L7 - Biosynthesis of AA and Molecules
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
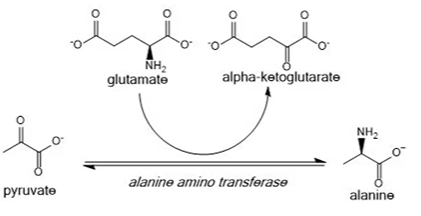
alanine synthesized
pyruvate + glutamate + alaATransferase > alanine + aKG
asparagine synthesized
by amidation of aspartate
asp + ATP + glutamine + asp synthetase > AMP + PPi + glutamate + asparagine
cat. by asp synthetase, needs ATP
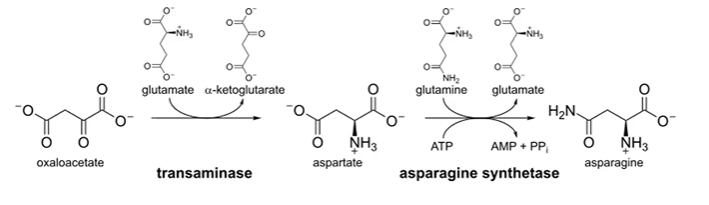
aspartate synthesized
OA + transaminase + glutamate > aspartate + aKG
asparagine + H2O + asparaginase > aspartic acid + NH3 (deamidation)
asparagine synthetase
NH3 donated by glutamine
aprotic tunnel, other side has b-aspartyl-AMP, which NH3 attacks
glutamate synthesis review
transamination:
aKG + AAx + transaminase > glutamate + aKAx
red amination:
aKG + NH3 + NADPH + GDH > glutamate + NADP+
hydrolysis
glutamine + glutaminase + H2O > glutamate + NH3
conditionally essential amino acids
arginine = synthesized in urea cycle
creatine = synthesized from arginine indirectly
creatinine = waste product and indicator of renal function
arginine is synthesized mostly in
urea cycle
creatine is mostly synthesized from ____ or phosphorylated by ____ to store energy as ____
arginine indirectly; creatine kinase; phosphocreatine
creatine is made in the ____ from the ____
liver pancreas kidneys, transamination of
arginine, glycine, methionine
creatinine
waste product and indicator of renal function;
filters stuff from blood in kidneys
phosphocreatine
high energy phosphate bonds for ATP shortage
in muscles, phosphorylates ADP > ATP
creatine kinase
serum levels, isoforms, can be used to diagnose acute heart attacks
SAM in creatine formation
arg + glyc > ornithine + guanidoacetate
guanidinoacetate + SAMeth > creatine + SAH
cysteine and selenocysteine
proteinogenic, incorporated into selenoproteins
UGA = stop codon
derivative of serine, uses PLP
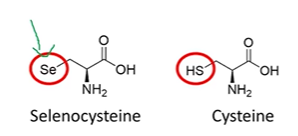
UGA stop codon
if not enough selenocysteine, we insert selenocysteine instead of stopping
tyrosine
phenylalanine hydroxylase
conditionally essential, synthesized from phenylalanine
precursor of neurotransmitters
phenylalanine hydroxylase
cat hydroxylation of C4 phenylalanine
BH4 dependent
PKU
genetic disorder, autosomal recessive
elevated phenylalanine or phenylpyruvate
damages in neuro, head size, etc.
treated with diet and supplements reducing phenylalanine and increasing tyrosine
specialized n molecules
thyroxine
thyroxine
controls metabolic rate, O2, ATP, fat, myosin, etc.
T4 = tetraiodothryonine = thyroxine = precursor
T3 = trioiodothrynonine = active
enzyme is a selenoprotein
SAM/Ado-Met
s-adenosylmethionine; abundant methylating agent
methionine + ATP, vitamin B12 indirectly affect levels
synthesis of homocysteine, creatine, and epinephrine
glutathione GSH
cellular reducing agent, made from glutamate, cysteine, and glycine
glutathione peroxidase GPX
selenoproteins to help scavenge free radicals
nitric oxide
messenger in Neurotransmission, blood clotting, BP
made from arginine + NO2Synthase + NADPH > citrulline + NO2
amino acid neurotransmitters
glutamate
aspartate
d-serine
glycine
glutamate
main excitatory neurotransmitter; stored in synaptic vesicles
CNS, memory, cognition, mood;
may bind NMDA receptor
aspartate
excitatory neurotransmitter, will bind NMDA
d-serine
co-agonist of NMDA type glutamate receptors
glycine
inhib neurotransmitter in spinal cord, brainstem, retina
epinephrine
adrenaline; hormone and neurotransmitter
binds to B adrenergic receptor
norepinephrine
more effect on blood vessels
binds to a receptors 1 and 2, B1, not B2
made from tyrosine
catecholamines
stress response: brain, nerve, adrenal
dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
comes from tyrosine
GABA
inhibitor neuro, reduces excitability
B6 dependent
comes from glutamate
serotonin
from tryptophan,
mood, sleep, digestion
BH4 dependent
histamine
vasodilator, decarboxylation of histidine
cimetidine
tagamet;
analog antagonist of histamine
dopamine
made in brain, adrenal glands
memory, mood, sleep, learning
parkinsons, ADHD, restless leg