Pathopharm 2- Exam 2
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
Gene
Fundamental unit of DNA, Changes in DNA can be linked to diseases.
Nucleotide sequence, Basic unit of heredity. Makes us what we are.
-Exons= Portion of genome that encodes proteins
-Introns= portion of genome that does not code for proteins
-Codon= Set of 3 nucleotides that signal specific amnio acid. Start at stop
Codon
Set of 3 nucleotides that signal specific amnio acid. Start at stop
-If fatty then would cause it to not be able to start or stop.
Introns
portion of genome that does not code for proteins
Exons
Portion of genome that encodes proteins
Epigenetic changes
Alterations in gene expression (gene showing it, doing its job) due to environmental stressors, behavior, or lifestyle.
-Is combination of genetic make up and all these factors above.
Pharmacogenomics
Gene function in health, disease, and responses to medications
Genetic
Study of inherited traits.
Genomics
Study of interaction of all genetic material (not only genes)
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Purpose= Regulates and repairs, when change occurs like HIV, changing cell, and damage cause it to not be able to repair.
Double-helical structure of nucleotides
Nucleotide= pentose sugar, phosphate, purine or pyrimidine nitrogen base
Nitrogen bases= DNA (adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine). A-T and C-G pairing. RNA= uracil replaces thymine A-U, C-G
Gene Mutation
Damage or change to gene that alters genetic code. May be inherited or occur sporadically. Point and frameshift mutations.
Germ cell mutation (sex cells)= Gametes affected= may be passed to offspring, radiation/x-ray.
Somatic cell mutation= Body cells (skin, bone, muscle), Not passed to offspring.
Gene Nomenclature
Names= Some genes have specific names, Ex= BRCA1 (Breast cancer type 1)
Location= Gene locus, Chromosome number, arm, and region,
-Short arm= p
-Long arm= q
-Further divided into regions, bands, and subbands.
Centromere= Junction, between p and q arms. Ex- cystic fibrosis- 7q31.2.
Human Karyotype
Humans= 23 pairs
-Autosomes= 1st 22 pairs
-Sex- 23rd pair
-XX= female
-XY= male
Y chromosome much small than X chromosome.
Chromosomal abnormalities. Ex= Down syndrome- Trisomy 21, 3 copies chromosome 21
Females should have what Karyotype?
XX
What karyotype should males have?
XY
-Y chromosome much smaller than X chromosome
Gene Expression: Transcription
DNA to mRNA (messenger RNA), Transcribes it.
RNA polymerase uses DNA as template to form mRNA strand.
Splicesosomes= excise introns
mRNA leaves nucleus
Gene Expression: Translation
mRNA to protein, Allows us to read it
Ribosome= mRNA transcript “read”
tRNA (Transfer RNA)= One end binds to 3-nucleotide sequence on mRNA. Other end contains corresponding amino acid for the nucleotide sequence.
Amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Regulating Gene Expression
All cells contain the same genes
Expression and rate of expression varies between cells
Enhancers and silencers
-Transcription factor binding sites on DNA that affect DNA transcription rates.
Inheritance Patterns are?
Allele- Gene inherited from one parent.
Genotype- Genetic code, Information, Passed on from family (curly hair)
Phenotype- physical expression of the genes. Structure and/or appearance.
Allele
Gene inherited from one parent.
Genotype
Genetic code, Information, Passed on from family (curly hair)
Phenotype
Physical expression of the genes. Structure and/or appearance.
Recessive Trait
One expressed only in a homozygous pairing. Need 2 Allele to be expressed.
1 Alleles needed for expression, Represented by lower case letter
Dominant Trait
One expressed in either a homozygous or a heterozygous pairing. Only need 1 Allele. Higher likelyhood of passing on.
1 Allele needed for expression, Represented capital letter.
Carrier
A person who is heterozygous for a recessive (1 copy) trait and does not manifest the trait.
Never show it. Heterozygous for recessive trait, Does NOT express, can pass
-Can pass it on to offspring, Don’t have it but can pass it on.
Heterozygous
Alleles carry different traits
Homozygous
Alleles carry same traits
Medelian Inheritance
One copy of gene is inherited from each parent.
-Punnett square= diagram used in genetics to predict the potential genotypes and corresponding phenotypic probabilities of offspring from a specific cross
How to do Punnett Square?
diagram used in genetics to predict the potential genotypes and corresponding phenotypic probabilities of offspring from a specific cross
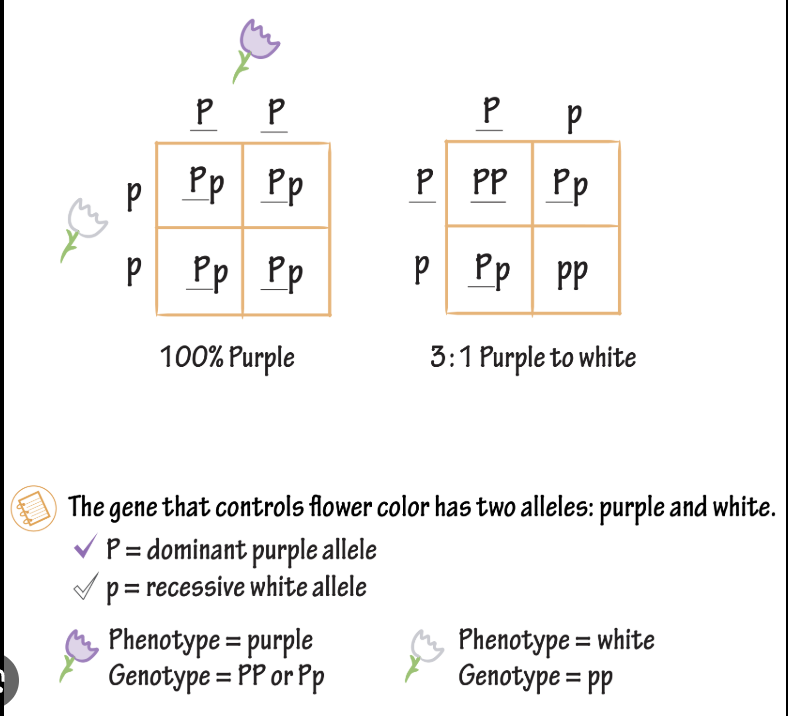
Autosomal Traits
1 copy of dominant allele needed for expression.
2 copies of recessive allele needed for expression.
Autosomal Dominant
A single mutant allele from an affected parent is transmitted to an offspring regardless of sex.
Autosomal Recessive
Manifested only when both members of gene pair are affected (both parents unaffected, but carriers)
X-Linked Recessive
Always associated with X chromosome; the inheritance pattern is predominately recessive. Only effect X chomosomes.
Sex-Linked Inheritance
AKA X-Linked. Male= 46 XY, Females= 46 XX
X chromosomes larger than Y chromosome. Some genes, no corresponding allele on Y chromosome. Allele on X chromosome expressed. Regardless if dominant or recessive.
Ex= hemophilia
Attacks X-chromosomes. Females are carriers since have 2 X, females pass it on.
Males will almost allows show illness since only 1 X, male don’t pass it on.
Genetic Penetrance
Ratio of people with phenotype compared to genotype (genetic). High penetrance indicates almost all individuals with the gene express.
-Ex= BRCA1 has 85% penetrance.
Higher rate the higher expressed physically.
Genetic Expressivity
Related to severity of genetic disorder. (the degree)
May vary from a given condition.
-May vary from person to person.
Ex= Marfan’s syndrome- Autosomal dominant, have problems with Collagen growing too fast.
Complex (Multifactorial) Inheritance
Combination of one or more genes plus environmental triggers
-Majority of disease have this pattern
-Ex= hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cancer
Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP’s)
Not on test, Changes in one nucleotide of gene sequence. Leads to Autosomal
-Ex= AACGT vs ATCGT
Can have profound effects if improper amino acid coded
-Ex= sickle cell anemia
Mitochondrial DNA
Not on test, Inherited from the mother (maternity testing), Responsible for high energy- if mitochondrial disease- low energy and lead to WBC bound, developmental delays.
Can be damaged by free radicals
-Lacks the repair process of DNA found in nucleus. Damage implicated in disease such as diabetes, cancer, and heart failure
Disorders can be inherited; neurodegenerative disorders, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-Defective mitochondrial DNA can be replaced with normal mitochondrial DNA. Also tend to affect tissue with high “energy” needs.
CRISPR
Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats.
-Gene “editing” in embryonic development
-Highly controversial , very expensive
-Finding where genetic disorder- remove and replace with normal code.
Pharmacogenomics
Interactions between a person’s genetics and medications
-Ex= Slow acetylator phenotype, Warfarin (Coumadin) response. Pharmacological management of hypertension in individuals of African ancestry.
What works better for body.
Oncogenes
Enables uncontrolled cell proliferation, leads to unregulated cell growth.
Direct synthesis of oncoproteins. Viral insertion of an oncogene may also occur.
Ex- Human papillomavirus leading to cancer. Cancer is unregulated cell growth.
-Proto-Oncogene= Control regulate cell growth, Normal genes that control cell proliferation, Mutation leads to activate oncogene
Proto-Oncogene
Control regulate cell growth, Normal genes that control cell proliferation, Mutation leads to activate oncogene
What enables uncontrolled cell proliferation?
Oncogene
Oncoproteins
Regulate cell cycle, produced from oncogenes.
Direct cell to undergo uncontrolled proliferation.
Defects leading to oncogene and oncoprotein formation increase cancer risk.
Tumor Suppressor genes
Inhibit (cell growth) uncontrolled cell proliferation
p53 tumor suppressor gene stops mitosis.
p53 mutation may lead to uncontrolled cell growth
Knudson’s “Two Hit” Hypothesis
Alfred Knudson proposed “two hit” hypothesis for cancer development.
-Both alleles must be damaged.
“First hit”= initial hereditary allele mutation. ex= breast cancer
“Second hit”= Mutation or damage (outside stressor) to other allele. Leading to cancer progression.
-Ex= Heart failure hereditary (first hit)→ Eating unhealthy (second hit)
Holds primarily true unless a disease is autosomal dominant.
Chromosomal Alterations
Aneuploidy- Different number of chromosomes than 46. Ex= Trisomy 21; Turner syndrome (chromosome missing) (45, XO)
Translocation- one piece of chromosome breaking off and joining another
-How much broke off and where did it go?
Deletion= piece of chromosome is broken off and lost
Aneuploidy
Different number of chromosomes than 46. Ex= Trisomy 21; Turner syndrome (chromosome missing) (45, XO)
Translocation
one piece of chromosome breaking off and joining another
Balance _= info broken off and swapped, no changes occur
-How much broke off and where did it go?
Deletion
Piece of chromosome is broken off and lost
The amount of “info” lost or removed often determines the severity of illness/injury.
Epigenetics
Behavior, lifestyle, and environmental factors
-Do not change DNA sequence. Change the way DNA is “read”
Reversible changes
Turn genes “on” or “off”
Ex of changes= DNA methylation, Histone modification, Non-coding RNA
Genetic Assessment includes?
Testing
Pedigree (genogram)= multigeneration history, family history.
Karyotyping
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Fluorescence in situ hydridization (FISH)
Southern blotting
Prenatal screening
Women 35 yeas or older
Abnormal ultrasound findings
Couples who are close blood relatives (incest) possible
Women who have a condition associated with increased risk of fetal problems.
Unexplained or multiple miscarriages
Family history of an inherited condition, intellectual disability, or birth defects- family may decide if want to stop pregnancy
-If adopted or family is unknown maybe have testing.
Maternal Serum screening
Proteins from placenta and fetus enter maternal circulation
Chorionic villus sampling
Usually for women age 35 years or older.
Performed between 10 to 12 weeks of pregnancy
Amniocentesis
Diagnosis fetal chromosome problems
Performed on amniotic fluid between 16 and 18 weeks of pregnancy
Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling
Also called cordocentesis
Examones fetal umbilical cord
Gene therapy
Cutting out genetic material and replacing it.
Ex Vivo= Genetically defective cells modified, and then readministered back to the patient
In Vivo= Directly delivers a normal copy of a specific detective gene into the target cells
Ex vivo
Genetically defective cells modified, and then readministered back to the patient
In vivo
Directly delivers a normal copy of a specific detective gene into the target cells
CRISPR-Cas9
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9.
Nuclease that cuts the genome at the specific location to make needed edit in sequence. Cell uses DNA repair machinery to proceed with making the desired change in genome.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR-T) gene therapy
Patient T cells (immune cells) obtained and genetically modified.
T cells attack patients specific cancer cells.
Help treat certain cancers, using gene therapy and virus attacks cancer instead of healthy cells.
Ethical concerns for gene therapy?
Patient counseling for genetic testing
New area of health care, health-care professionals are exploring the best options
-Very expensive!! Often a Tx of last resort.
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Autosomal dominant. Lack of LDL receptors, elevated cholesterol, Atherosclerosis.
High risk of high cholesterol.
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Autosomal dominant
Adenomatous polyps in colon, Increased colon cancer risk
Colonscopy screening from young age. Colon cancer risk.
Marfan’s syndrome
Autosomal dominant
Connective tissue disorder. Fibrillin-1 (FBN 1) gene mutation.
Aorta, heart valves, lungs. Aortic rupture, effects heart and lungs.
Neurofibromatosis (NF)
Autosomal dominant
Two forms: NF1 and NF2
Typical age of onset of symptoms is late teenage years
Signs and symptoms: Cafe-au-lait sports, optic nerve tumor.
Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Autosomal recessive- need both allies to be presented
Most common lethal inherited disease in Caucasians. Defect in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene (CFTR), 7q31.
Disrupts lung function (excess mucus) and pancreatic secretions (malabsorption of nutrients)- blocks. End-stage lung disease is the principal cause of death
Newborns secreened in U.S.
Treatment= Pancreatic enzyme supplements, bronchodilators, mucolytics, nutritional supplements
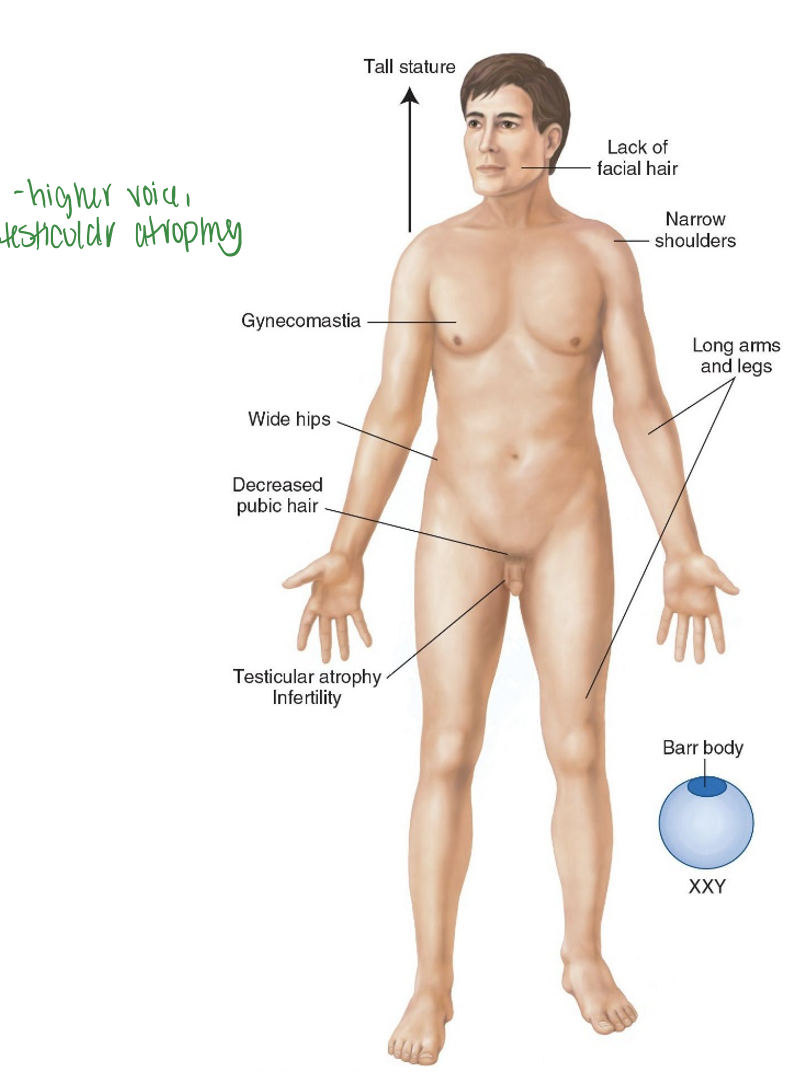
Klinefelter Syndrome
47 (should have 46), XXY (get extra X).
Decreased cognitive development Testosterone replacement needed. Effects men, Don’t develop male secondary characteristics due to Extra X
Treat with testosterone treatment, may lead to infertility if not treated. Higher voice, testicular atrophy.
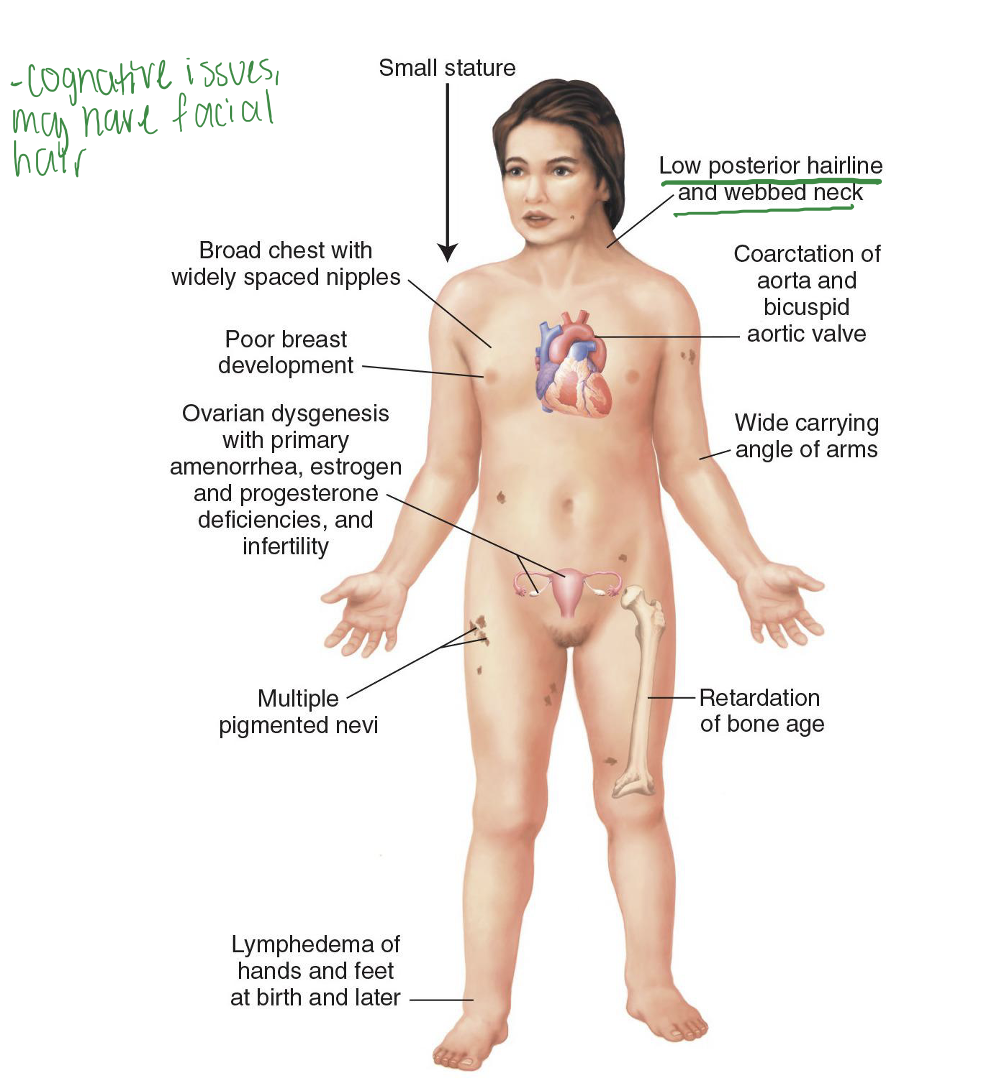
Turner syndrome
45, XO Karyotype. May result in spontaneous abortion. Variations in disease severity.
Effects women. Missing X, estrogen deficiency. Cognitive issues, may have facial hair
Fragile X syndrome
Disorder of X chromosome at Xq27.3.
Characterized by long repeating sequences of CGG.
Cognitive impairment.
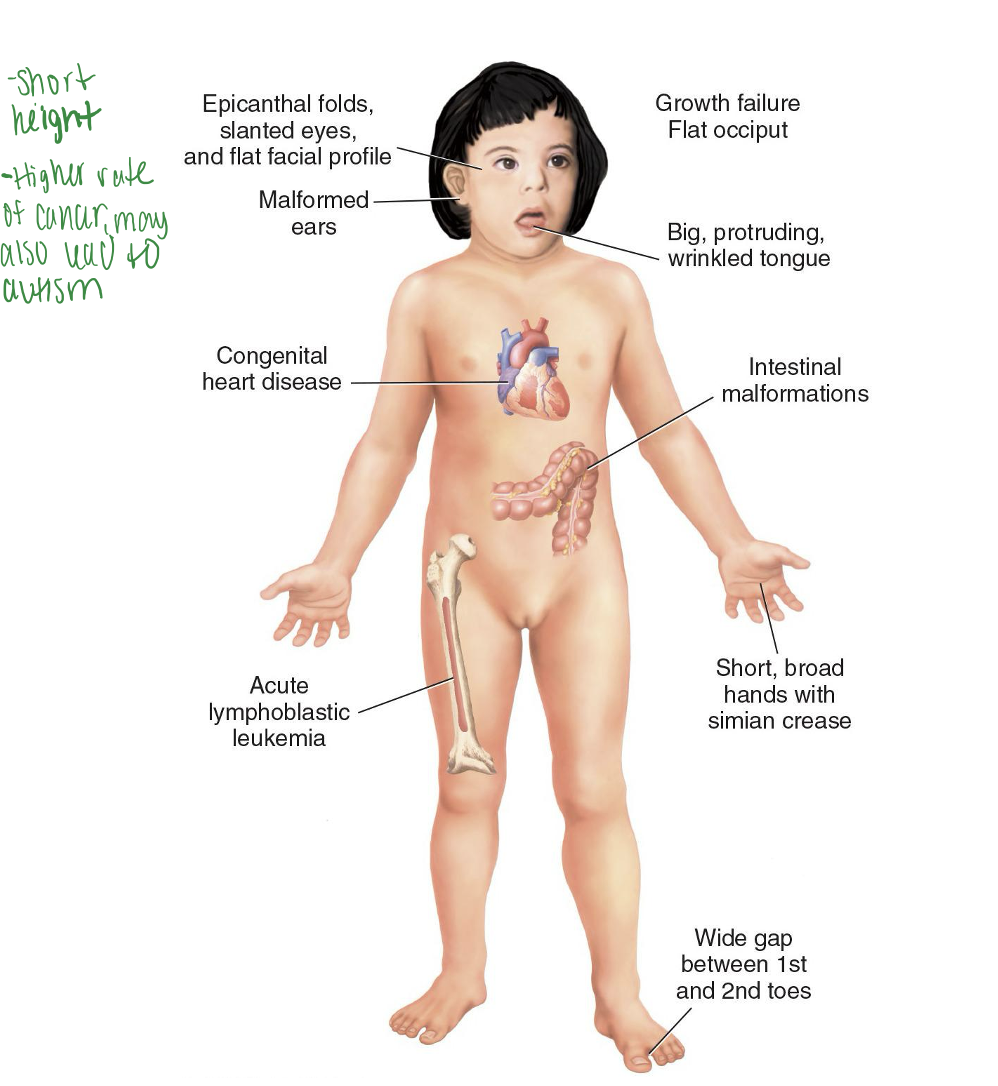
Down syndrome
Most common chromosomal disorder
Trisomy 21
Wide variation of severity
Flat facial profile, epicanthic folds around the eyes. Short height, higher rate of cancer, may also lead to autism
80% have IQ of 25 to 50
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Disruption or deletion of genes on chromosome 15, Can’t stop eating, Paternal- Inherit From father.
Hypothalamic dysfunction leading persons to overeat; hypotonia, low IQ, short stature, and hypoginadism.
What is interesting is not “what” is missing but “who” it came from
Angelman’s Syndrome
Disruption or deletion of genes on chromosome 15, Comes from mother.
Neurological problems- neuro/cognitive issues.
What is interesting is not “what” is missing but “who” it came from
Factors in Cancer
Neoplasm- abnormal growth, appearance, and function of cells. New growth
-Cancer is unregukated cell growth
2nd leading cause of death- age is primary factor. Body deteriorate as we age.
Tumor suppressor genes- guard against cancer.
Proto-oncogenes- regulate cell growth
Immunocompetence→ Immune system should destroy abnormal cells with aging, immunocompetence declines
TP53→ Tumor suppressor gene, p53- protein “Guardian of the genome”
Factors included in Epigenetics
-Do not change DNA sequence→ Change way DNA sequence is read, Reversible changes (turn genes “on” or “off”), change how it is read.
-Epigenetic mutations (epimutations)→ May lead to cancer. Modifiable changes- smoking, poor diet, lack of excercise, drugs, exposure to environmental chemicals. Unlike genetic mutations, epimutations are reversible.
-Transgenerational inheritance
-Epigenetic treatment or epi-drugs= Reverse abnormal epigenetic modifications, Not cytotoxic, Goal is to “reprogram” cancer cells by targeting enzymes involved in epigenetic changes.
Ex= DNA methylation→ chemical group is added to DNA, can turn a gene “on or off”. Histone modifications→ Histones are proteins, wind around DNA, can turn a gene “on or off”. Non-coding RNA modification→ Not used to make proteins. Influences how ribosomes read the RNA to make proteins.
Basic concepts of cancer
-Cell cycle regulation, Immunocompetence (related to tumors)→ good immune system that protect against cancer.
-Tumor classification and staging, Cancer genetics, Role of viruses in cancer.
-Stages of carcinogenesis, Metastasis and tumor angiogenesis, Biomarkers
-Paraneoplastic syndromes, cancer cachexia.
Cell cycle
Cells need to start and stop when told to
Stages: G0, G1, G2, S, and M
Checkpoints within cycle
-Repair, recycling, or apoptosis if needed, Cancer cells do not stop at checkpoints.
Cancer cells disregard growth inhibition signals- Growth does Not stop due to cancer.
-Grow on top, around, beside other cells. Cancer cells may break free. Material not require- leads to cancer.
Cancer continues to grow and take up space leading to death.
What is the role of viruses?
Certain viruses are oncogenuc
-HPV, HIV/AIDS, Epstein-Barr virus- can lead to cancer
Cancer cell cycle
unregulated cell division resulting from failures in the cell cycle control system, leading to continuous proliferation, evasion of cell death, and tumor growth. Mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes disrupt checkpoints (G1, G2, M), causing cells to ignore signals to stop dividing or die.
Stages of Carcinogenesis
Initiation→ 1st step, Alteration in a gene or genes, Mutation happens and leads to..
Promotion→ Relatively lengthy and reversible. Pre-neoplastic cells accumulate, process can be altered by chemopreventive agents.
Progression→ Phase between a premalignant lesion and the development of invasive cancer.
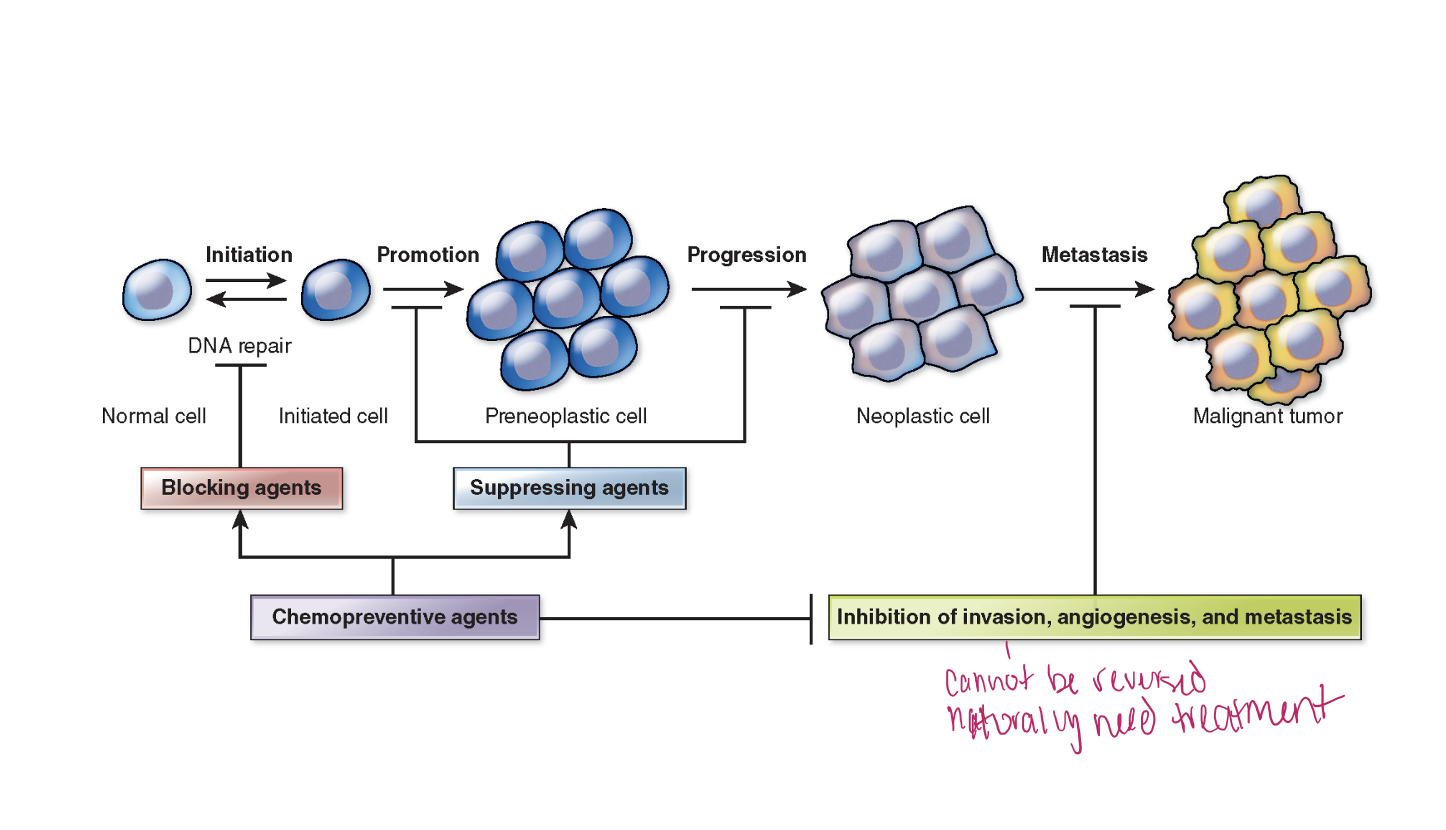
Metastasis
Malignant cancers→ spreads to more body parts.
Movement of cancer cells from primary location to distant site.
Lymphatic or circulatory system→ To move to distant site, and make their own blood supply to spread use.
Body loses control and cancer takes control and continues to grow, takes nutrients. Once take all space and nutrients and break off and move to different part.
-Move through Intravasation to get into blood vessels/lymphatic. Cancer Hides in platelets or cells to not get caught (tumor cell embolus)
-Angiogenesis= cancer creates new blood vessels to take nutrients
-Extravasation= finds way into another spot and begins to grow more.
Tumor angiogenesis
Cancer cells need blood supply
Secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Biomarkers of Cancer Cells
Identify unique markers of cancer affecting patient- specific genes, protein, enzymes, growth factors, or other substances, images, biopsy, Usually multiple tests.
Used to assign treatments, monitor progress, evaluate prognosis. Serial measurements most important.
Identified from- Biopsy of cancer cells, blood, urine, stool, or other tissues or bodily fluids depending on cancer type.
Therapies= Biological, targeted, and immunotherapies work on cancers with specific biomarkers.
Testing known as: Tumor testing, tumor genetic testing, genomic testing or genomic profiling, molecular testing or molecular profiling, tumor subtyping, immunophenotyping, immunohistochemistry.
Neoplasia
“New growth”, tumor, Benign or Malignant
Benign vs Malignant (soap box)
Benign- cell expansion, number does NOT change. Stable cell number. Abnormal cells that remain localized, Don’t spread
Malignant- Change in cell number, more being made, Spread to other areas
Adenoma
Benign tumor, glandular tissue, or organ
Lipomas
Derived from fat cells, collection of fat, very common
Hemangioma
Collection of blood vessels skin or internal organ
Desmoid tumors
Can be highly invasive but do not metastasize
Nevi
Noncancerous moles on the skin
Myoma
Muscle tumor
Carcinoma
Malignant epithelial cells that line inner and outer surfaces.
Adenocarcinoma
Cancer of the glandular or ductal tissue
Sarcoma
Mesenchymal origin, such as connective tissue, cartilage, and bone, malignant
Osteoma
Benign tumor of bone.
Osteosarcoma is malignant
Chondroma
Benign tumor of cartilage
Chondrosarcoma is malignant
Leukemia
Cancerous changes in the leukocytes. Can’t do job and look different
Lymphoma
Cancerous lymphocytes in the lymphoid tissues.
Staging/classification of Benign tumors
Well-differentiated; remain localized, cohesive and well-demarcated from surrounding tissue. Typically don’t become malignant, usually in capsule.
Often are a change in cell size NOT number. Remove and should be gone.
Can cause injury- Does not spread but size number can effect other organs like brain _ tumor can cause seizures due to size- push on brain.