Models of Memory Cognitive Psychology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Memory
Cognitive process where information flows from different stores that encodes, stores and retrieves information.
Basic Store (division) of memory
Short-term memory
Long-term momery
Multiple types of memory
Semantic memory
Episodic memory
Procedural memory
Facial recognition
Other divisions of LTM
Conscious/Explicit memory
Unconscious/Implicit memory
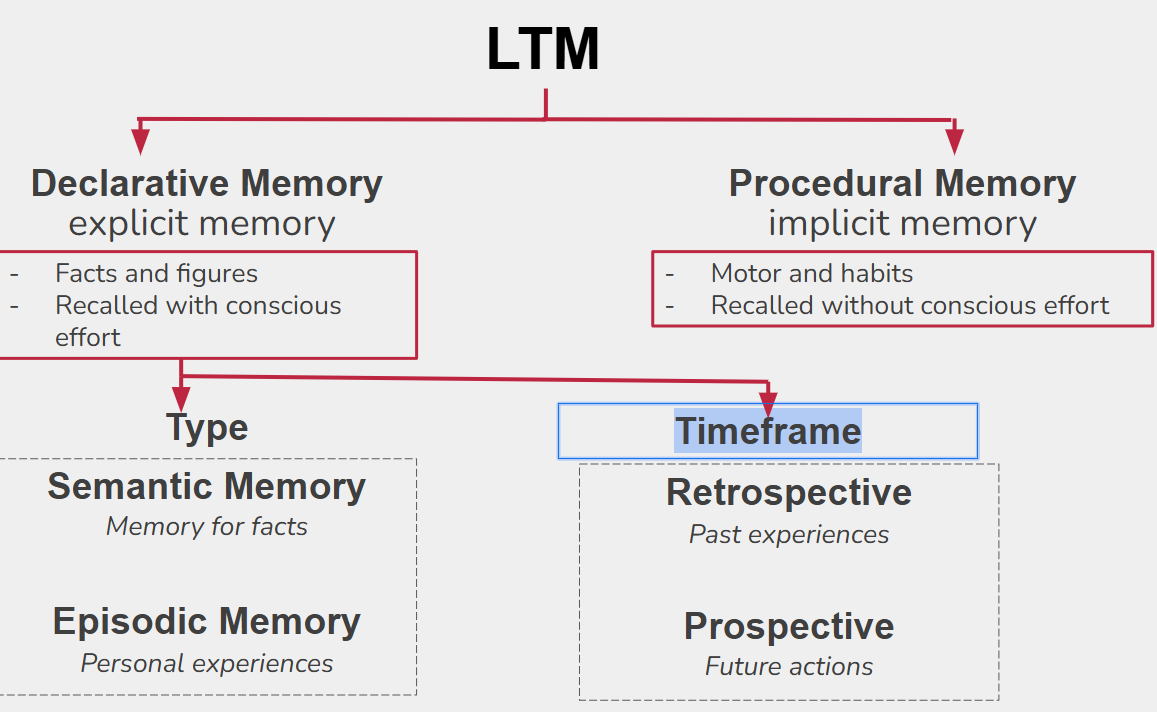
Conscious/Explicit/Declarative memory
Facts and figures
Recalled with conscious effort
Conscious/Explicit/Declarative memory is divided to two
Type
Timeframe
Type is divided to two
Semantic Memory Memory for facts
Episodic Memory Personal experiences
Timeframe is divided to two
Retrospective Past experiences
Prospective Future actions
Semantic Memory
Memory for facts
Episodic Memory
Personal experiences
Retrospective
Past experiences
Prospective
Future actions
Models of memory
Multi-store memory model
Levels of processing memory model
Working memory model
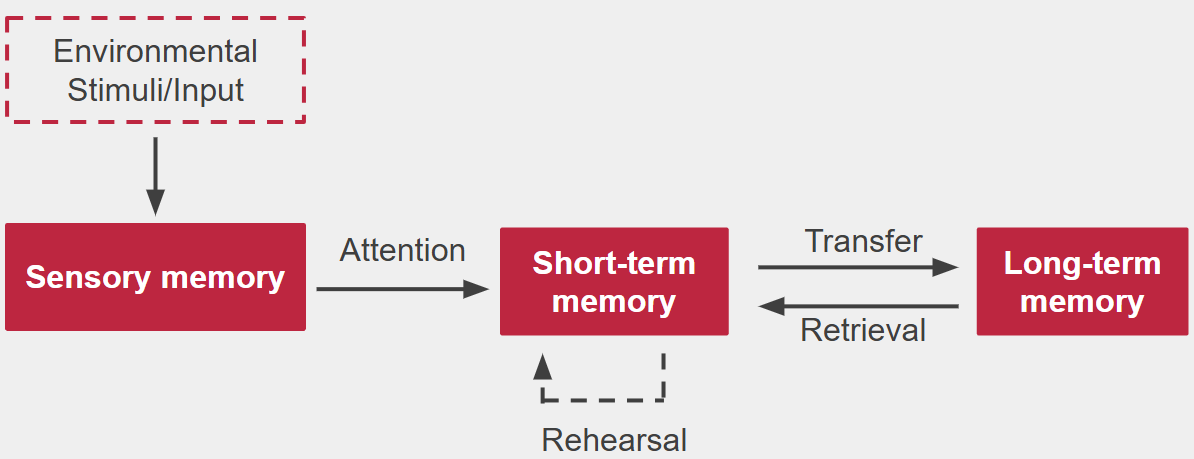
Multi-store memory model
Theorized by Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968)
compose of 3 separate components:
Sensory memory
Short-term memory
Long-term memory
Sensory memory
Detect information and hold it until it is transferred to STM store or be lost.
Does not process information
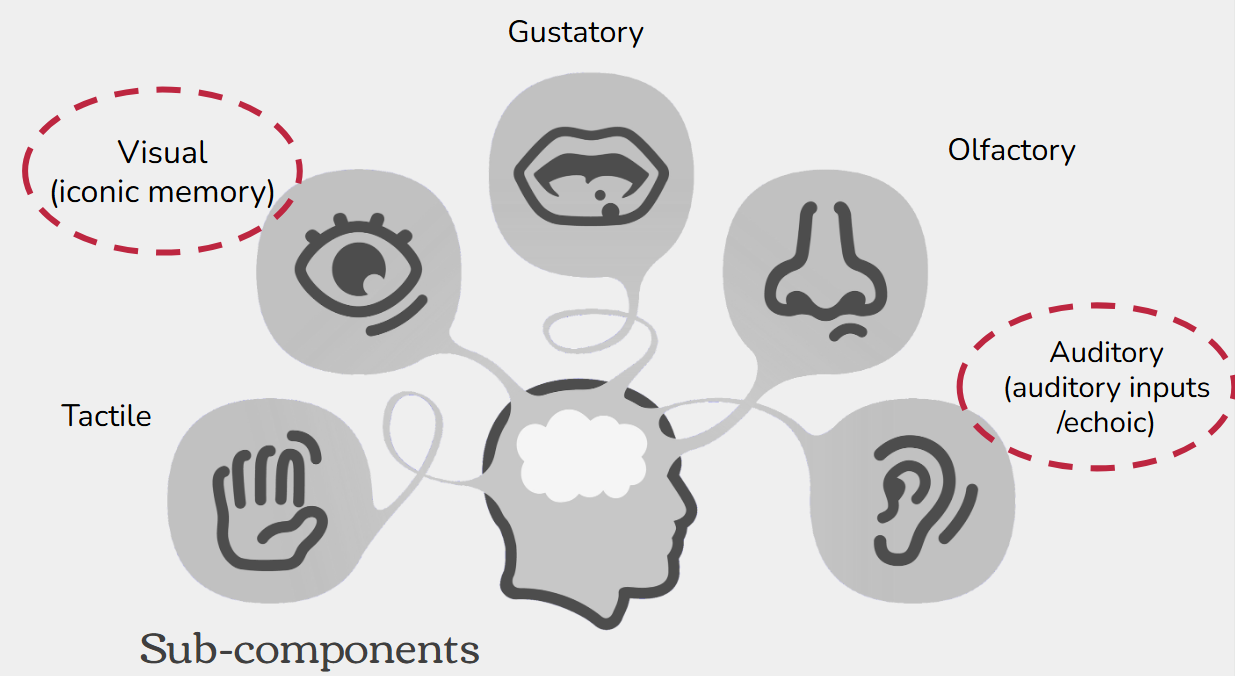
Capacity of Sensory Memory
The capacity is limited by perception
Duration
Short
Iconic/Visual memory– 1 second
Echoic memory – 2-5 seconds
Short-term memory
“Working Memory”
Relies on both visual and auditory
Information undergo primitive transformation
Capacity of Short-term memory
- Capacity: 7±2 chunks of info
(GA Miller’s article : “The Magical Number Seven” 1956)
Magic 7:
Seven Wonders of the World
Seven Deadly Sins
Telephone no.*
Duration of Short-term memory
Duration: not longer than 30 seconds
(acoustic info is longer)
Rehearsal
A cognitive process of repeating the short-term memory to become a lont-term memory
Long-term memory
A place for storing large amounts of information for indefinite periods of time.
Capacity of Long-term memory
The capacity is unlimited
Duration of Long-term memory
The duration is unlimited
Contextual cues
trigger memories from the past/distant memories
Components of the multi-store memory model that requires testing:
Are the memory stores distinct and separate?
Are there really three memory stores? Not more? Not less?
Are the sensory modalities within sensory memory just modalities? Not separate store?
Is there a physiological basis for the memory stores or are they just constructs?
Is rehearsal necessary for information to transfer from STM to LTM?
Does information really flow in one direction?
Serial position effect
Coined by Hermann Ebbinghaus
Tendency to recall the first and last items on a list better than items in the middle
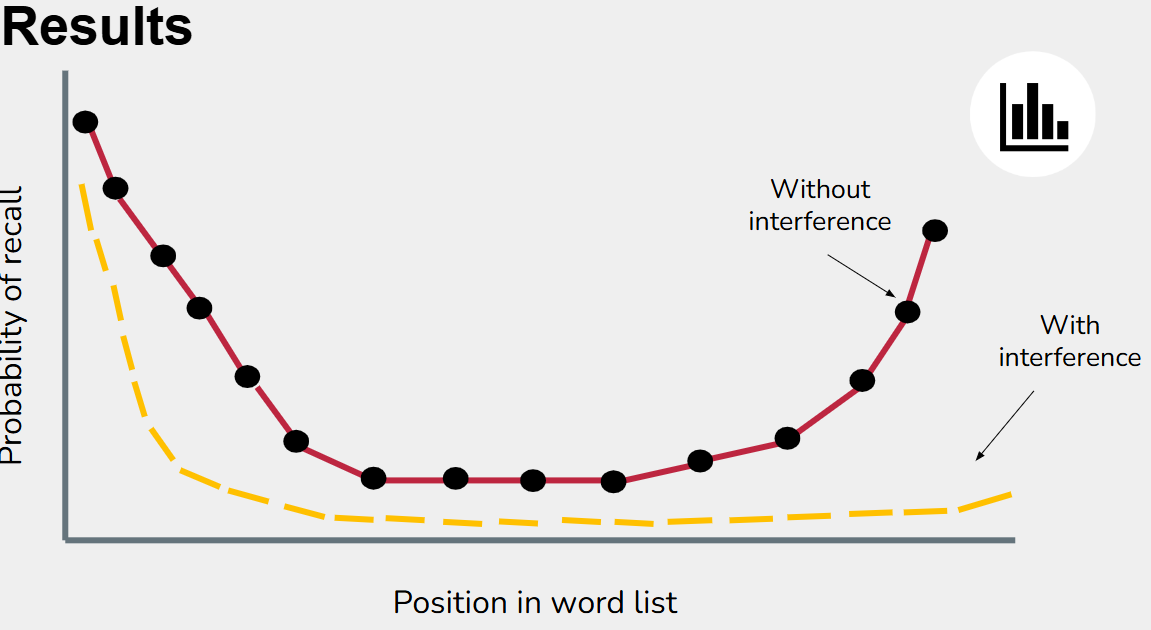
Studies supporting the multi-store memory model
Glanzer and Cunitz 1966
Sperling 1960
Strengths of Multi-Store Model
Parsimonious
Influential
Highly heuristic
Criticism for the Multi-Store Model
Focuses on the structure and not the process.
Rehearsal may not be the only way for information to transfer from STM to LTM
Founder of Levels of Processing Model of Memory
by: Craik and Lockhart (1975)
Definition of Levels of Processing Model of Memory
Recall is a function of depth of processing.
shallow processing
deep processing
“the deeper the processing, the stronger the trace at LTM”
Shallow Processing
Only takes into account superficial features of the stimulus.
Example:
Physical properties
Acoustic properties
- Repeat it: pronounce
Deep Processing
Semantic processing
Building the stimulus into the structure of meaningful connections and associations
“mental image”
Criticisms for Multi-Store Memory Model
C R A I K & L O C K H A R T 1 9 7 5
Results of Craik and Tulving 1975
Both recall and recognition memory performance was significantly better for those words that were preceded by a semantic question.
Conclusion of Craik and Tulving 1975
Conclusion:
LTM is not only due to rehearsal
LTM is a function of how the information was processed at the stage of encoding
Multi-store memory model: information flows in one direction.
LTM memory is not a unitary store.
Working Memory model
Focuses on the structure of the STM.
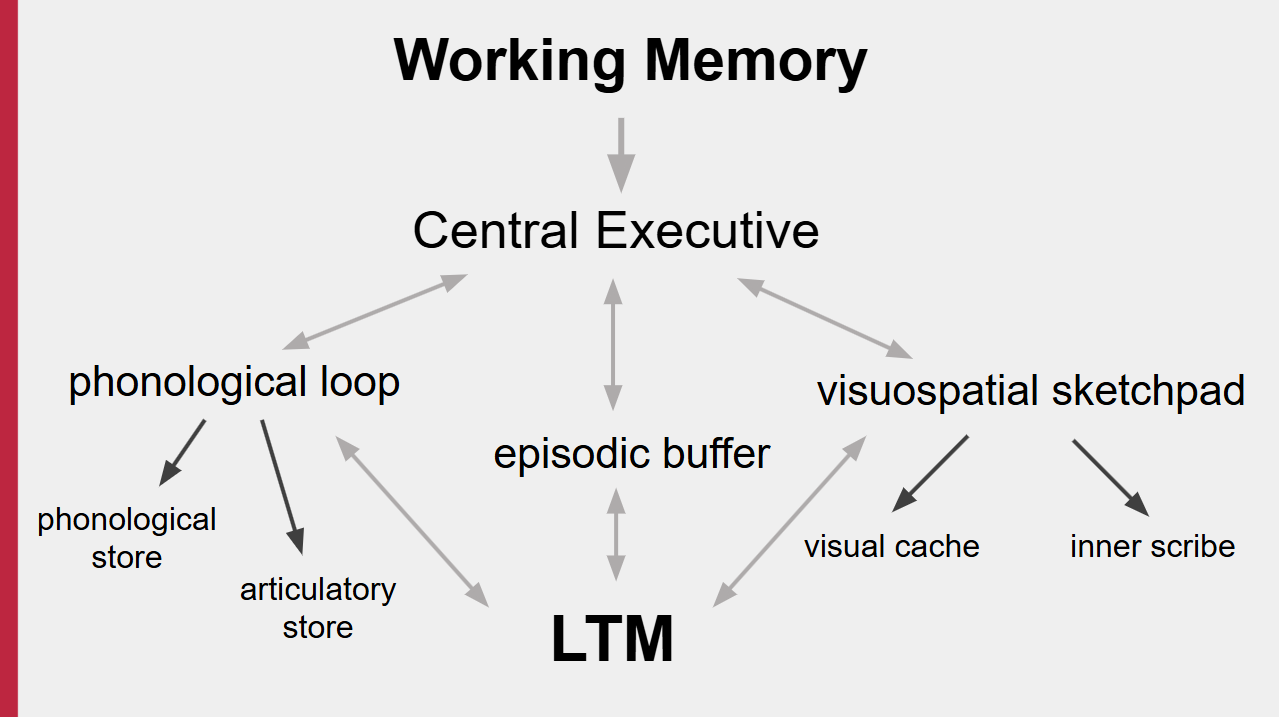

Founder of Working Memory Model
by: Baddeley and Hitch (1974)
Central Executive
A system that decides which information is attended to by which parts of the memory to send that information to be dealt with.
Give priority to particular activities.
Central Executive is divided to 3
phonological loop
episodic buffer
visuospatial sketchpad
Phonological Loop
Deals with spoken and written material.
The store of the phonological loop
Inner ear
Holds information in a speech-based form 1-2 seconds
Spoken words enter the store directly.
Written words are converted first
Articulatory control process of the phonological loop
inner voice
Rehearsing information from the phonological store
Phonological/verbal recoding
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Episodic Buffer
Integrates information from the visuospatial sketchpad and the phonological loop and links it to LTM.