A4 - Axial Skeleton - Anatomic Variants
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
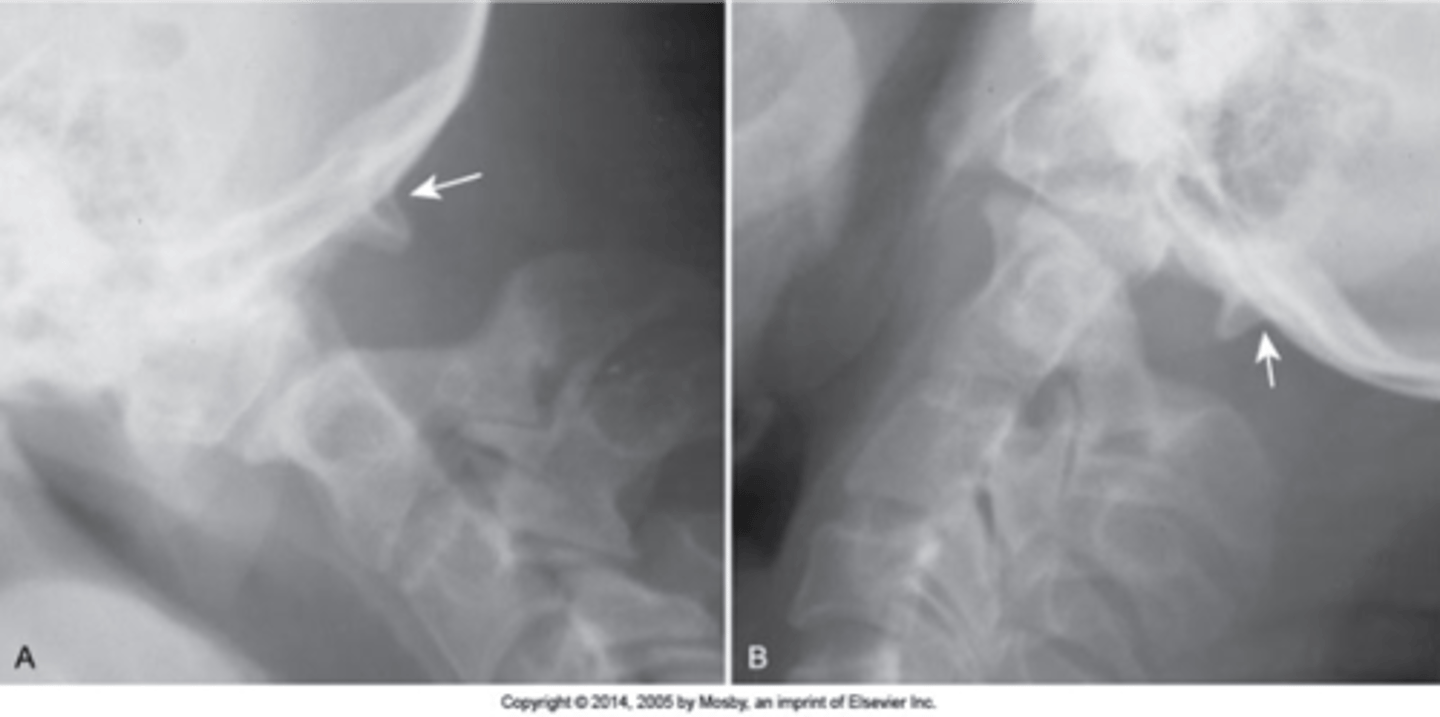
Occipitalization
C1 is fused to the occiput and there is a decreased/absence of space between the occiput and C1
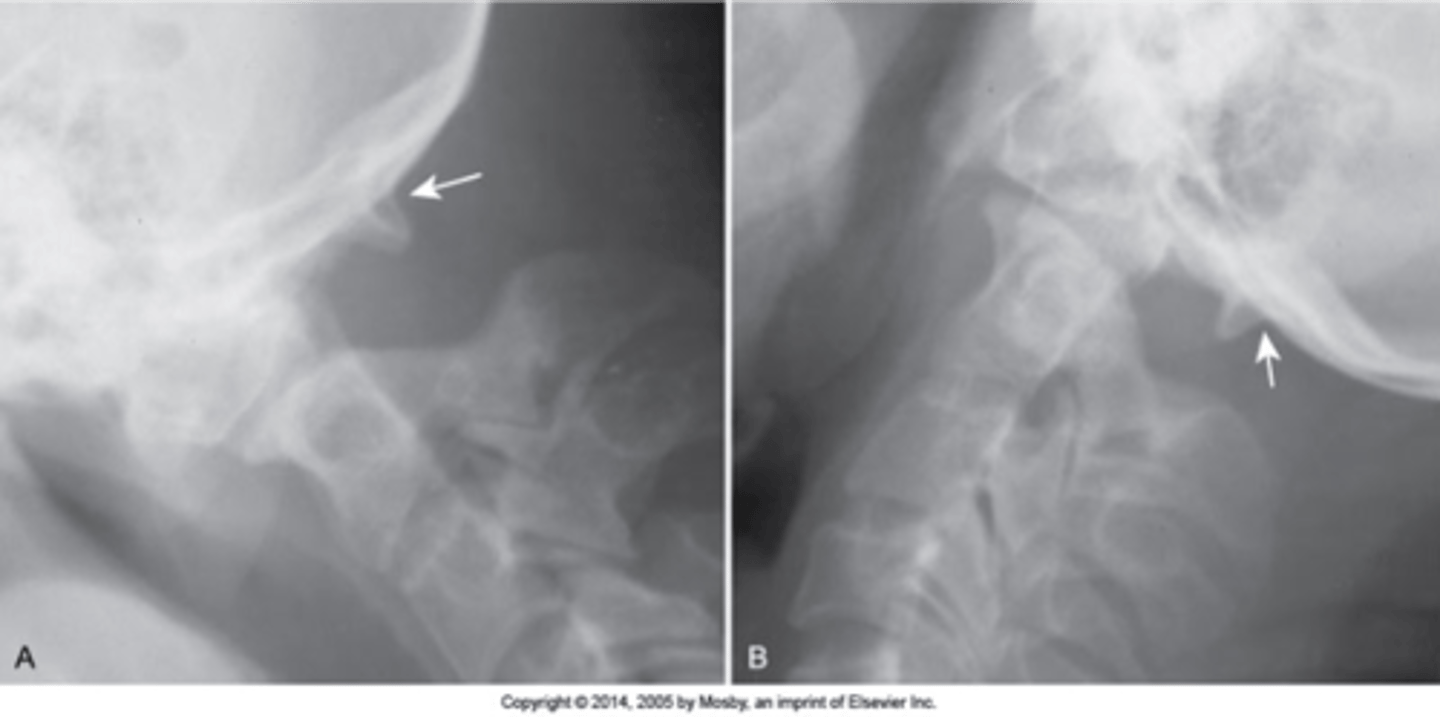
Atlantodental instability
Occipitalization is associated with _____
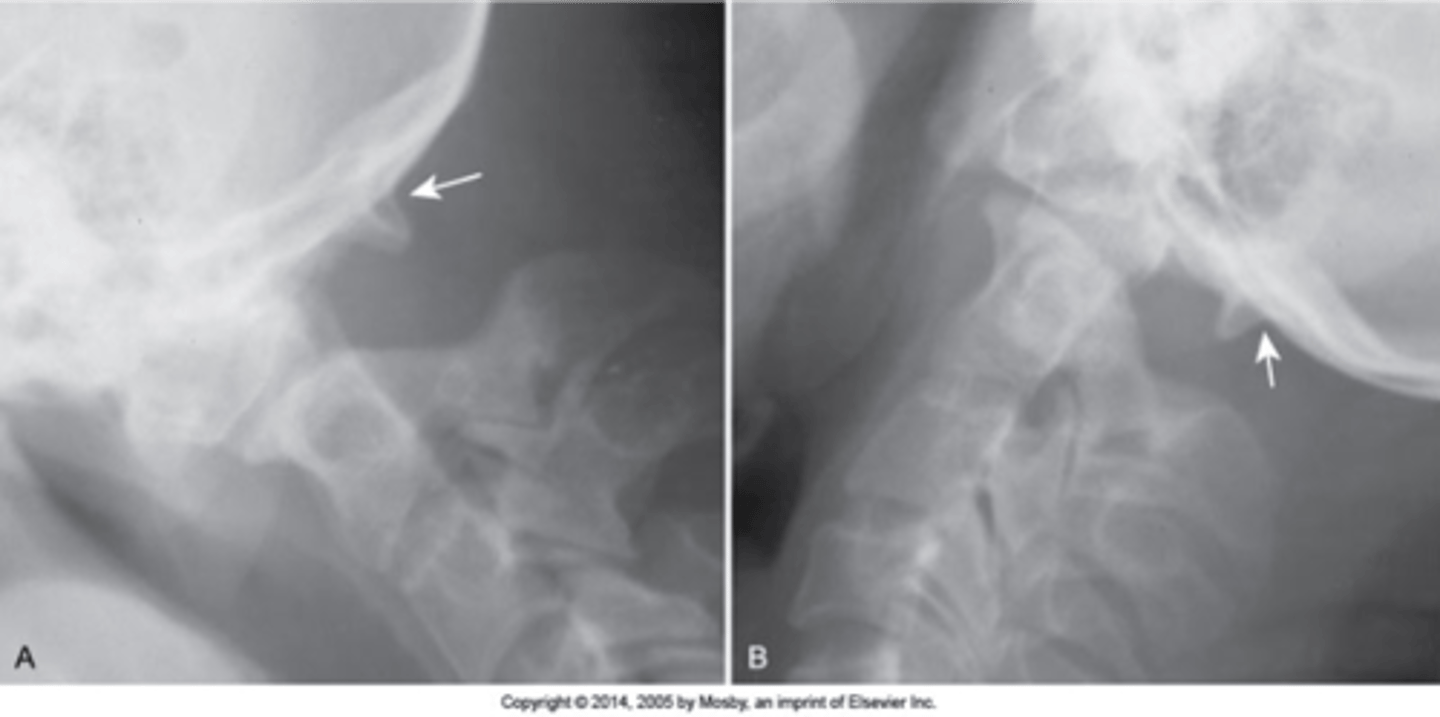
Flexion/extension
With occipitalization, you should do _____
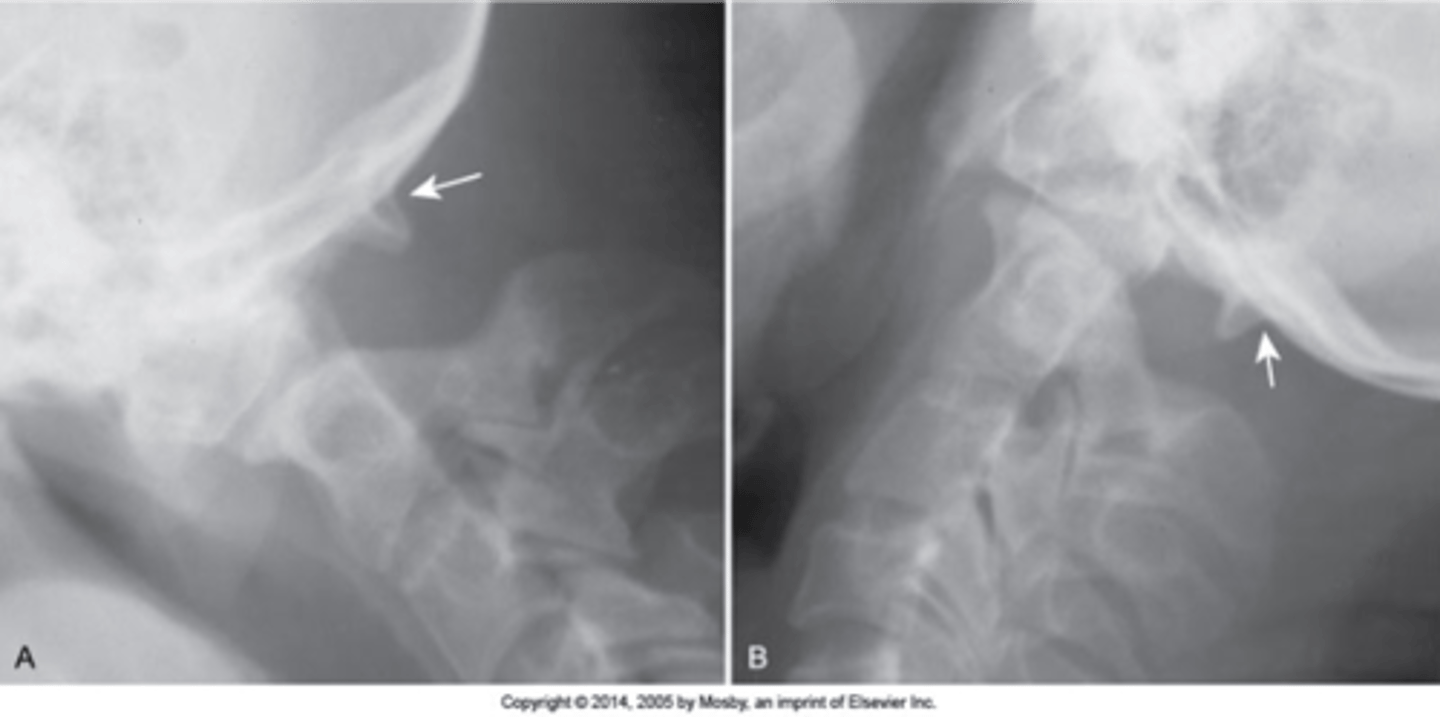
Decreased
Occipitalization is associated with _____ ROM, can have short neck/low hairline
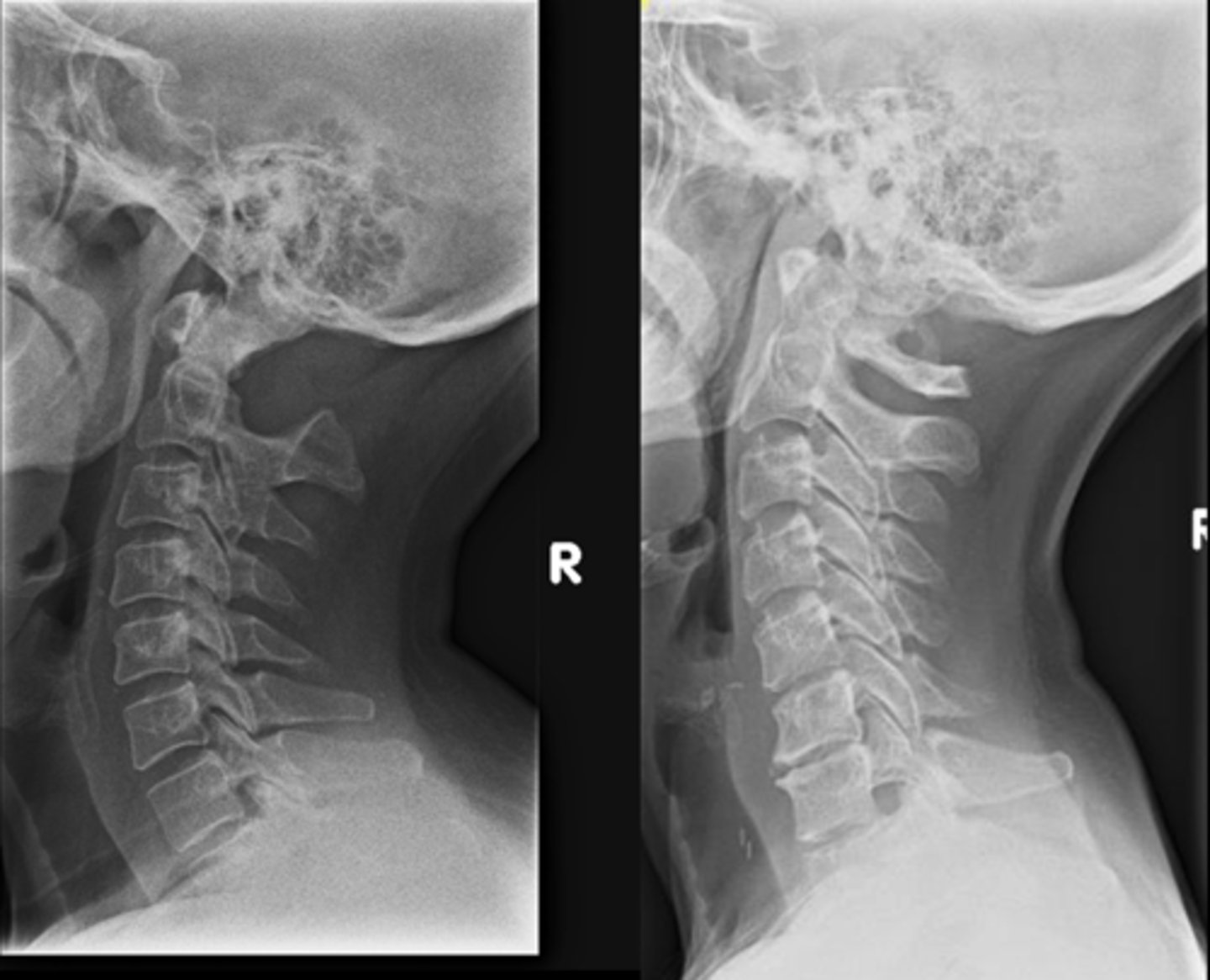
Agenesis of the posterior arch
Partial or complete failure of development of the posterior arch of C1
Primary
_____ radiographic findings of agenesis of posterior arch:
- Lack of an ossified posterior arch and the posterior tubercle (posterior tubercle may still be present at times)
- There is still a fibrocartilage non-ossified posterior arch present
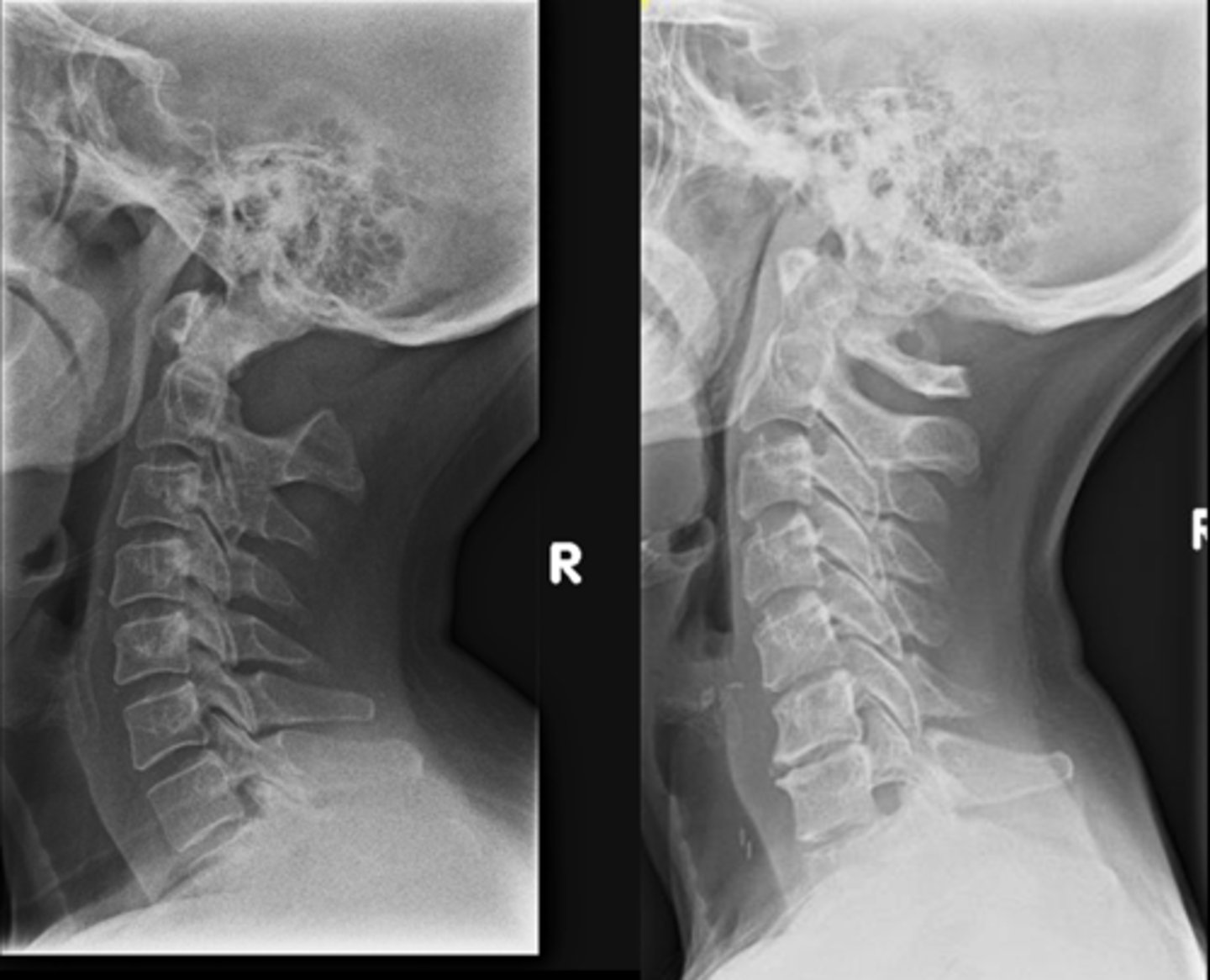
Secondary
_____ radiographic findings of agenesis of posterior arch:
- Hypertrophy of the anterior tubercle
- Enlargement of the C2 spinous process (megaspinous of C2)
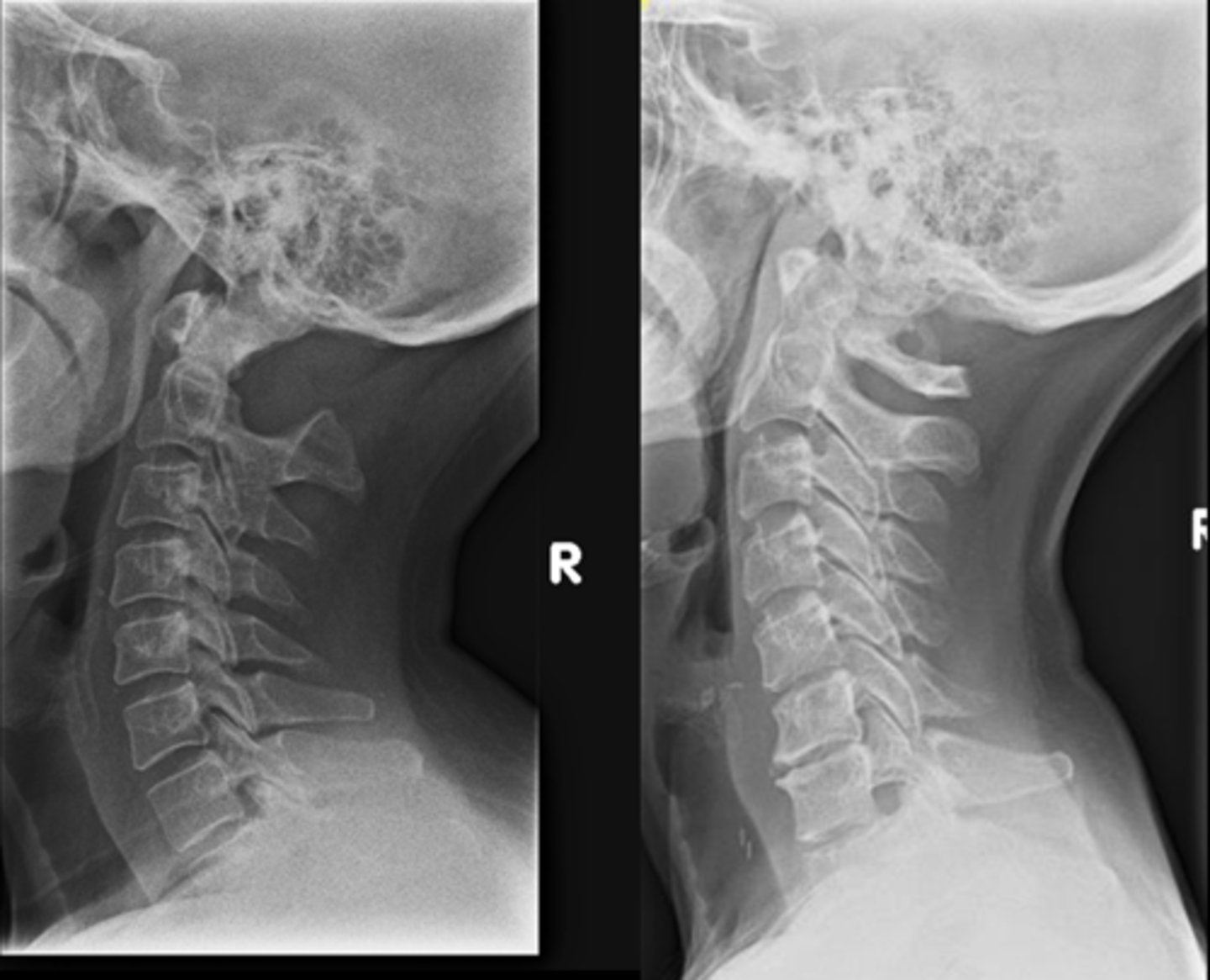
Transverse ligament
Agenesis of the posterior arch is associated with an absence or laxity of the _____
Atlantodental interspace
There is increased atlantodental/atlantoaxial instability with an increased _____
>3 mm
Normal ADI measurement in adults
>5 mm
Normal ADI measurement in children
Posterior ponticle
Calcification of the inferior/oblique aspect of the atlanto-occipital ligament/membrane
15%
Posterior ponticle is present in _____ of the population
Arcuate foramen
The hole that is formed by the ossification that the vertebral artery must pass through
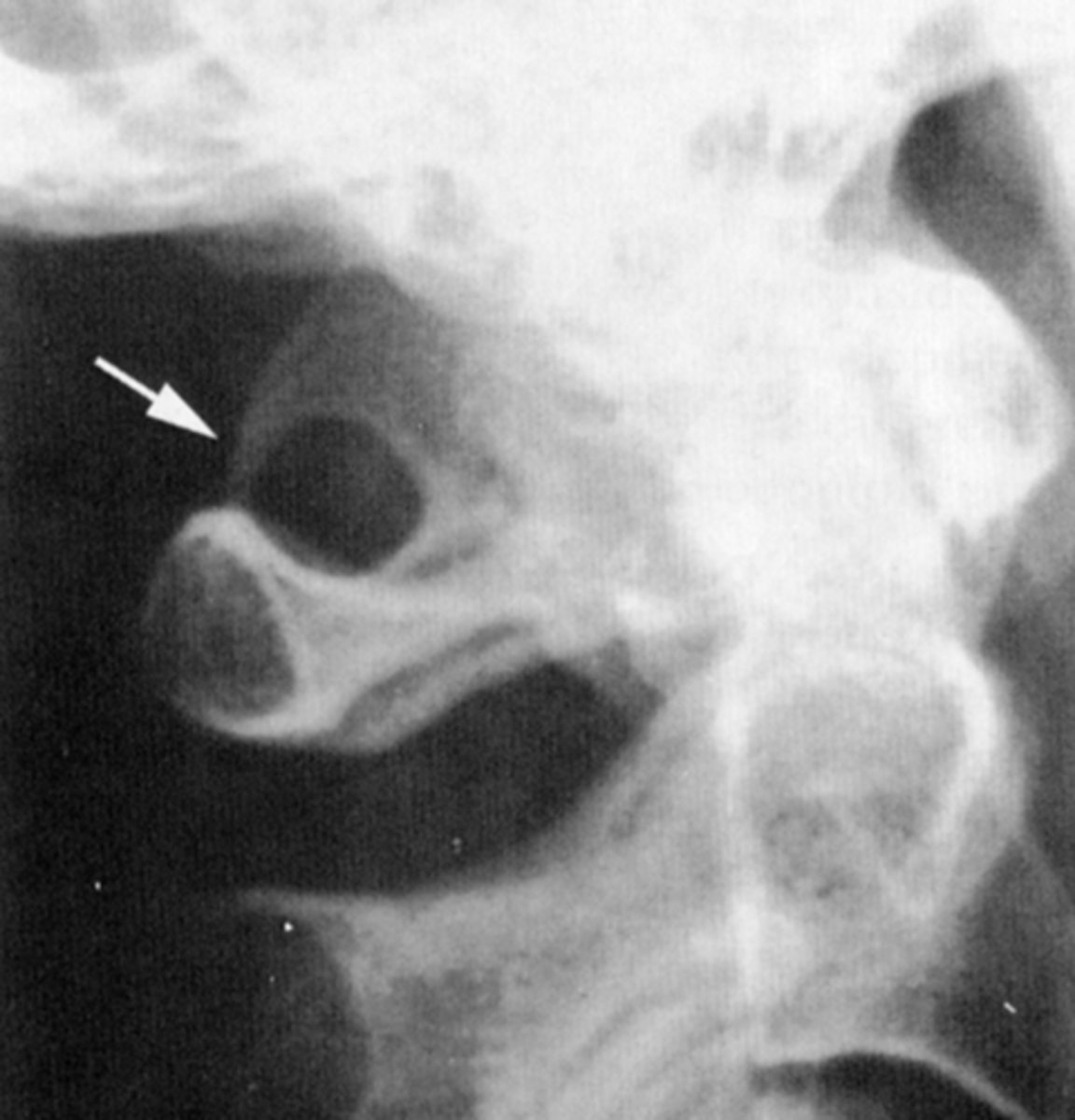
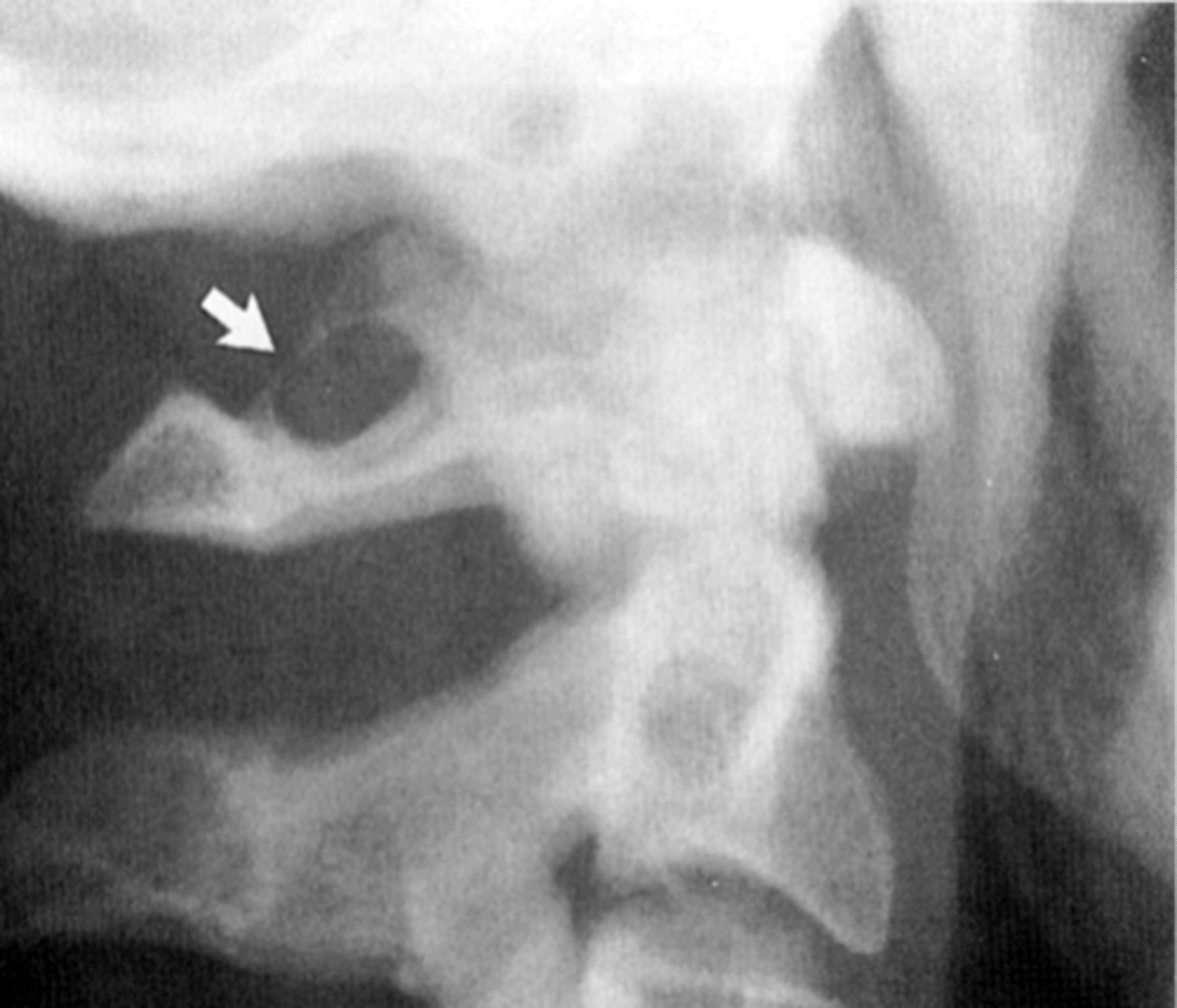
Os Terminale (of Bergmann)
"V" shaped lucent area at the very tip of the dens with a small rounded ossicle within the radiolucent area
12-13
Os Terminale (of Bergmann) is normal until _____ years of age
Growth center does not fuse to the dens
How does Os Terminale (of Bergmann) occur?
None, incidental finding
Clinical significance of Os Terminale (of Bergmann)
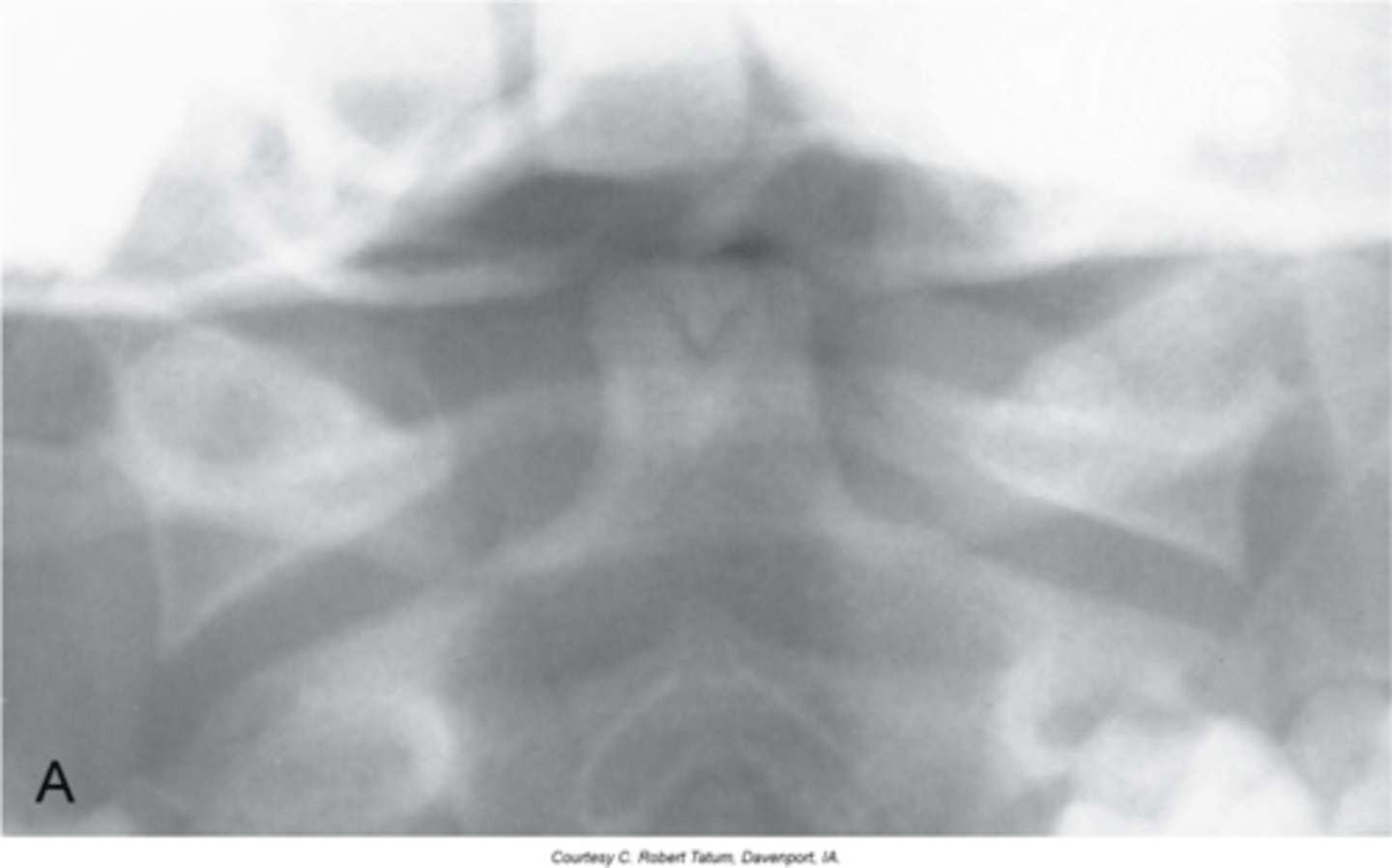
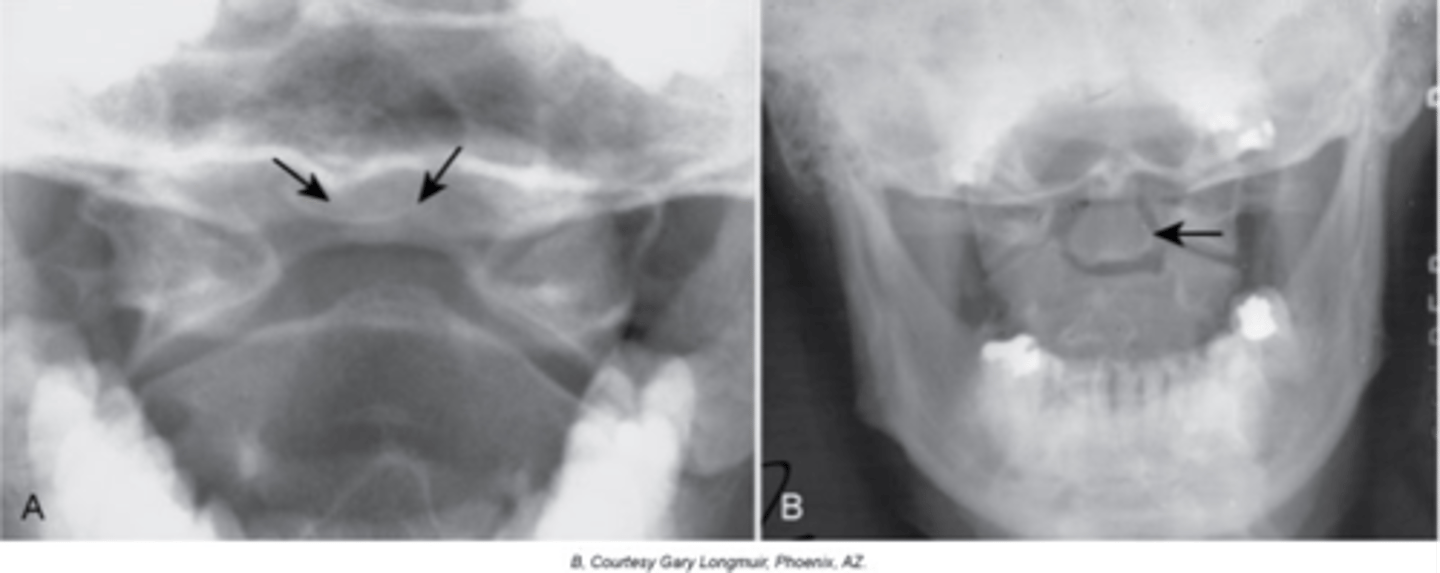
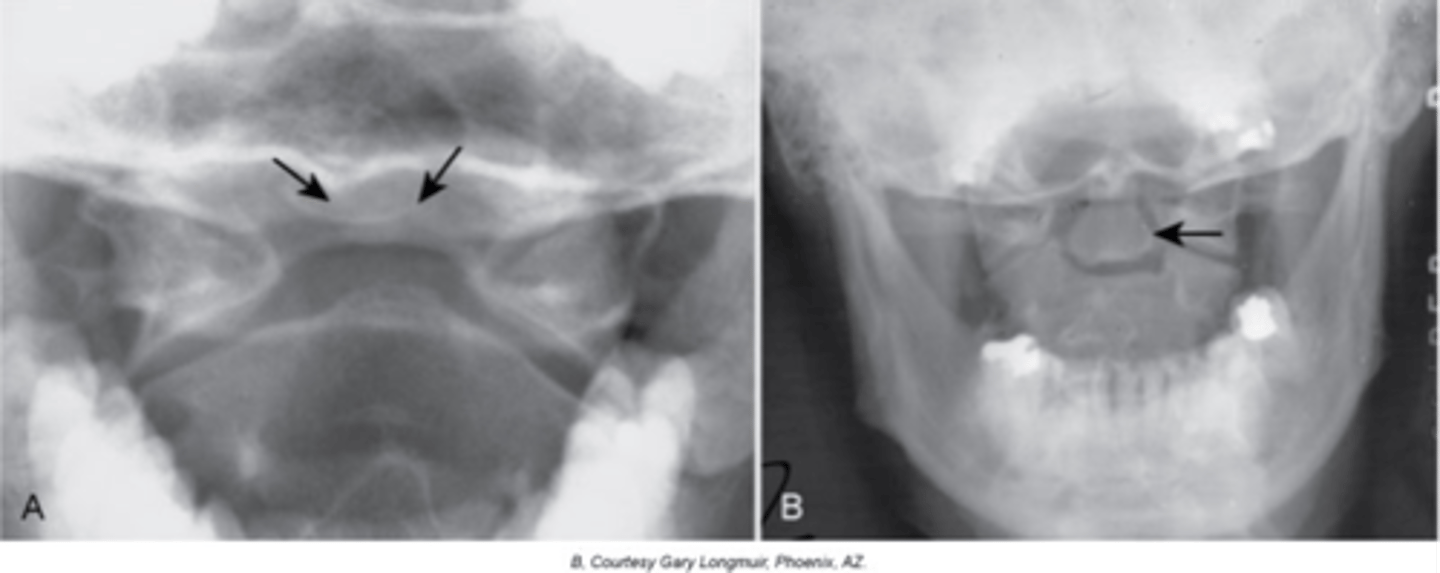
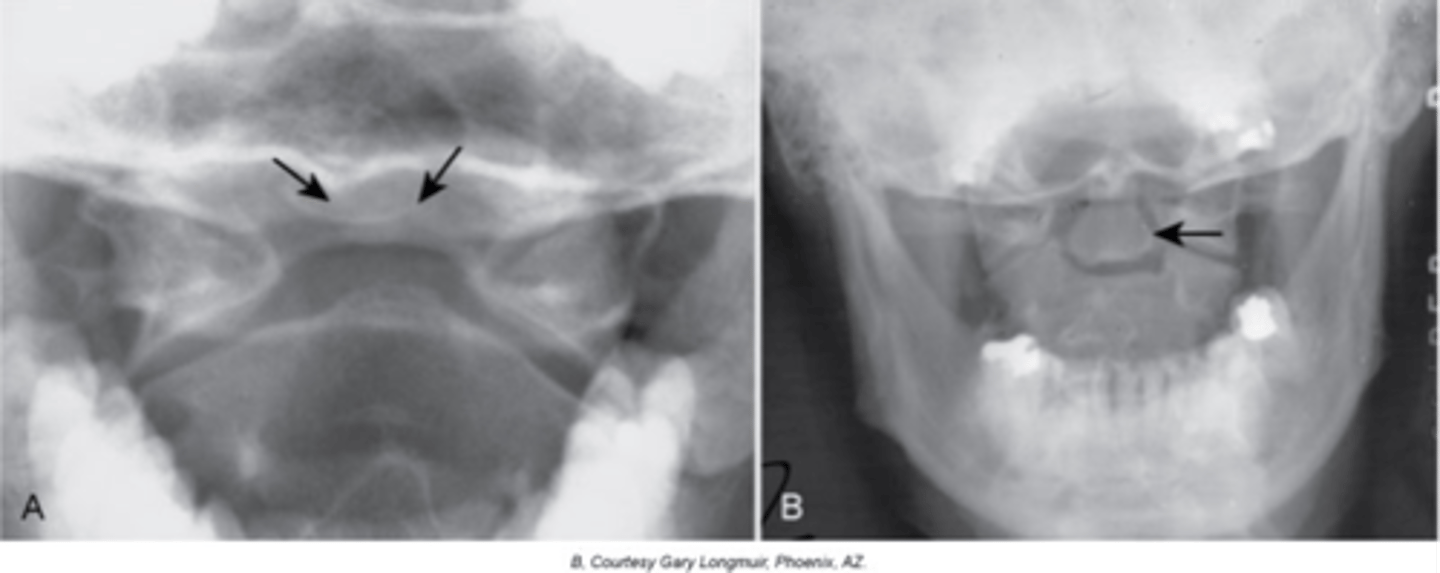
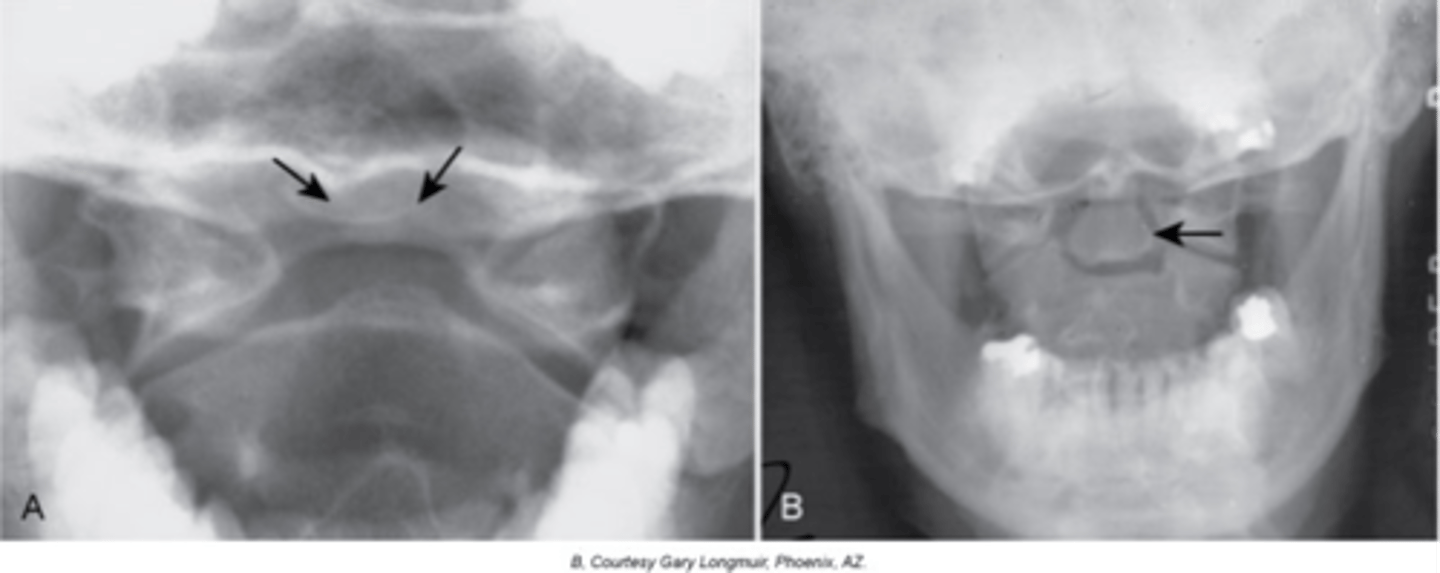
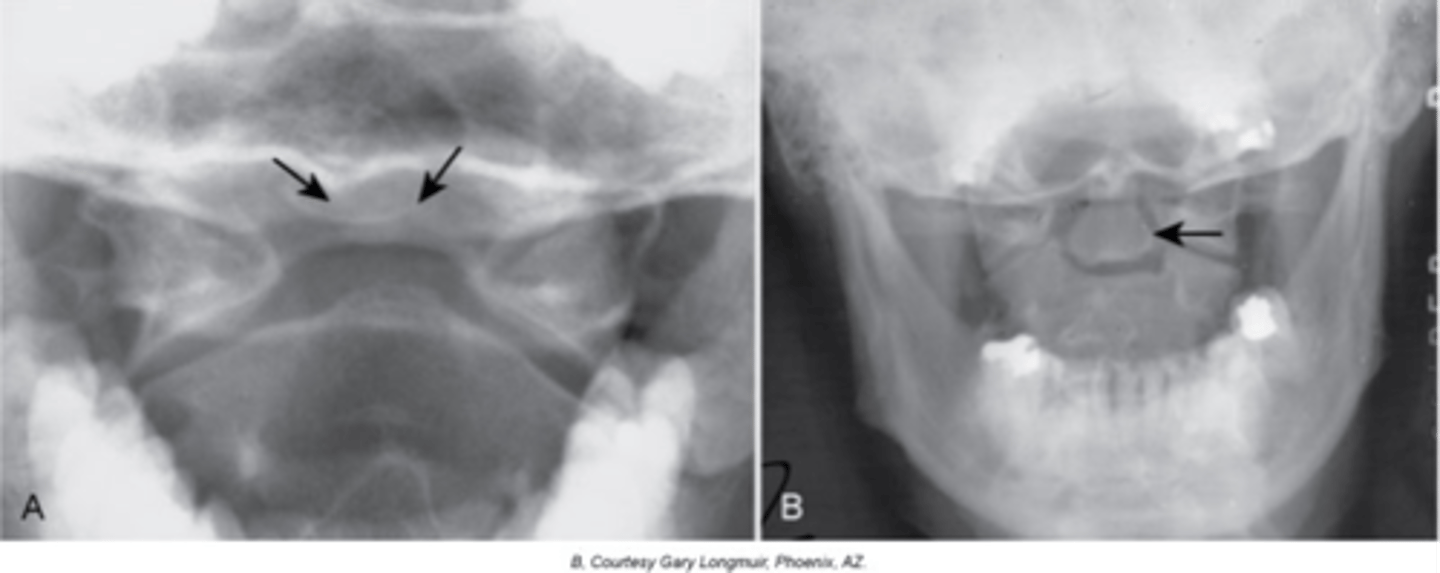
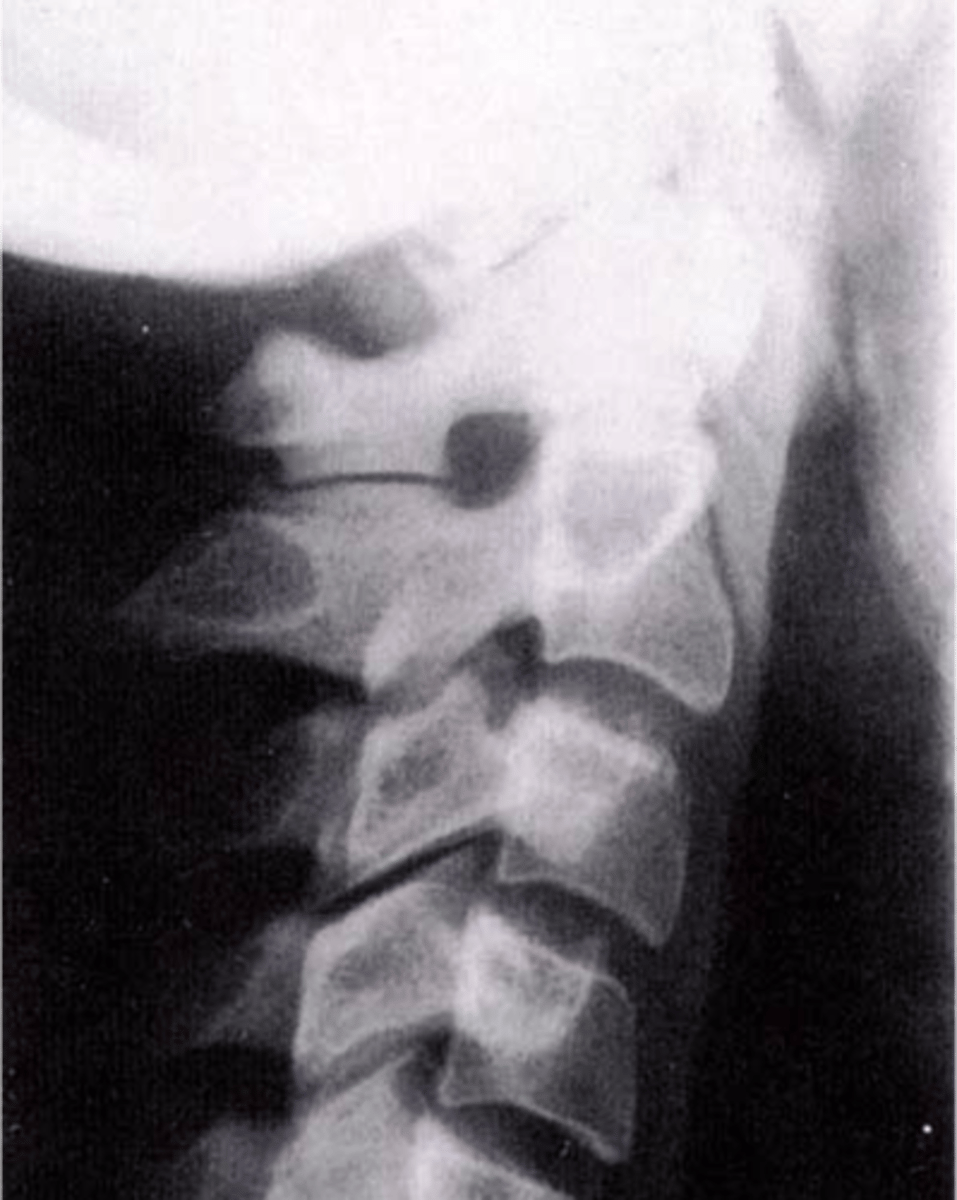
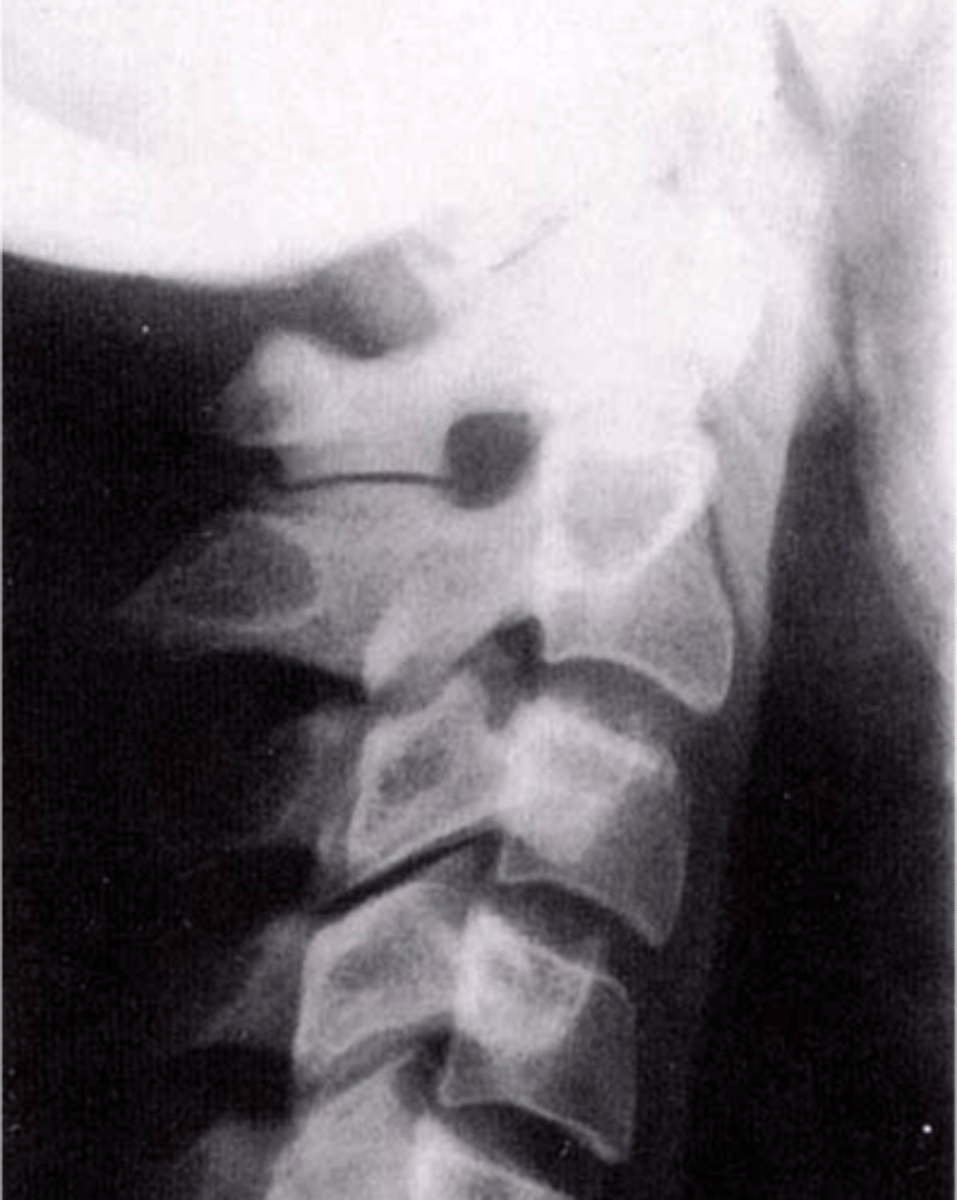
Os Odontoideum
Lucent area at the base of the dens, resulting in a well-corticated cleft between the body of C2 and the dens
Cephalic
With Os Odontoideum, the ossicle may be smaller than a normal dens and _____ in location
Anterior tubercle
With Os Odontoideum, hypertrophic changes of the _____ are very common and hint that it is a long lasting condition, not an acute traumatic fracture
5-7
With Os Odontoideum, normal cleft prior to _____ years of age
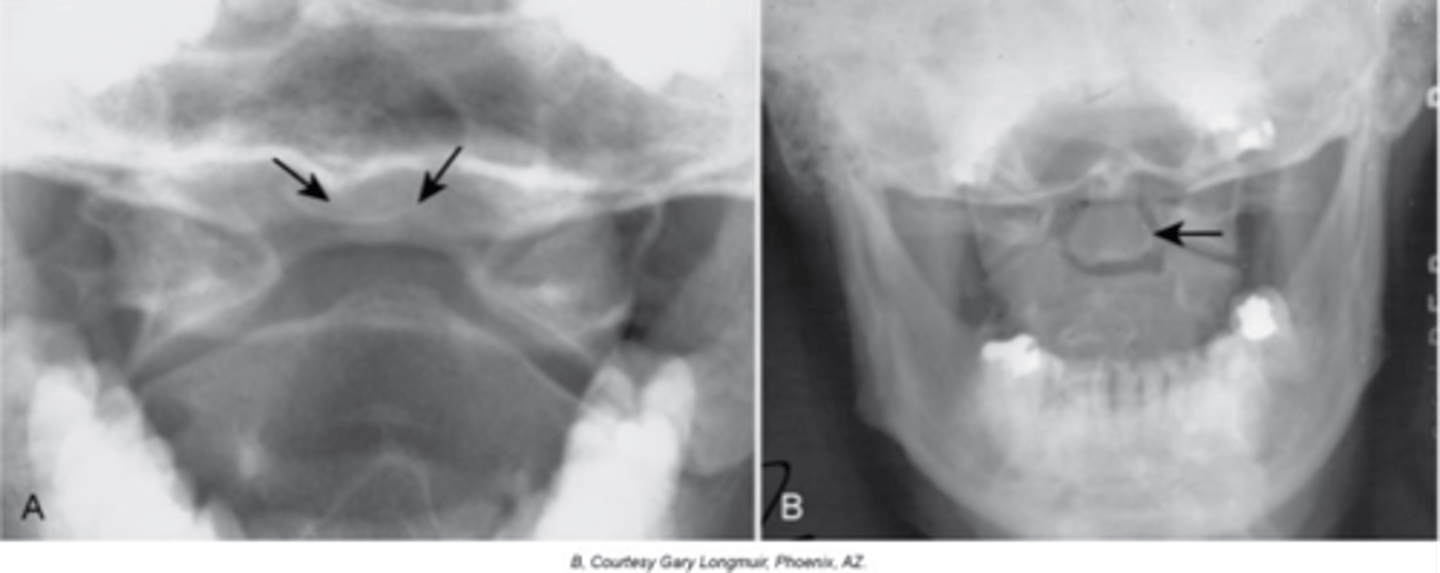
Failure of calcification of an ossification center
How does Os Odontoideum occur?
- Instability
- May have recurrent torticollis, neurologic symptoms, crepitus, and abnormal motion
- Contraindication to chiropractic adjustments
- Can be confused with acute fracture
Clinical significance of Os Odontoideum
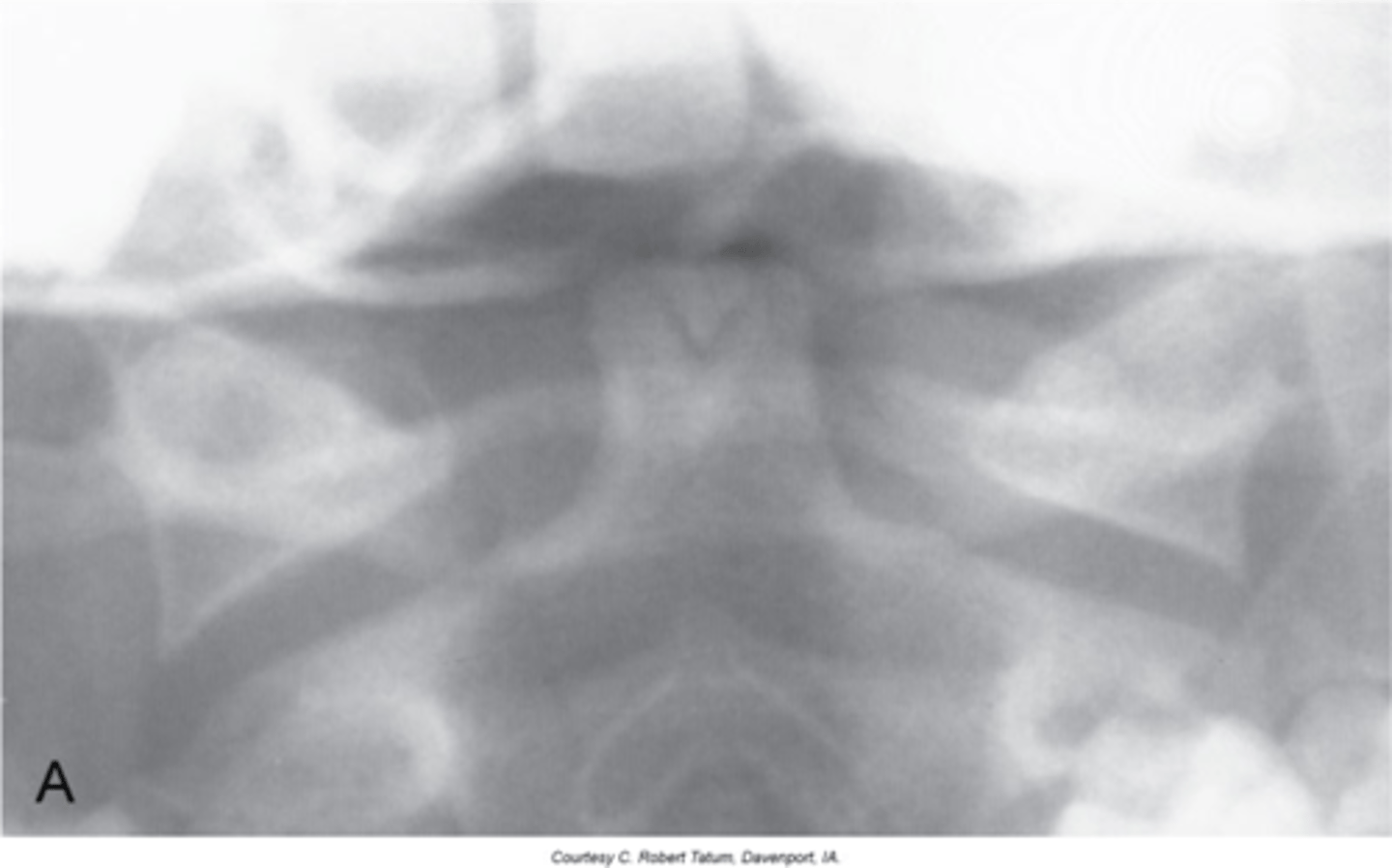
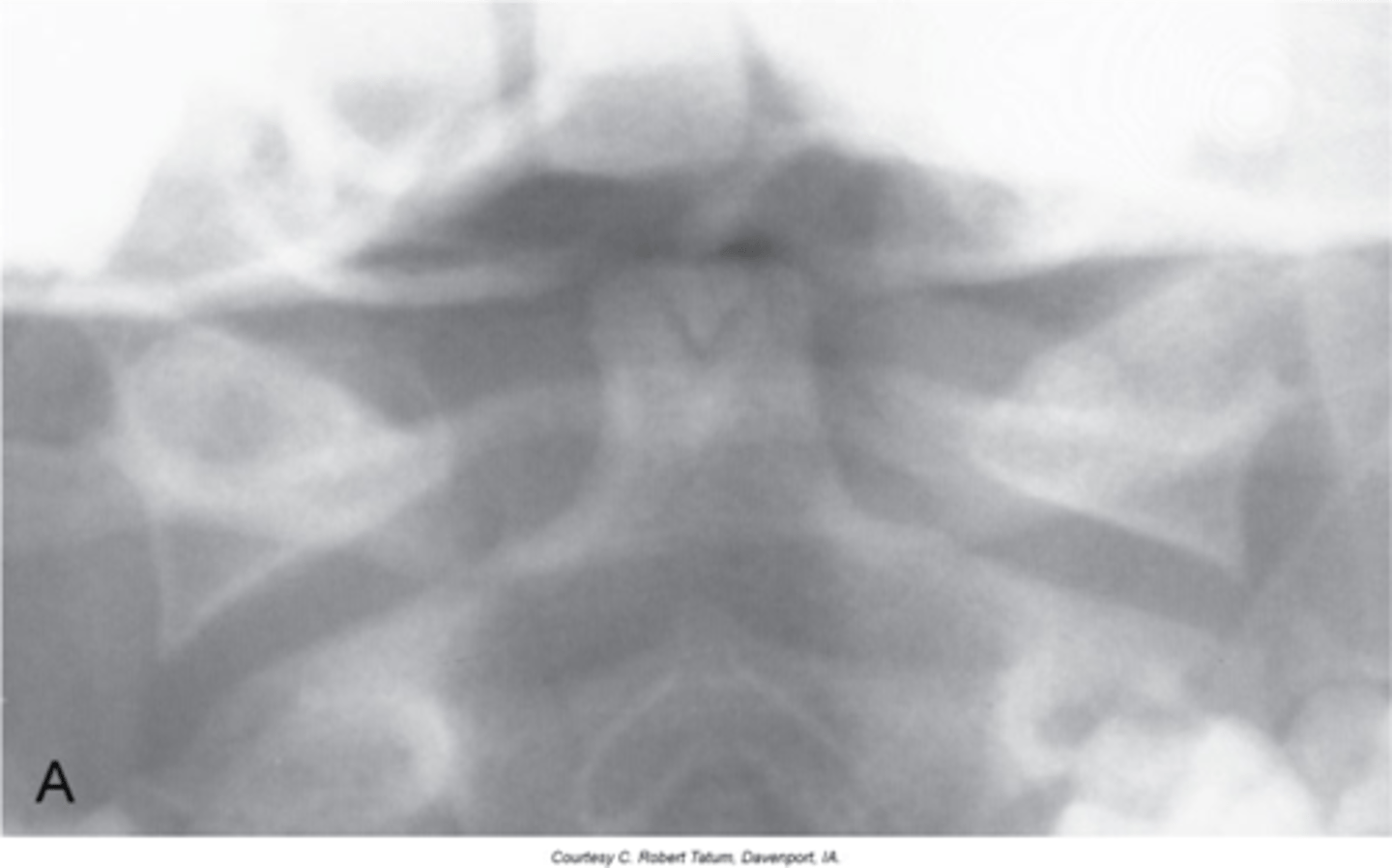
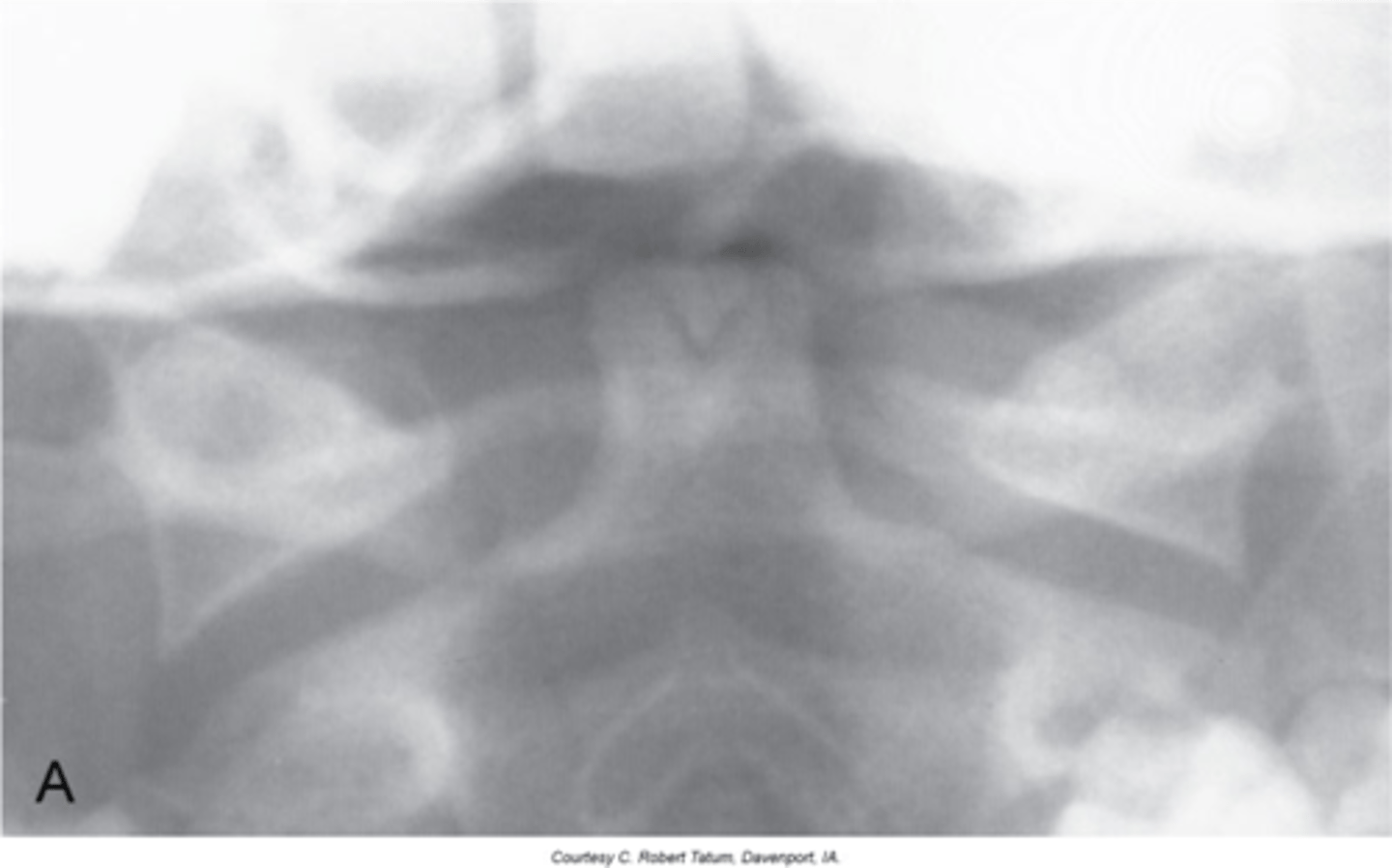
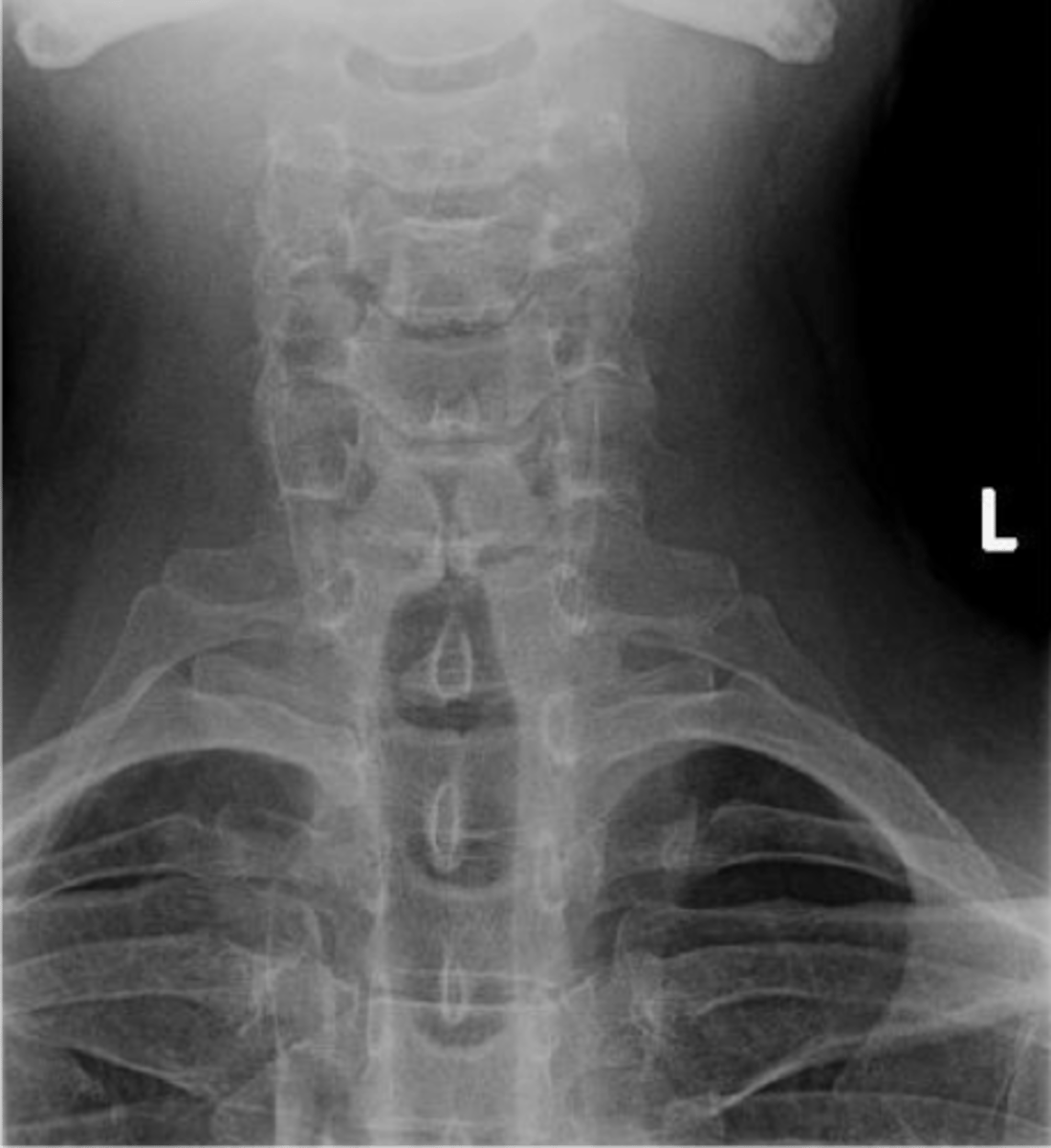
Spina Bifida Occulta
Midline defect (cleft) within the posterior neural arch
- Fibrocartilaginous bridge between the osseous ends of the bones
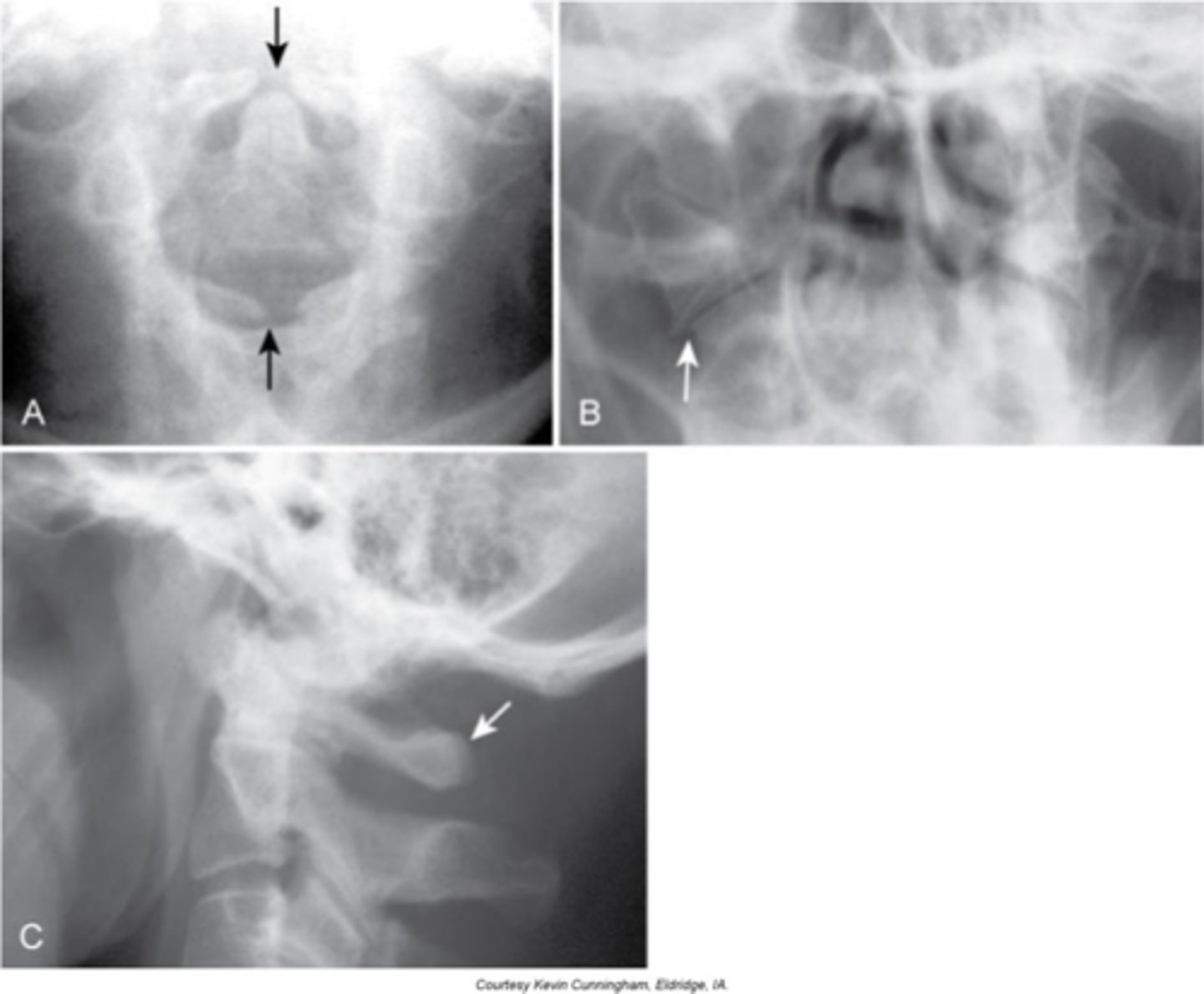
Spondyloschisis
No spinous process at C1
Locations:
- MC at L5/S1, second MC at C1
- Also more common at transition zones
Lack of spinolaminar line
With Spina Bifida Occulta, what will a lateral view show?
Vertical lucent cleft through the spinous process
With Spina Bifida Occulta, what will AP/PA views show?
None, don't scare patients
Clinical significance of Spina Bifida Occulta
Spina Bifida Occulta at C6
ID abnormality
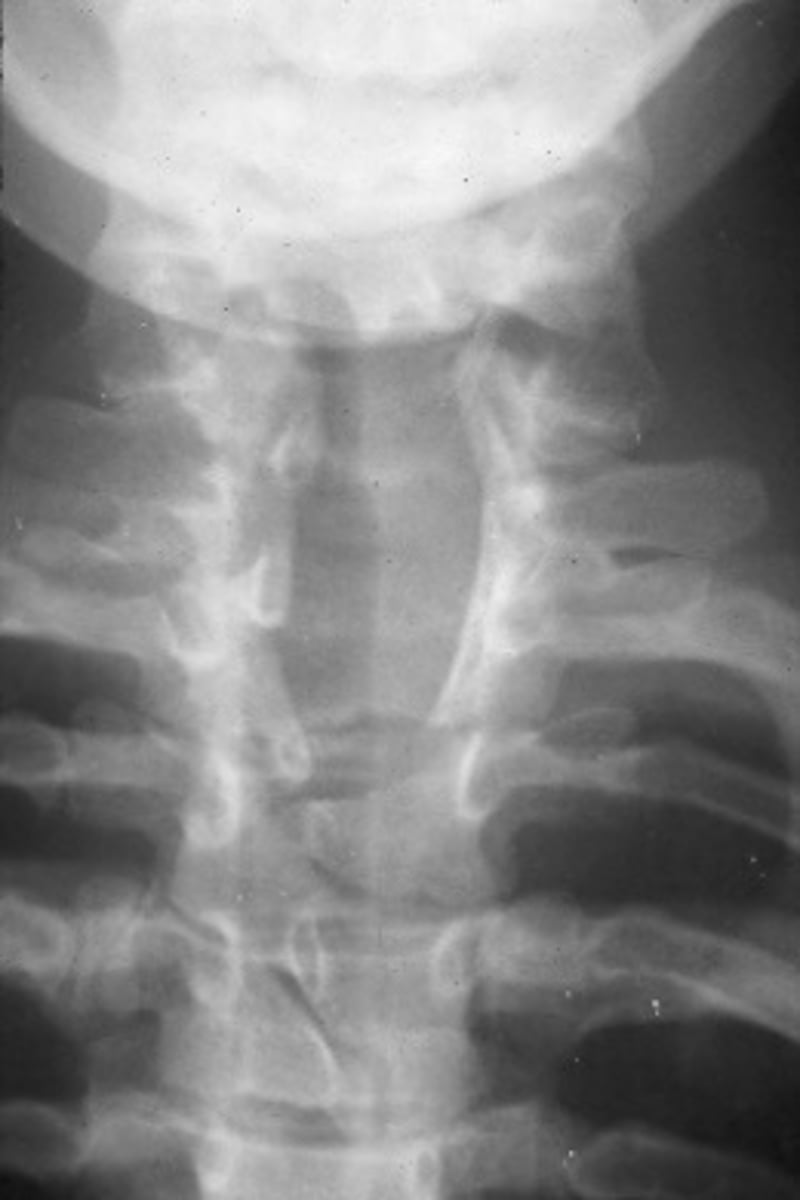
Spina Bifida Vera (manifesta)
Defective fusion of the posterior elements
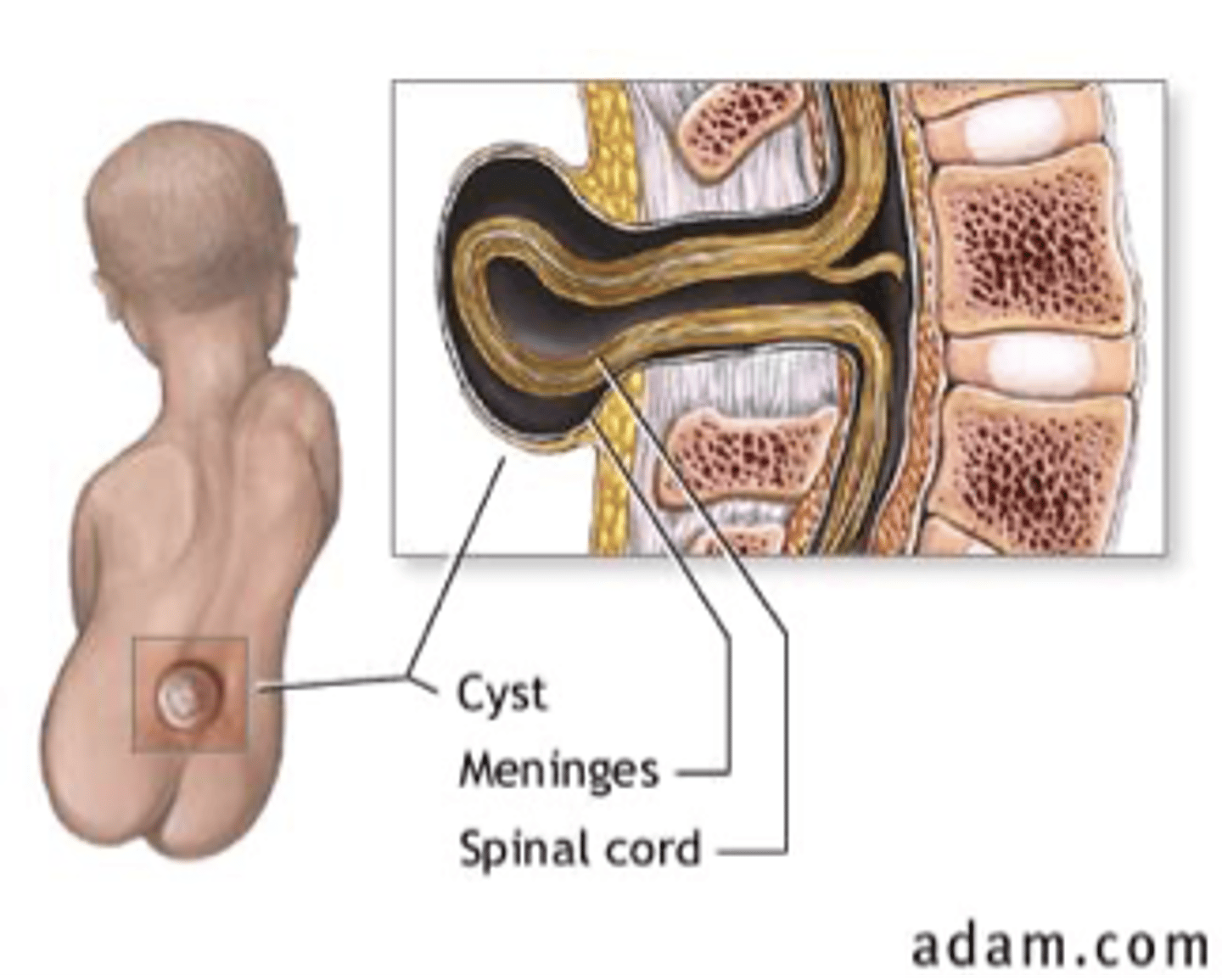
Meningocele
Protrusion of the meninges
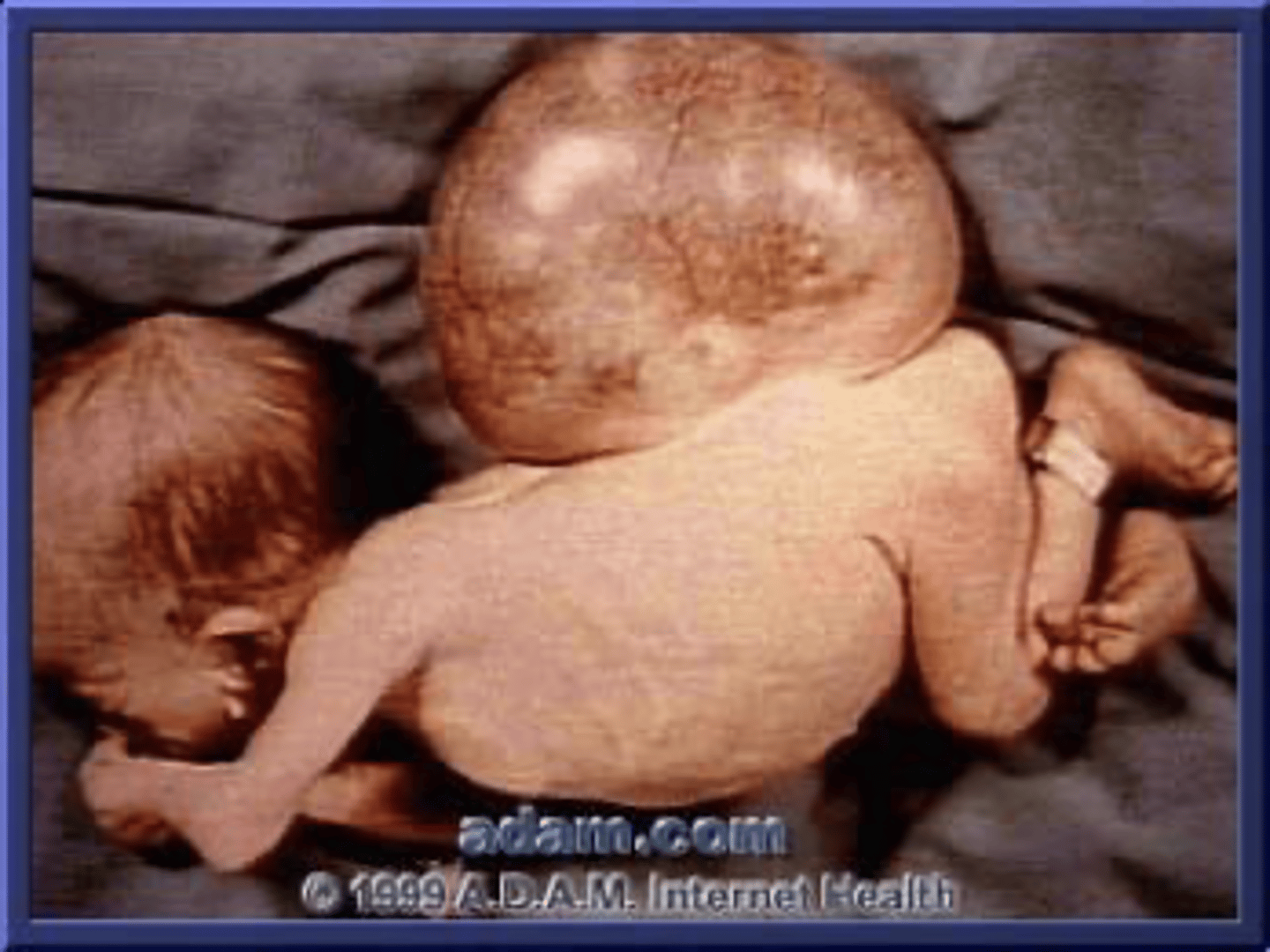
Myelomeningocele
Protrusion of the meninges and nervous tissue
Large multilevel split posterior elements
Spina Bifida Vera appearance
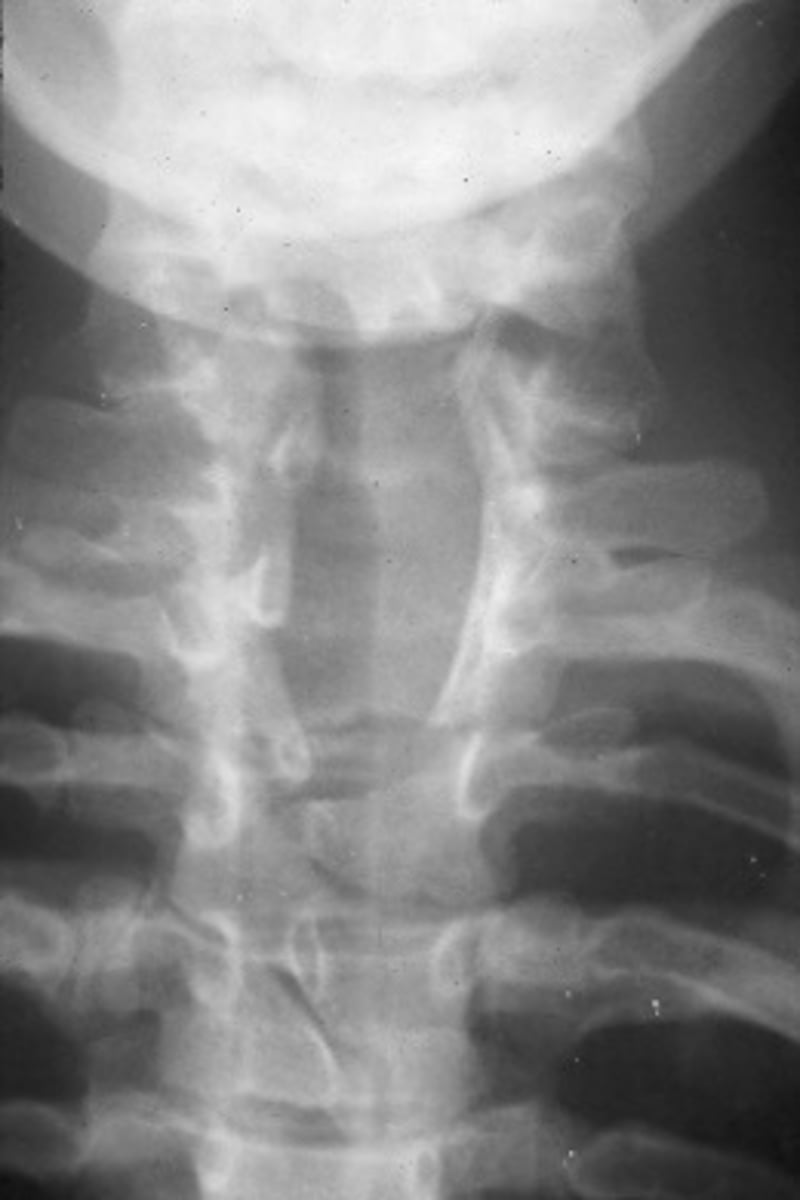
Many, discovered in utero/at birth
Clinical significance of Spina Bifida Vera
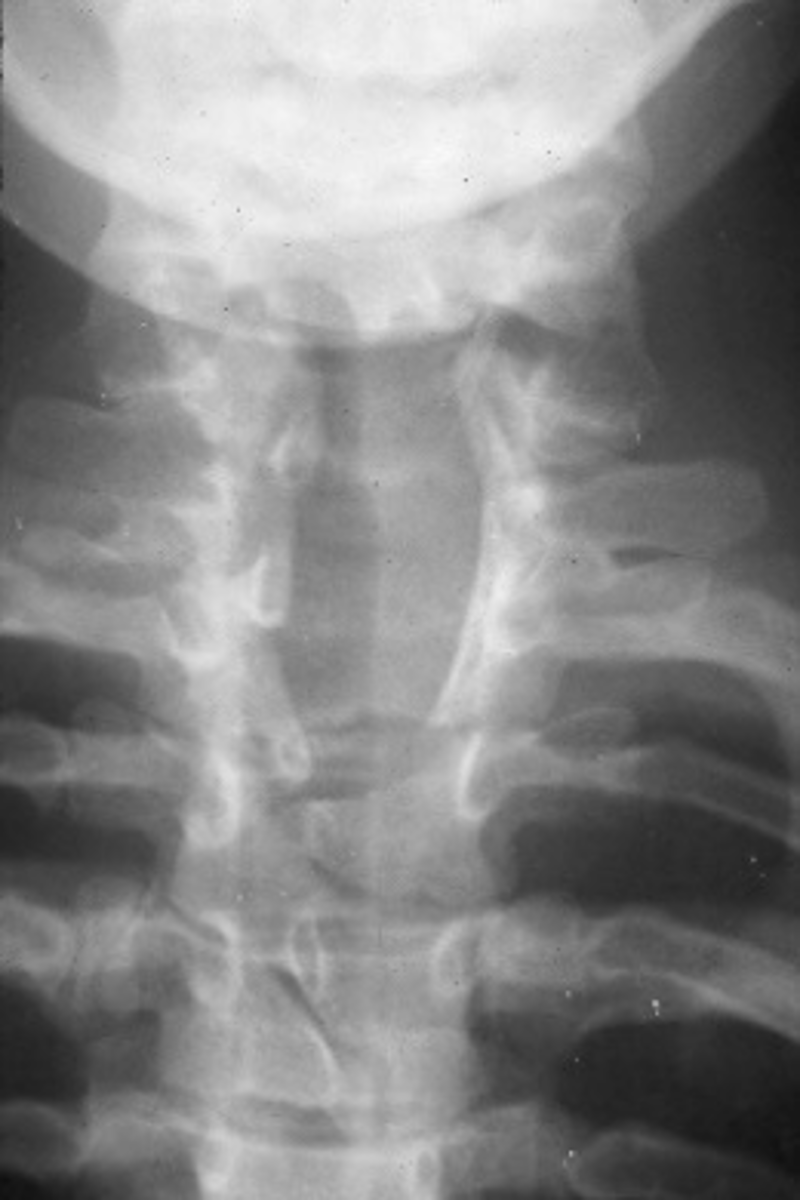
Cervical ribs
- Accessory ribs above T1
- MC at C7 and rarely at levels above C7 without C7 being involved
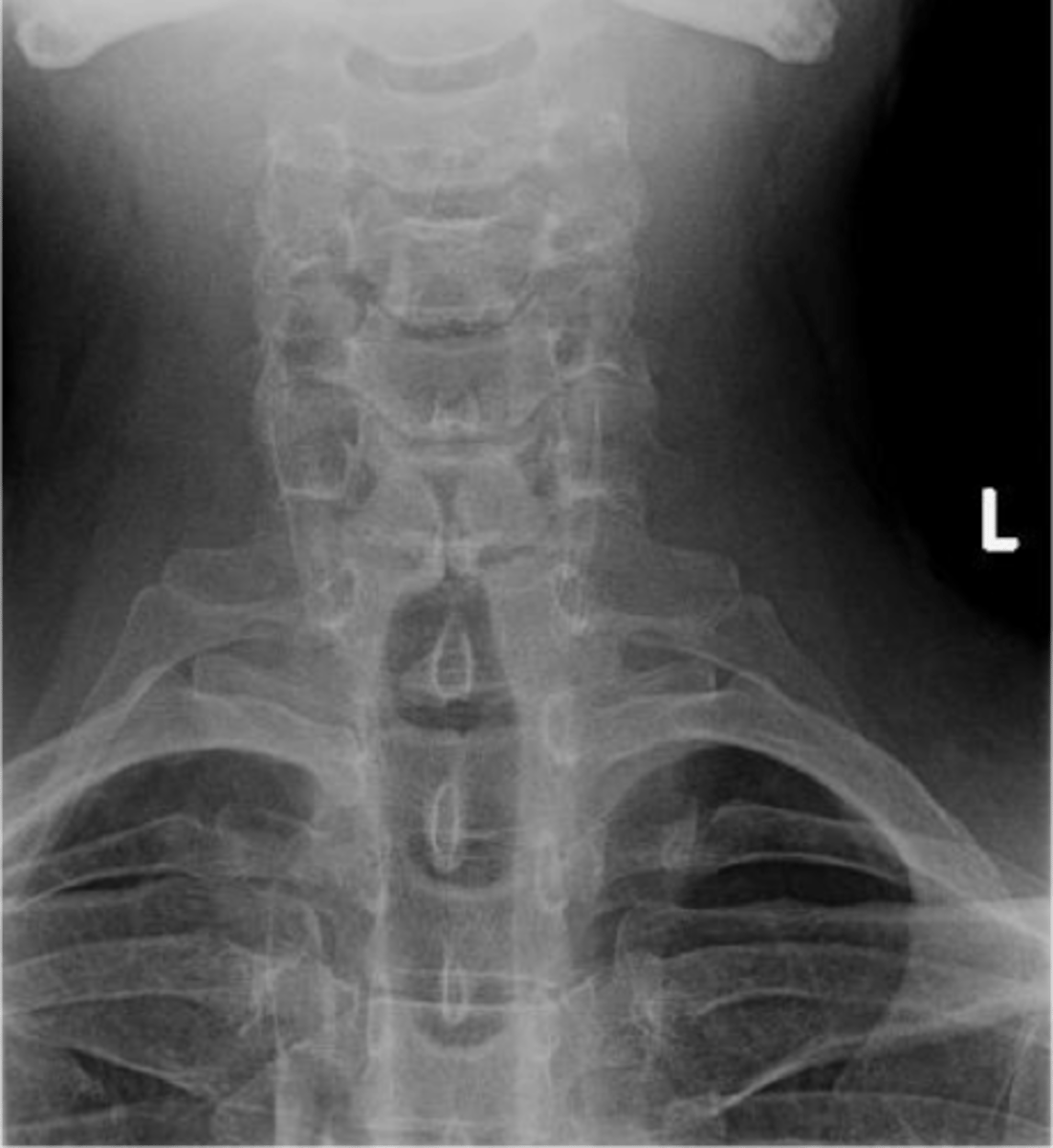
- Joint space/cortication at the transverse process (may be full rib or small piece)
- Hyperplastic/elongated C7 transverse process (no joint space, C7 transverse process goes past lateral margin of T1)
Cervical ribs appearance
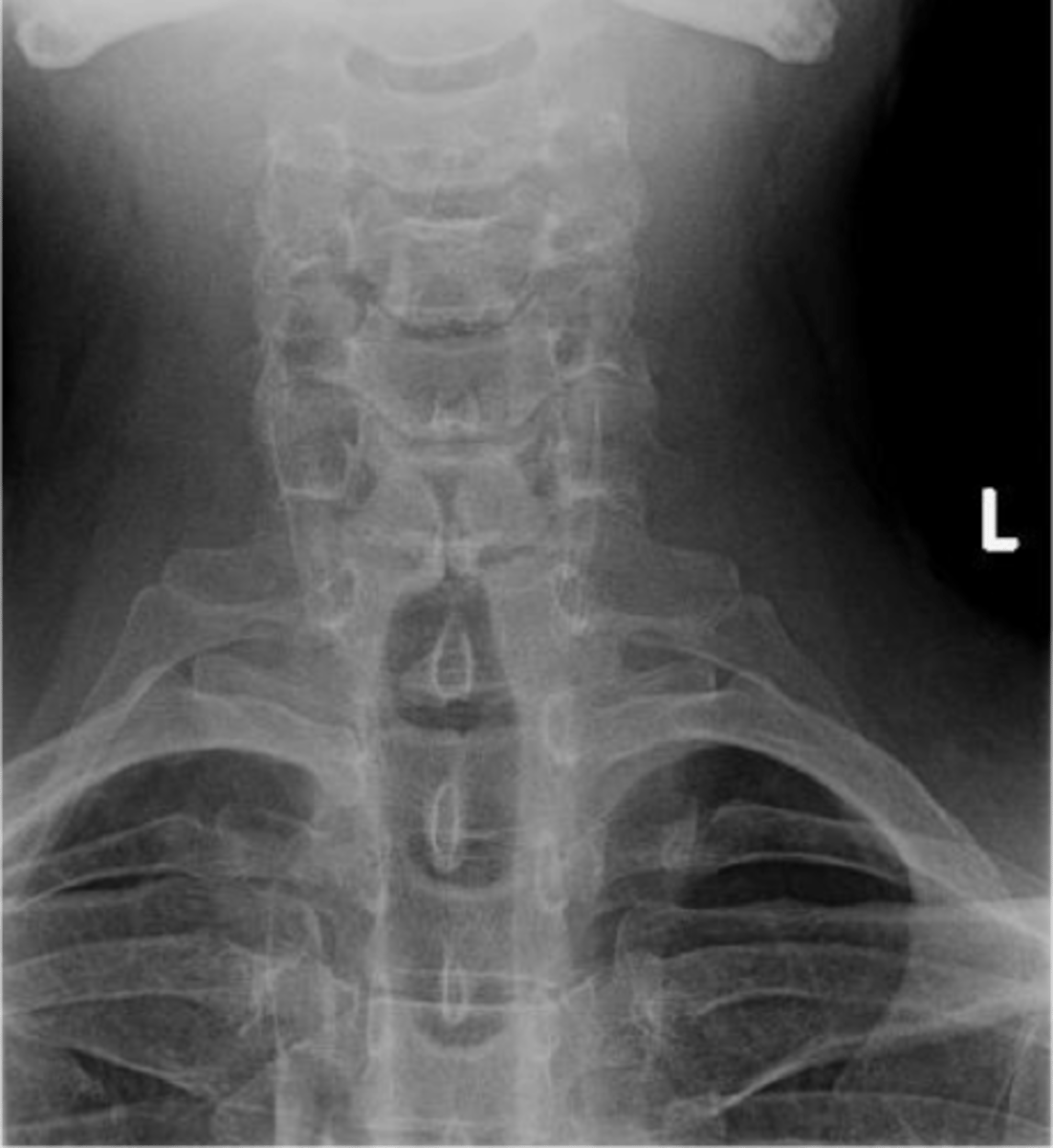
Some may be associated with thoracic outlet syndrome
Clinical significance of cervical ribs
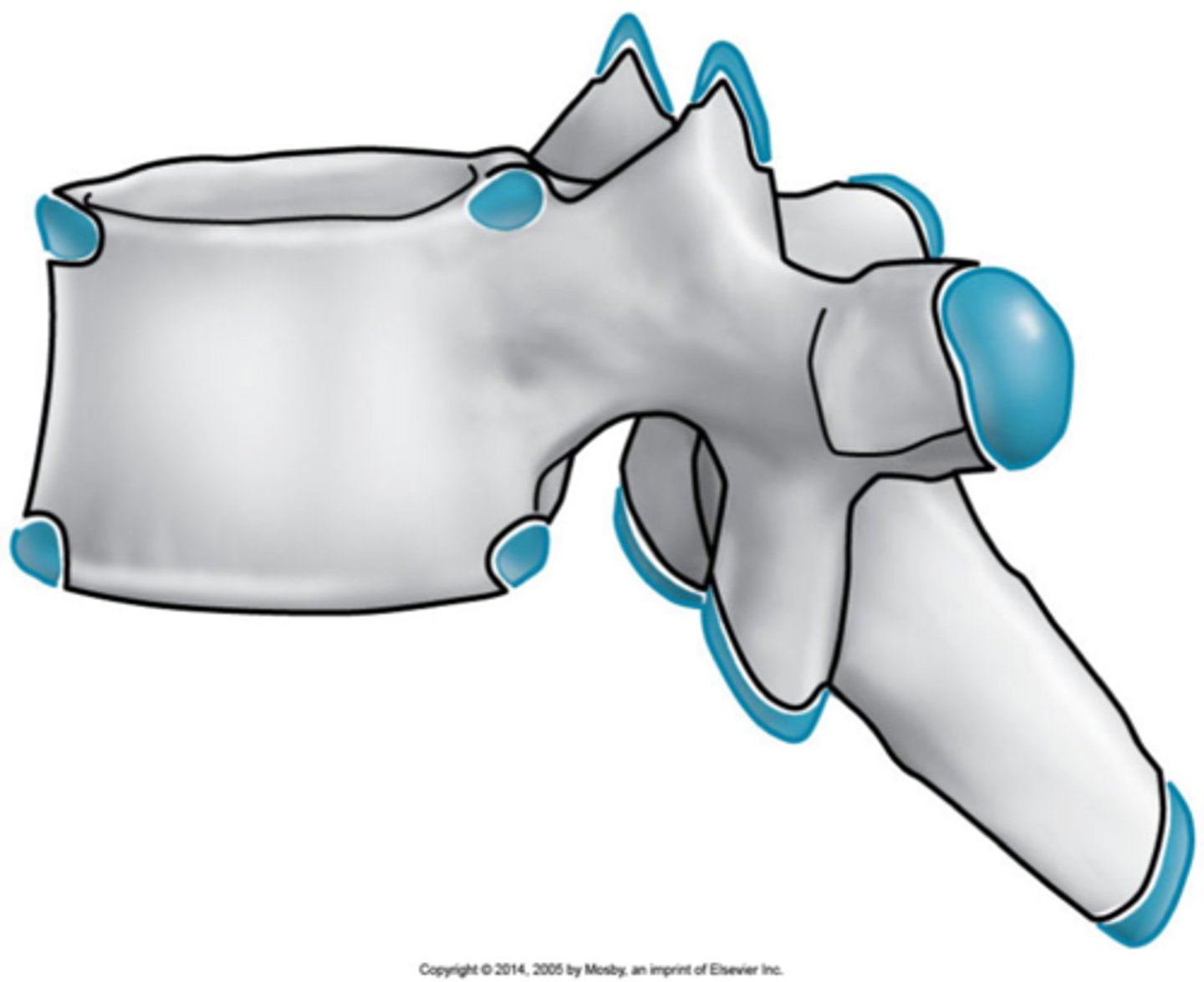
Secondary growth centers
At times, the growth center does not fully ossify, this leads to a lucent cleft between the secondary growth center and the parent bone
Synostosis
Congenital fusion
Arthrodesis
Surgical fusion
Ankylosis
Pathologic fusion
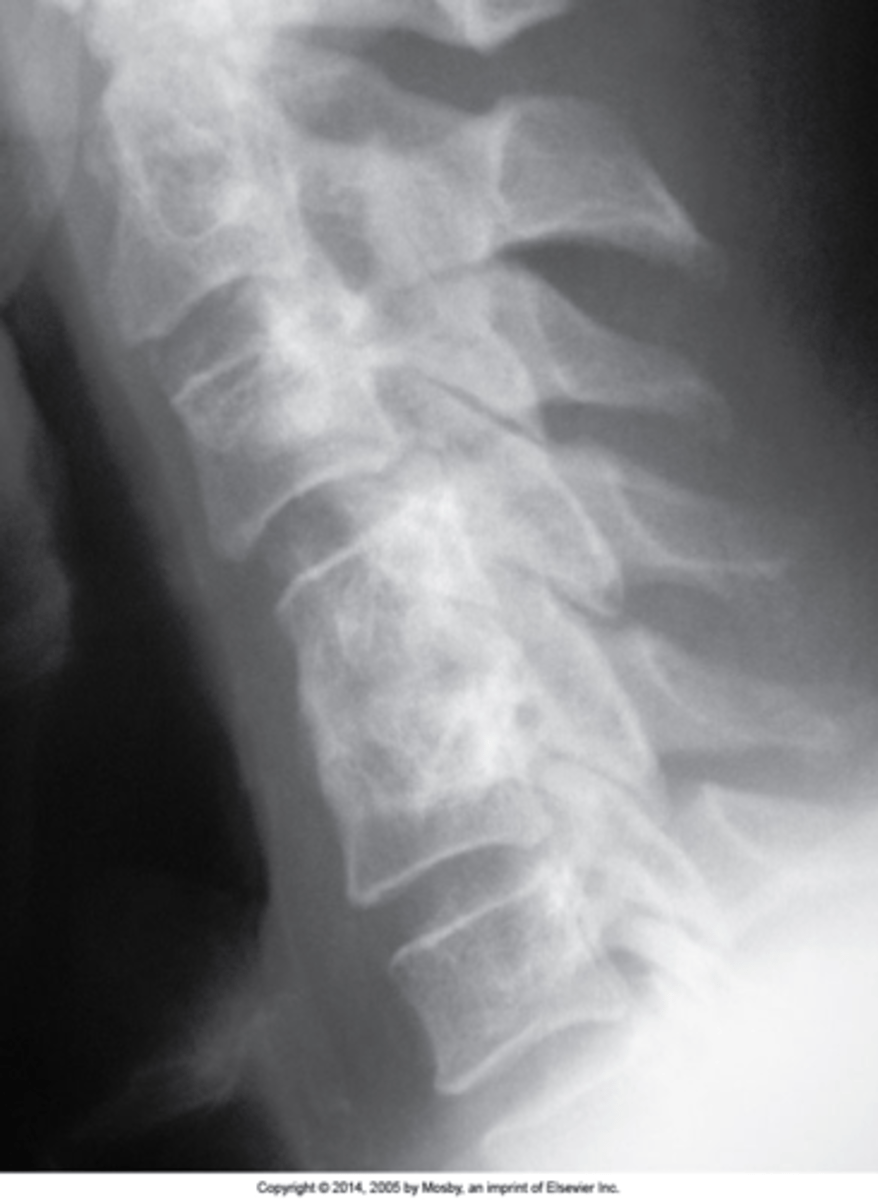
Block vertebrae
- Nonsegmentation (somites/sclerotomes that didn't pinch apart)
- Didn't fuse because it was never separate
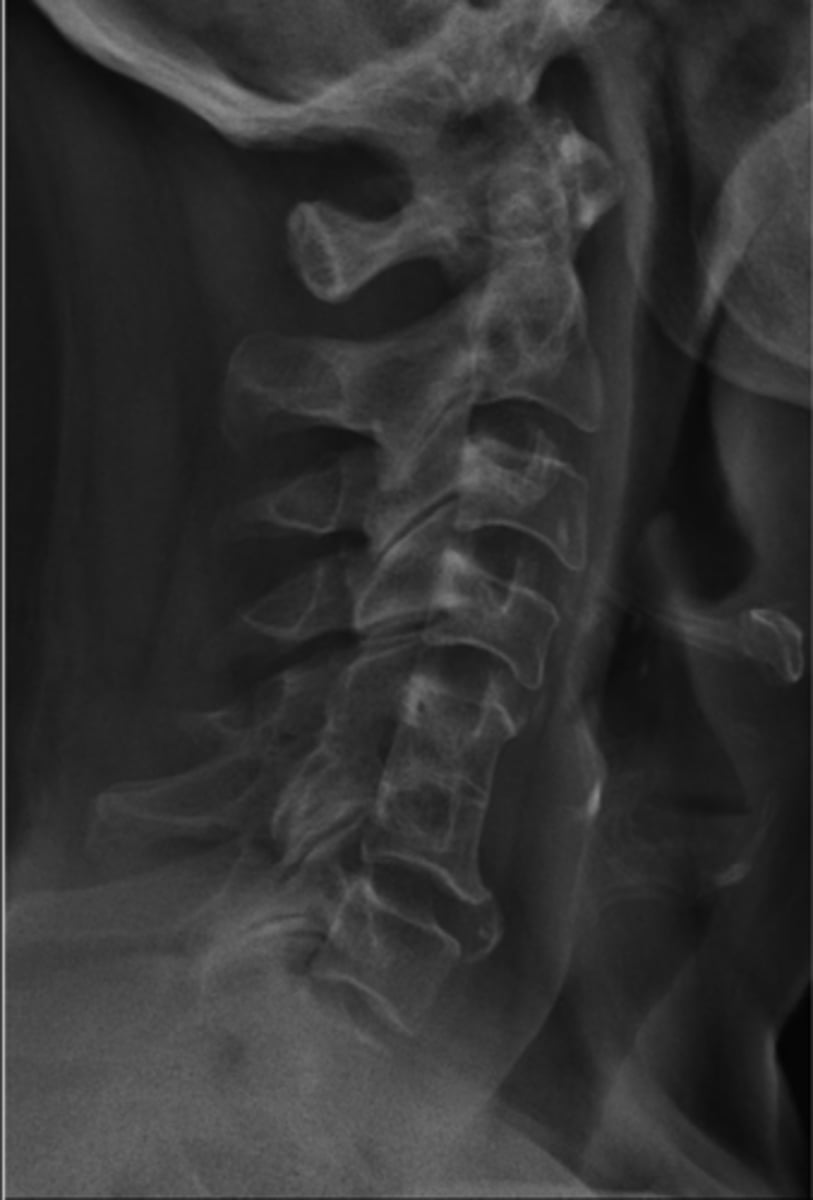
Cervical
Block vertebrae are most commonly found in the _____ spine
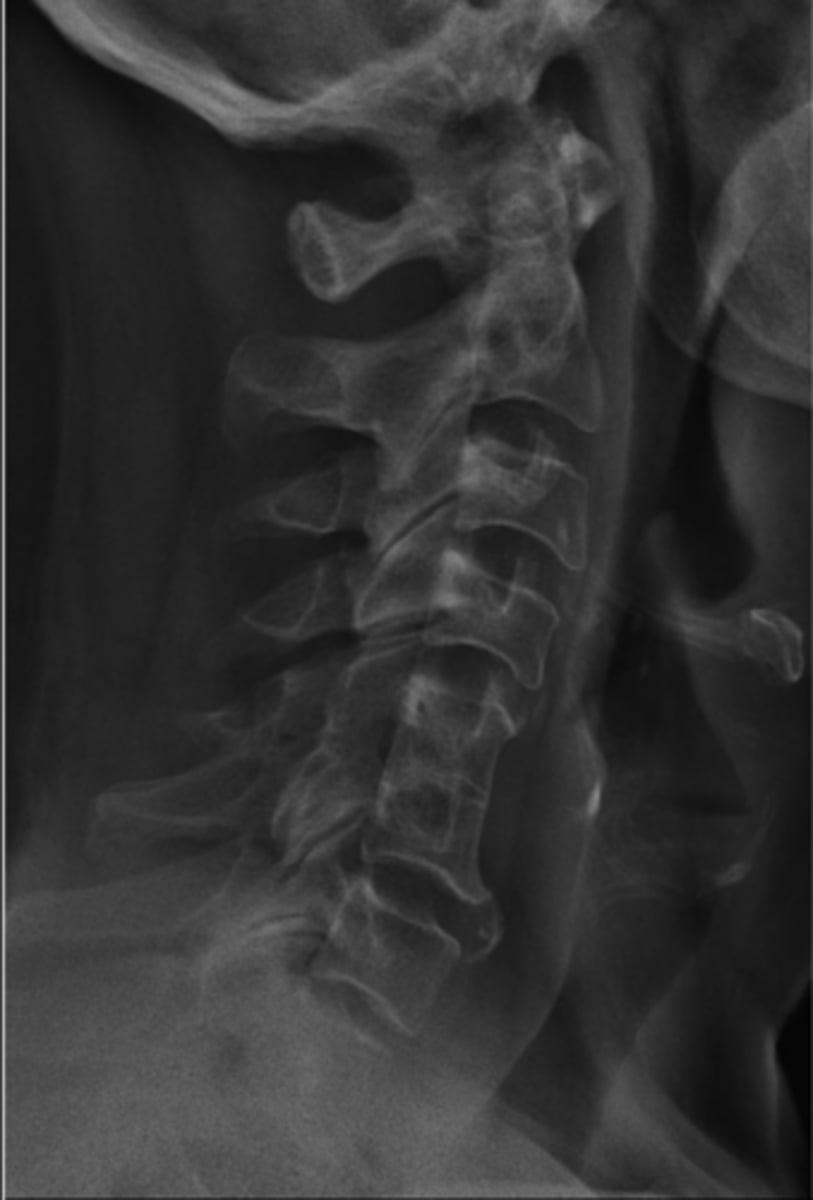
- Wasp waist
- Rudimentary (small) disc
- Fusion of the posterior elements (facet joint fusion in 50%)
- Enlarged IVF/neuroforamen of the fused segment with a more lateral orientation
Block vertebrae appearance
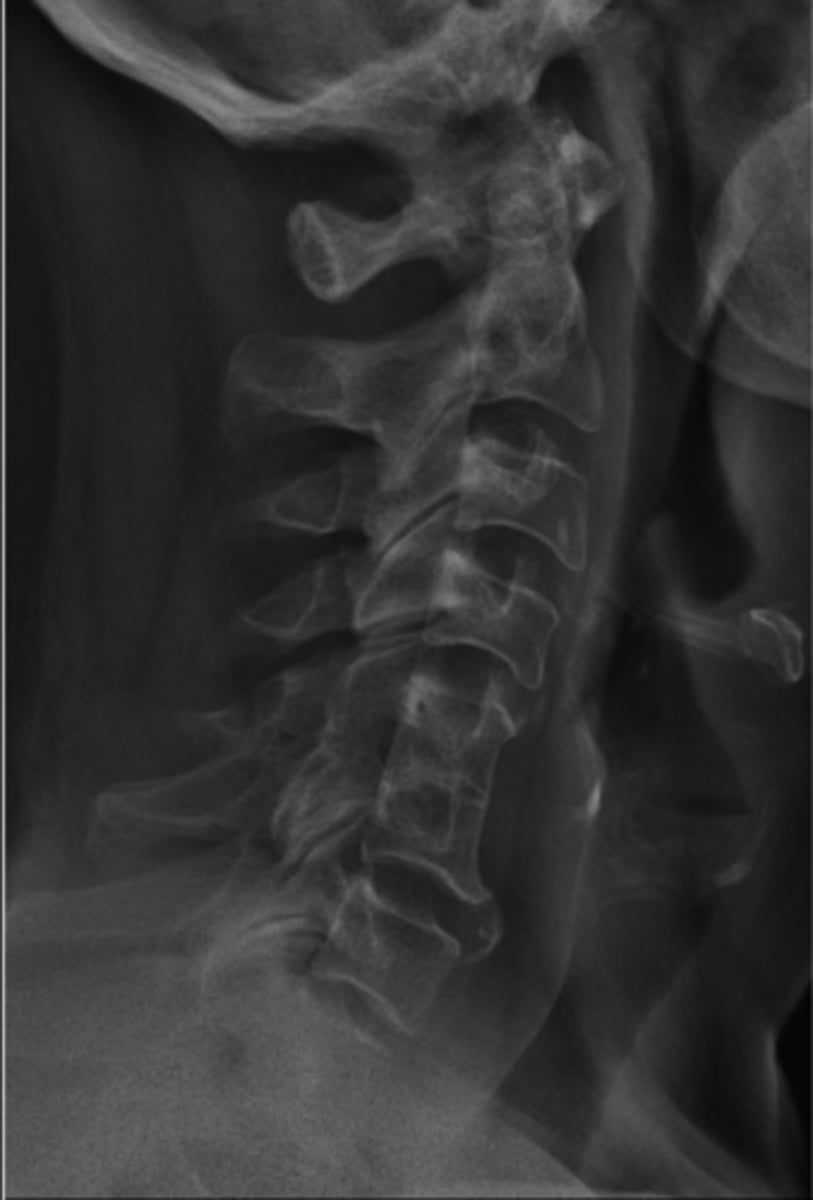
- It will adjust as one segment
- Adjacent segments will degenerate (degenerative disc disease) more rapidly because of increased motion/stress
- Increased occurrence of disc pathologies at the adjacent segments
- Associated with Klippel-Feil
Clinical significance of block vertebrae
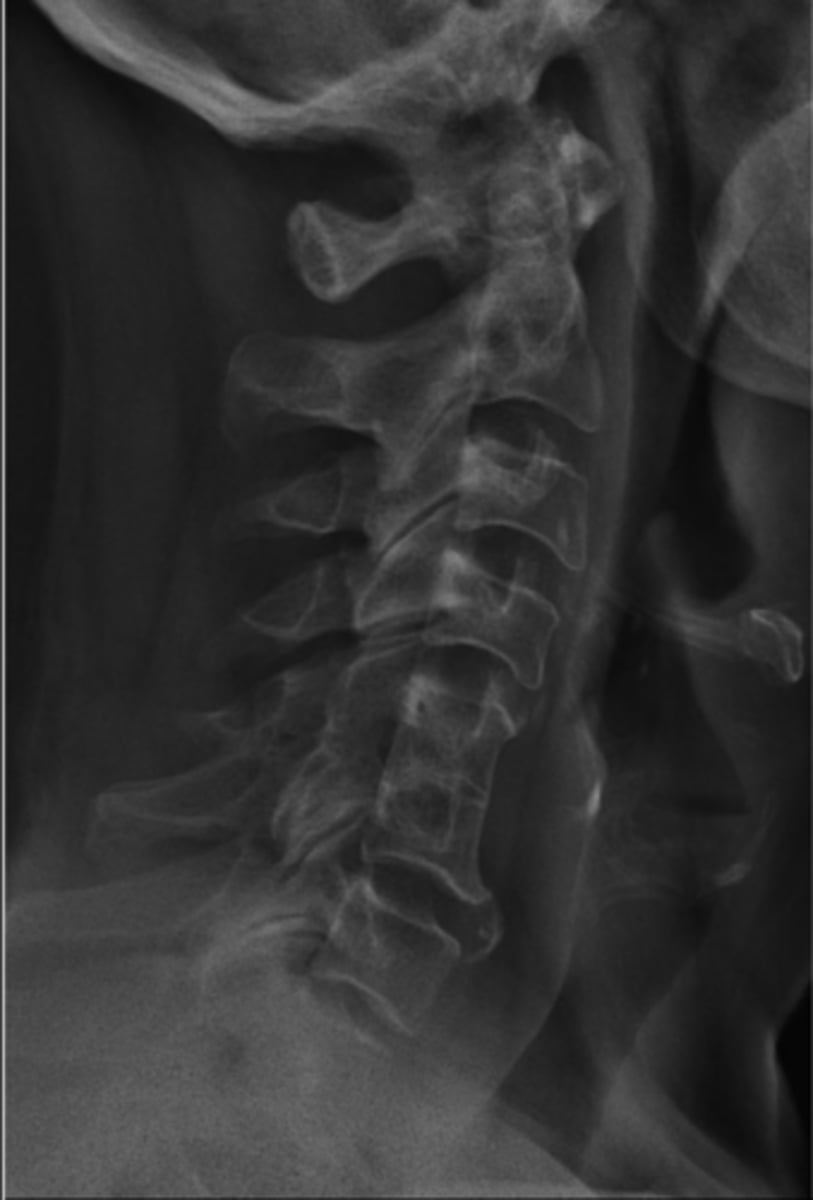
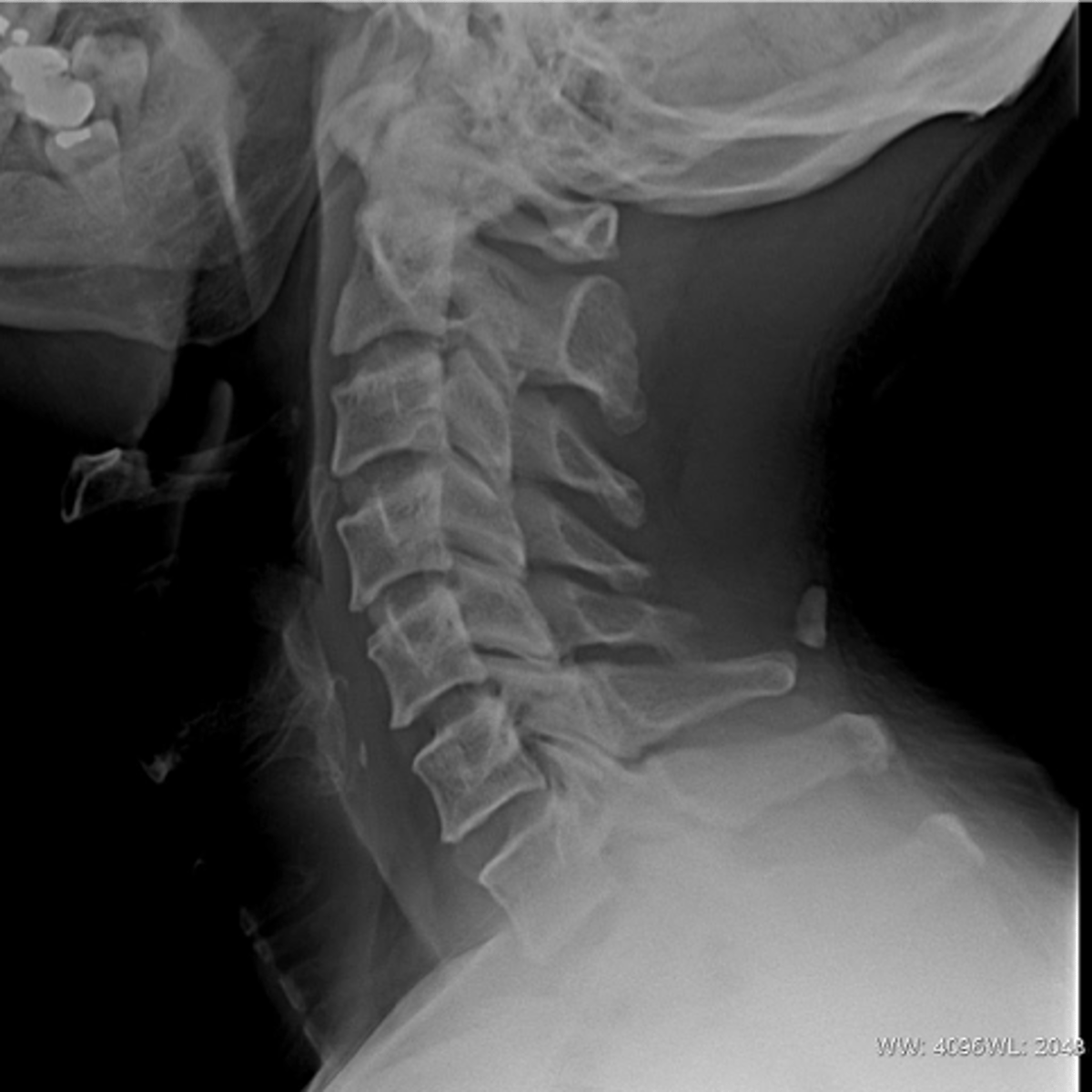
Klippel-Feil syndrome
Abnormality during fetal development - short neck (webbed), low hairline, and decreased range of motion of the cervical spine
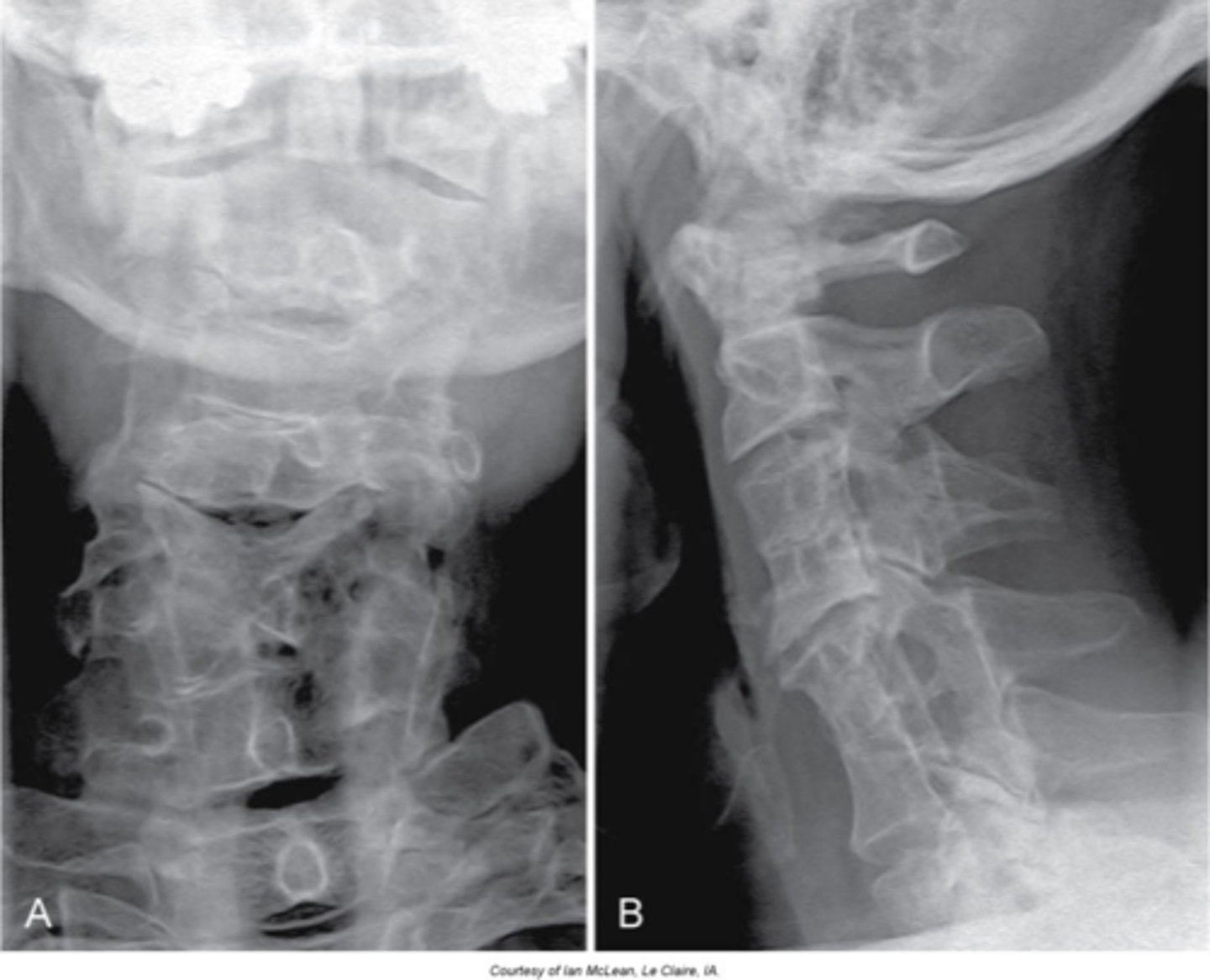
Females
Klippel-Feil Syndrome is more common in _____
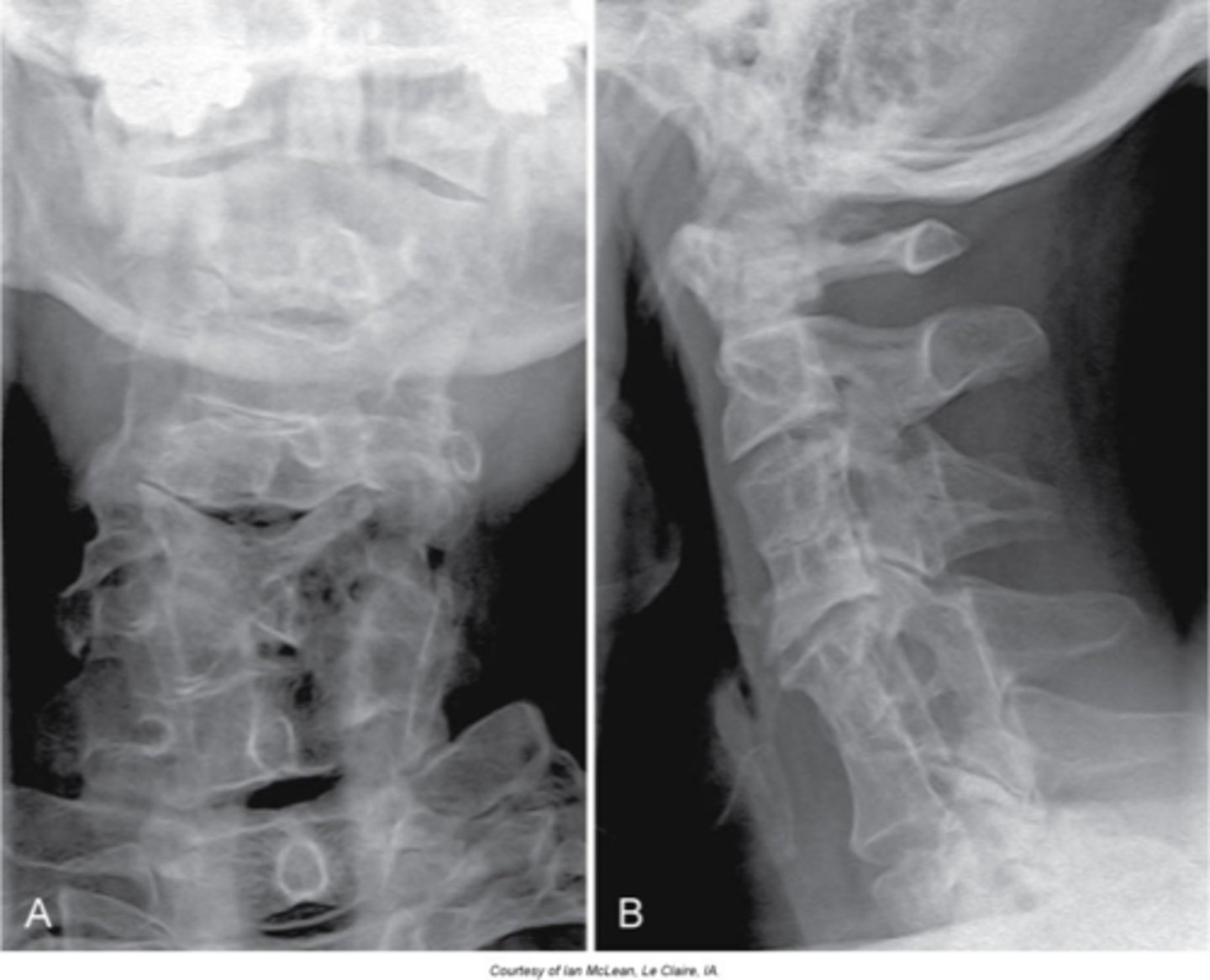
- Multiple block vertebrae
- May have a Sprengel deformity
Radiogaphic appearance of Klippel-Feil Syndrome
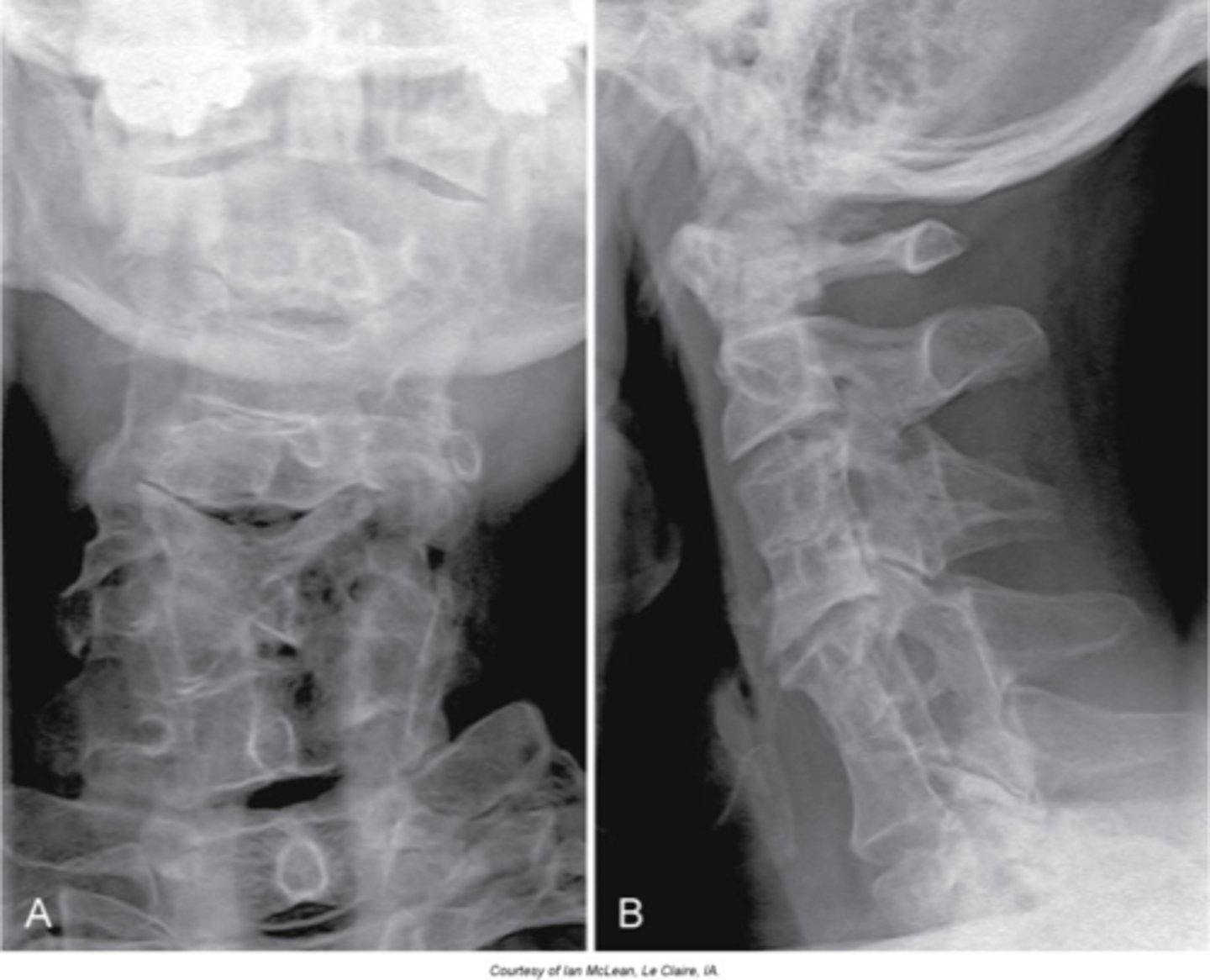
- Commonly have disc herniations
- Associated with vascular anomalies
- Associated with kidney anomalies
- Spinal cord abnormalities (MRI if neurologic symptoms)
Clinical significance of Klippel-Feil Syndrome
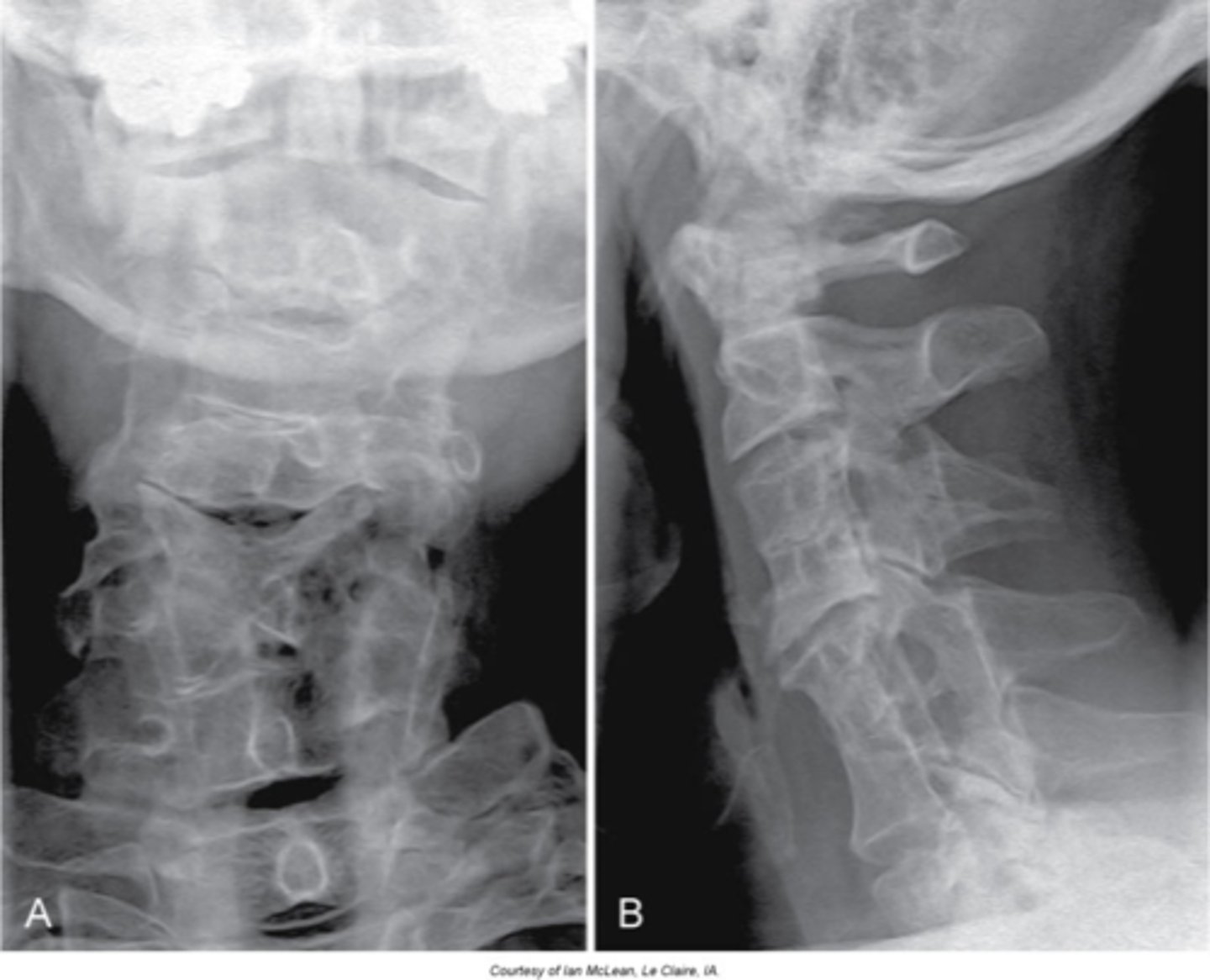
Sprengel's deformity
- Congenital elevation of the shoulder
- Improper migration of the scapula
- May occur without Klippel-Feil Syndrome
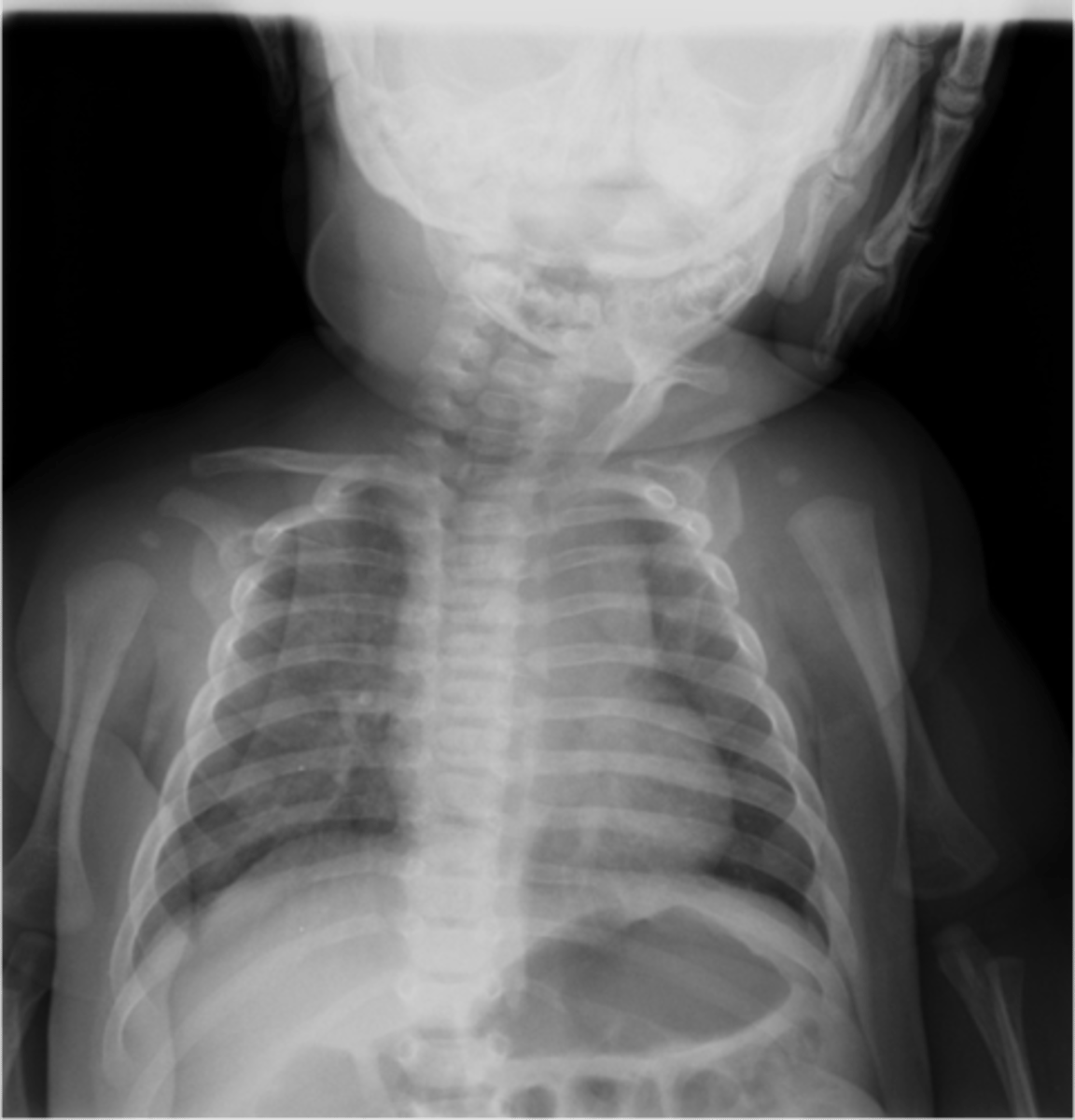
Omovertebral bone
May be fibrocartilaginous (can't see on x-ray)
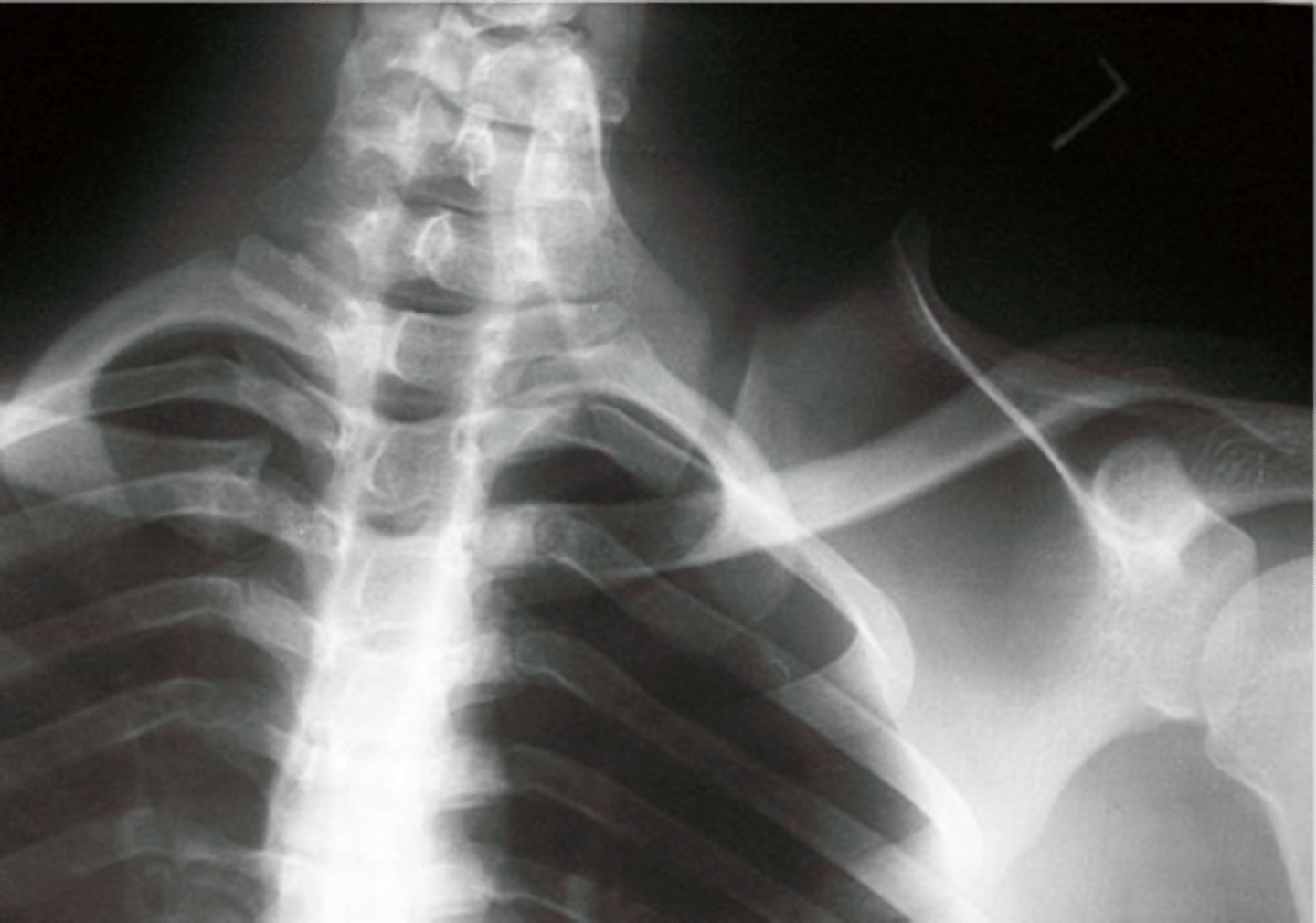
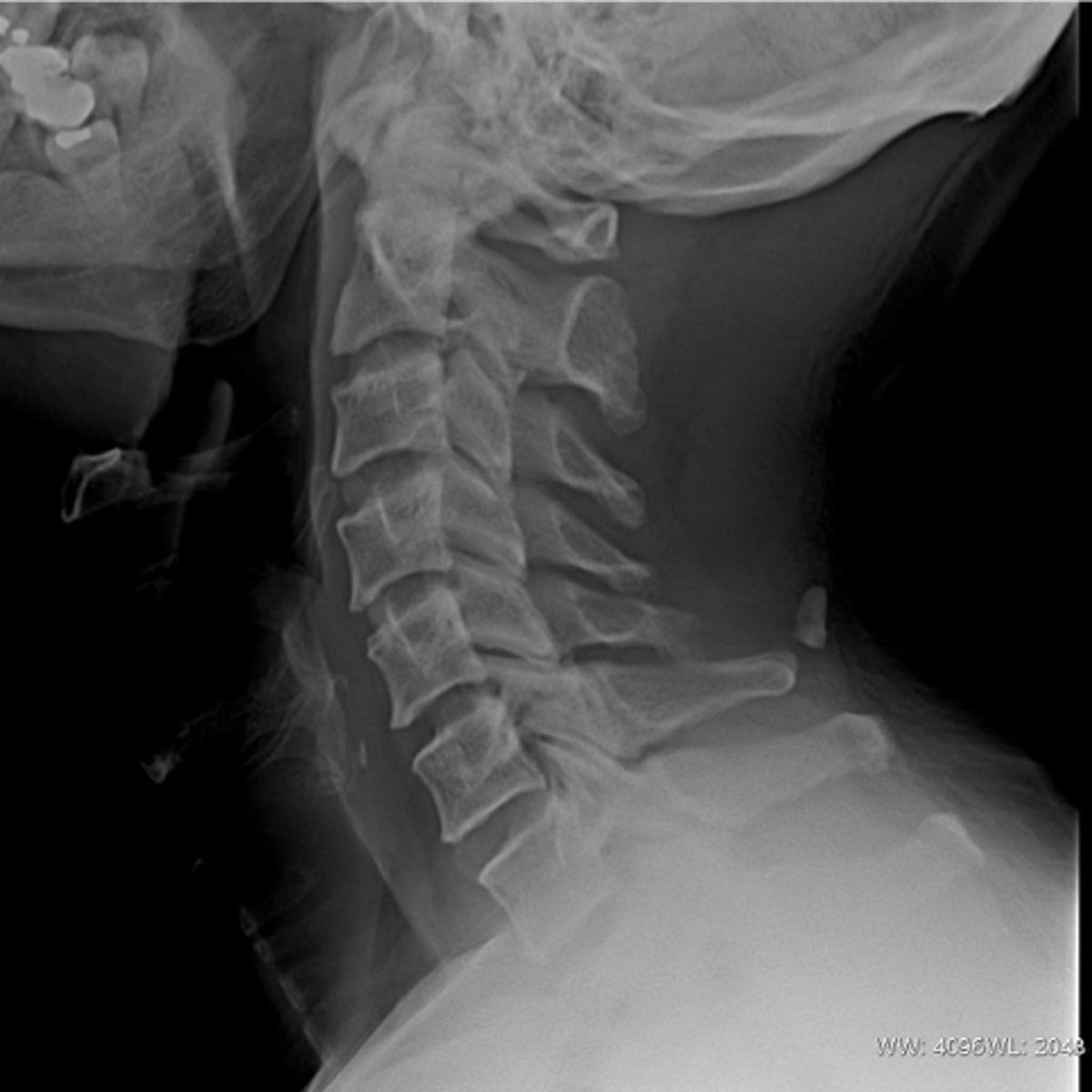
Nuchal bone (ossicle)
- Isolated ossification within the nuchal ligament
- Posterior to the spinous process of the cervical spine
- Smooth, well-corticated
- Often far enough from the spinous process so as not to be confused with a fracture fragment
Radiographic findings of nuchal bone (ossicle)
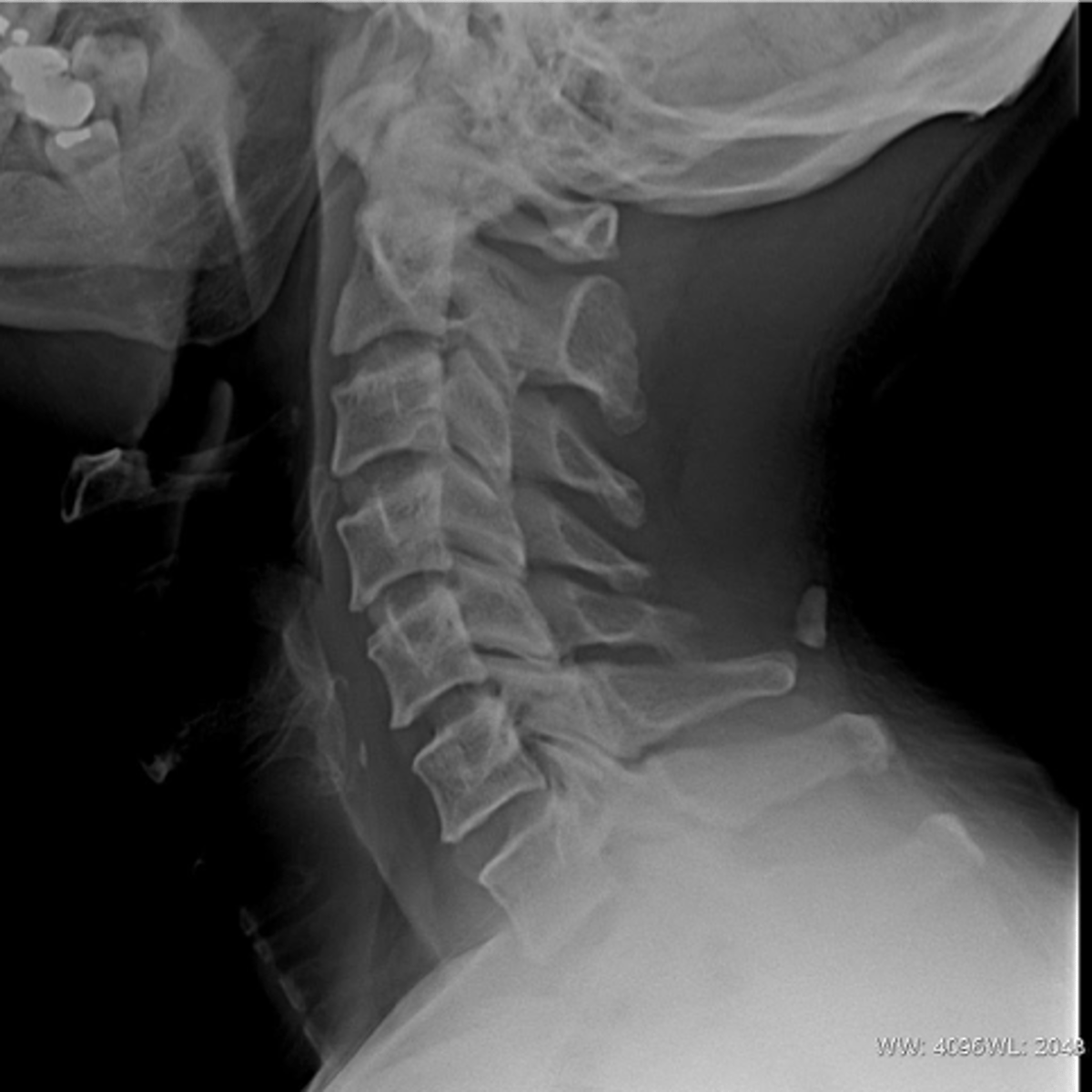
None
Clinical significance of nuchal bone
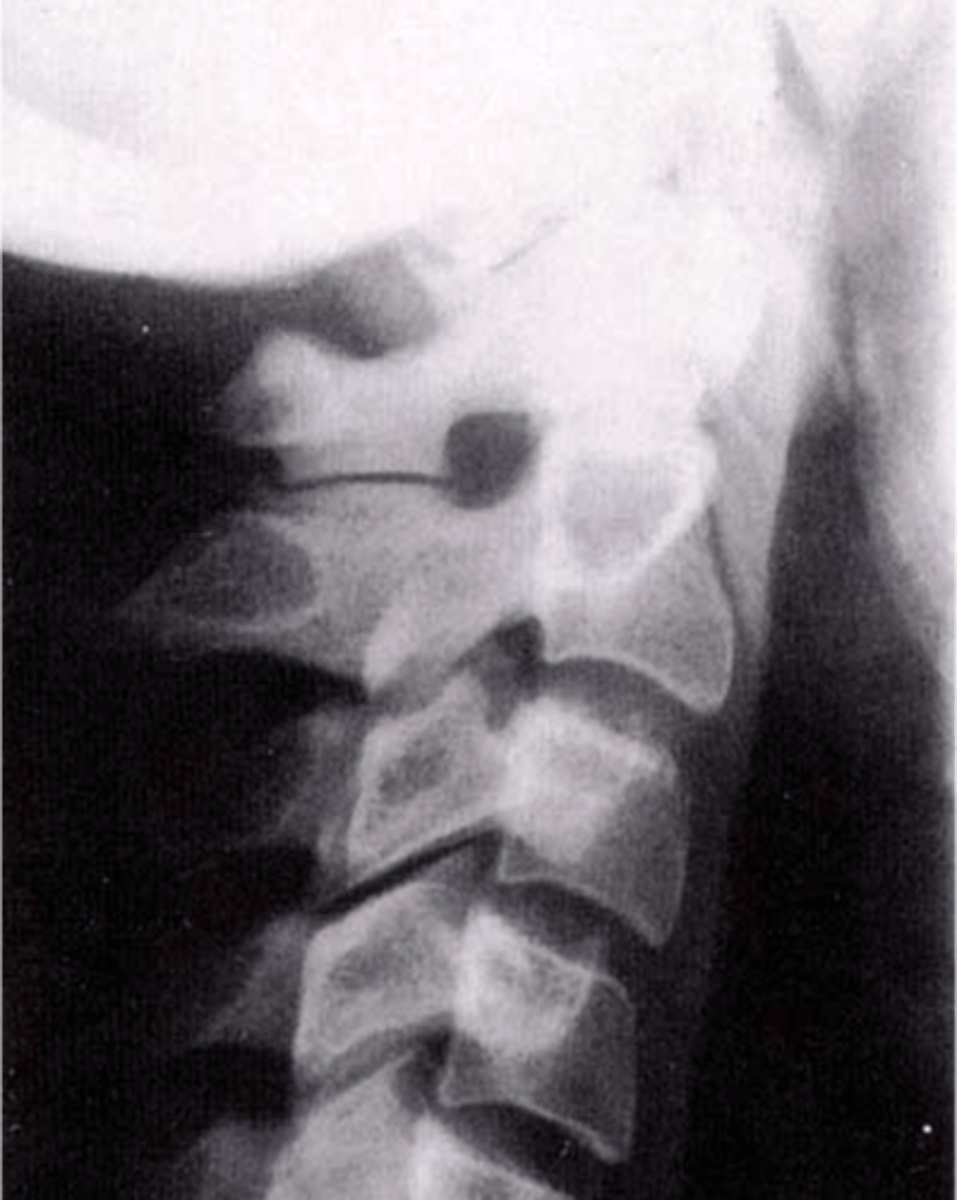
Accessory articulations
Can occur between spinous processes posteriorly or transverse processes laterally
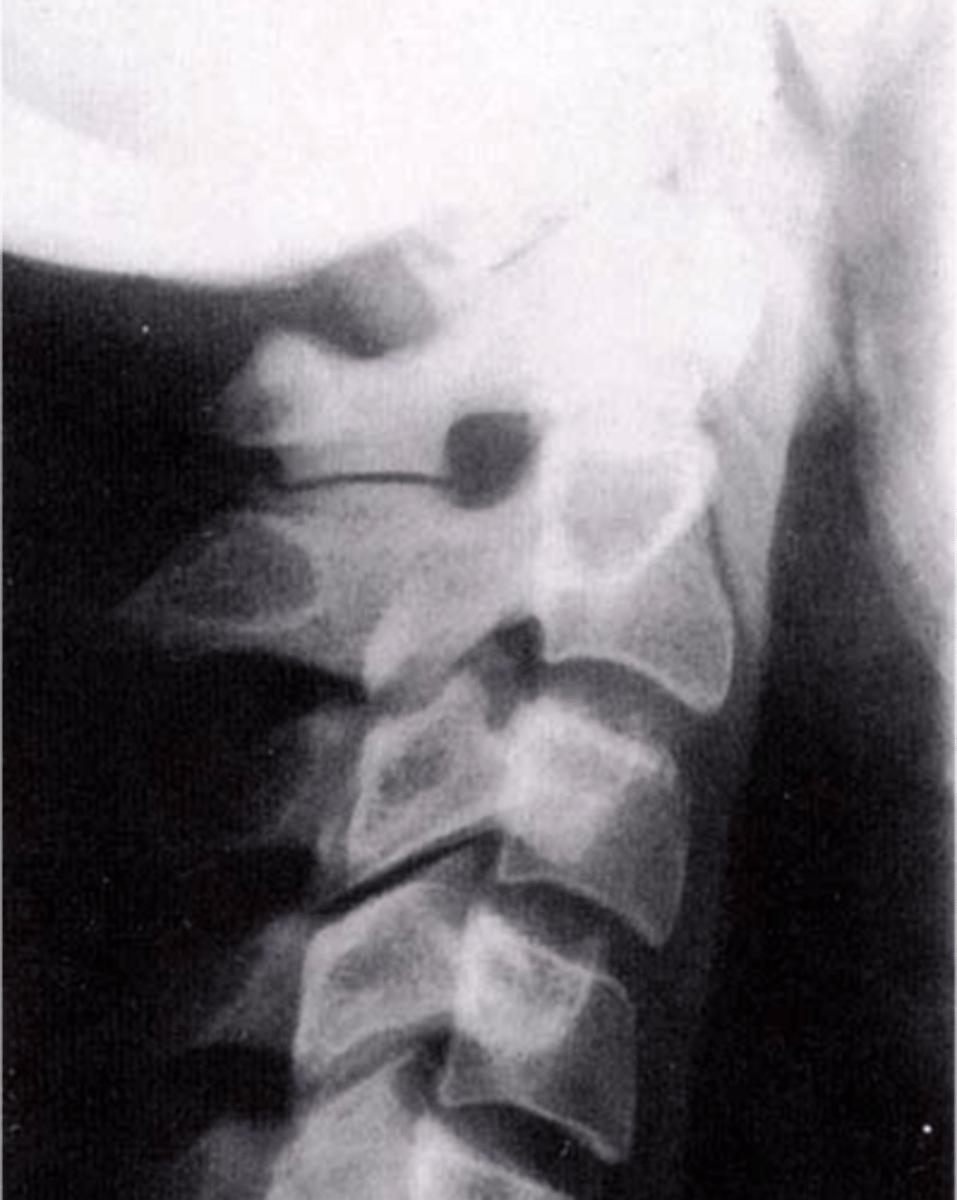
ROM
Accessory articulations are often asymptomatic, but can restrict _____
Butterfly vertebrae
- Failure of the ossification centers to meet in the middle of a vertebral body due to a central cleft
- The two pieces are not mobile and are attached
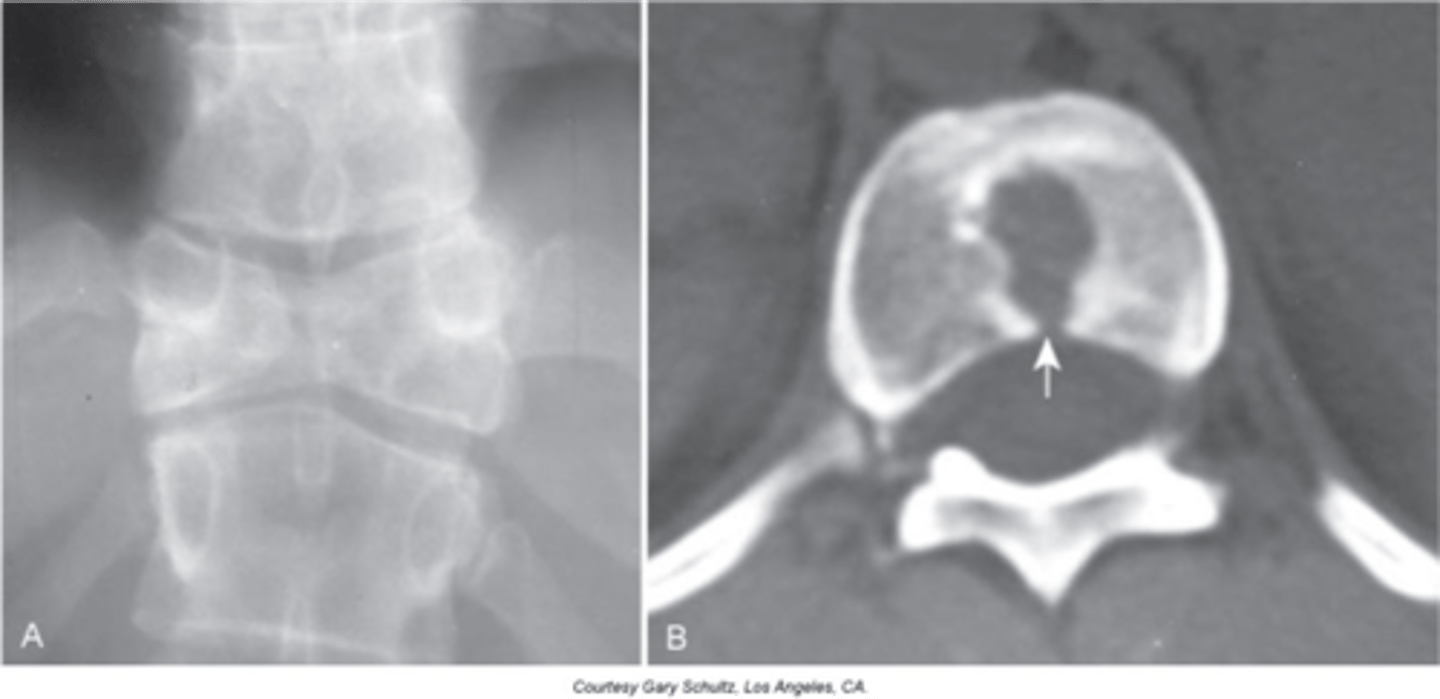
Two lateral wedge-shaped parts of a single vertebral segment that point medially
Butterfly vertebrae appearance
- Can lead to scoliosis due to asymmetry of the two pieces
- Commonly occurs with other spinal anomalies
- Assess patient for neurologic alterations
Clinical significance of butterfly vertebrae
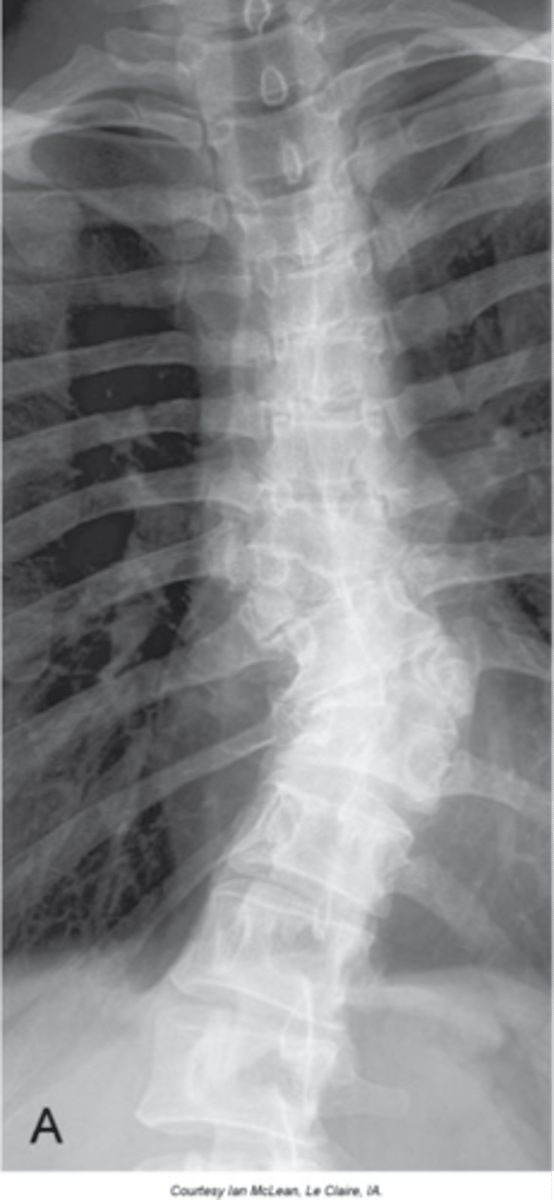
Hemivertebra
- Failure of ossification and, at times, segmentation of a vertebrae
- Most commonly they are lateral, but anterior and posterior ones do occur
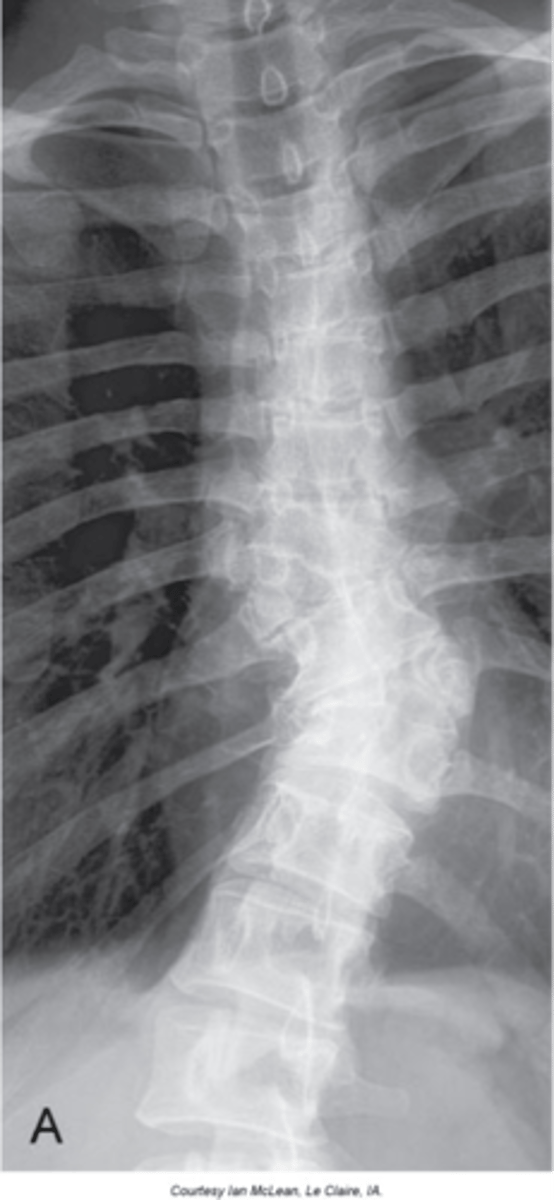
- Wedge shaped vertebral body
- Commonly fused to another segment
- Will have its own transverse process and rib if thoracic
- Common to see multiple on opposite sides of the spine
Appearance of hemivertebra
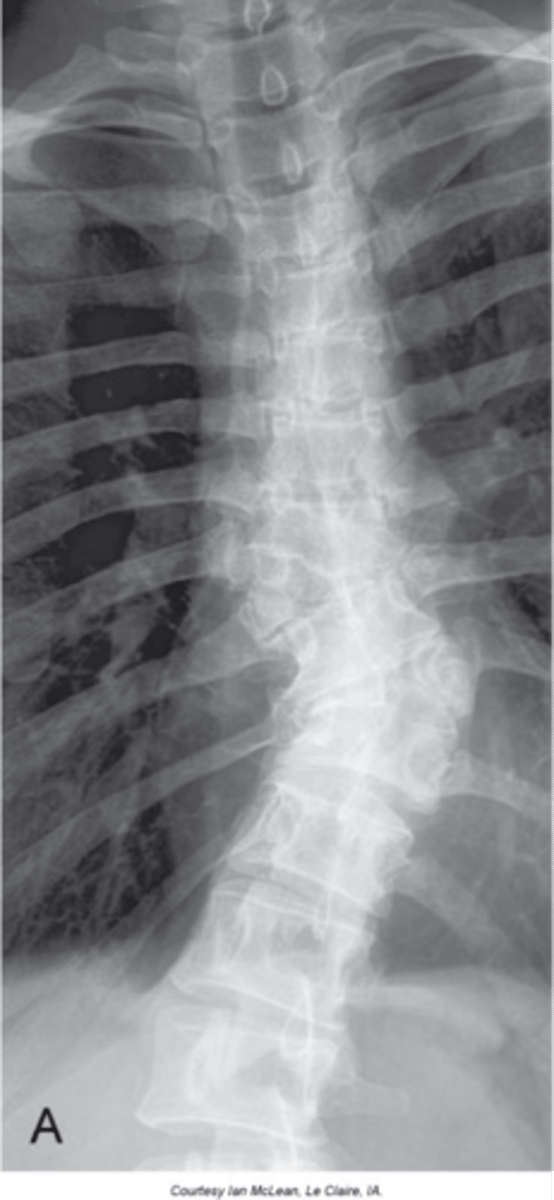
Cause of structural scoliosis
Clinical significance of hemivertebra
Nuclear impression (persistent notochord)
- Indentation of the vertebral endplate that has absolutely no relation to trauma
- Normal developmental appearance
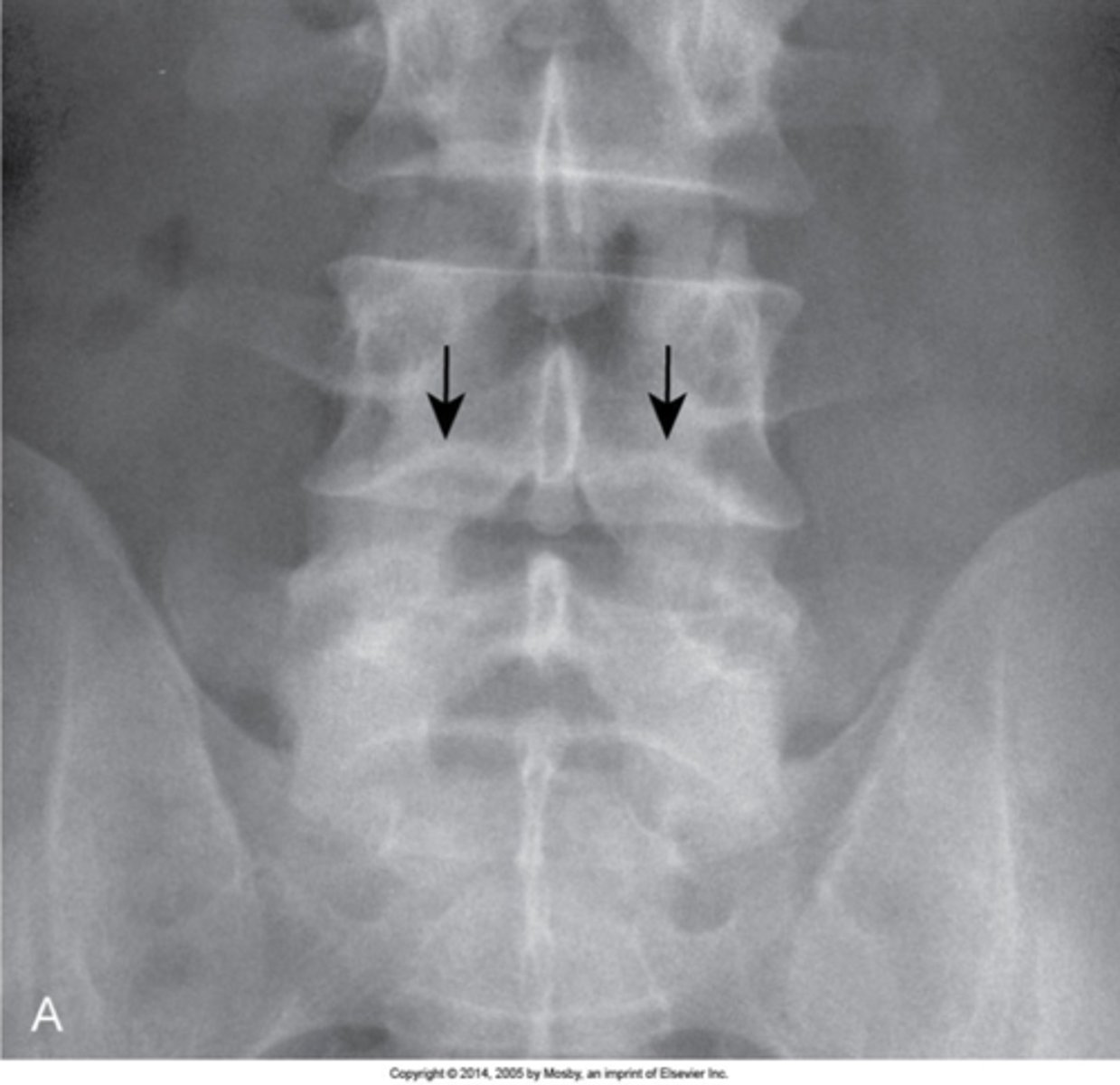
- Smooth, long transition of indentation onto the vertebral endplate
- Margins should be obtuse in angulation
- Should be little to no change in the appearance of the adjacent medullary bone (no sclerosis)
Nuclear impression appearance
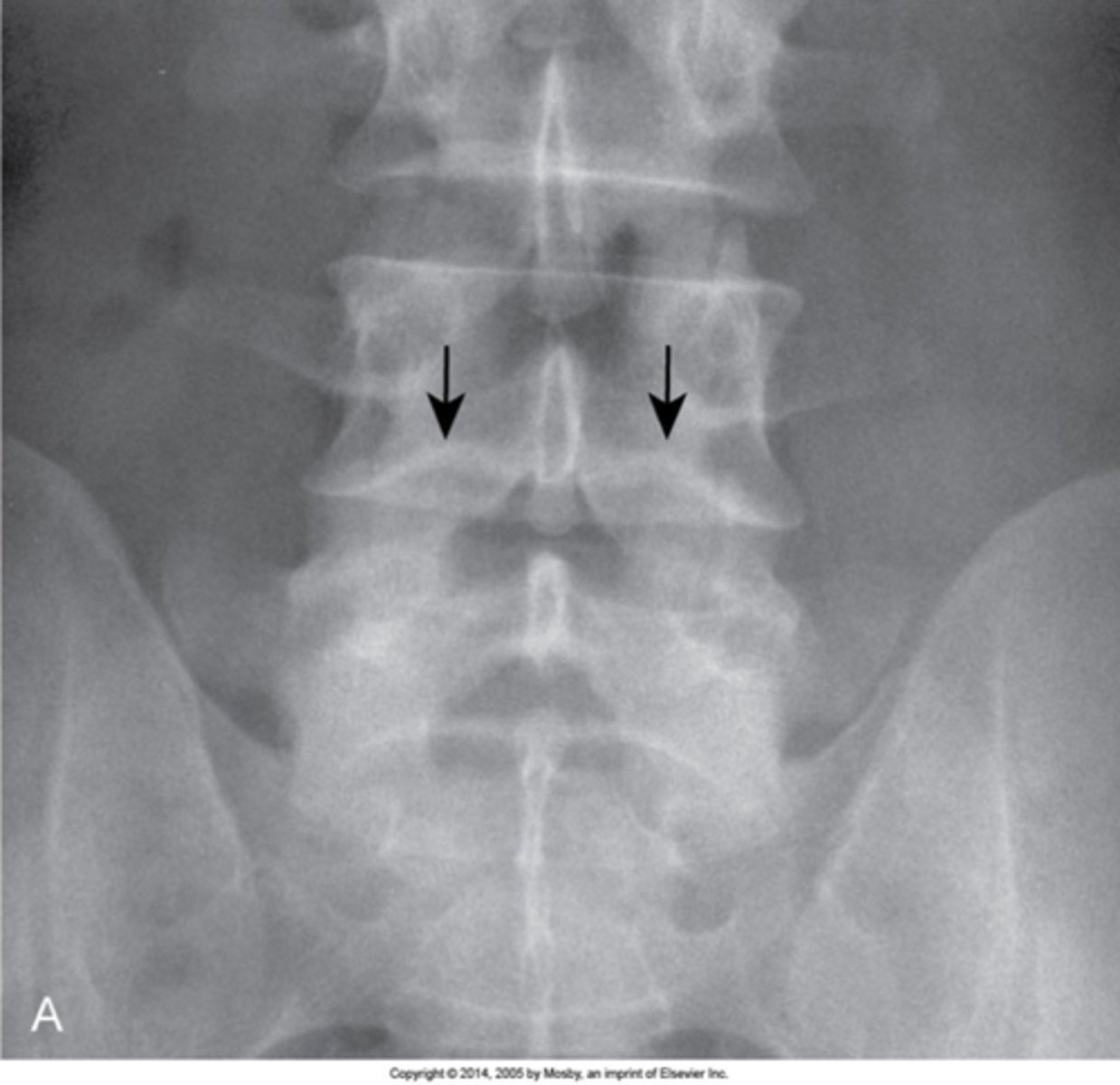
None, not to be confused with fractures, Schmorl nodes, central insufficiency fractures of the spine
Nuclear impression clinical significance
Schmorl's nodes
- A disc herniation that goes through the vertebral endplate into the medullary aspect of the disc
- MC at the thoracolumbar junction
True
T/F Schmorl's nodes have more abrupt margins than a nuclear impression
Sclerotic margins
Over time, Schmorl's nodes develop _____ due to a large inflammatory reaction
- When acute, they can be extremely painful. The nucleus of a disc is foreign material to the rest of the body so a large inflammatory reaction ensues
- Most are asymptomatic, especially those that occur in childhood/adolescence
- In older individuals, these can occur secondary to trauma and/or weakened bone
Schmorl's nodes clinical significance
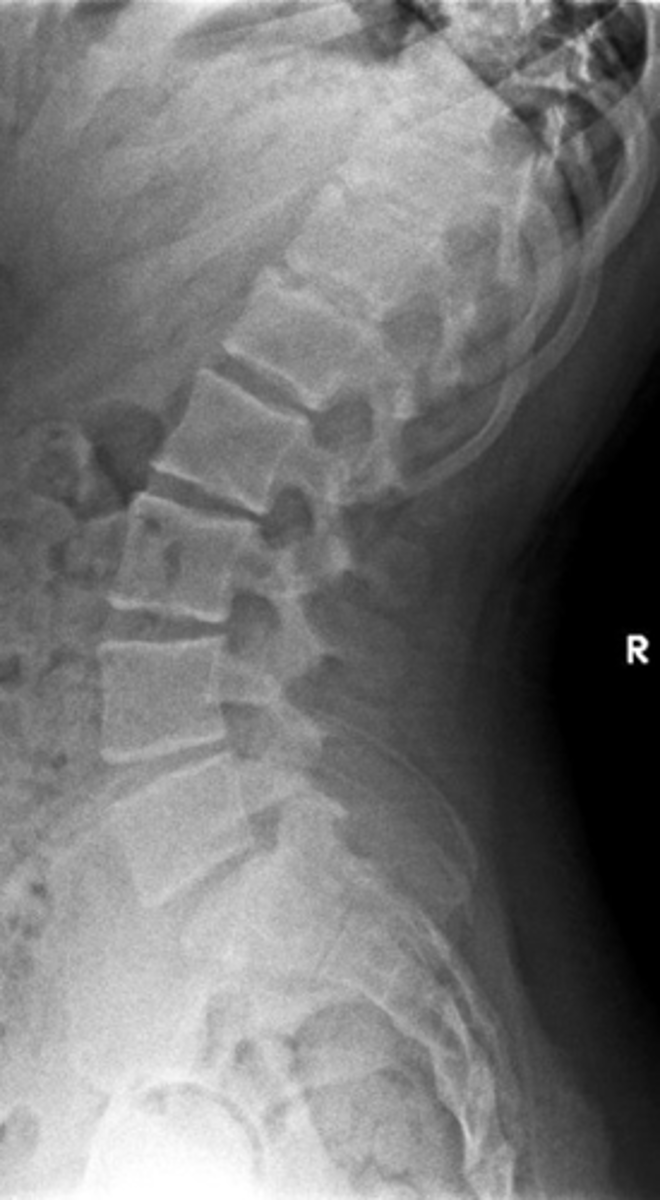
Scheuermann Disease
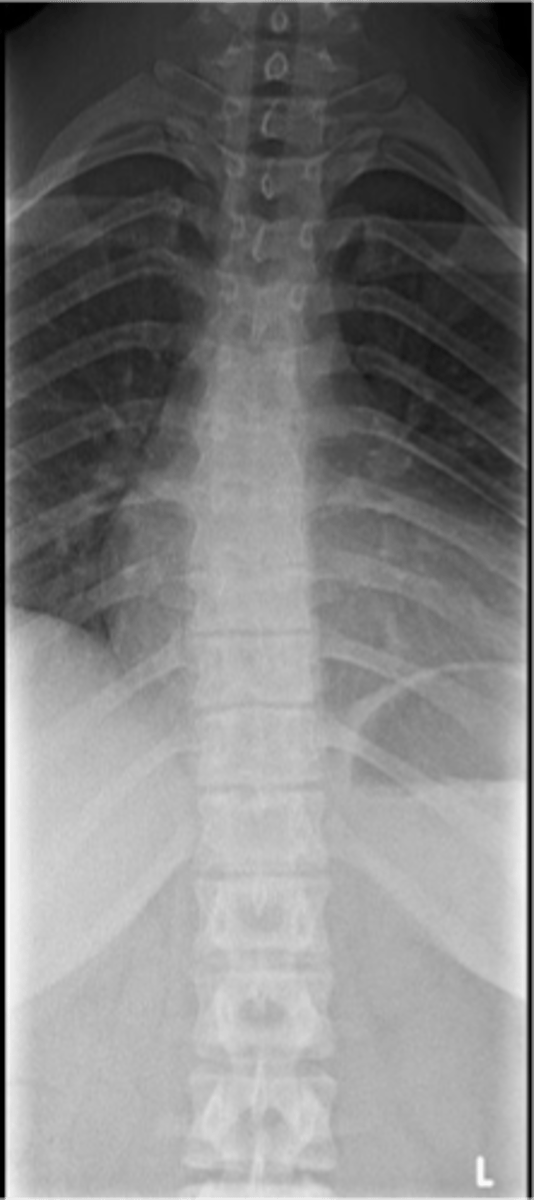
Apophysitis in the spine
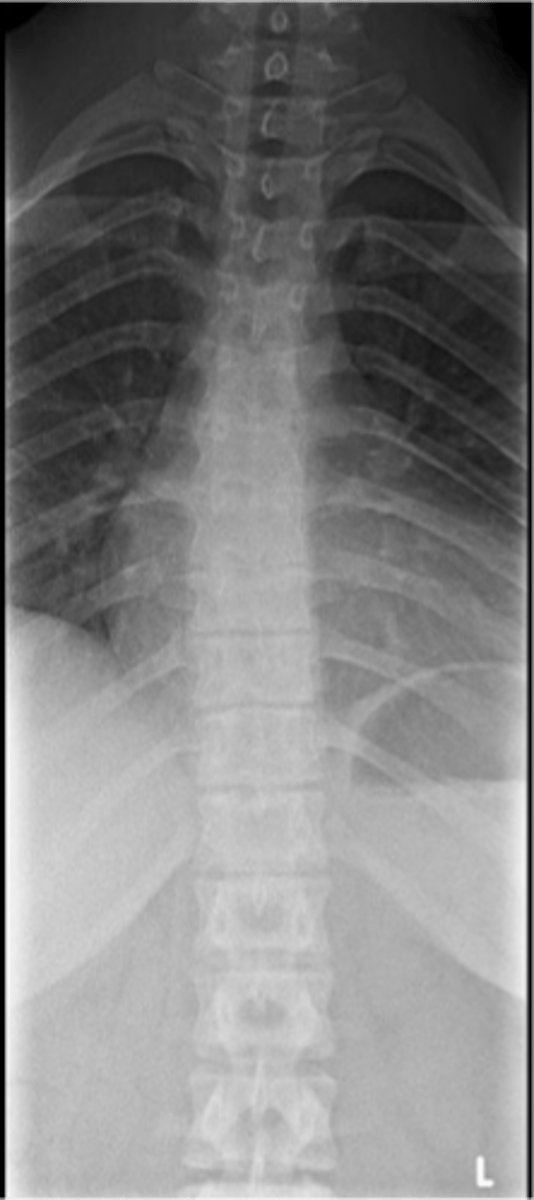
- Juvenile thoracic kyphosis
- Discogenic disease
Another term for Scheuermann Disease
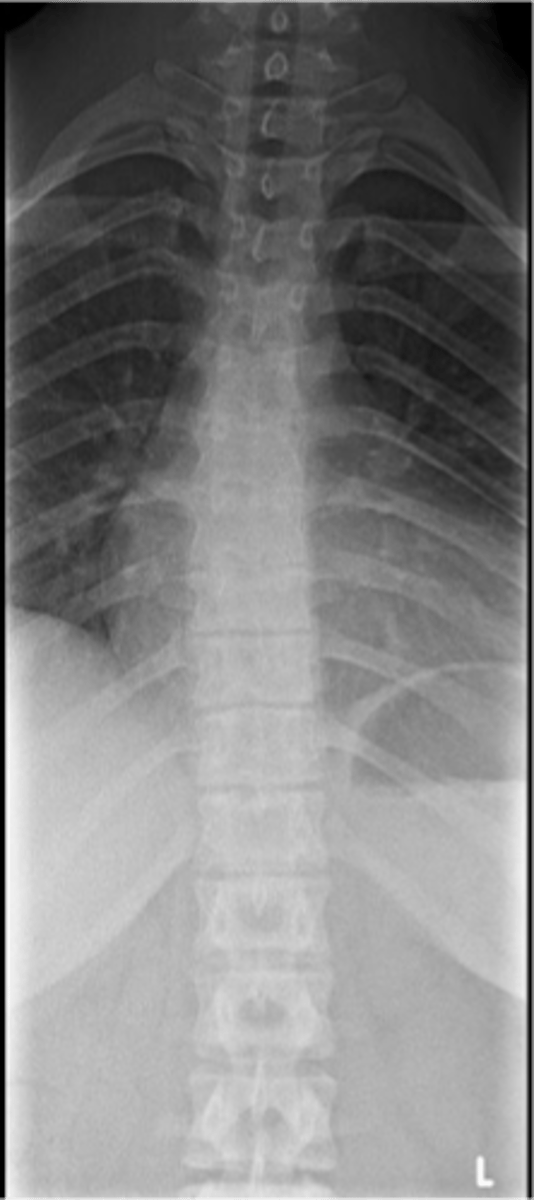
- Decreased disc height
- Increased AP diameter of the vertebral body
- Endplate irregularities to include Schmorl's nodes
- Increased thoracic kyphosis
Scheuermann Disease findings
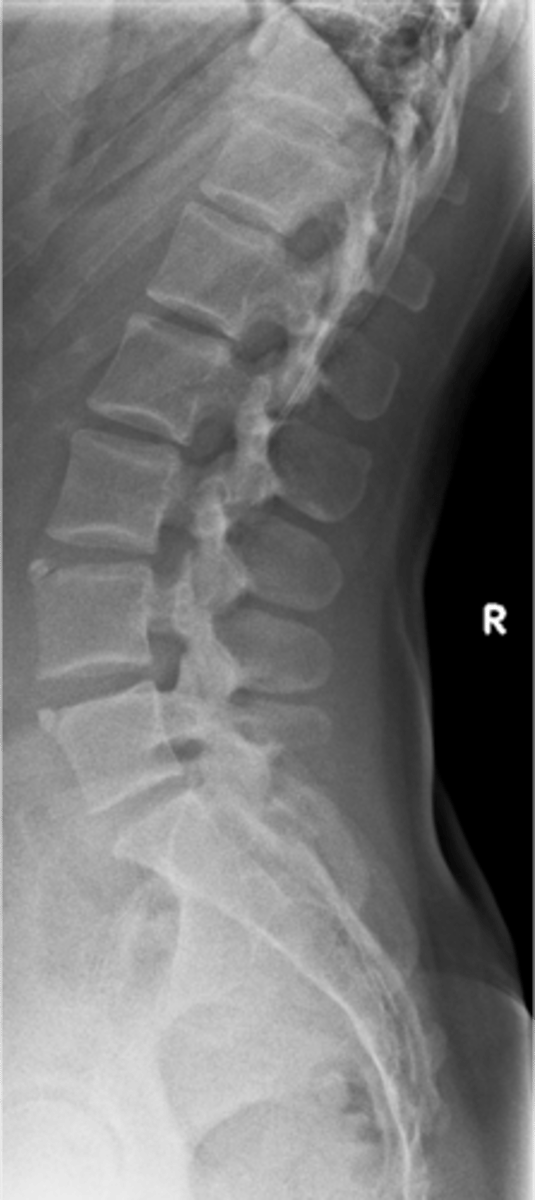
Limbus bone
A Schmorl's node that cleaves off a peripheral piece of the vertebral body
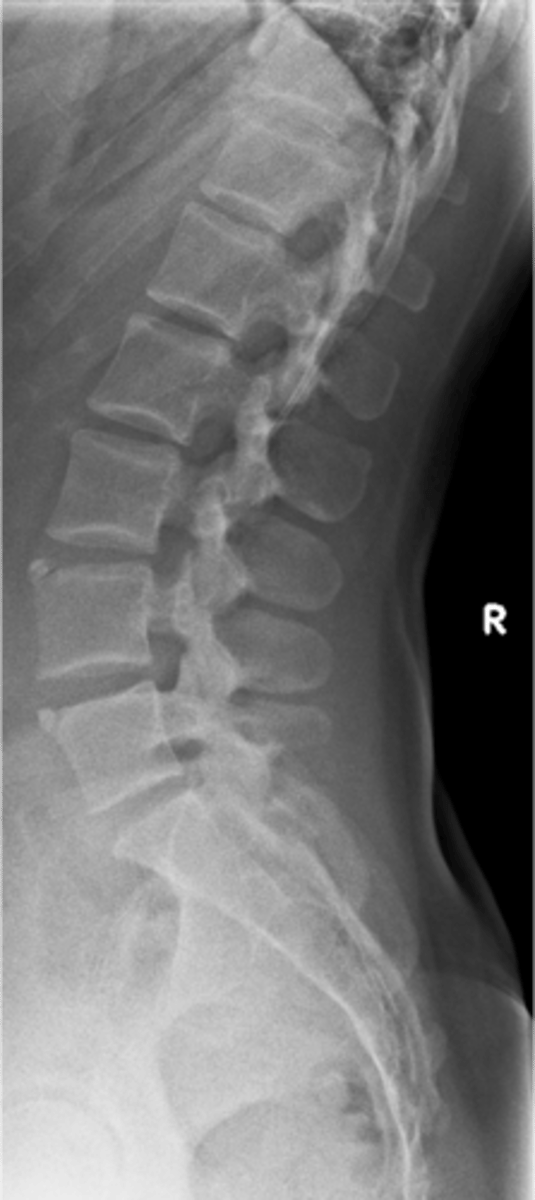
Anterior
A limbus bone is usually at the _____ endplate, however, they can be found anywhere at the margins of a vertebral body
Piece of the vertebral body separated from the remaining vertebral body by a lucent cleft, leaving a triangular fragment
Limbus bone appearance
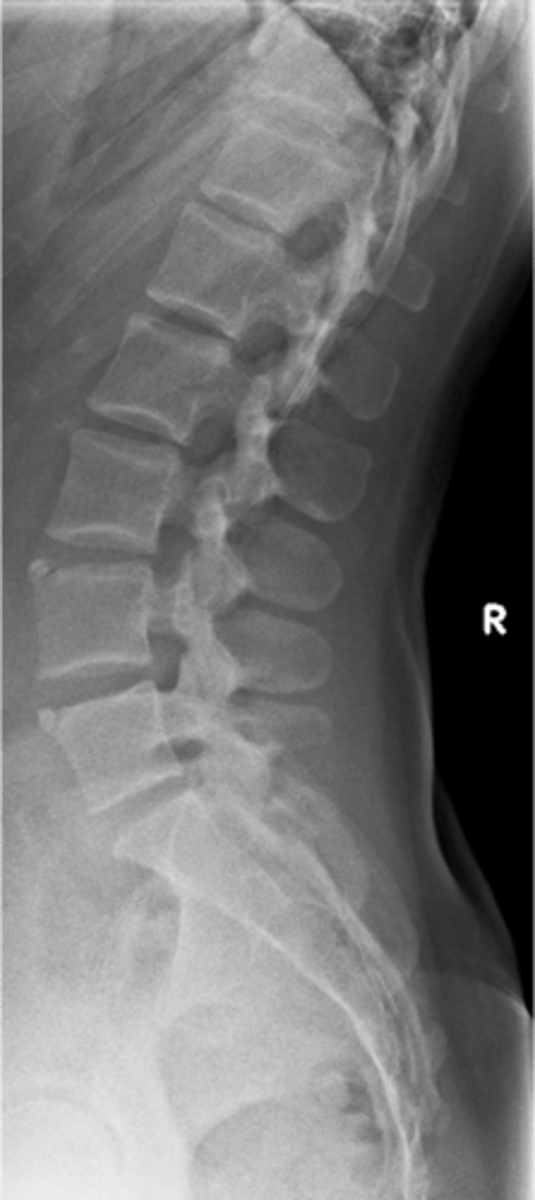
- Painful when acute
- Posterior limbus bone indicates there is a disc herniation into the spinal canal (neurologic symptoms may be present)
Limbus bone clinical significance
Intercalary bone
Calcification of the annulus fibrosis, commonly dystrophic calcification (post-traumatic alterations, which attracts calcium)
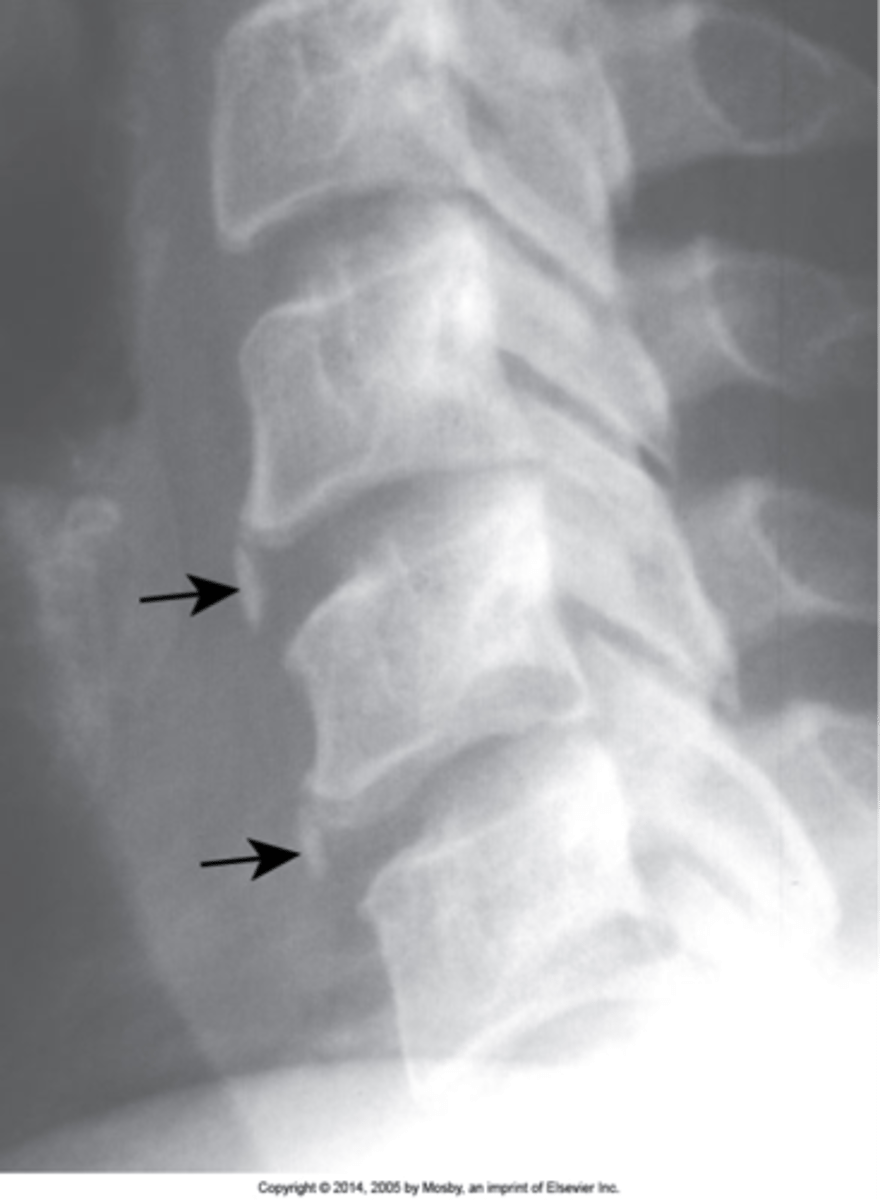
Vertical linear calcification of the annulus fibrosis not attached to the vertebral body
Intercalary bone appearance
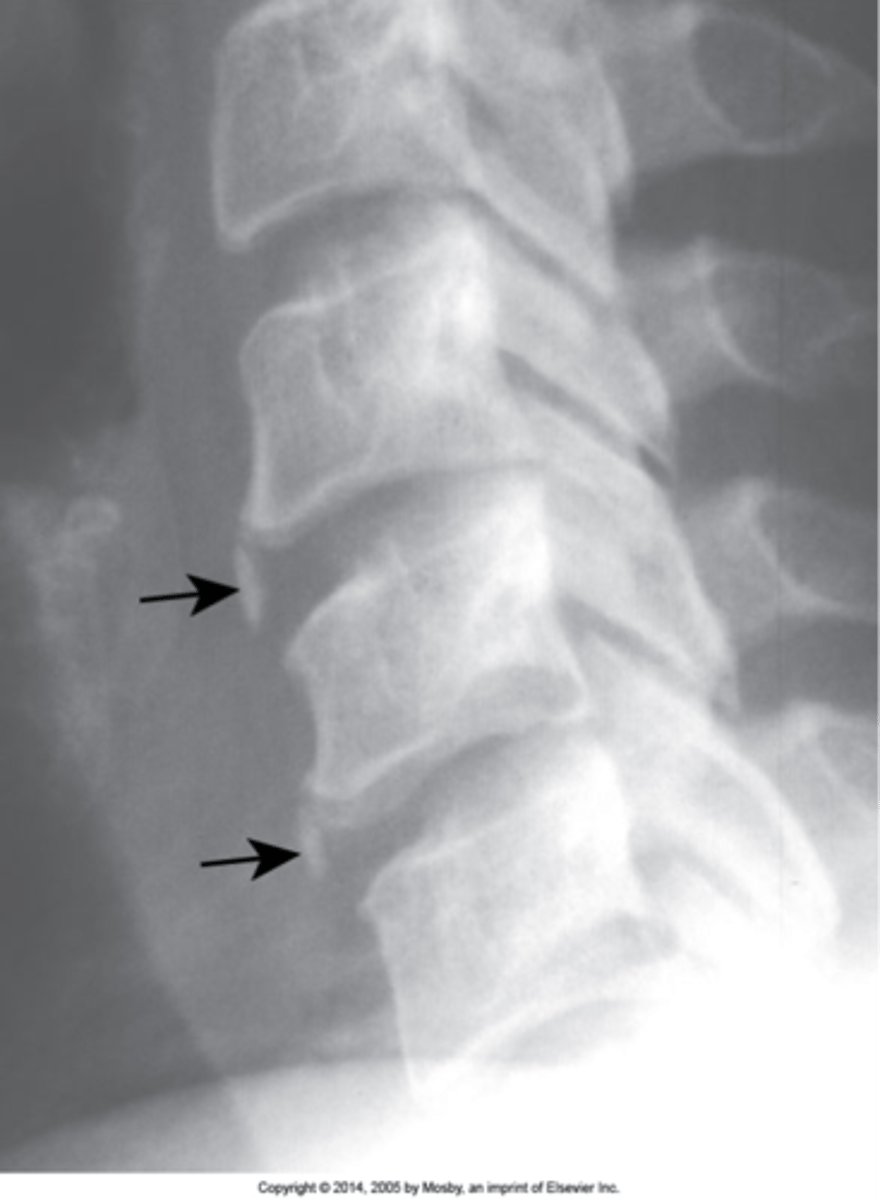
None
Intercalary bone clinical significance
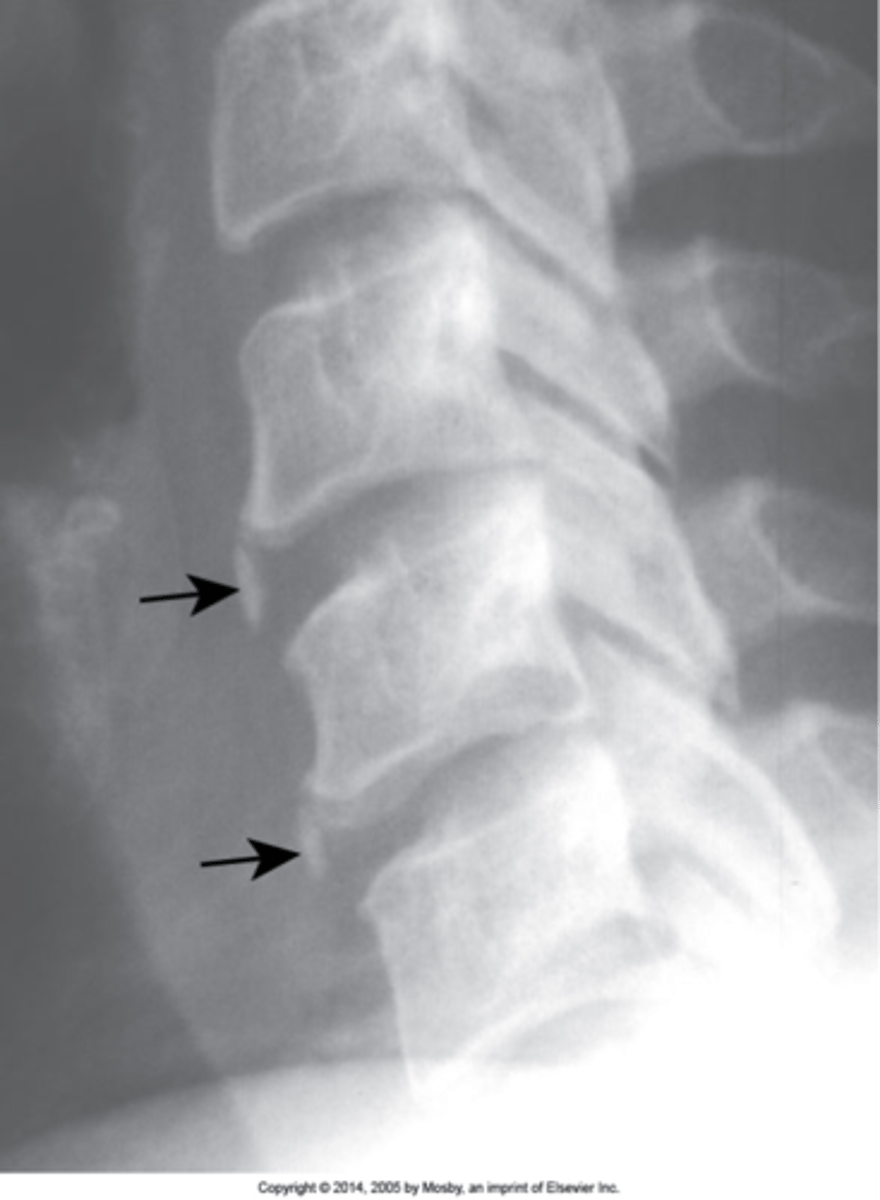
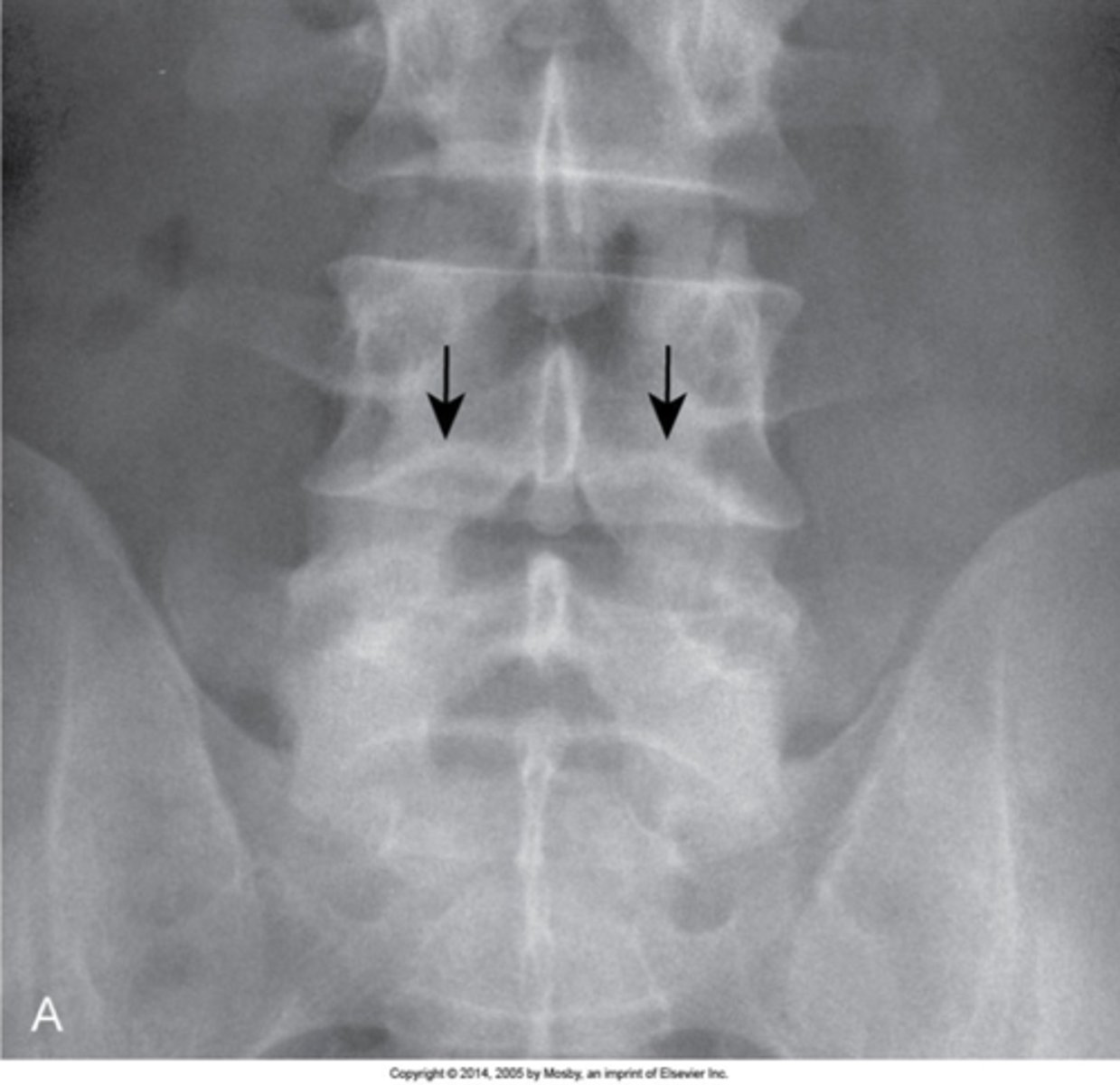
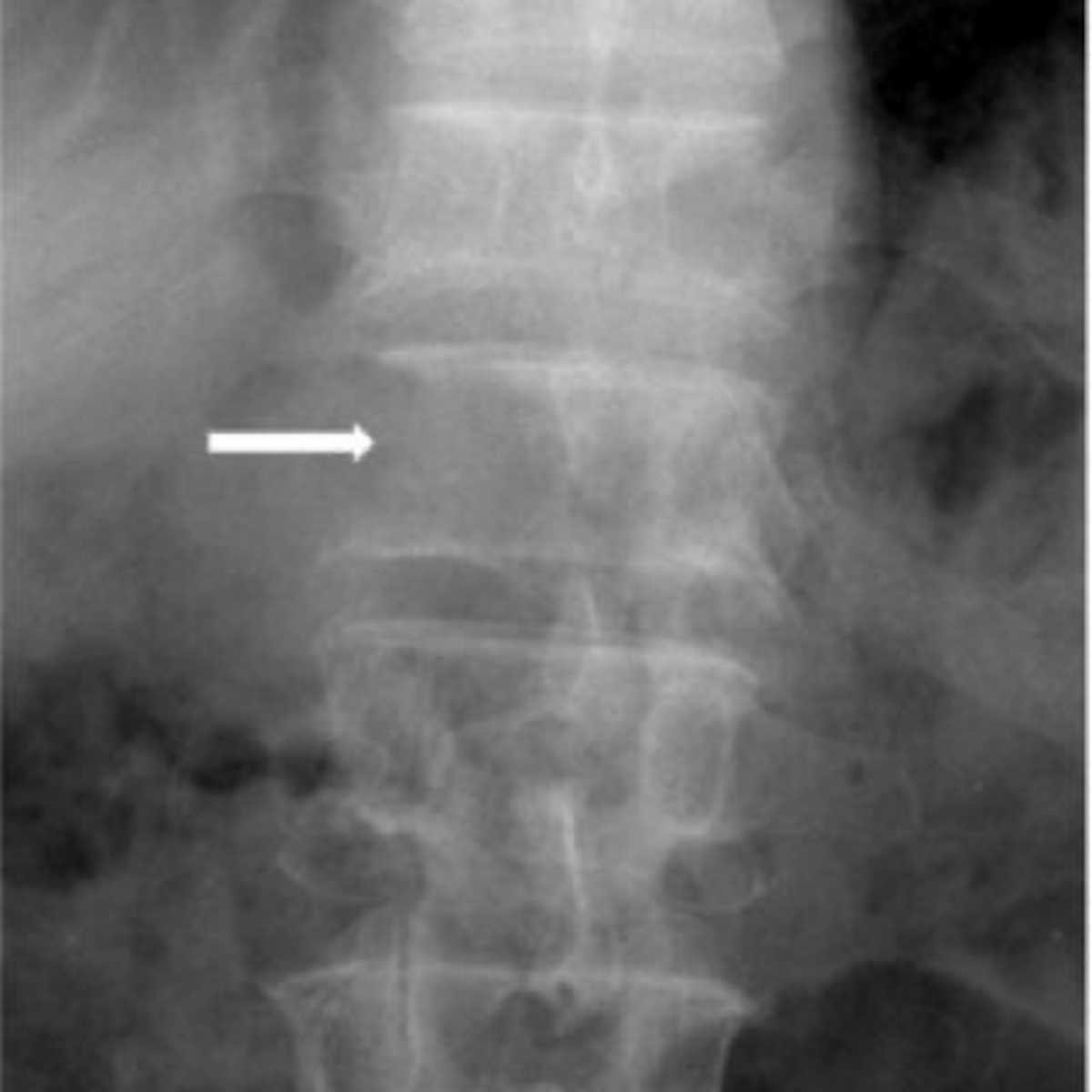
Pedicle agenesis
Congenital absence of one of the pedicles. Can be found in any region of the spine
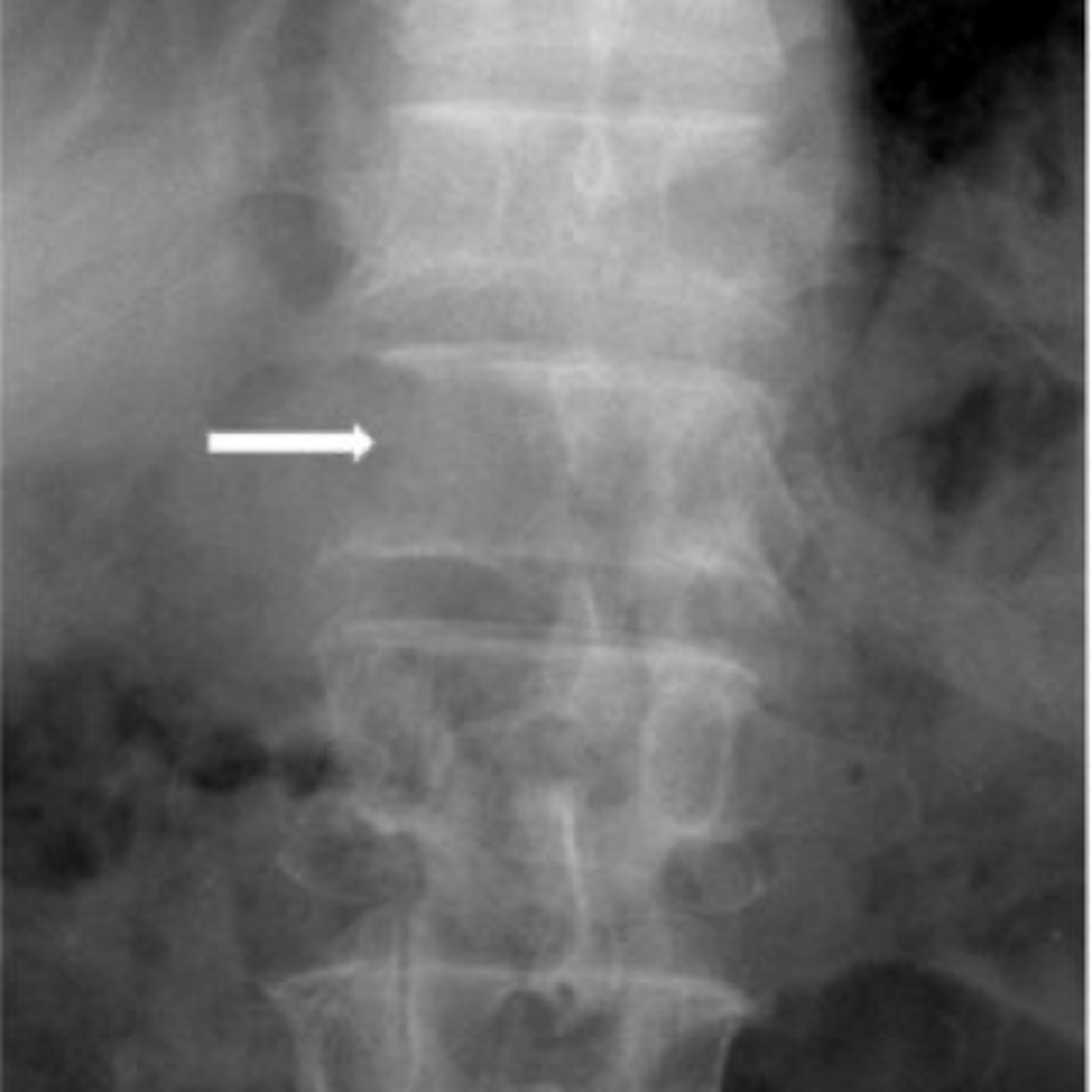
- Missing pedicle on one side of the spine
- Contralateral pedicle will be sclerotic (Wolff's law)
- Contralateral sclerosis is not always present
Pedicle agenesis appearance
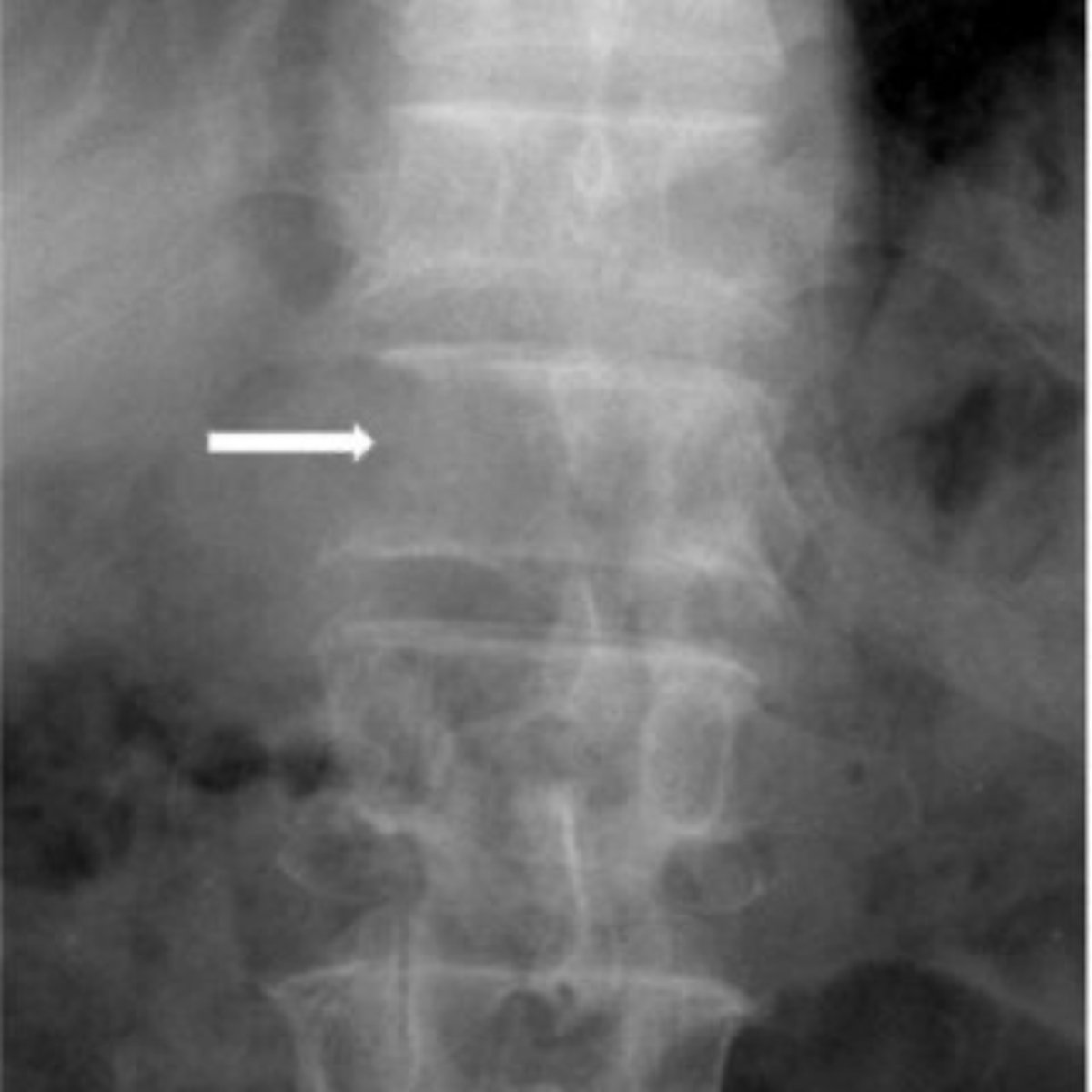
Pathologies like metastasis can destroy a pedicle, trying to tell apart congenital absence from a pathology is very important and can be difficult, look to the contralateral pedicle of increased opacity
Pedicle agenesis clinical significance
Hahn Venous Clefts/Fissures
- Vascular groove/vascular impression
- From the entrance of Batson's venous channel into the back of the vertebral body
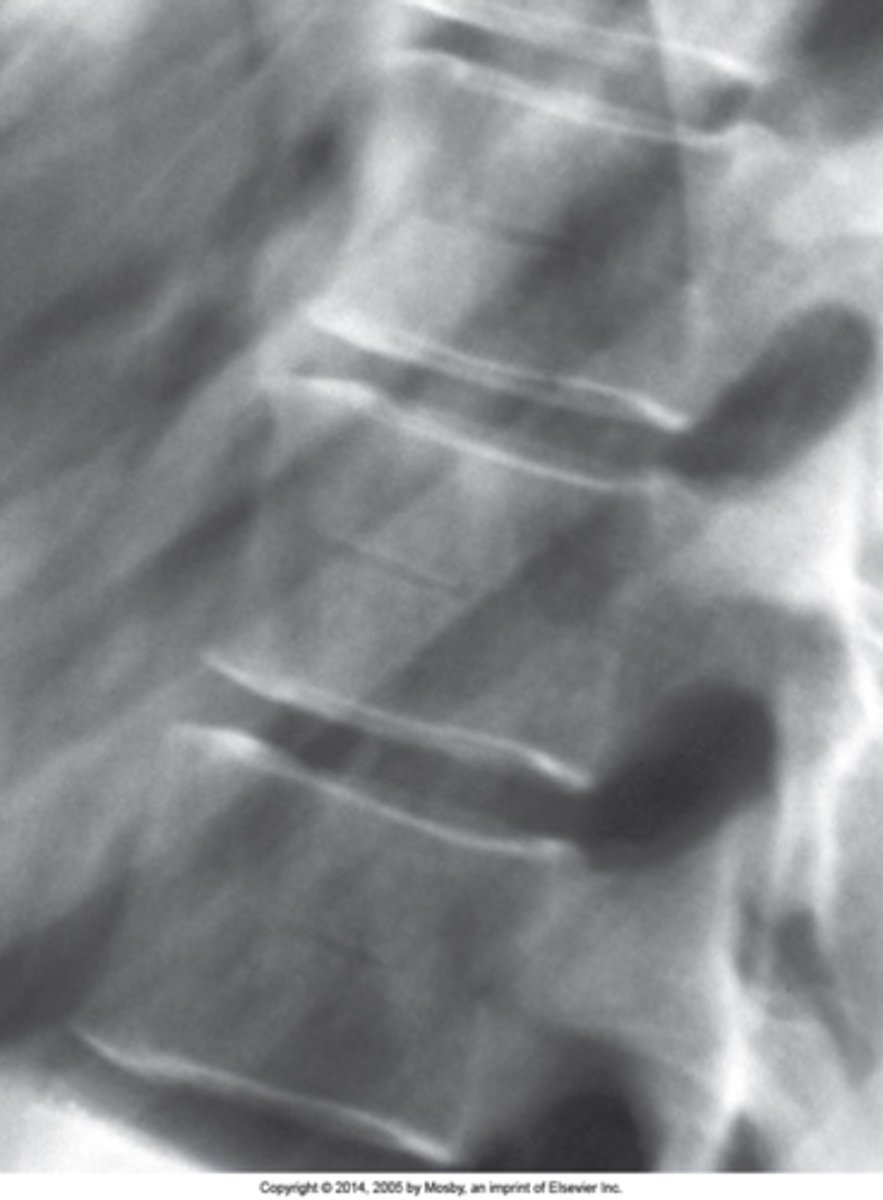
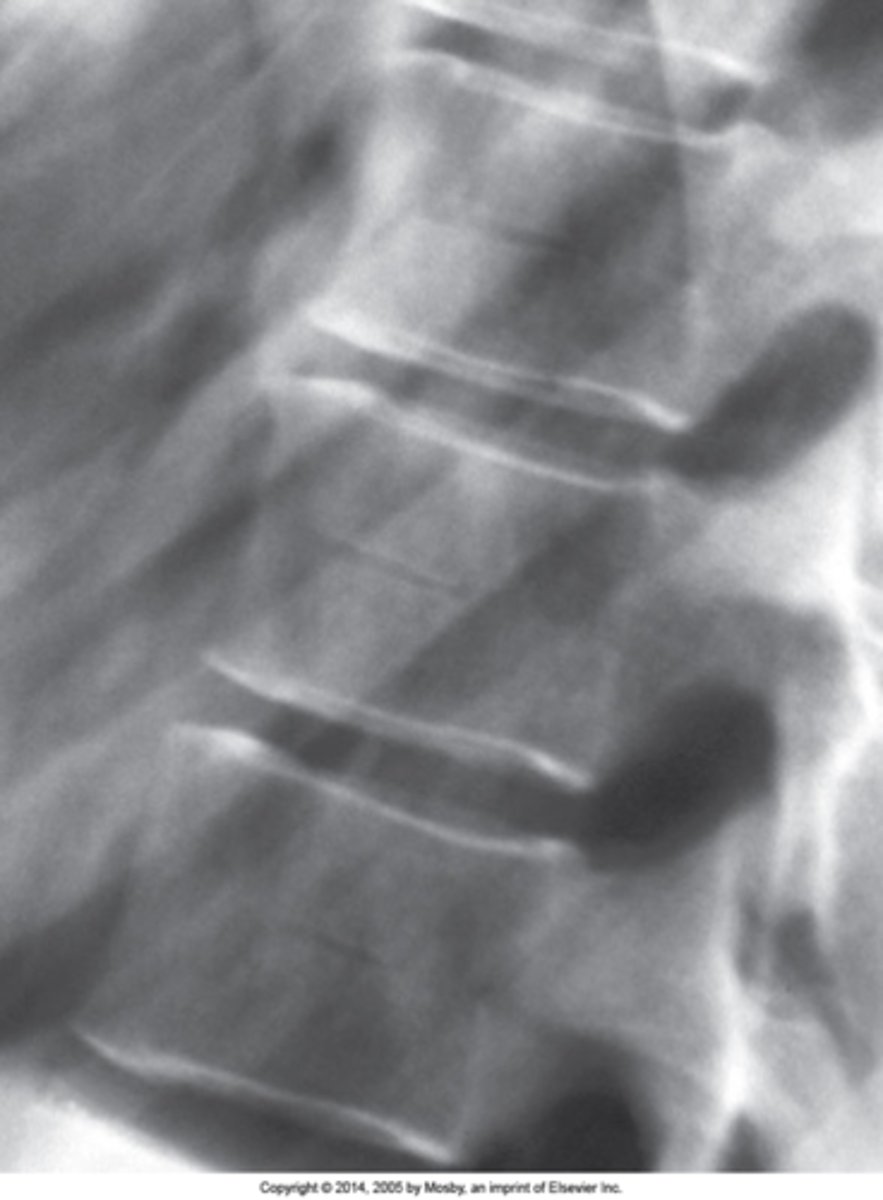
Radiolucent channel running through the mid aspect of a vertebral body with sclerotic margins
Hahn Venous Clefts/Fissures appearance
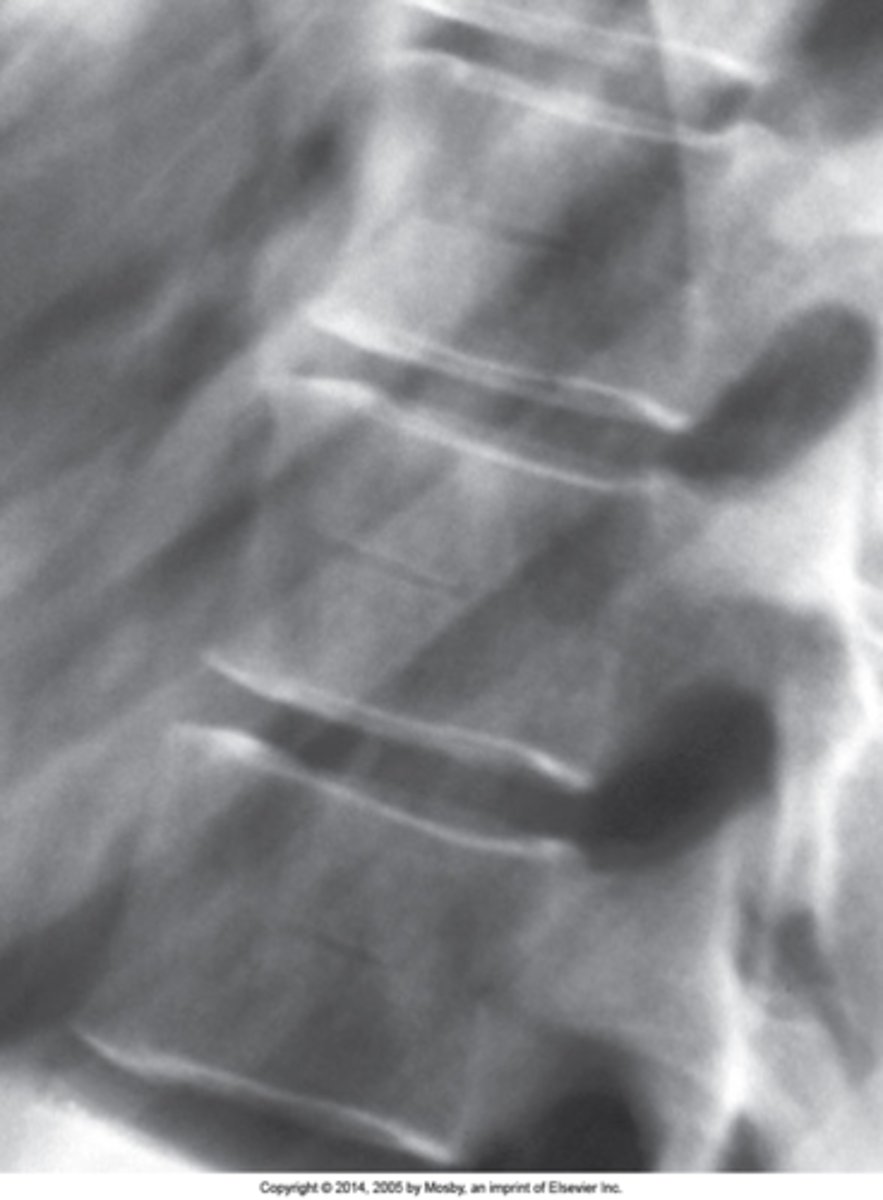
Mid-to-lower thoracic
Hahn Venous Clefts/Fissures are best seen in the _____ spine
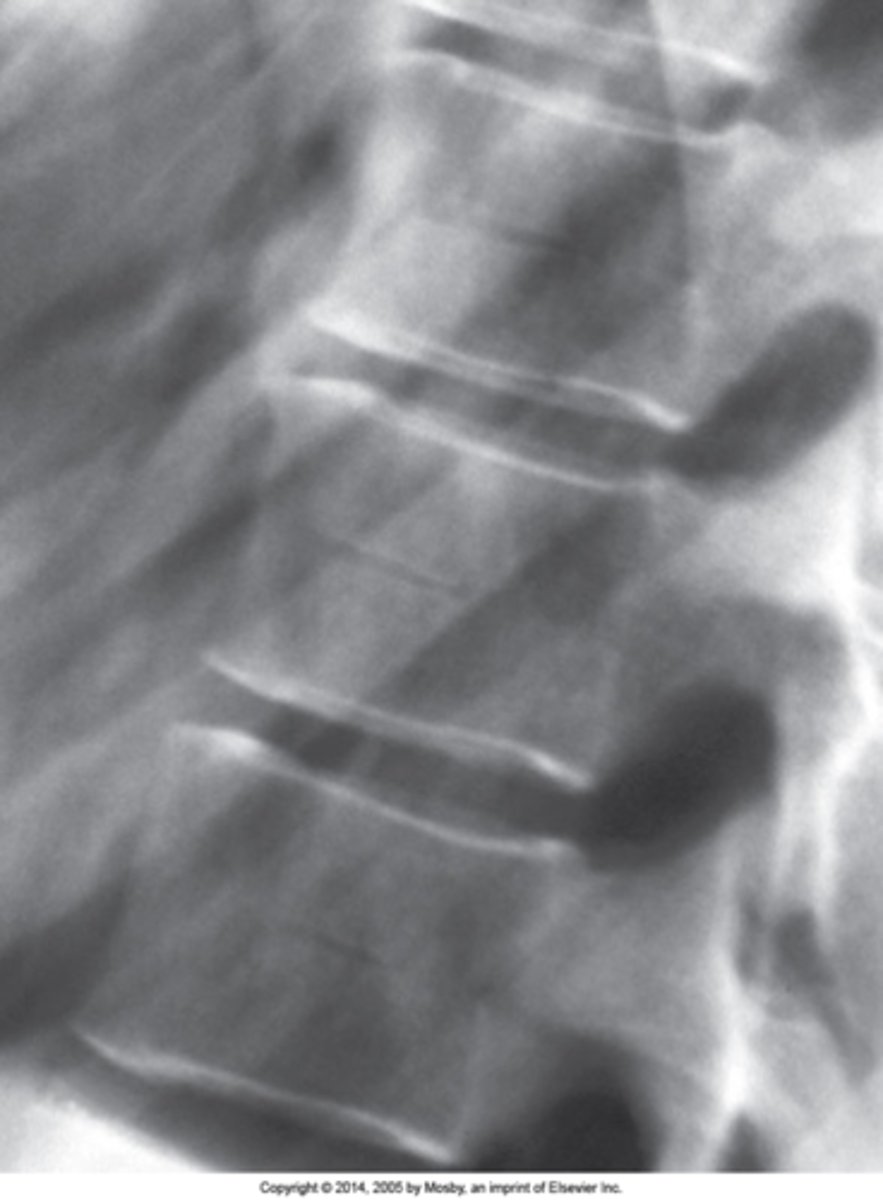
None
Hahn Venous Clefts/Fissures clinical significance
Clasp-Knife
Failure of fusion of the posterior arch of S1 with concurrent hypertrophy of the spinous process of L5
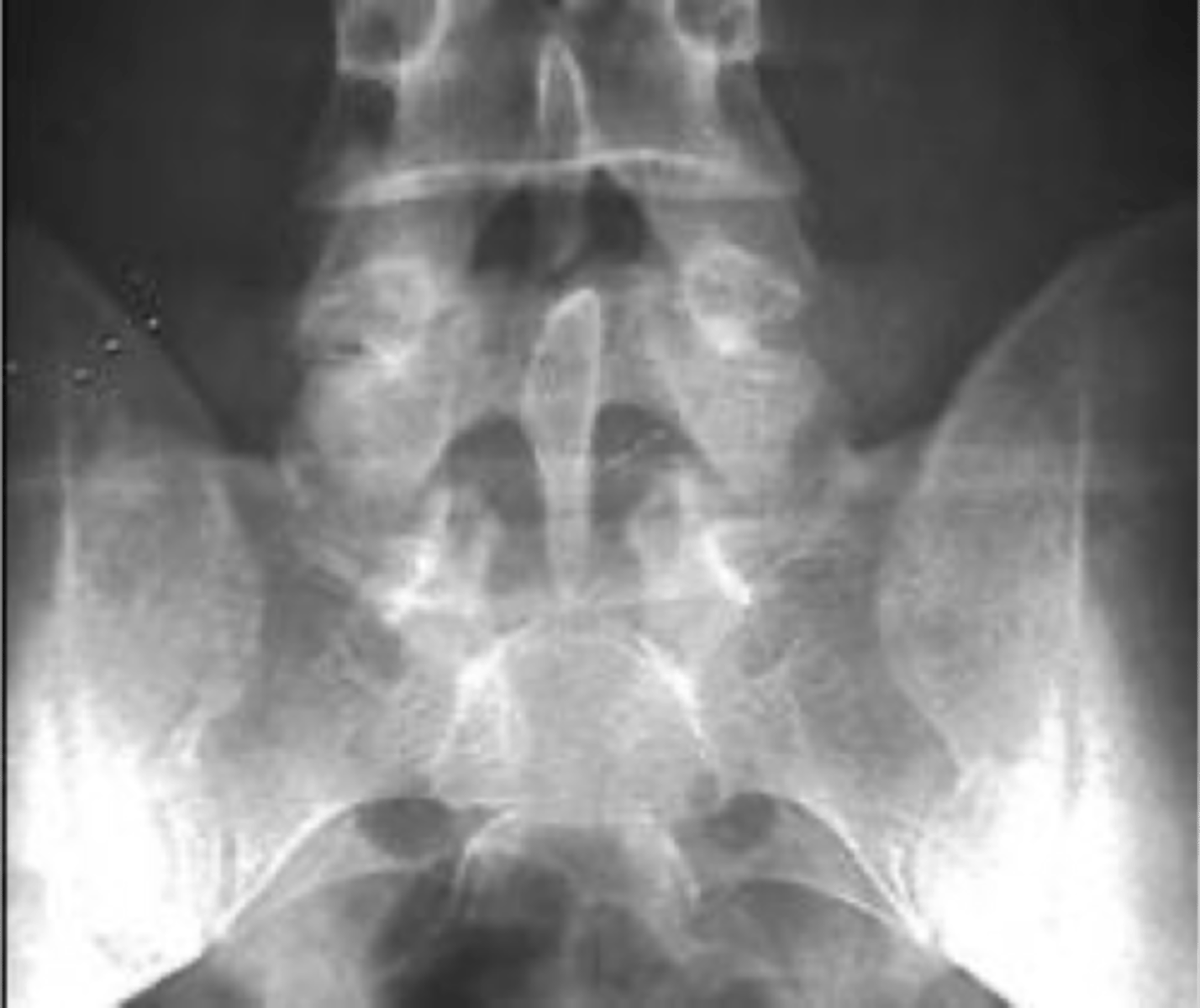
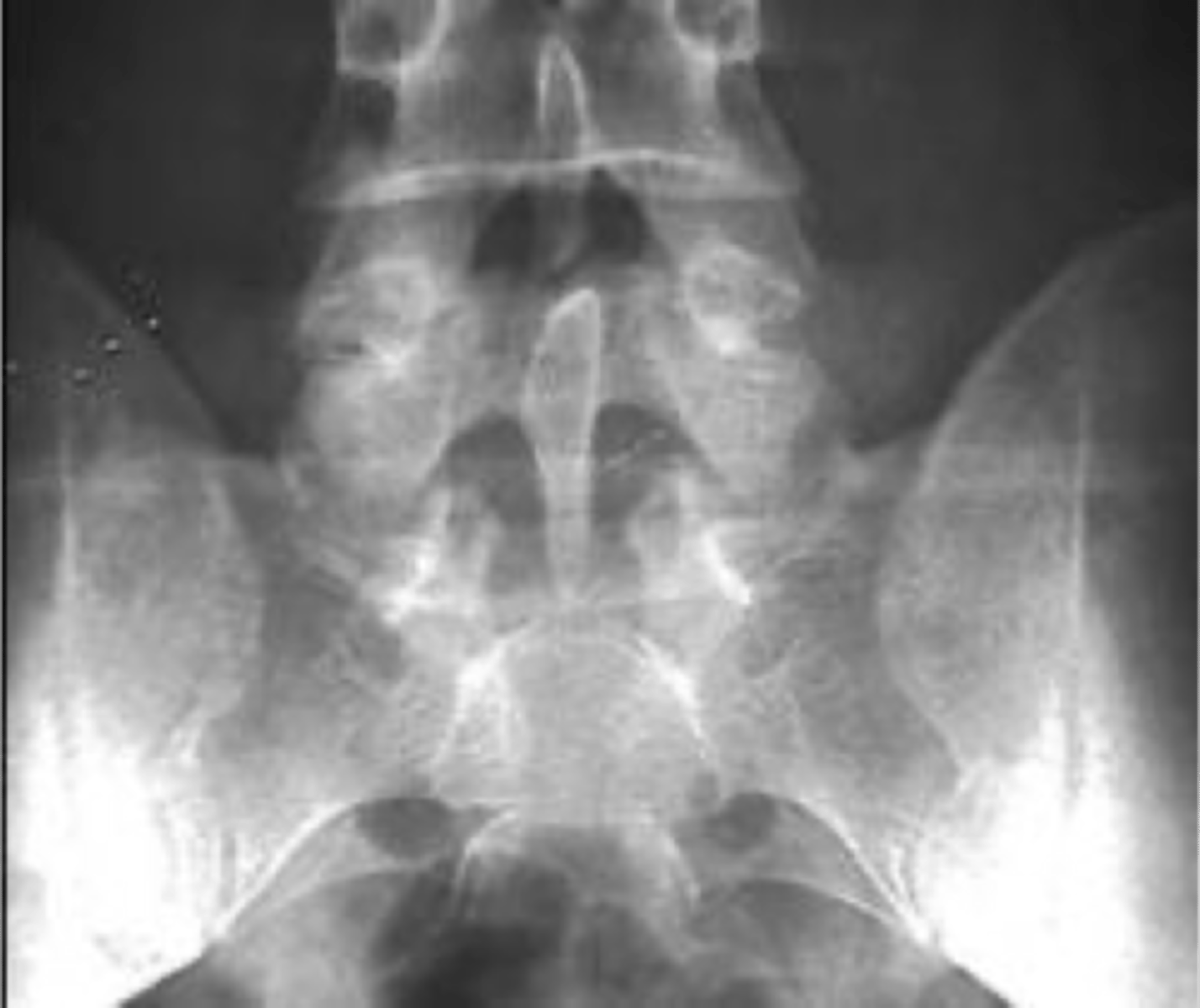
Non-union of the posterior arch of S1 and enlargement of the spinous process of L5
Clasp-Knife appearance
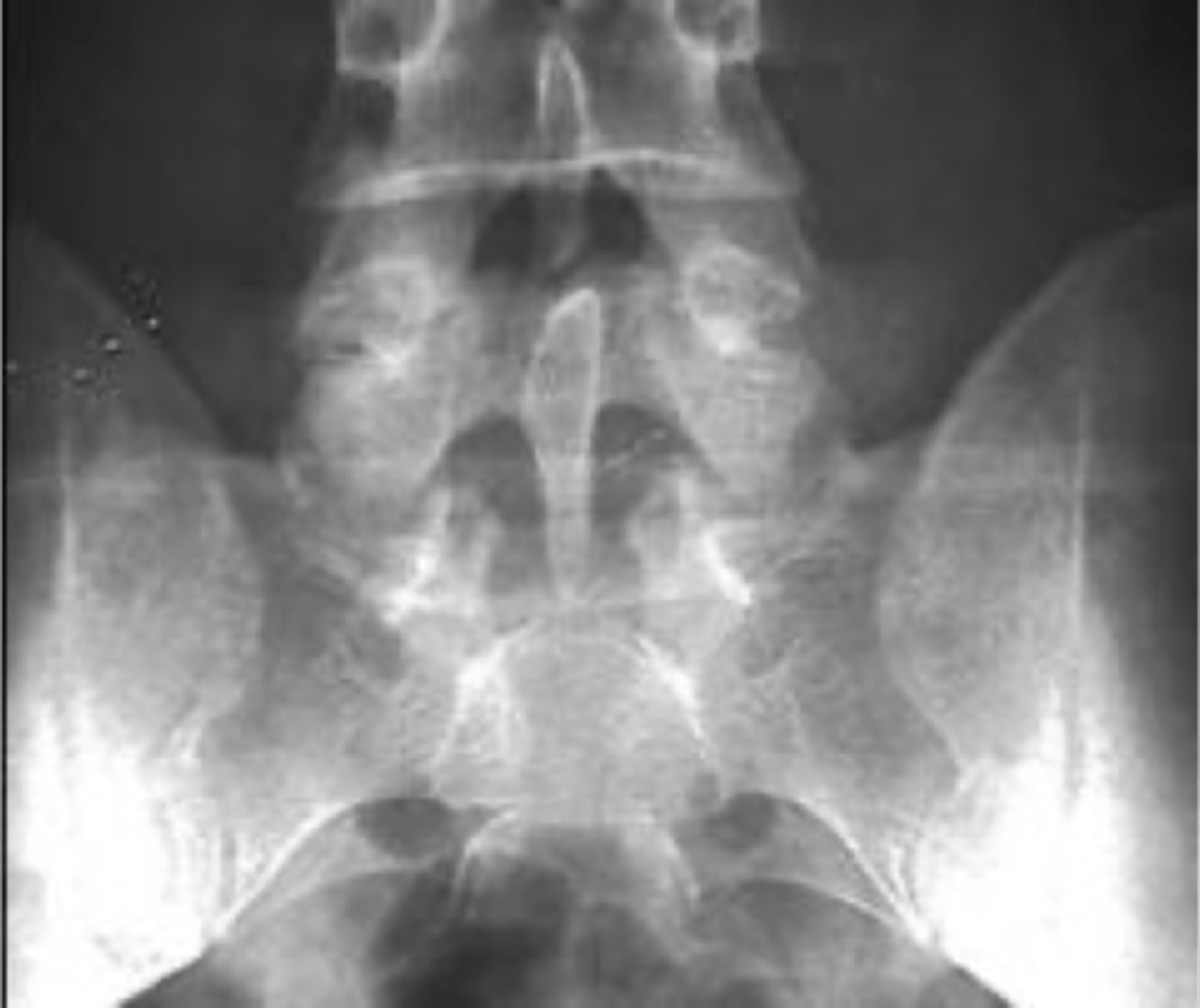
- Once thought to cause compression of neurologic structures (no cord here), unlikely and currently thought of as an incidental finding
- Very rarely there have been reported patients with radicular symptoms when extending the lumbar spine
Clasp-Knife clinical significance
Facet tropism
S1 superior articular processes are orientated in different planes (one coronal and one sagittal). Normally they should be coronal at the location (rarely at L4/L5)
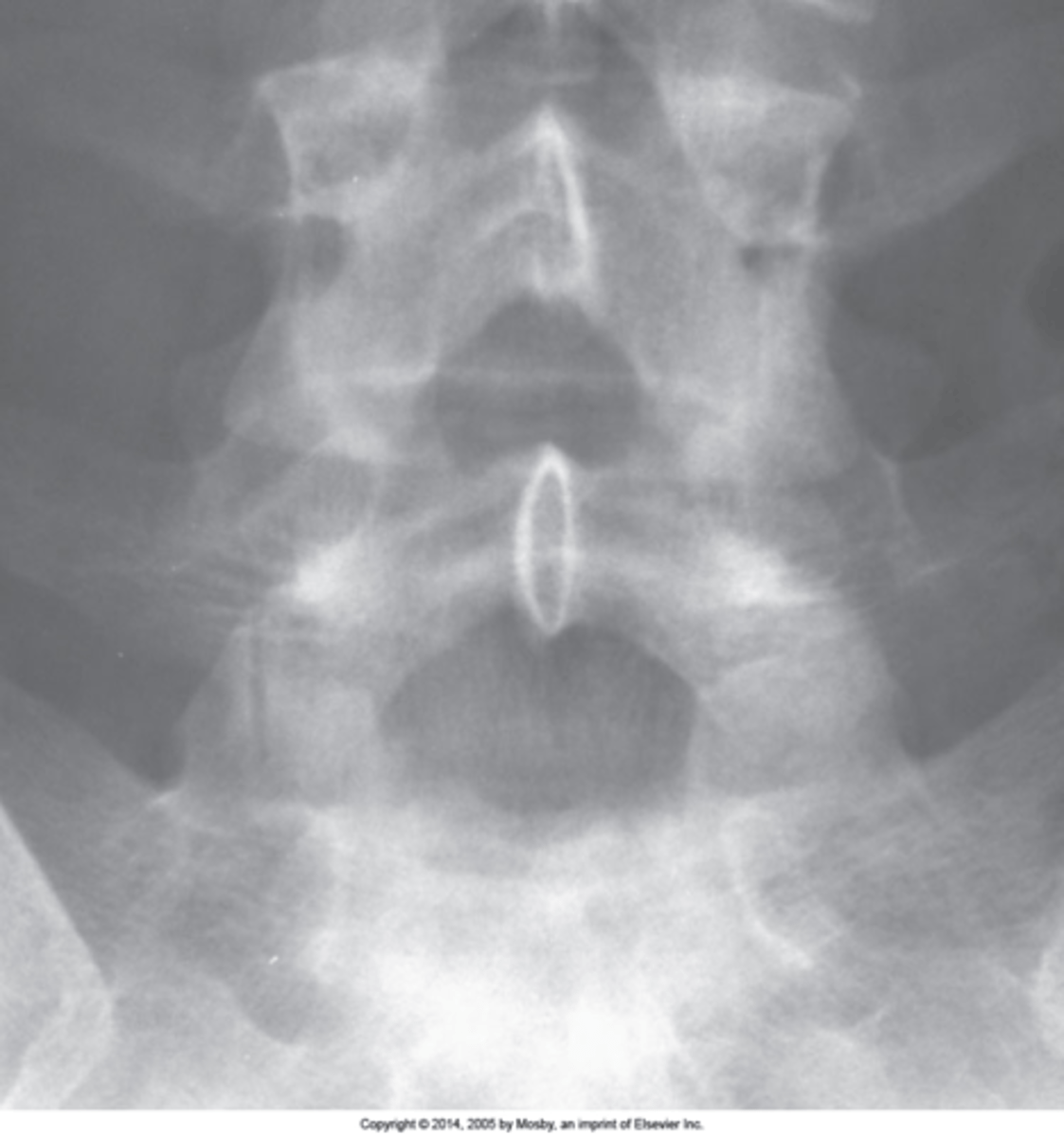
One facet in coronal plane and one in sagittal plane
Facet tropism appearance
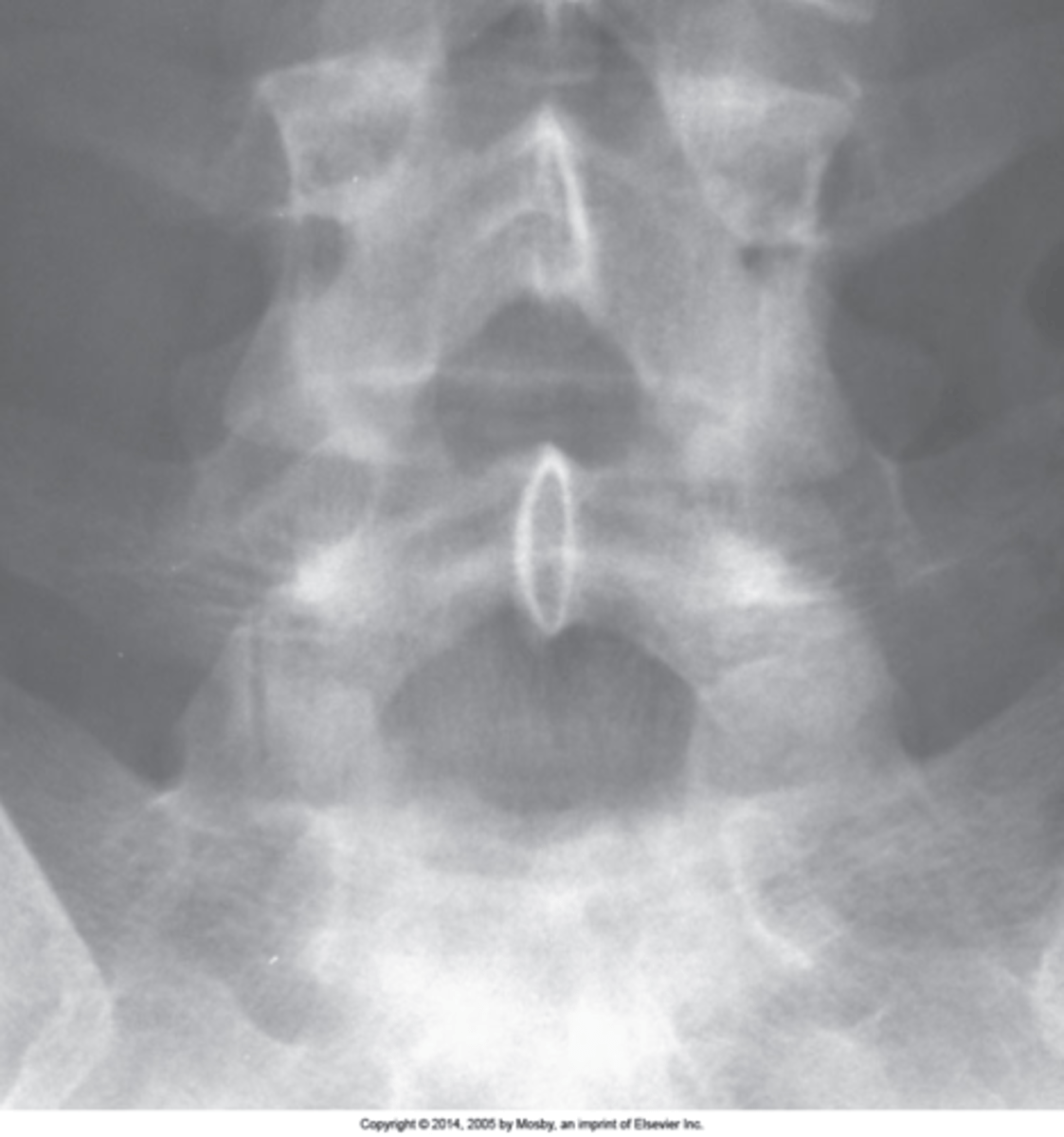
Rotated
The appearance of facet tropism can be seen when the patient is slightly _____
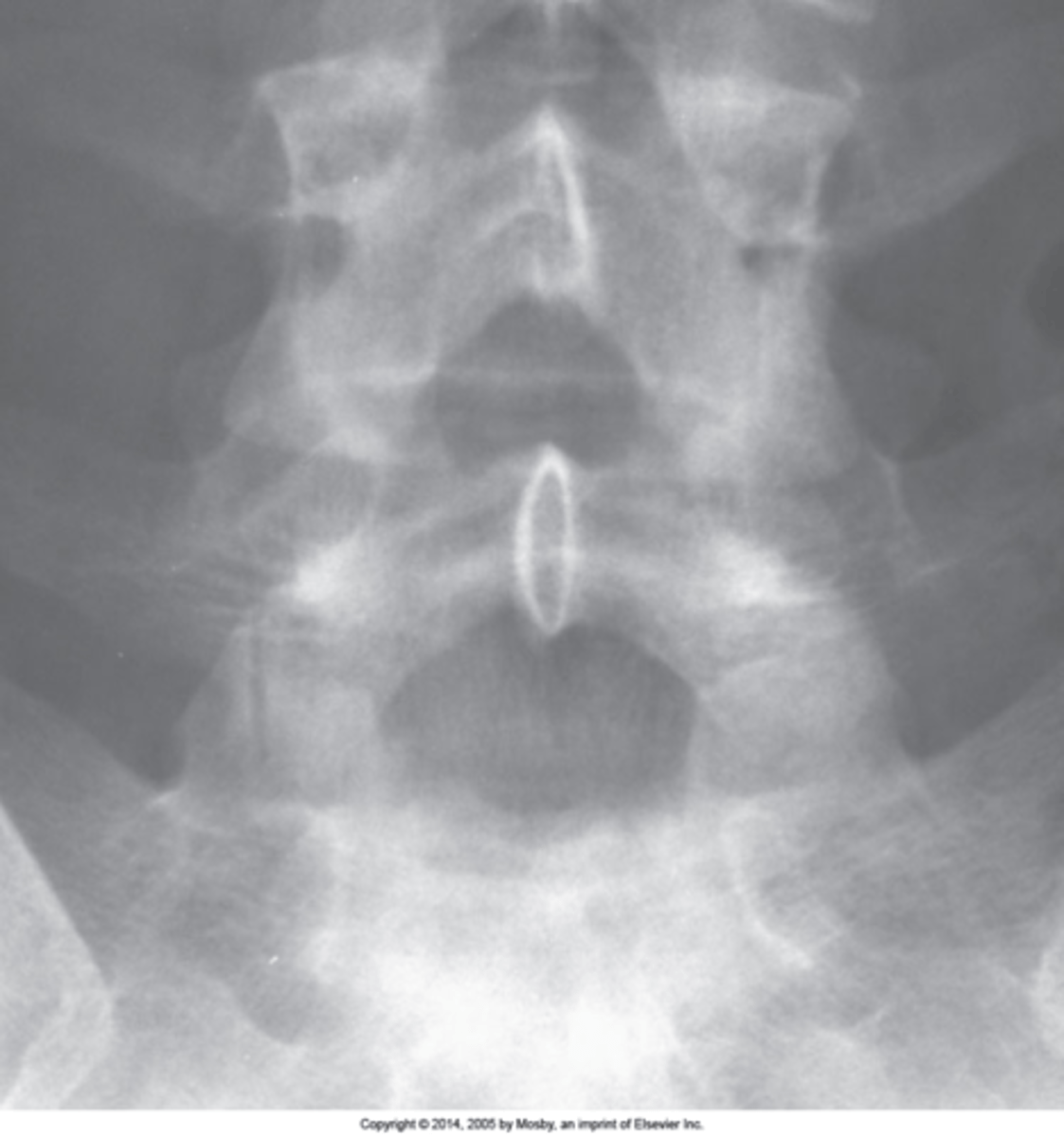
L5/S1
Facet tropism changes the biomechanics at _____
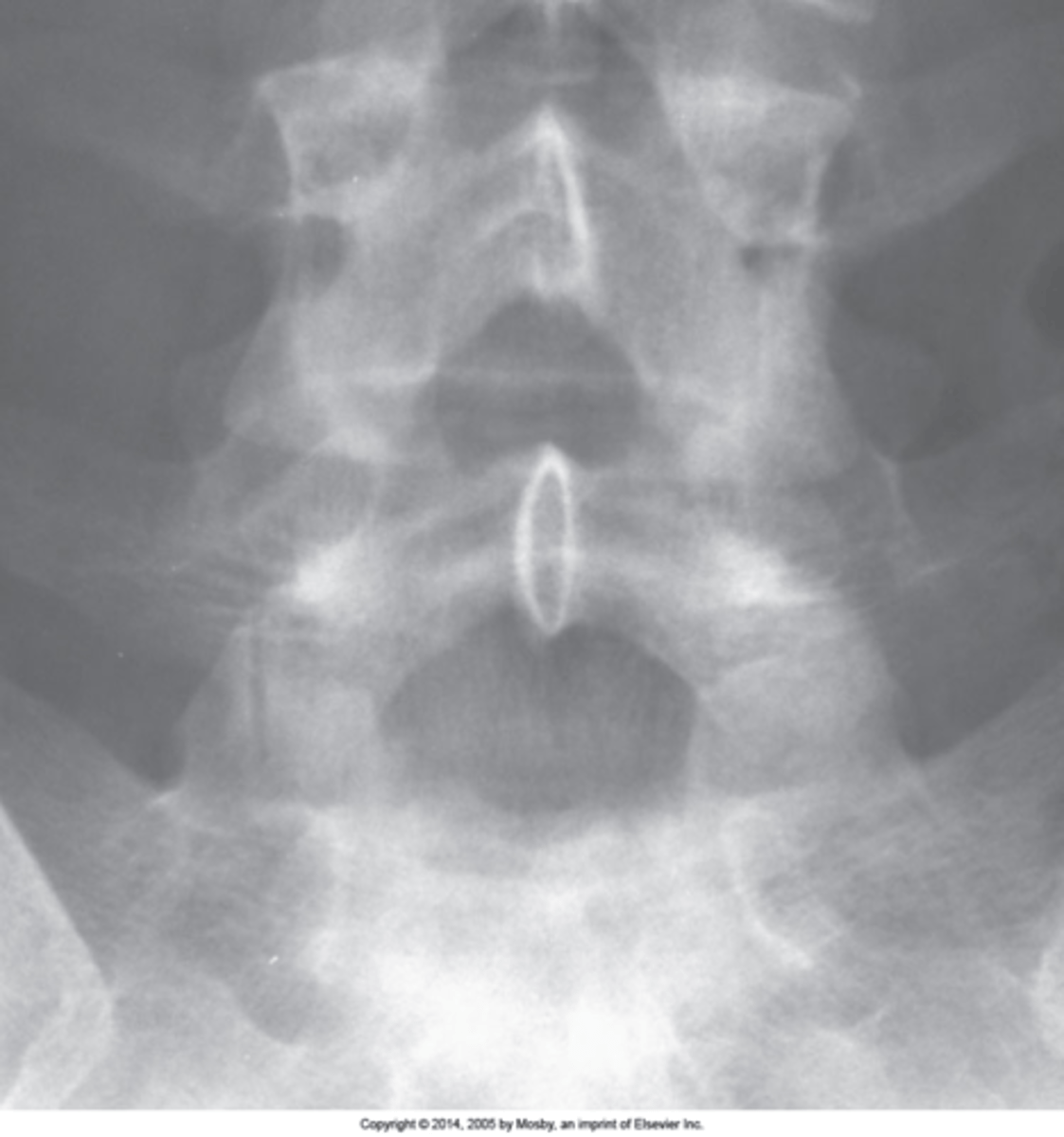
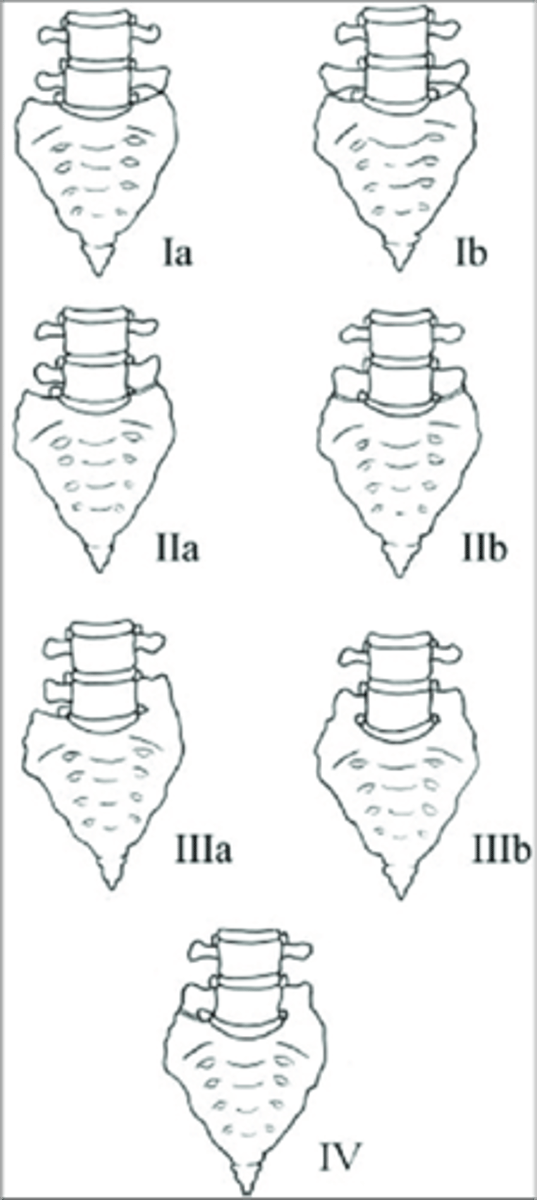
Lumbosacral Transitional Segments
- L5 can act like a sacral segment or even become part of the sacrum (sacralization of L5)
- S1 can act like a lumbar segment, or become a full lumbar segment (lumbarization of S1)
- Can be difficult to tell which of the two has occurred (must count the thoracic vertebral bodies for an accurate conclusion)
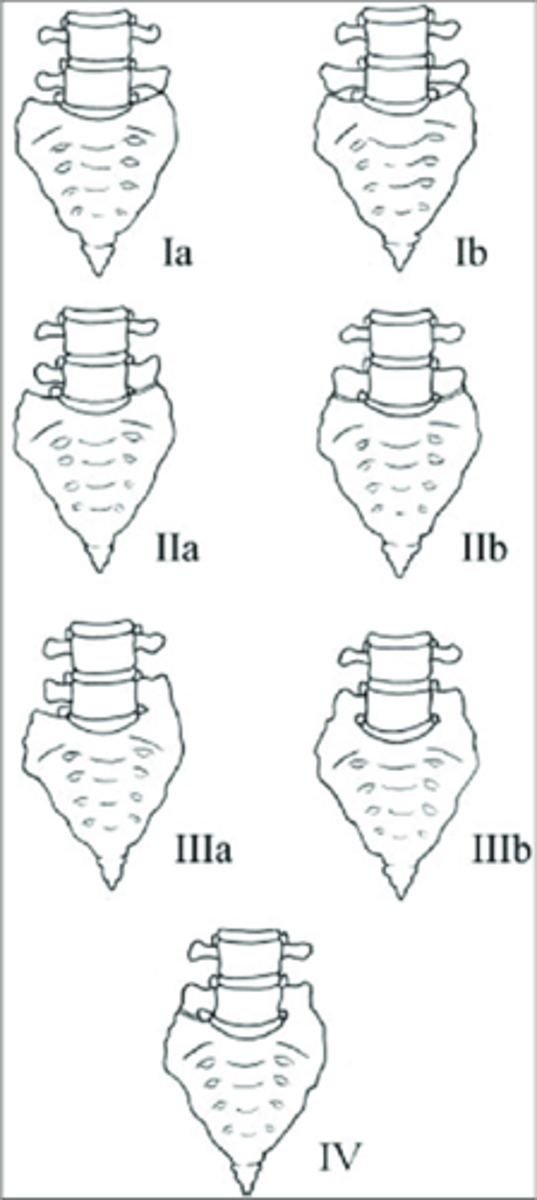
- Hyperplasia of one/both transverse processes
- May articulate or be fused to the adjacent sacral alae on one or both sides
- Look for a rudimentary disc below the transitional segment
Lumbosacral Transitional Segments appearance
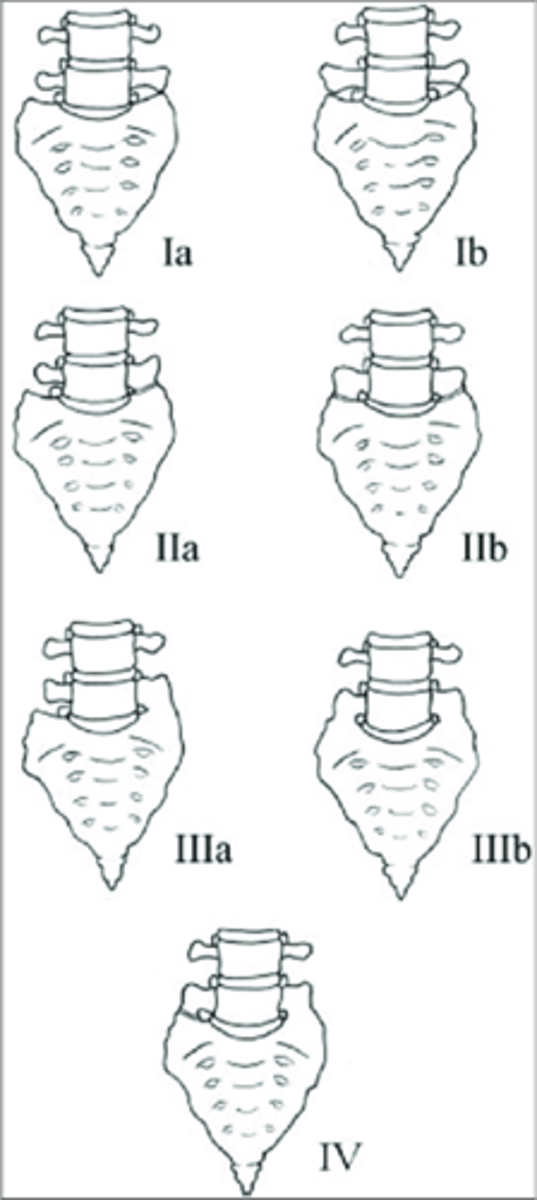
Hypoplastic/small
Lumbosacral Transitional Segments result in a _____ disc space
- Accessory articulations can be symptomatic
- Type II most significant
Lumbosacral Transitional Segments clinical significance
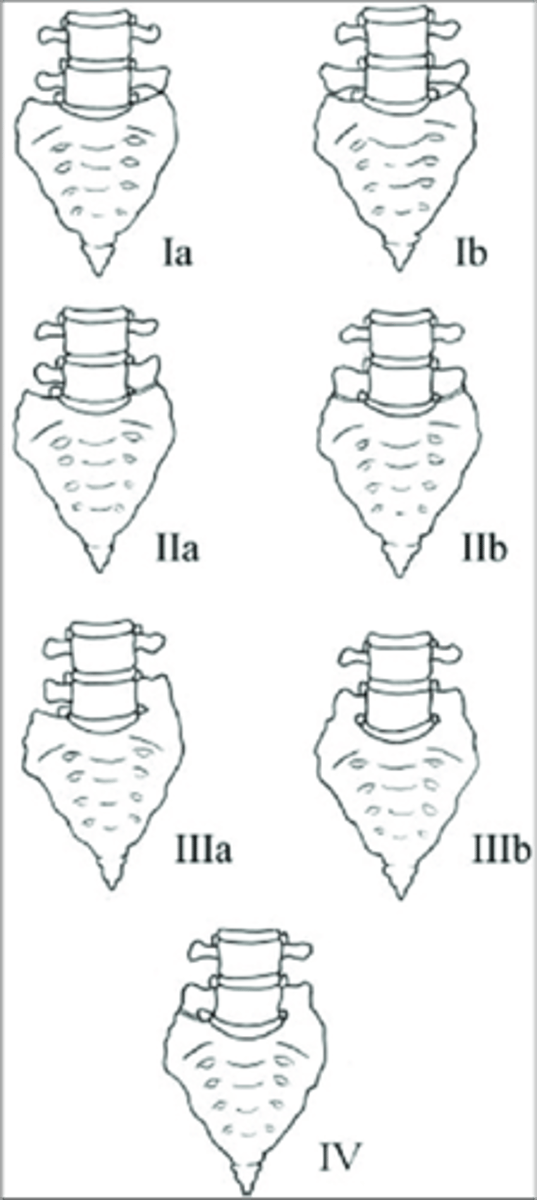
Type I lumbosacral transitional segment
- Spatulated transverse processes
- No articulation
- No fusion
- No predisposition to disc herniation
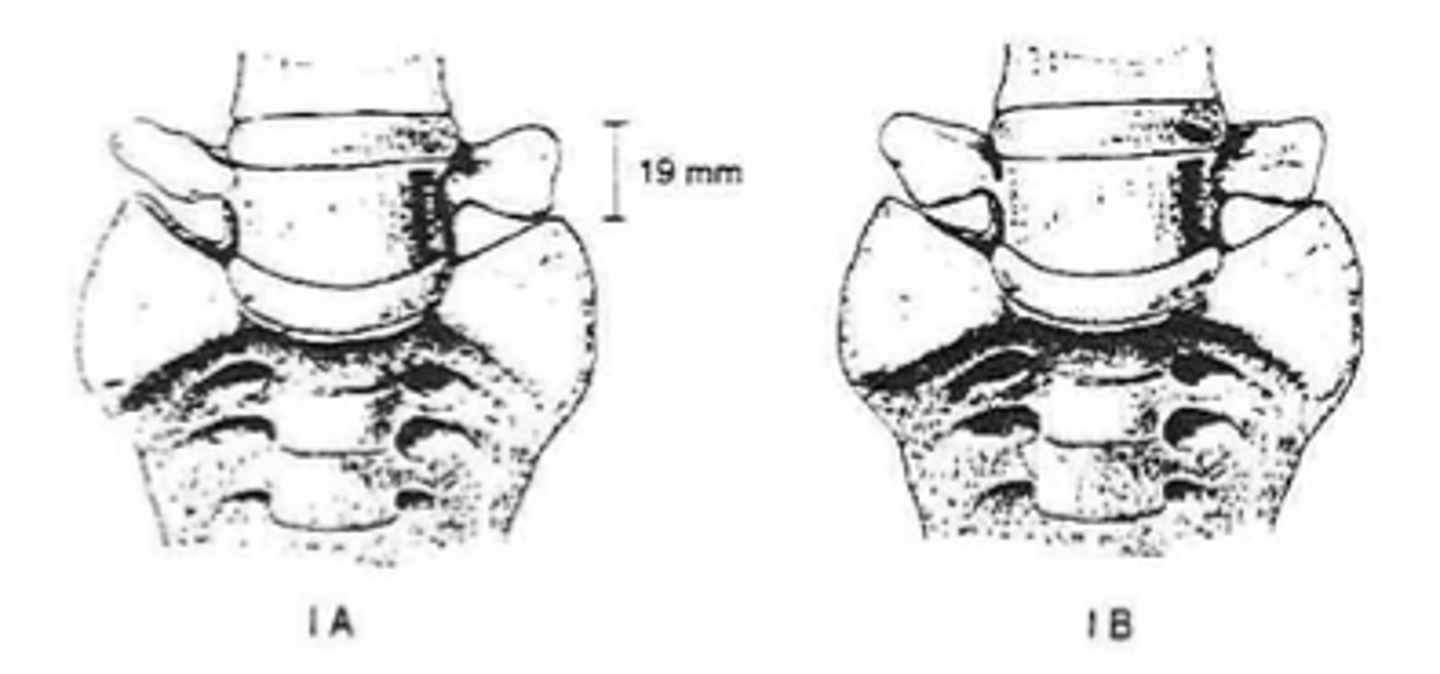
>19 mm
Type I lumbosacral transitional segment measurement