CNS L5 - Color Vision
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
wavelength
the distance between 2 wave peaks
different wavelengths correspond to different colors
visible spectrum
400 nm - 700 nm (violet, red)
Why did evolution give us eyes that see 400-700 nm?
The power in sunlight peaks there
Earth’s atmosphere is most transparent to these wavelengths.
And sea water, where eyes first evolved is most transparent < 500 nm
3 kinds of cones for sensing color
red cones (63%)
green cones (31%)
blue cones (6%)
Cone characteristics
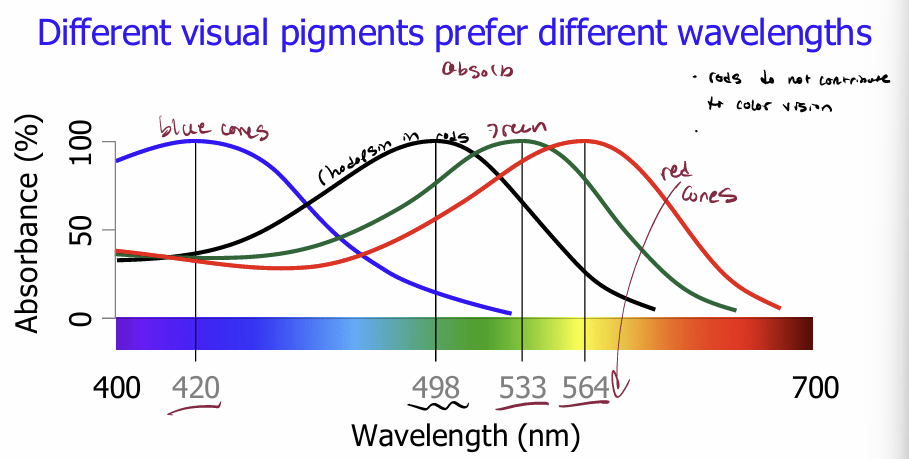
Each type of cone has its own type of visual pigment
All these pigments are similar to rhodopsin but not identical to it, and so all prefer different wavelengths of light
Trichromats
ones who sense color with 3 types of cone
Different visual pigments prefer ________ _________
different wavelengths
The brain infers color by comparing data from the ____ ____ __ _____
3 types of cones
yellow light affects…
red and green cones, but NOT blue ones — brain perceives yellow
You can be fooled:
a red and a green light, with no yellow, can produce the same cone activities as a yellow light would, and so the brain sees yellow either way.
We can produce any color perception by mixing 3 wavelengths
Any color we can experience corresponds to a pattern of activity in our 3 types of cone. It is possible to produce any such pattern by mixing just 3 colors of light
The Primary Colors
Red, green, blue
Not all colors are in the …
rainbow
Spectral colors
those that can be evoked by light of a single wavelength
rainbow colors, from violet through blue, green, yellow and orange to red
Extraspectral colors
colors (such as purple or white) that are evoked only by a mix of wavelengths
e.g. we see purple when 2 or more wavelengths affect red and blue cones more than green cones.
Ganglion cell color signals are …
Combinations of cone signals
R + G cells (the yellow channel)
ganglion cells that are excited by red light and by green light
R - G channels
ganglion cells that are excited by red light and inhibited by green
G-R channels
ganglion cells are inhibited by red and excited by green
R-G , G-R
the red-green opponent channel
B - R - G or B - (R + G)
i.e. blue minus yellow
Others are yellow minus blue. These 2 types form the blue-yellow opponent channel.
ganglion cells that are excited by blue light and inhibited by red and green
Opponent channels explain…
afterimages
As you stare at something green, your G – R cells gradually fatigue. When you look away, those fatigued cells are less active than your R – G’s, and so you see red. And similarly for blue versus yellow.
We aren’t sure the responsible cells are in the retina, as there are color-opponent cells in LGN and visual cortex as well
red-green color blindness (Daltonism)
where people have trouble distinguishing those colors.
Inheritance pattern of Daltonism
color blind fathers have color-normal daughters who have color blind sons
Location of blue cone pigment gene
chromosome 7
Women are seldom color blind because …
if one X-chromosome codes a faulty pigment then the other X-chromosome compensates
tetrachromat
One having 2 different red cone pigments
common in women
richer color perception
reflectance
the intrinsic color of a surface — its tendency to reflect certain wavelengths of light and absorb others
eg: yellow banana reflects yellow light more than other wavelengths
reflectance of an object carries information about it, e.g. about ripeness
The light an object sends to our eyes depends on…
reflectance and illumination
illumination
the color and intensity of the light source
color constancy
our brains can usually infer the reflectance, so we see the ripe banana as yellow even in green light.
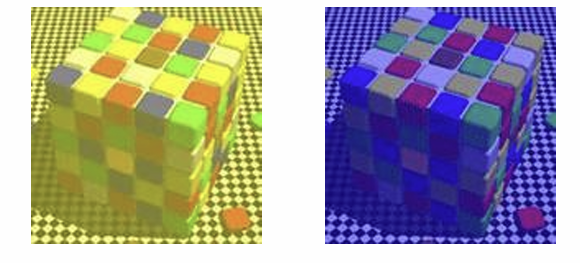
A demonstration of color constancy
■ The 2 pictures show the same cube in yellow and in blue light. You correctly see the blue facets in the left picture as blue, and the yellow facets in the right picture as yellow.
■ But the light these facets send to your eyes is the same, as you can see in the next slide, where I hide everything except one blue facet on the left and one yellow facet on the right ...
These comparisons which underlie constancy give rise to illusions
In each vertical pair, the center squares are identical in color, but their surroundings affect our perception of brightness, hue, and saturation
