Biological Bases of Behavior
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Monozygotic vs. Dizygotic
Monozygotic=identical twins; most share a placenta
Dizygotic=fraternal twins; no more different than siblings
Twin studies
Helps with understanding of nature vs. nurture (monozygotic twin studies)
Genetic findings: twins have more similarity in personality, tastes, abilities, attributes, higher concordance rates with mental health issues in monozygotic twins
Many adoption studies done
Environmental findings: parenting can impact some factors (attitudes, politics, education, faith, etc.); trauma/stress & poverty in the family matters
Interaction & Epigenetics
Interaction between nature & nurture (ex.: genetics & stress’s impacts on mental health); risk, protective benefits, etc.
Epigenetics=area of scientific research that studies how environment can influence genetic expression by “turning off or on” genes or impacting which are expressed/inhibited
Nervous System
Involved in EVERY function of human body
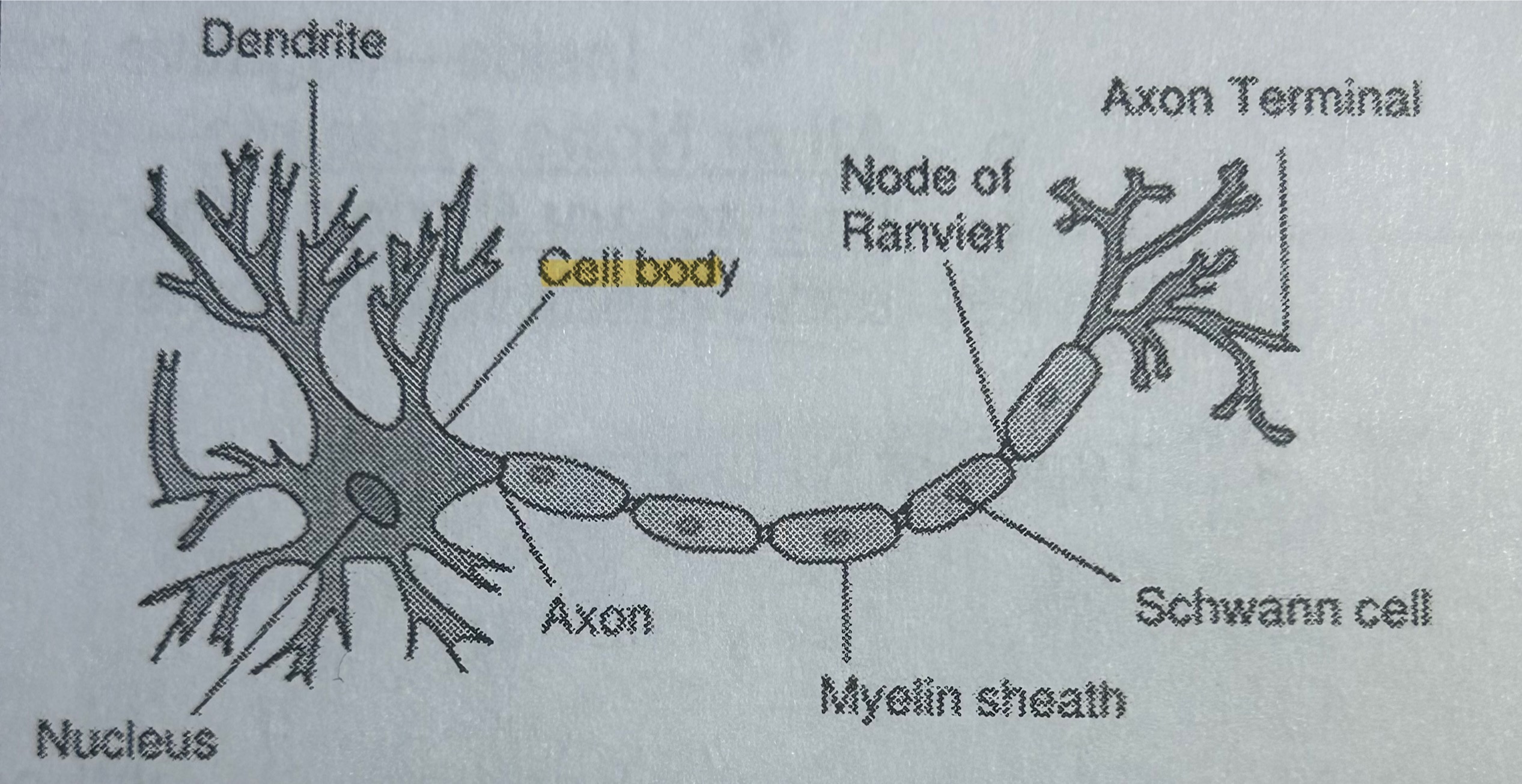
Soma
Part of a neuron; the cell body that contains DNA (NOT TESTED)
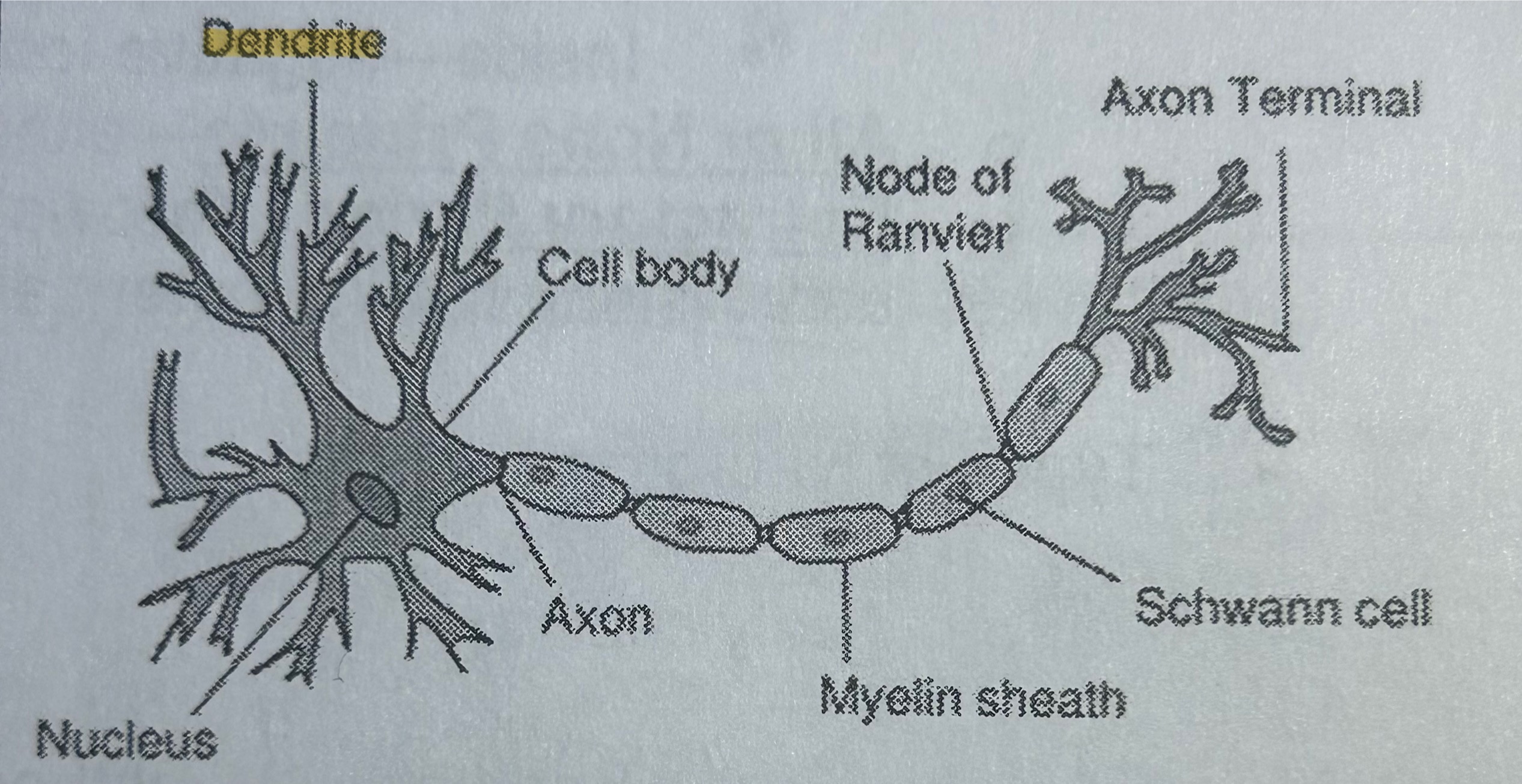
Dendrite
Part of a neuron; receives messages & can grow to make connections w/ other neurons (NOT TESTED)
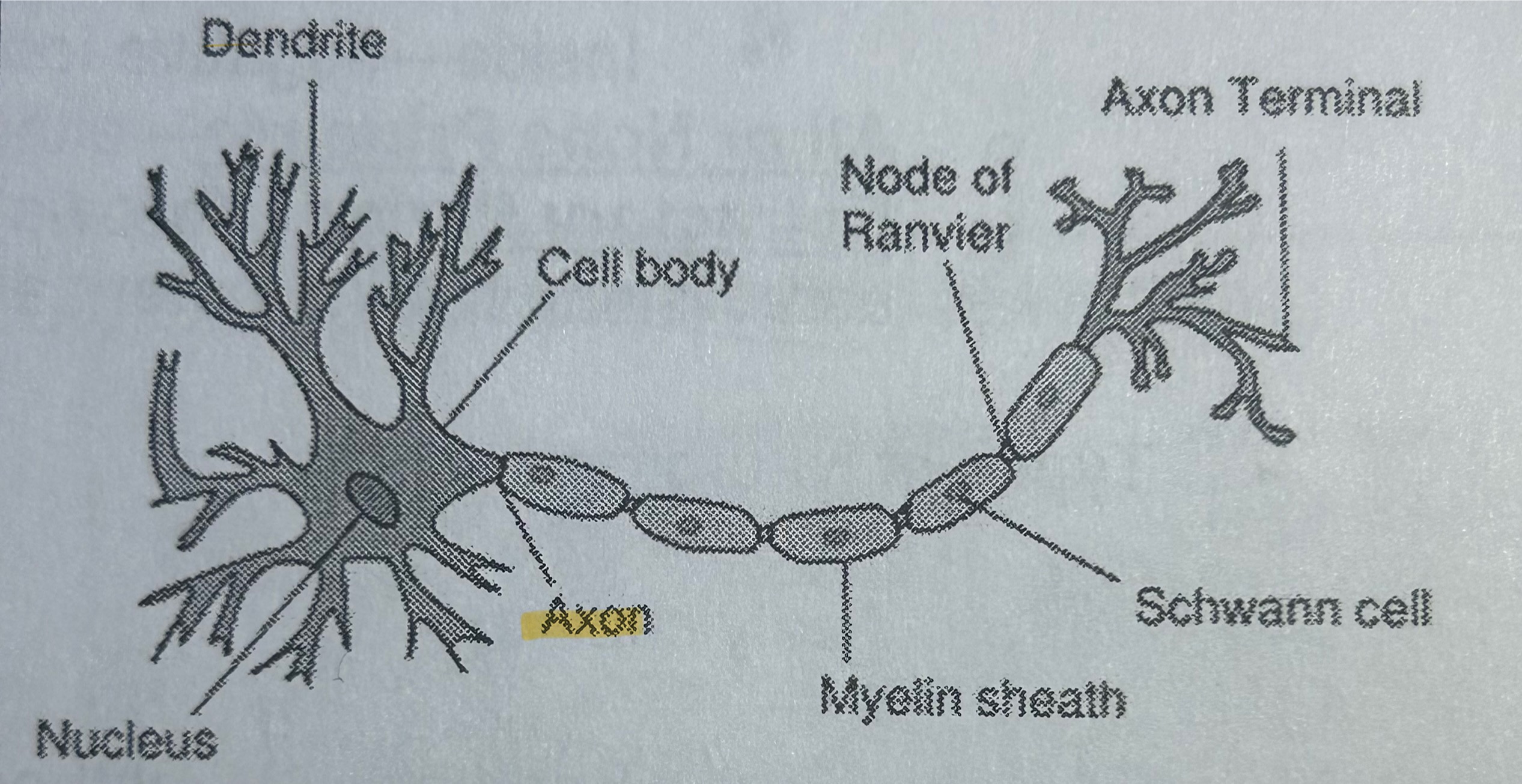
Axon
Part of a neuron; sends a message (NOT TESTED)
Synapse
Part of a neuron; gaps between neurons (NOT TESTED)
Terminal
Part of a neuron; receives electrical impulses & sends chemical ones (electrical messages travel in neurons; chemical messages travel between neurons) (NOT TESTED)
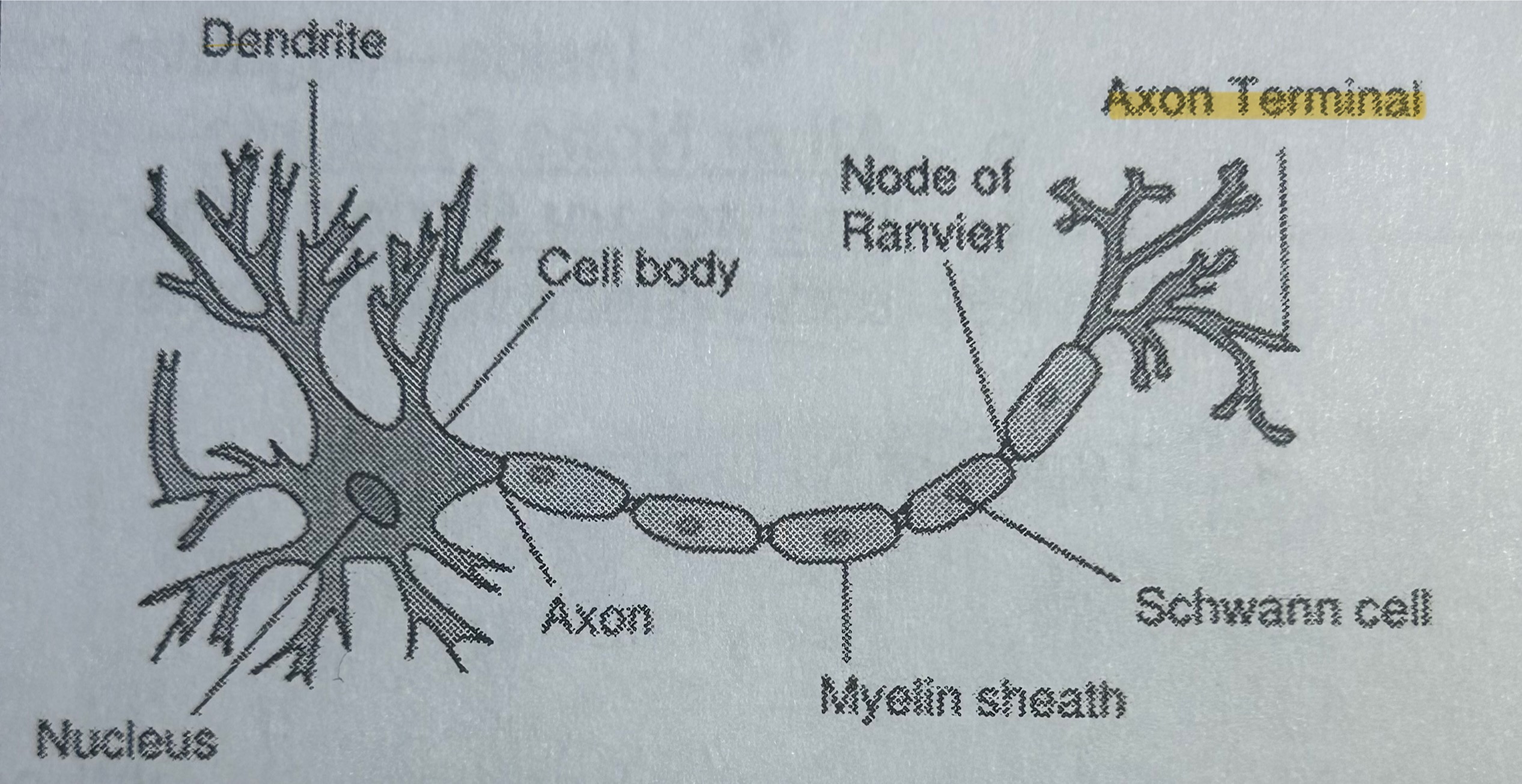
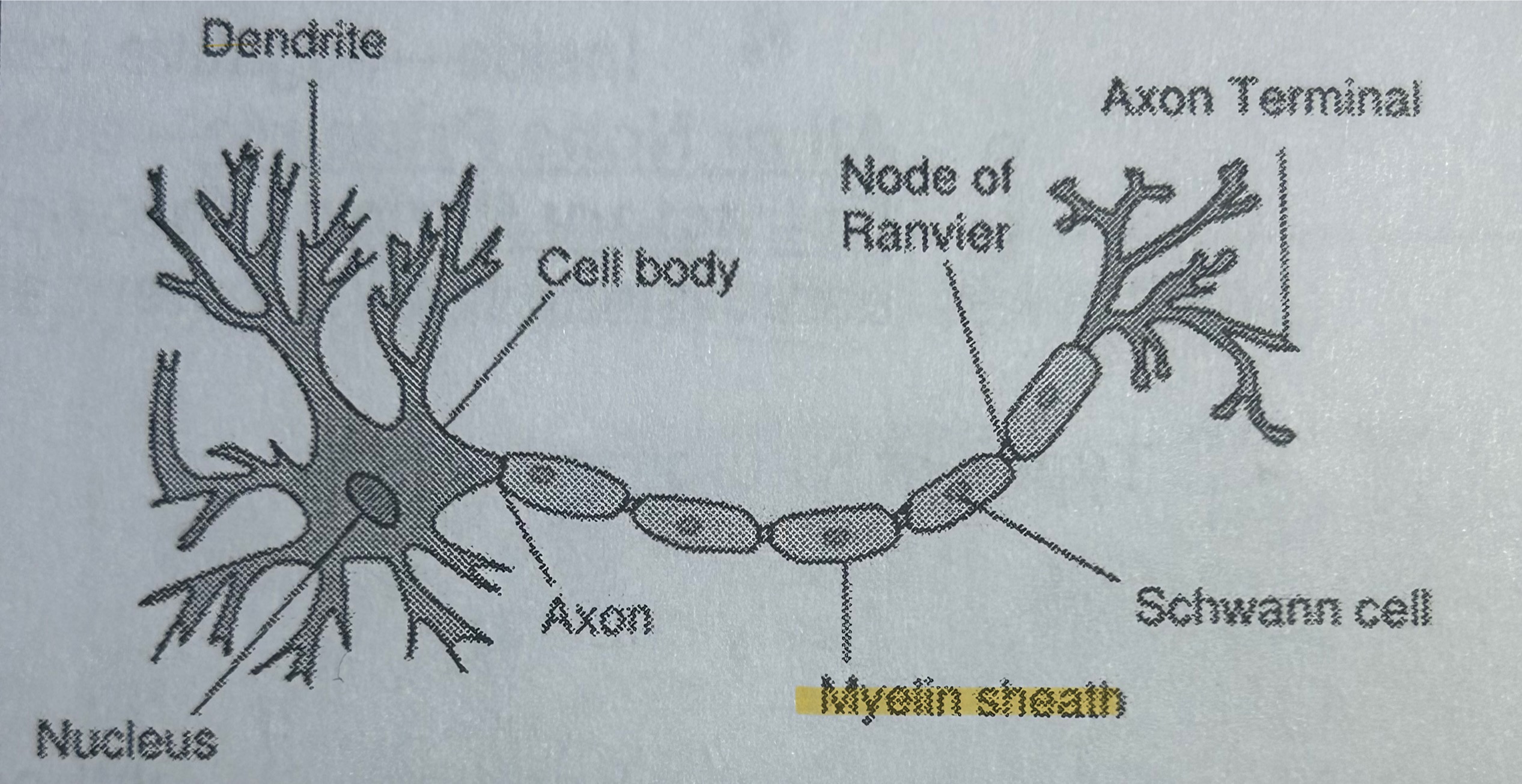
Myelin
Part of a neuron; fatty substance that insulates & allows for faster transmission of messages (NOT TESTED)
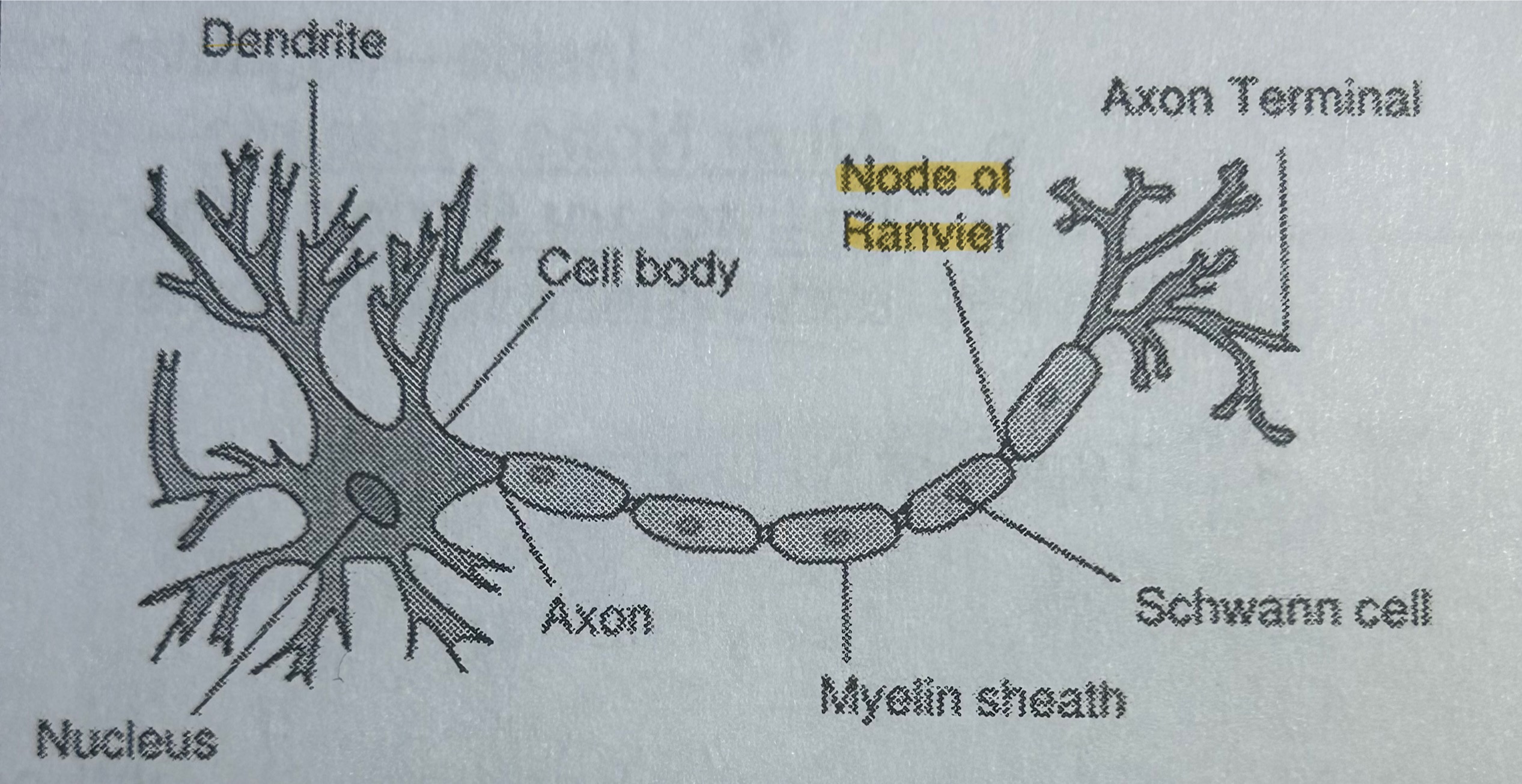
Nodes of Ranvier
Part of a neuron; gaps of exposed axons where action potential is transmitted (NOT TESTED)
Neurotransmitters
Part of a neuron; chemical messages sent between neurons (NOT TESTED)
Multiple Sclerosis
Immune system attacks protective myelin sheaths that cover nerve fibers, causing communication issues between brain & body; eventually can cause permanent damage/deterioration of nerve fibers
Motor neuron
OUTPUT from brain & spinal chord to muscles & glands
Sensory neuron
INPUT from sensory organs to brain & spinal chord
Interneurons
Carry info between each other & found only in the brain & spinal chord; involved in complex functions such as the reflex arc; acts as a “go between” between sensory & motor neurons
Glial cells
Hold neurons in place & provide them w/ nutrients; acts as the “glue” of the nervous system; functions in myelination, cleaning up debris, structural/nutritional support, etc.; there are 10-50 glial cells per neuron
Neuron firing
Occurs when an electrical signal is passed along the axon, resulting in the release of neurotransmitters from terminal button
Neurotransmitter messages gathered by dendrites & cell body
Messages transmitted along axon in brief electrical impulse (action potential)
Causes release of chemicals (neurotransmitters) into synaptic gap where other neurons’ dendrites can receive it
Any excess neurotransmitter is reabsorbed in reuptake
Action potential
Electrical impulse that travels along a neuron’s axon
Reuptake
Process by which neurons can reabsorb excess neurotransmitter
Threshold
Lvl of stimulation needed to trigger a neural impulse
Strength of stimulus does NOT affect impulse’s speed
Strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire more often
Thicker axons are faster
Myelinated axons are faster (impulse jumps “bump to bump”)
Excitatory vs. Inhibitory signals
Excitatory=increases likelihood of neuron firing
Inhibitory=decreases likelihood of neuron firing
Each type affects polarization
Polarization
Differential electrical charge inside & outside neuron
Stimulus threshold
When a neuron reaches its stimulus threshold, it is sufficiently stimulated & the axon depolarizes, beginning action potential; sodium ions rush in & potassium ions rush out, continuing down length of axon
Resting potential
While waiting for sufficient stimulation, neurons are at their resting potential
Electrical charge of a neuron when it’s not active
When not active, fluid inside & outside of neuron are not in balance
Inside=negative ions; outside= positive ions
All or None Principle
A neuron fires or it does not
Refractory Period
Follows action potential; neuron is unable to fire and must re-polarize to establish resting potential
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Type of neurotransmitter; main functions include enabling muscle action, learning, memory
Alzheimer’s
Ach-producing neurons deteriorate
Myasthenia Gravis
Ach receptor sites are blocked, causing symptoms such as impaired movement, impaired vision, impaired breathing, excessive fatigue, etc.
Dopamine
Type of neurotransmitter; main functions include reward/pleasure & motivation
Parkinson’s
Occurs when one has too little dopamine
Symptoms include loss of control over muscle movement, etc.
Schizophrenia
Occurs when one has too much dopamine
Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions inappropriate emotions, etc.
Antipsychotics are used to treat Schizophrenia, reducing dopamine levels, BUT this can lead to Parkinson’s-like symptoms
Serotonin
Type of neurotransmitter; main functions include links to emotional state, appetite, arousal, sleep, impulse control; related to depressive disorders (anti-depressants often increase serotonin levels)
Norepinephrine
Type of neurotransmitter; main functions include speeding heart rate, raising BP, involvement in general arousal; linked to bipolar/depressive disorders
Endorphins
Type of neurotransmitter; main functions include relieving pain & increasing sense of wellbeing; linked to runners high
GABA
Type of neurotransmitter; called Gamma Aminobutyric Acid; main functions are inhibitory; linked to anxiety & intoxication
Glutamine
Type of neurotransmitter; main functions are excitatory and include links to learning, strengthening synaptic connections; disruption leads to MS
Substance P
Type of neurotransmitter; main function includes pain perception
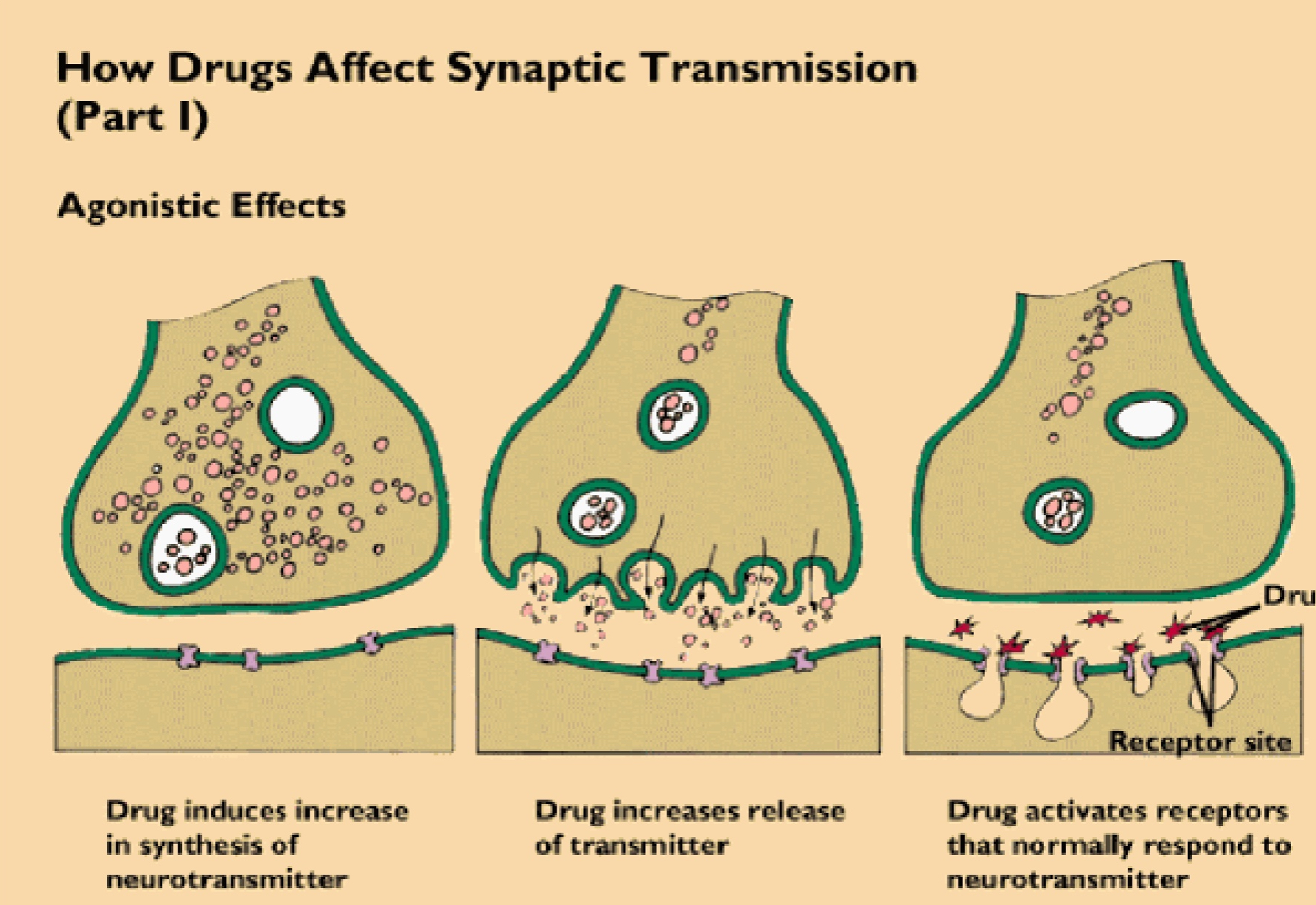
Agonists
Type of drug; enhances neurotransmitter function; increases neurotransmitter synthesis/release; mimics; blocks reuptake
Ex.: L-dopa releases dopamine (used to treat Parkinson’s); LSD mimics serotonin, causing abnormal brain cell activities, leading to hallucinations, perpeption distortion, etc.; black widow venom increases Ach release, causing violent muscle contractions
Antagonists
Type of drug; inhibits neurotransmitter function; blocks neurotransmitter synthesis/release; blocks receptor sites
Ex.: herbal poisons affect Ach and can cause paralysis; alcohol inhibits glutamine, making it hard for glutamine to excite nervous system (depressant)
Nervous system structure
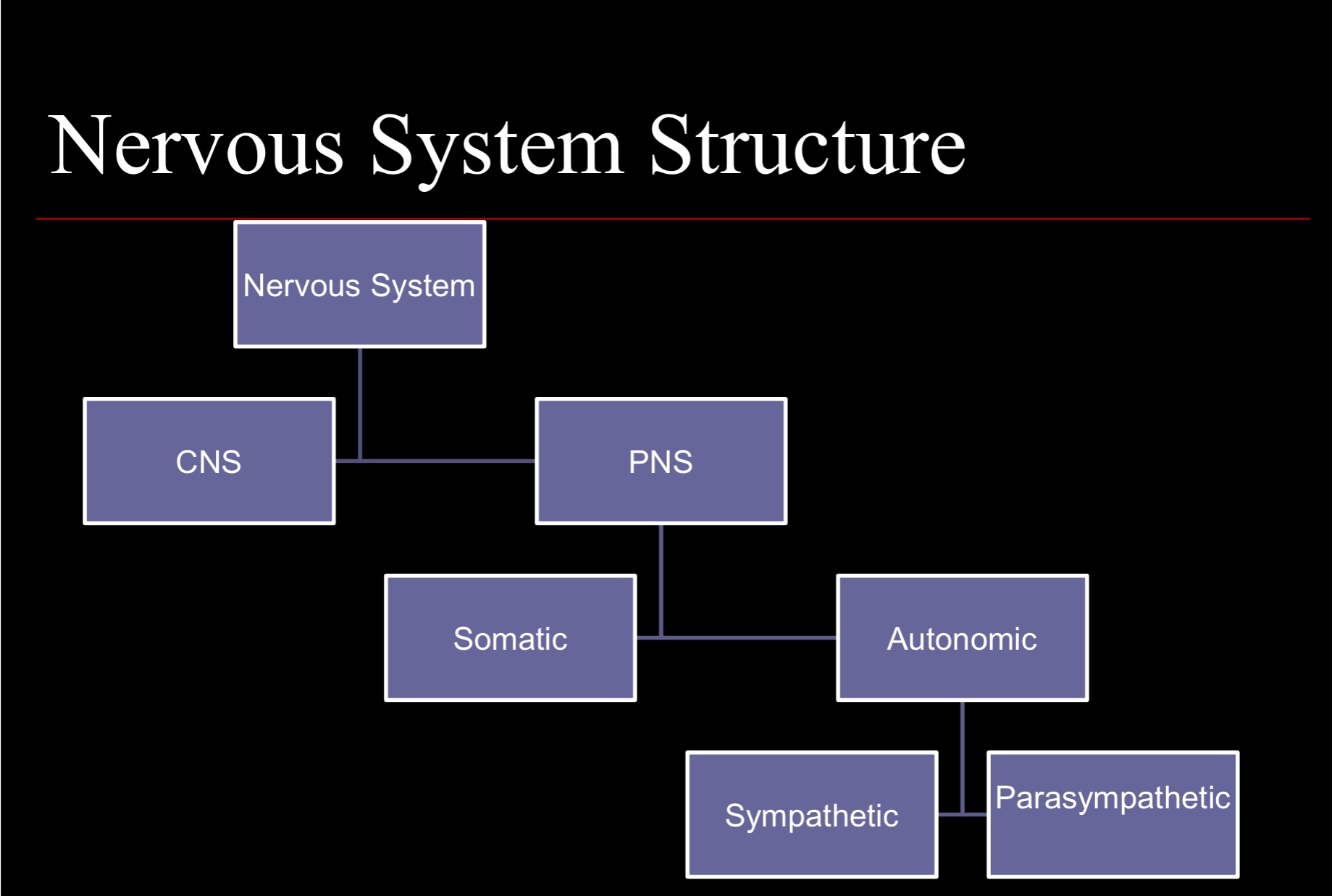
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain & spinal chord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Transmits messages to/from CNS; without it, our brains would be isolated from the world; has 2 parts: somatic, autonomic
Somatic
Part of PNS; consists of sensory & motor neurons; transmits (sights, sounds, smells, body temp., body pos., etc.) & sends (purposeful body movements such as winking, running, posture, balance, raising hands, etc.) messages to/from body;
Autonomic
Part of PNS; deals with automatic functions (heartbeat, respiration, digestion, eye dilation, etc.); has 2 parts: sympathetic, parasympathetic (often have opposite effects/balance each other out)
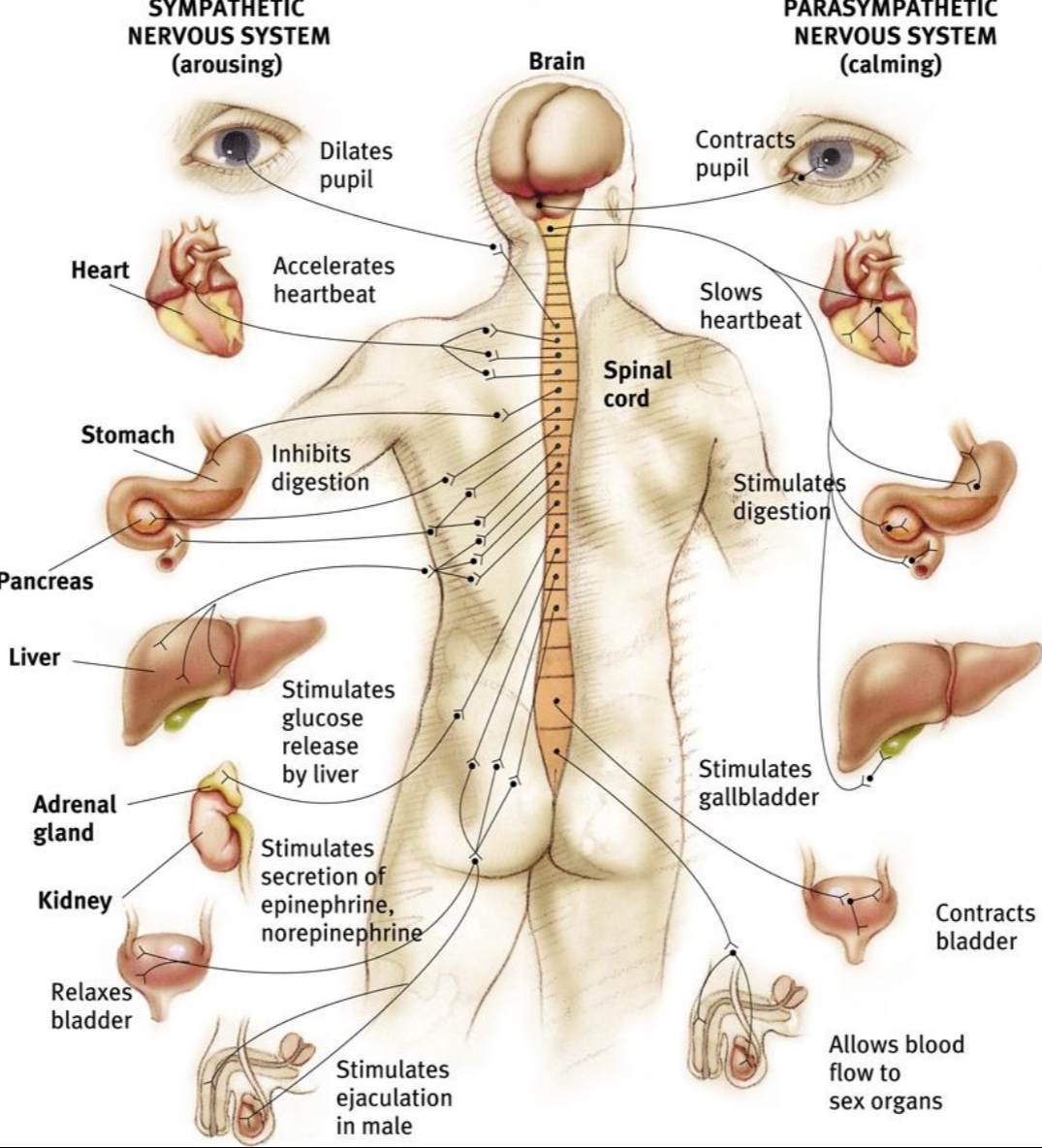
Parasympathetic
Part of autonomic section of PNS; replenished energy (slows us down); promotes hunger, digestion, relaxation (decreases heart rate, BP, etc.), etc.
Sympathetic
Part of autonomic section of PNS; expends energy (fight or flight); promotes fear (increases heart rate, BP, etc.), inhibits digestion, etc.
Phineas Gage
A railroad worker who suffered major brain damage to his frontal lobe in a freak accident during which an iron rod pierced his skull; Gage survived but his personality had changed; Gage had become more irritable, profane, and dishonest, causing him to eventually lose his job
The Brain (interesting facts/details)
Brain is about the size of a large grapefruit
Weighs just over 3 lbs
Consists of over 86 billion neurons
Each neuron is linked to 10,000 other neurons
Forebrain
Outermost layer of brain (NOT TESTED)
Midbrain
Relay station processing visual/auditory info (NOT TESTED)
Hindbrain
Automatic functions (NOT TESTED)
Pons
Part of hindbrain; deals with sleep, left-right coordination
Medulla
Part of hindbrain; deals with vital life functions (breathing, heartbeat, etc.)
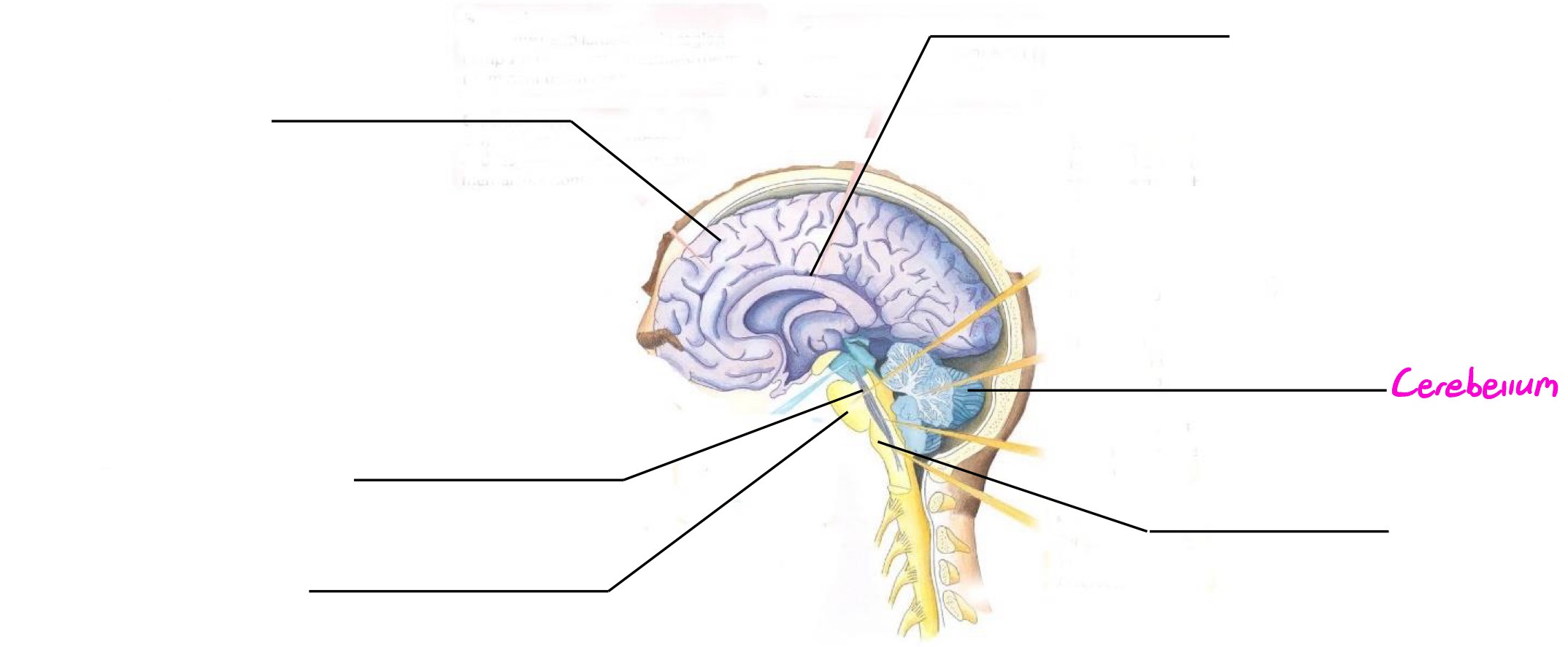
Cerebellum
Part of hindbrain; coordinates movement, balance, posture
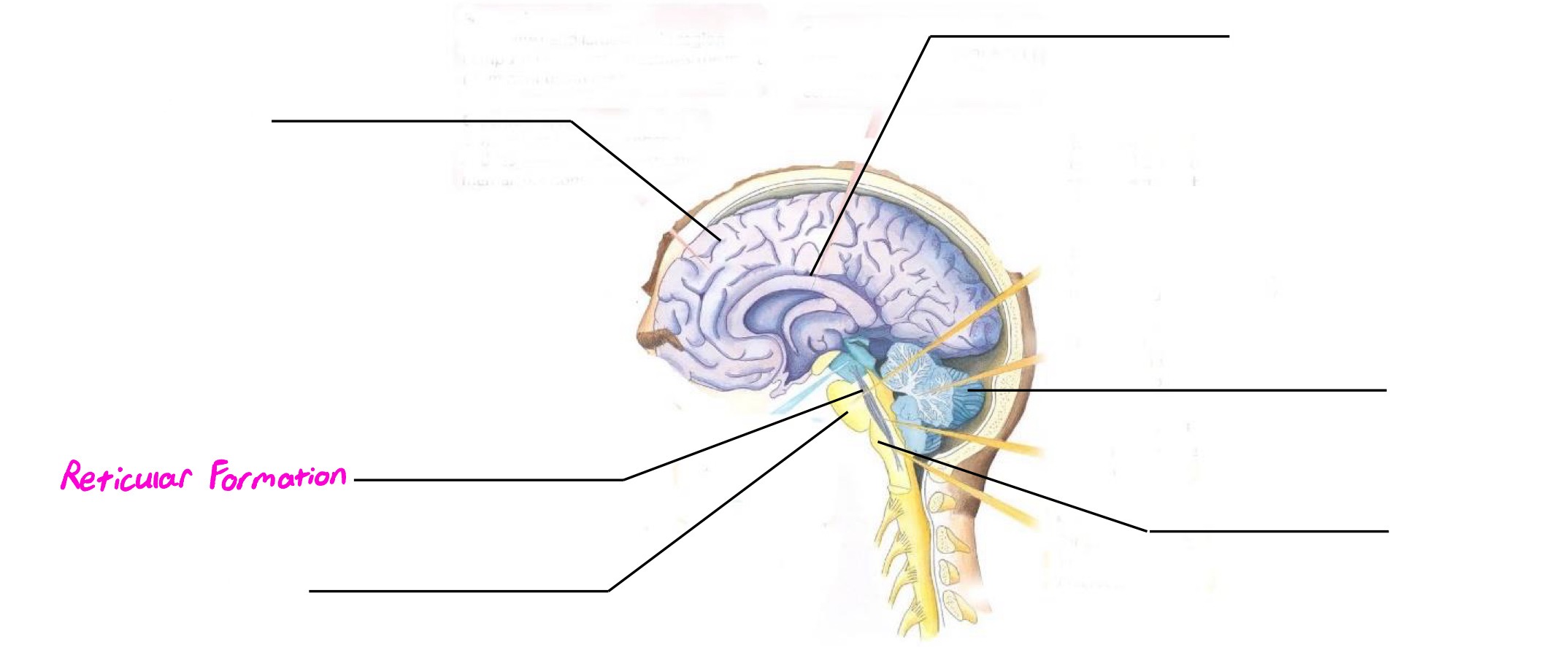
Reticular Formation (Reticular Activating System)
Part of hindbrain; deals with attention, alertness, arousal
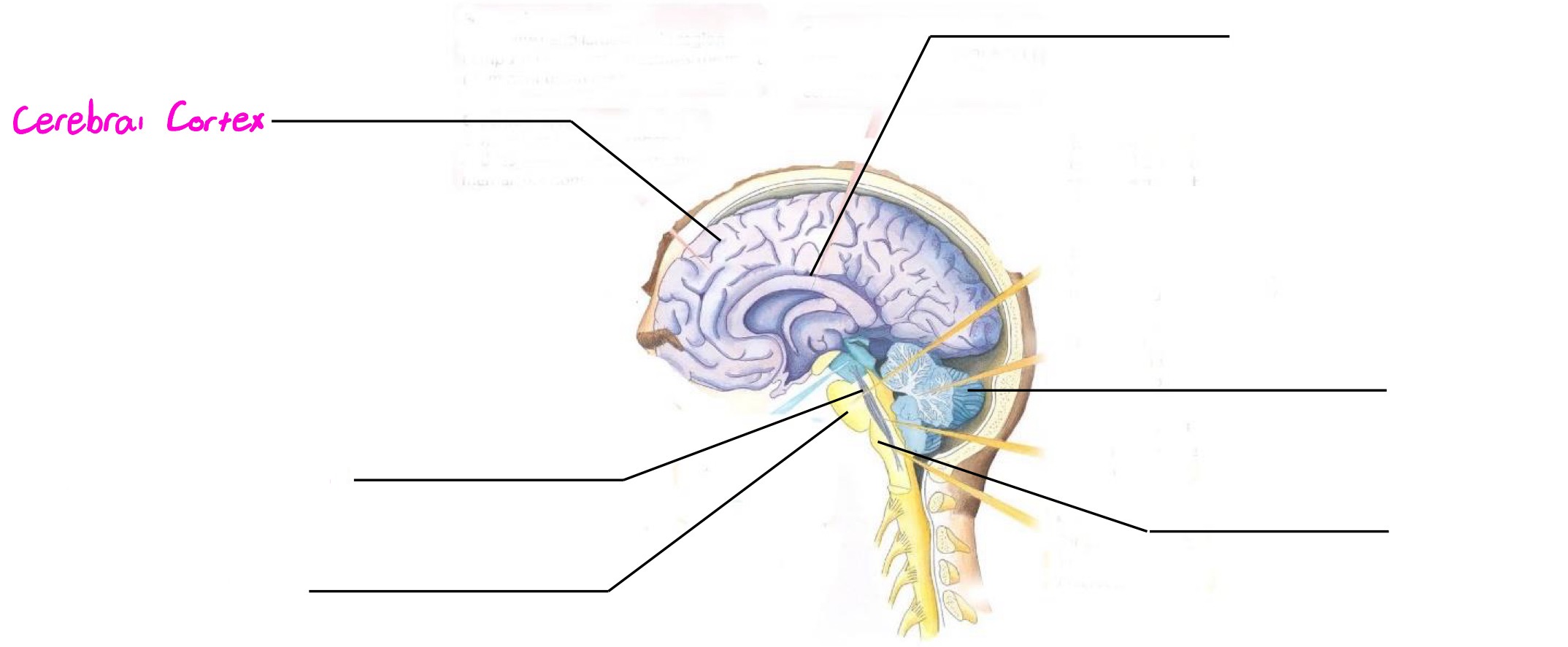
Cerebral Cortex
Part of forebrain; deals with sophisticated mental functions; devised into 4 lobes & 2 hemispheres (each hemisphere controls opposite side of body)
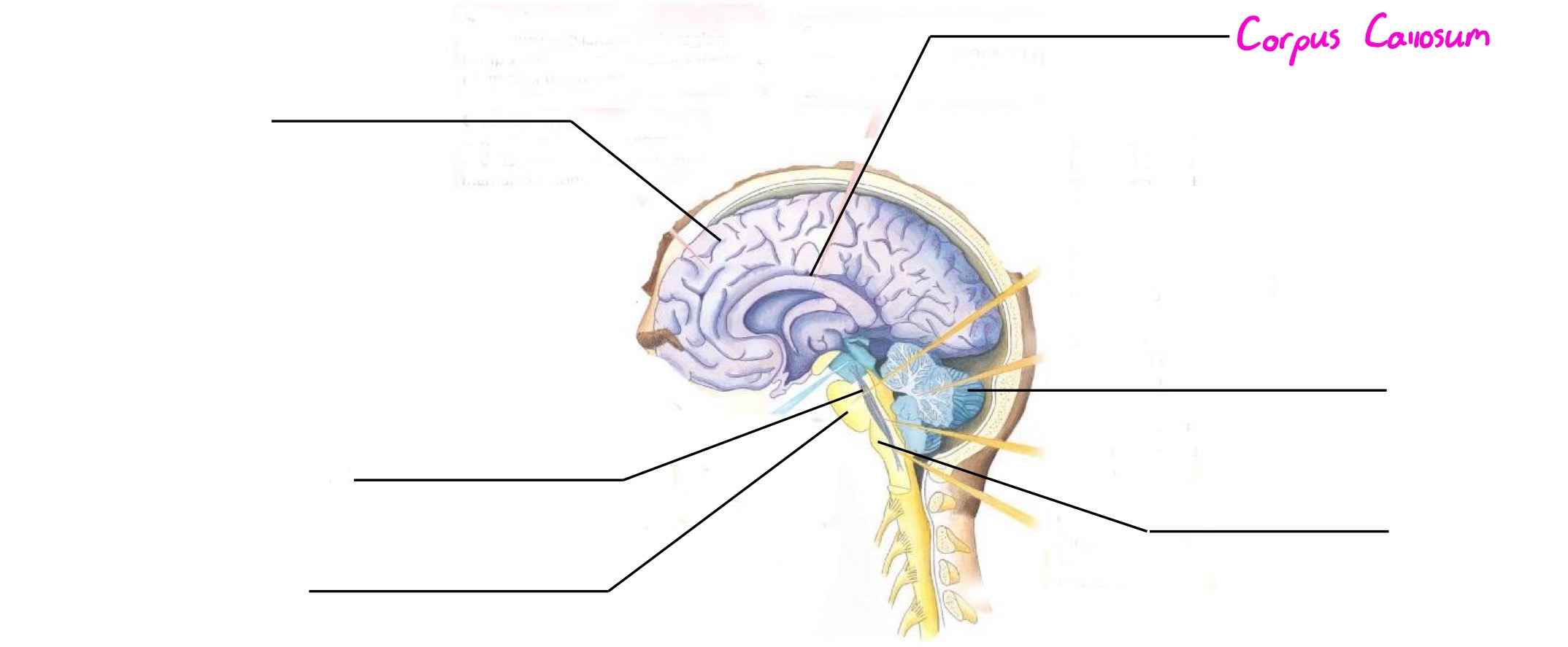
Corpus Callosum
Part of forebrain; thick band of axons connecting 2 hemispheres of cerebral cortex
Left Hemisphere
Left hemisphere of cerebral cortex; deals with language (speech, writing, etc.), logic, math, sequentiality, chronology, order, etc.
Right Hemisphere
Right hemisphere of cerebral cortex; deals with emotion, creativity, spatial relationships, pattern recognition, art, music, some math reasoning (geometry, etc.), etc.
Split brain
When the corpus callosum is severed (often done for people who get seizures from epilepsy or other diseases; prevents electrical signals from spreading to both hemispheres of the brain and lessens seizure prevalence); ultimately prevents the two sides of the person’s brain from communicating, making it so that each side of the body can appear to be controlled by a separate being in certain cases
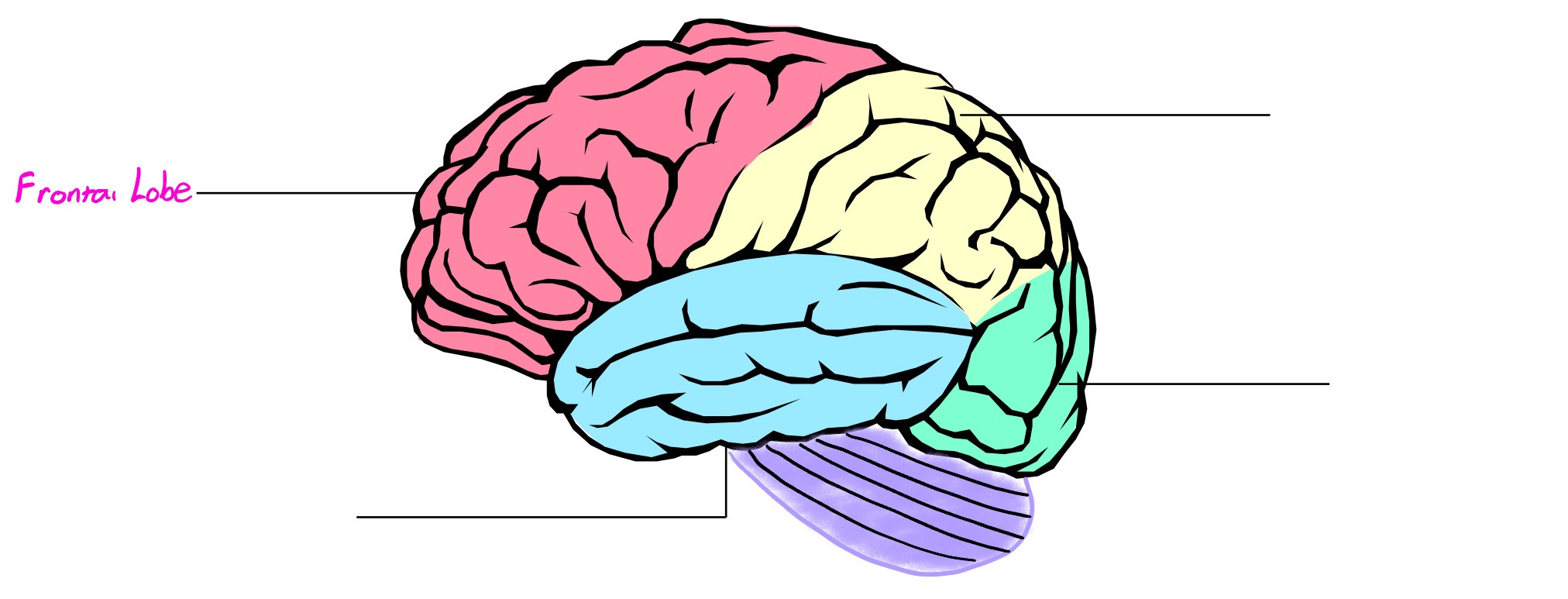
Frontal Lobe
Lobe of cerebral cortex; deals in reasoning, planning, speech, movement, critical thinking
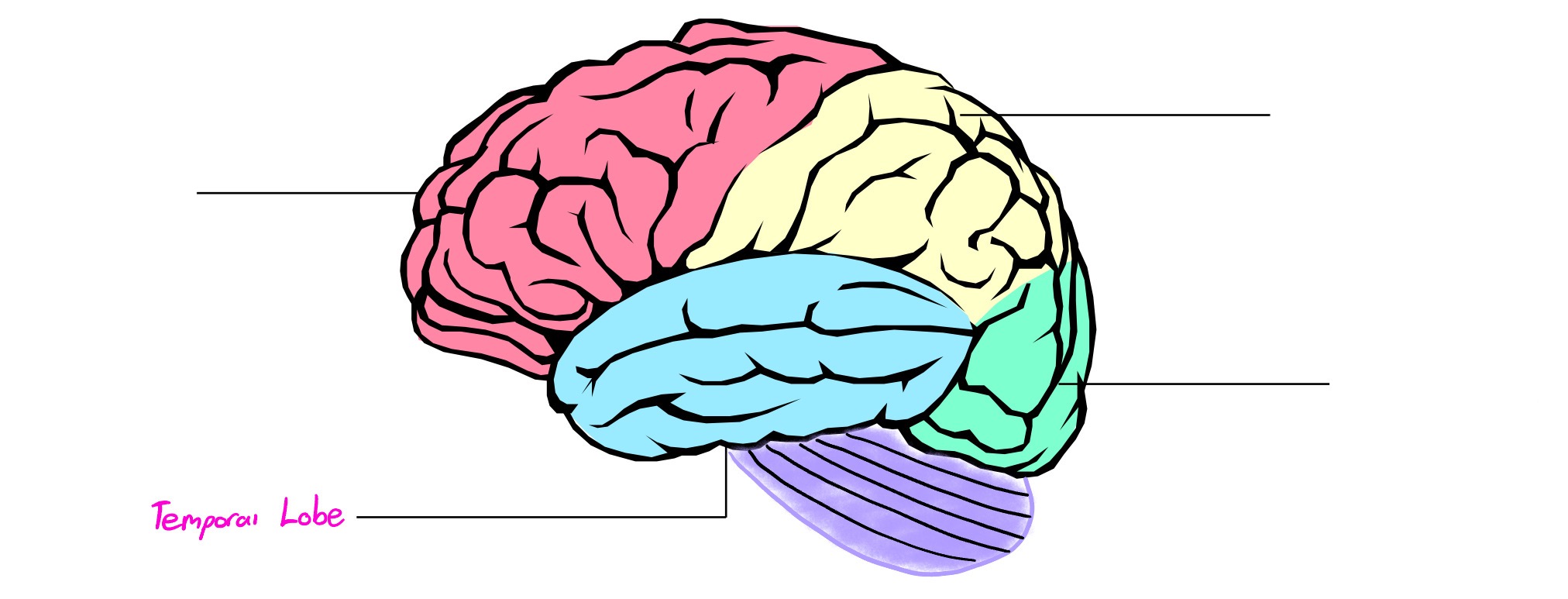
Temporal Lobe
Lobe of cerebral cortex; deals in hearing, memory
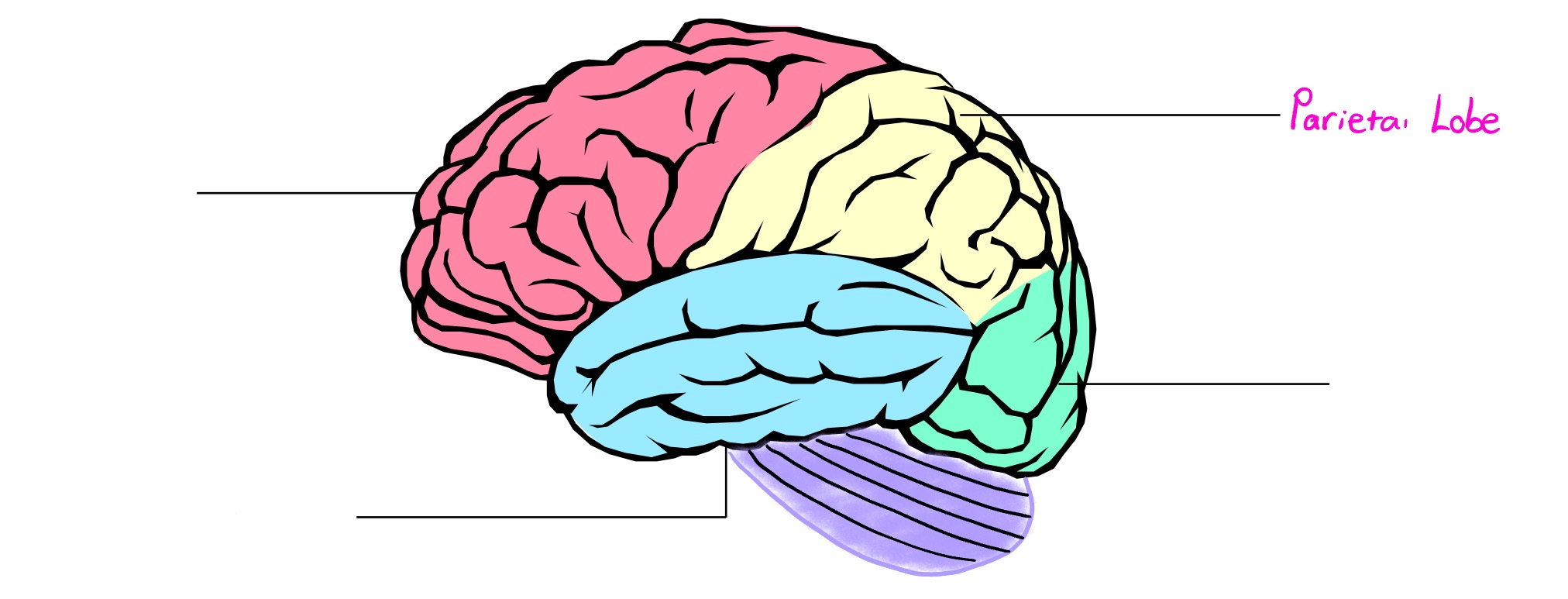
Parietal Lobe
Lobe of cerebral cortex; deals in perception of touch-based info (pressure, temp., pain, etc.)
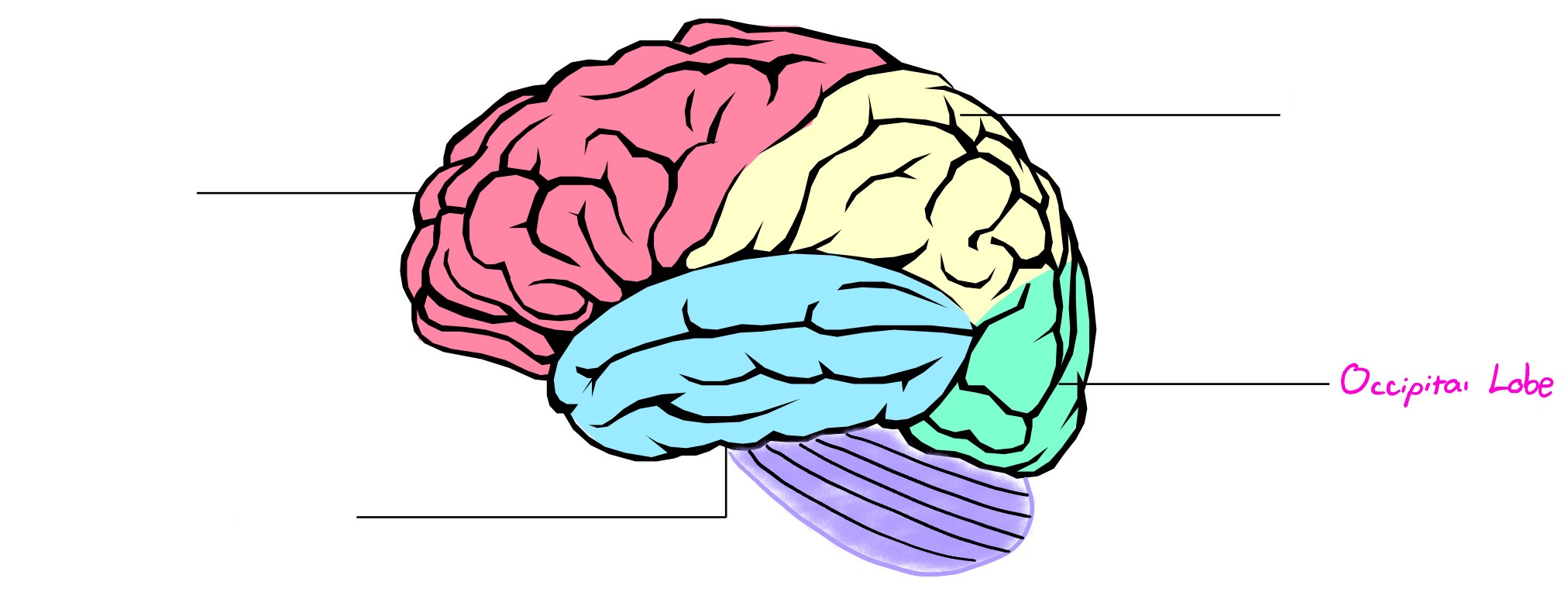
Occipital Lobe
Lobe of cerebral cortex; deals in visual info
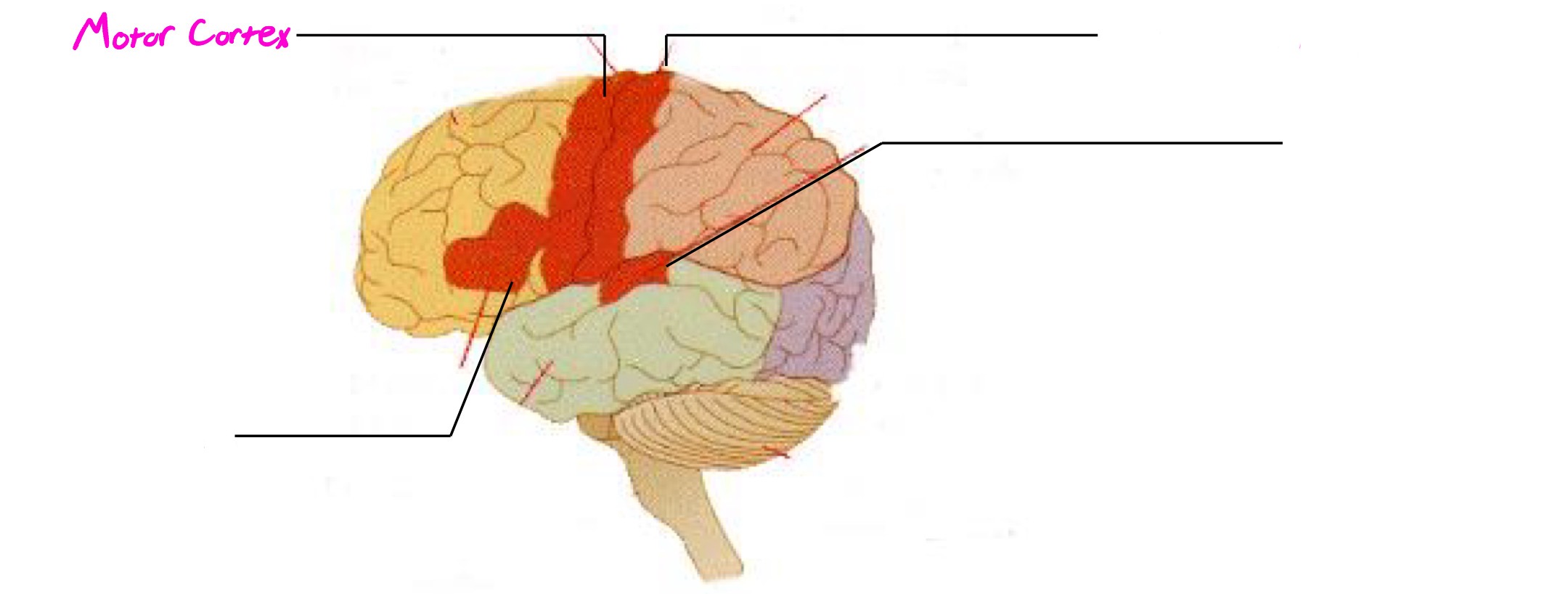
Motor Cortex
A strip located in frontal lobe; registers motor info/movement
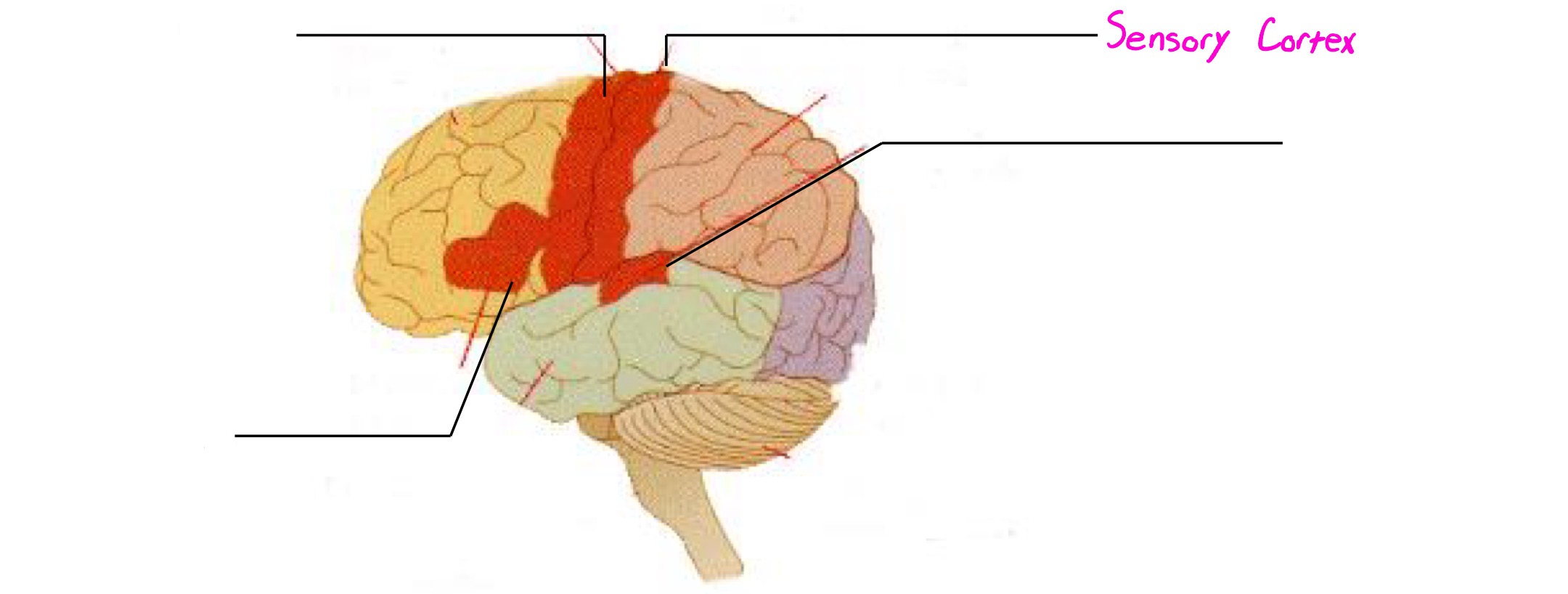
Sensory Cortex
A strip located in parietal lobe; registers sensory info
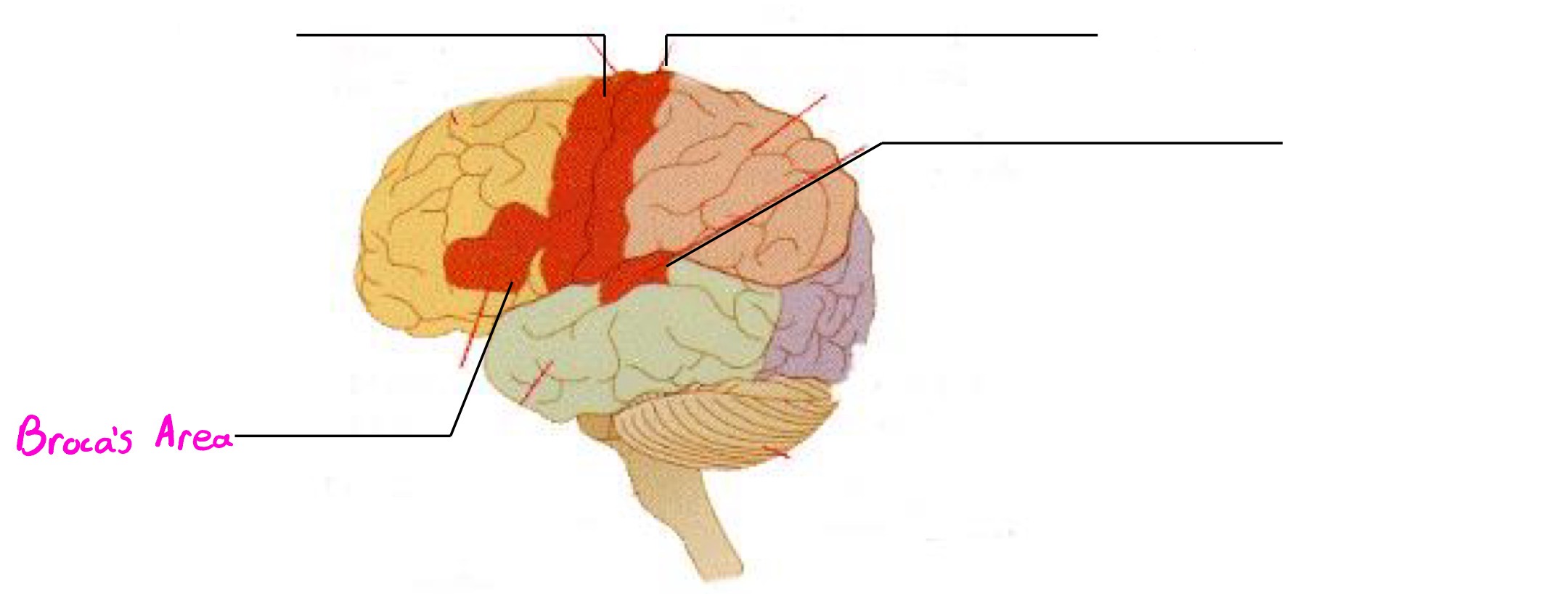
Broca’s Area
Deals in speech production
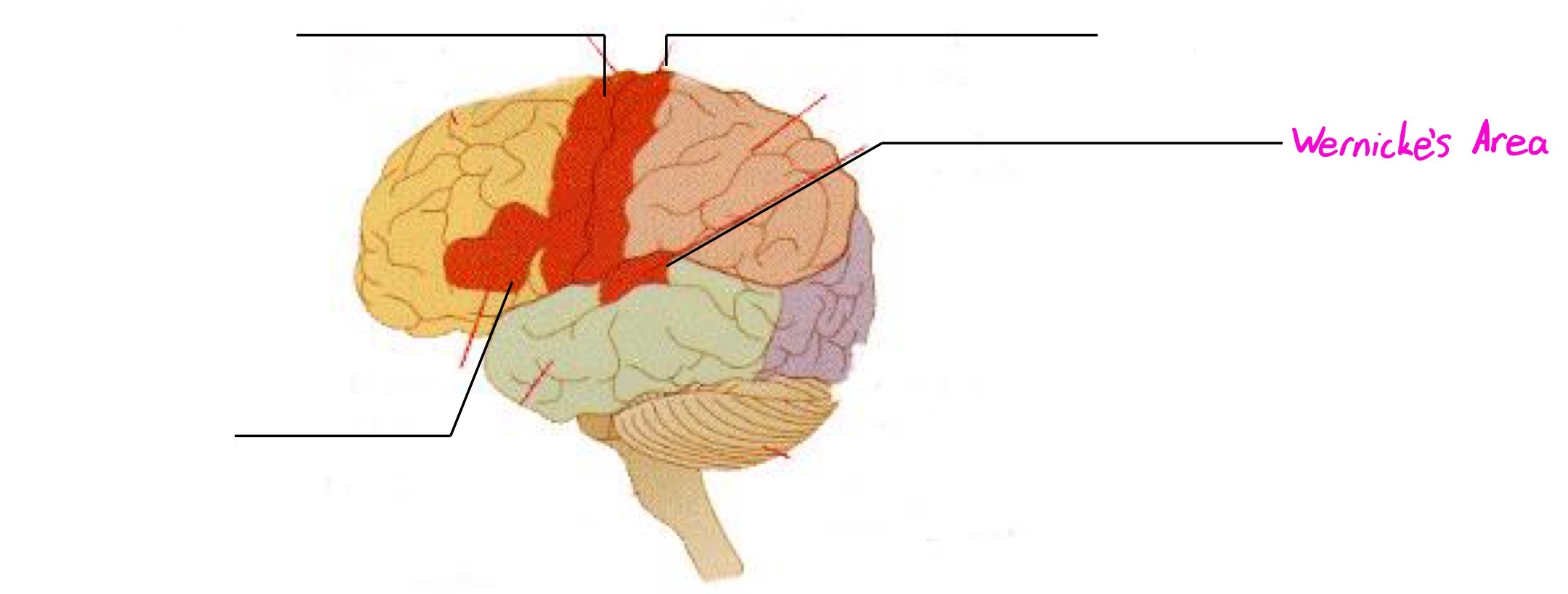
Wernicke’s Area
Deals in understanding speech (interpreting auditory code)
Angular Gyrus & Visual Cortex
Deal in reading/seeing words
Aphasia
Partial/complete inability to articulate ideas/understand language due to brain injury/damage
Broca’s Aphasia
Inability to produce speech BUT ability to understand it
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Inability to understand speech BUT ability to say things; what people say often doesn’t make sense (“word salad”)
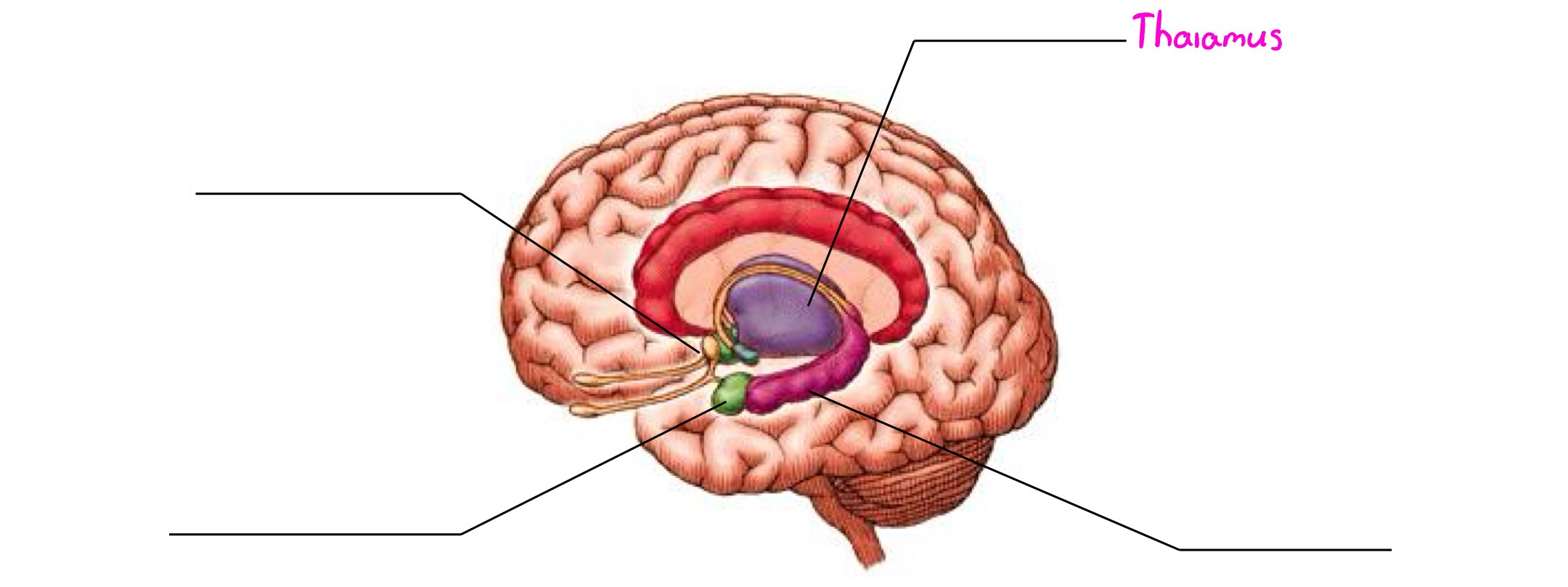
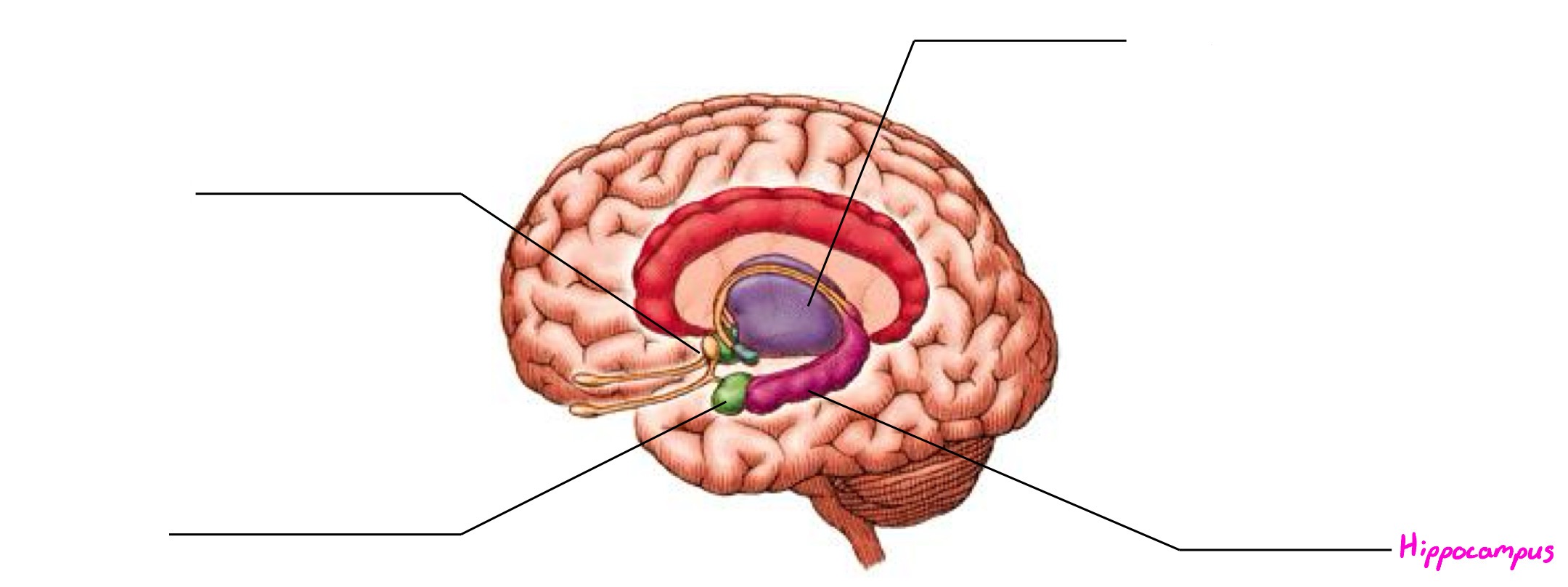
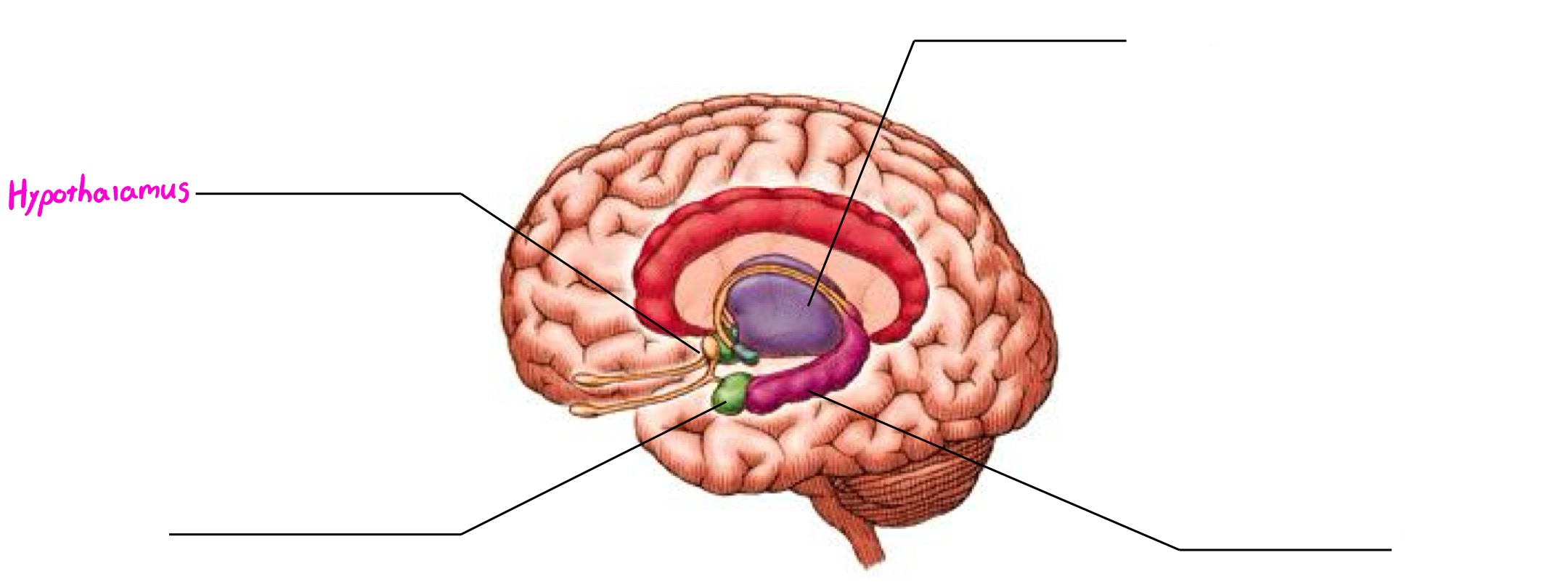
Limbic System
Deals in motivation, emotion, memory
Amygdala
Part of limbic system; almond-shaped structure; involved in emotion & memory (usually negative emotions such as anger, fear, etc.)
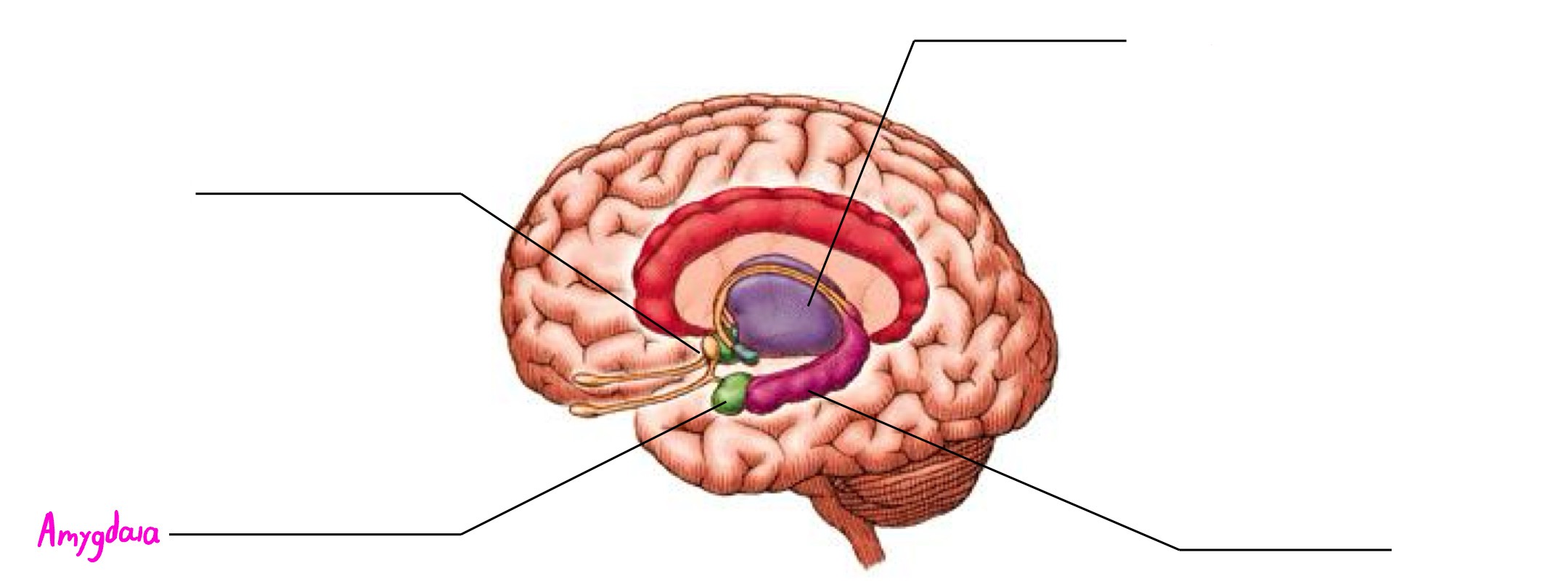
Hippocampus
Part of limbic system; wishbone-shaped structure; involved in forming new memories (long-term)
Hypothalamus
Part of limbic system; peanut-sized structure; maintains homeostasis; links endocrine system to brain; involved in motivation & emotional drives (hunger, thirst, sex, body temp. reg., etc.)
Thalamus
Part of limbic system; processes & integrates info from all senses EXCEPT smell & relays info to appropriate higher brain centers