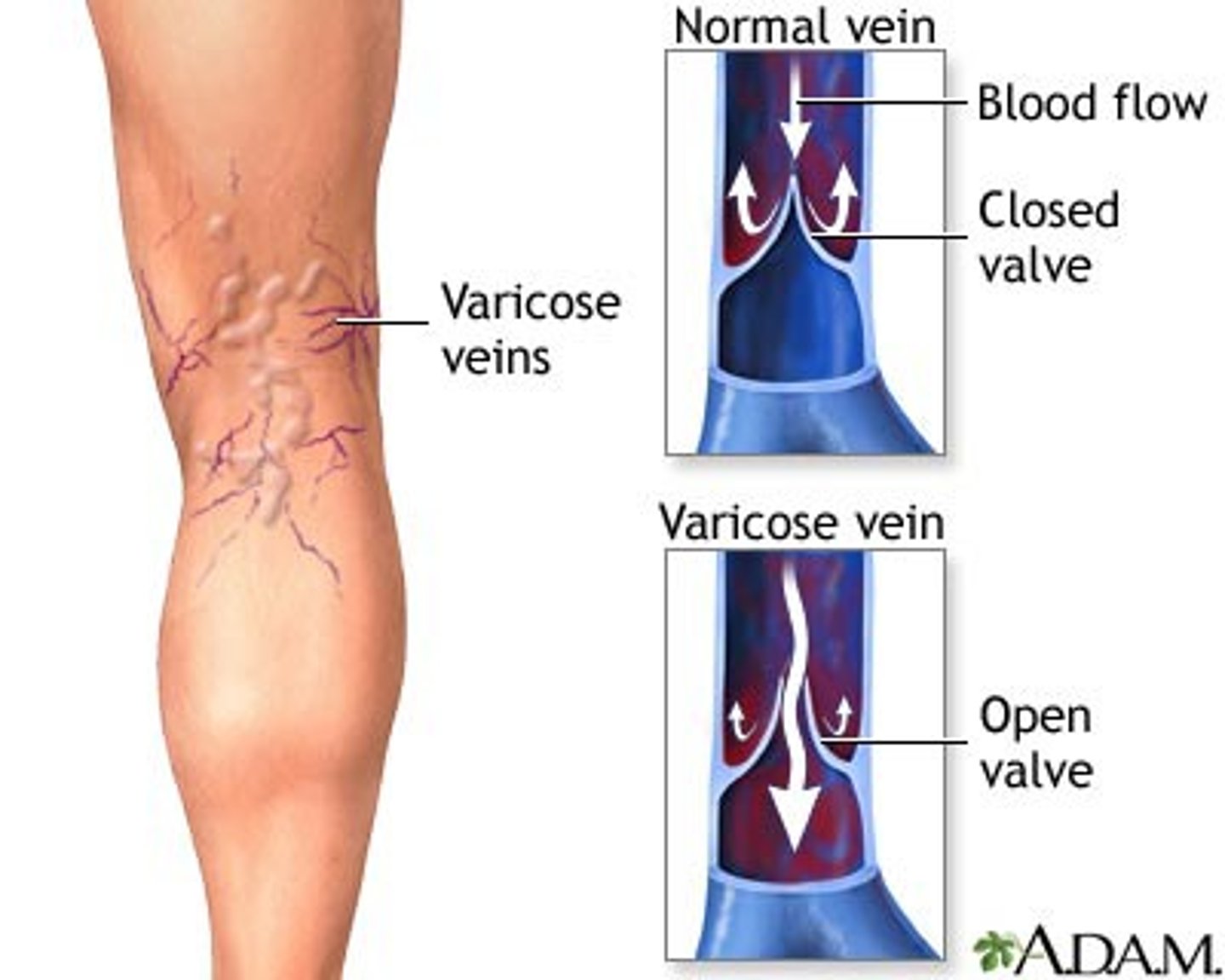
what are the risk factors for varicose veins?
-pregnancy
-obesity
-prolonged sitting and/or standing
-alcohol use and liver disorders
what are the clinical manifestations of varicose veins?
-shiny hairless pigmented skin on the legs and feet
-venous stasis ulcers
-irregular purplish bulging veins
-pedal edema
what is lymph edema?
-unusual swelling in the extremities
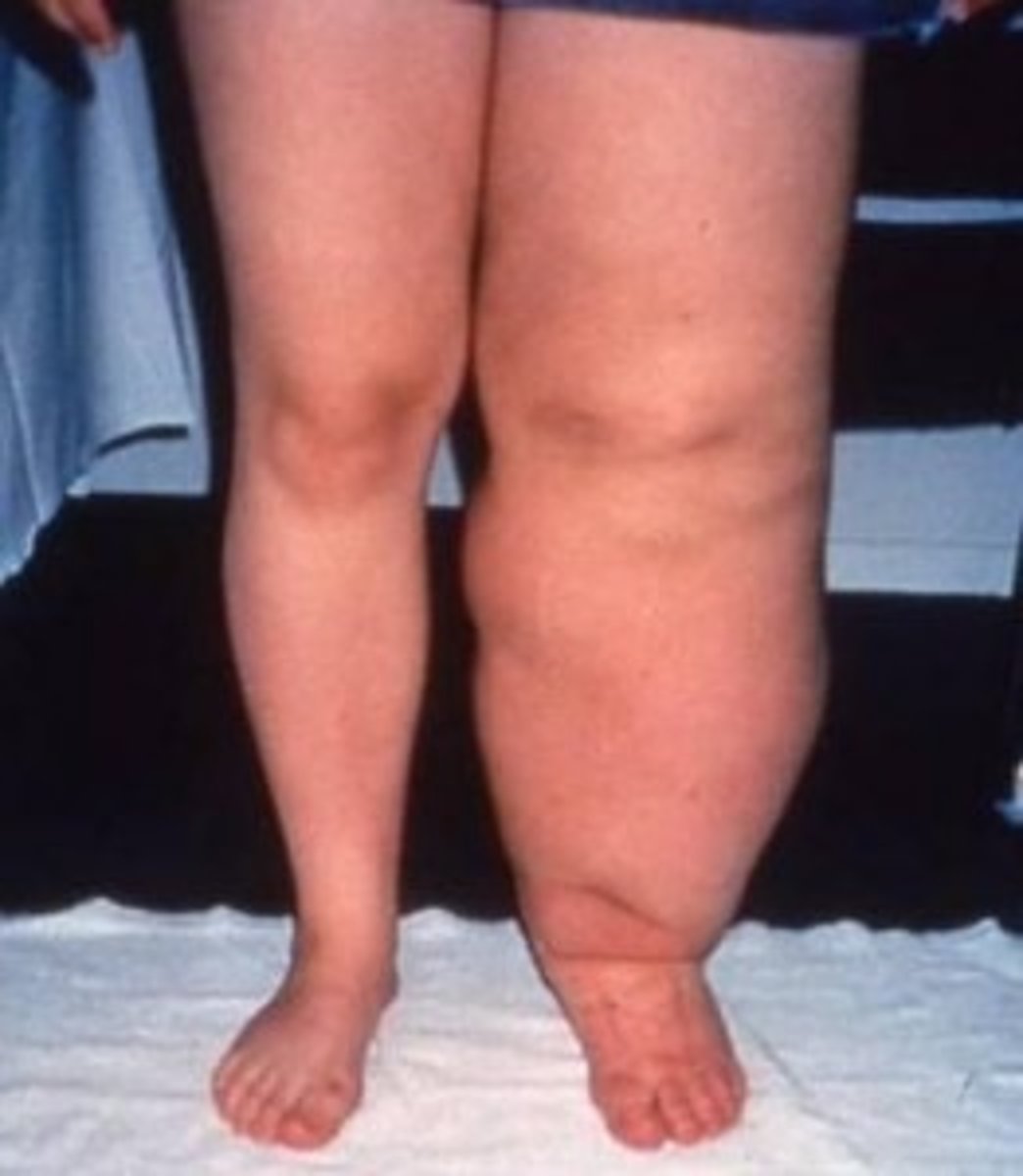
what causes lymphedema?
-rare and caused by congenital absence or decrease in the number of lymphatics
-lymph accumulation in the extremities that causes swelling and usually due to an obstruction of a lymph node
what is a myocardial infarction?
-death of the myocardium from the sudden blockage of coronary blood flow
-aka a heart attack
-myocardial oxygen supply cannot meet body's oxygen's supply
-myocardial cells die
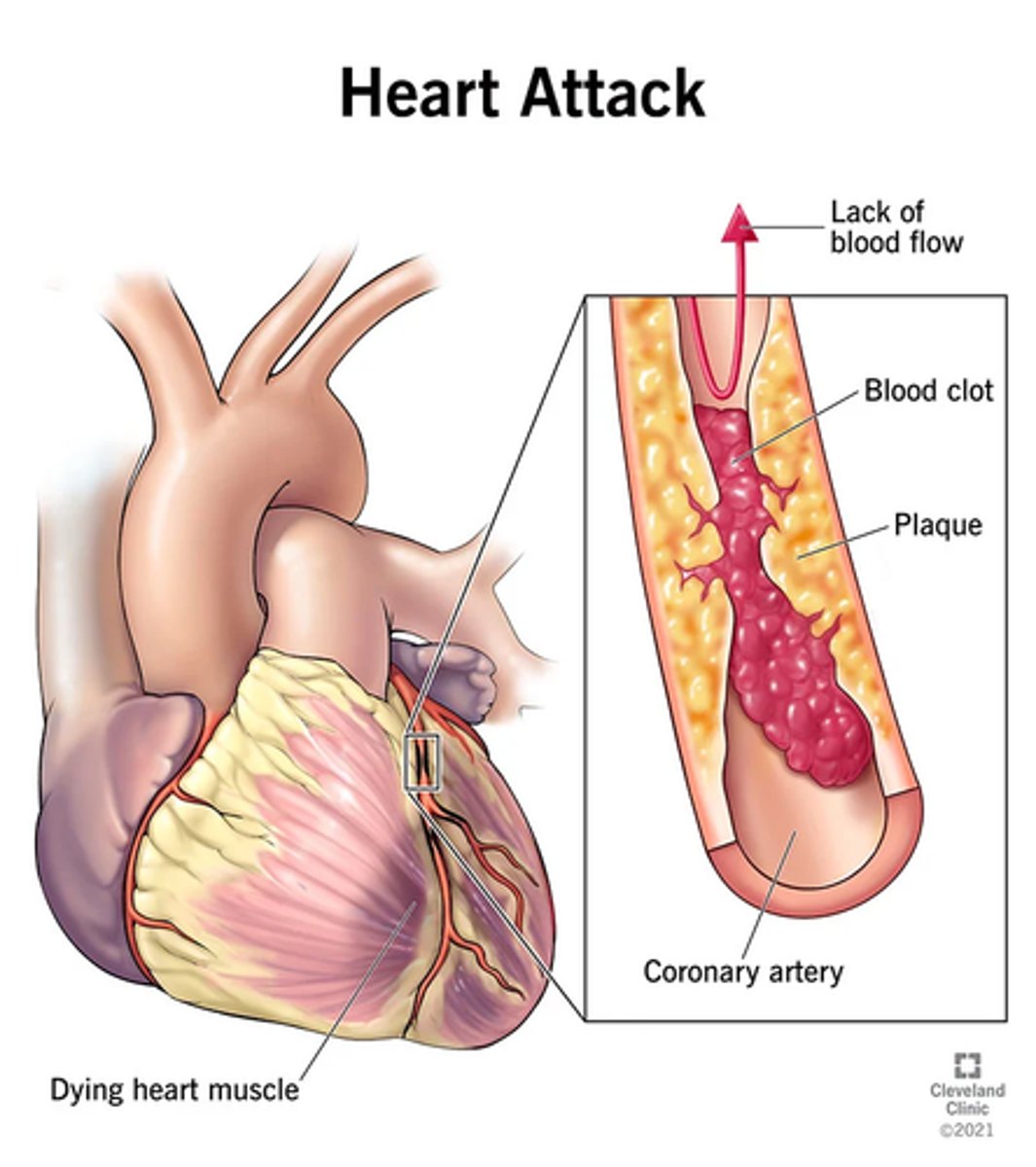
what are the risk factors associated with myocardial infarctions?
-dyslipidemia
-diabetes mellitus
-hypertension
-stress
-tobacco use
what are the manifestations of myocardial infarctions?
-diaphoresis
-elevation in cardiac biomarkers like triponin
-unstable angina that radiates
-indigestion sensation
-sleep disturbances
-dysrhythmias
what is hypertension?
-PROLONGED elevation in blood pressure creates excessive cardiac workload due to vasoconstriction increasing afterload
-decreased renal blood flow inappropriately activates renin- angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
what are the risk factors associated with hypertension?
-increased age
-african american
-fluid retention
-family history
-obesity
-high sodium intake
-high vitamin D intake
-stress
-smoking and alcohol
-inactivity
what is primary hypertension?
-most common
-develops gradually over time
-no identifiable cause
what is secondary hypertension?
-more sudden and severe
-caused by other factors such as renal disease, diabetes, adrenal gland tumors, certain medications can trigger hypertension
what is malignant hypertension (hypertensive crisis)?
-intense and non-responsive to interventions
-BP is at least 180/120 and the patient is
SYMPTOMATIC!
what are complications associated with hypertension
-cardiovascular disease (heart is working over time)
-stroke and brain complications
-kidney damage
-hypertrophy
-eye damage
-aneurysms and peripheral artery disease
what is orthostatic hypotension?
-orthostatic hypertension is a sustained increase in blood pressure (≥20 mmHg systolic or ≥10 mmHg diastolic) within 3 minutes of standing up from sitting or lying down
-lack of normal blood pressure compensation in response to gravitational changes on the circulation
what is virchow's triad?
1. circulatory stasis
2. hypercoagulability
3. vascular damage
*these are the 3 main risk factors for clot formation (thrombi/emboli)
*a clot will form when you have at least one (often more) of these factors according to virchow's triad
what is hypercoagulabilty in virchow's triad?
-when the blood is more likely to clot than normal
-causes like major trauma, cancer, or infection/sepsis