GERIATRICS MUSCOLOSKELETAL
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
• Changes reflect the aging process.
• A decline in muscle mass and a reduction in muscle strength leading to risk of fractures, frailty, reduction in the quality of life and loss of independence.
Bones
• consists of protein and the mineral (calcium and phosphorus).
Calcium
Bones
necessary for bone strength, muscle contraction, myocardial contraction, blood clotting, and neuronal activity.
Cardiovascular
Hormones
Bones
also play an important role in bone maintenance.
o Calcitonin
o Parathyroid hormone
o Insulin and thyroxine
o Estrogen and testosterone
Calcitonin
Hormones
hormone produced by the thyroid gland
helps to lower blood calcium levels
Parathyroid hormone
Hormones
a hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands
primarily regulates blood calcium and phosphate levels by acting on the bones, kidneys, and intestines
Insulin
Hormones
produced by the pancreas
helps regulate blood sugar (glucose)
thyroxine
Hormones
produced by the thyroid gland,
helps regulate metabolism, growth, development
controls how much energy your body uses (the metabolic rate).
Estrogen and testosterone
Hormones
essential sex hormones found in both males and females, though in different concentrations
Vertebrae
• The _____ supports the head and allows for flexible movement of the back.
• The spinal cord, the nerve tissue that extends downward from the brain, passes through the vertebral canal
Joints
are the places where bones meet
Cartilage
allows free movement of the joint surfaces
Bursa
Many of these joints contain a ____, which is a fluid sac that provides lubrication to enhance joint mobility
Tendons
are structures that connect the muscles to the bone
Ligaments
are structures that connect bones to other bones
Muscle strength
• is an important determinant of functional capacity in older people.
• Types of muscles:
o Cardiac - heart
o Smooth–hollow organs
o Skeletal - largest
Sarcopenia
EXPECTED AGE-RELATED CHANGES
increased risk of disability, falls, unstable gait
Decreased muscle mass, muscle strength & function.
osteoporosis
EXPECTED AGE-RELATED CHANGES
Decreased myosin adenosine triphosphatase activity
Excessive loss of calcium from bone combined with insufficient replacement.
It is characterized by porous, brittle, fragile bones that are susceptible to breakage.
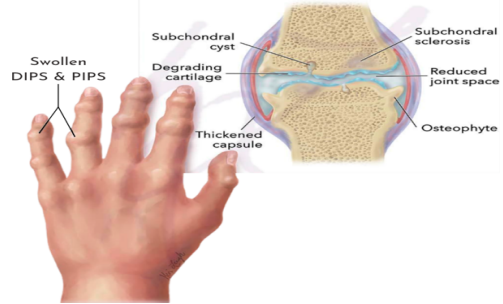
Osteoarthritis
EXPECTED AGE-RELATED CHANGES
Deterioration and drying of joint cartilage
Limited range of motion, joint instability
Most common form
Not a normal part of aging.
The cartilage within a joint begins to break down & the underlying bone begins to change.
OTHERS:
• Death of chondrocytes leads to degeneration of articular cartilage
• Loss of cartilage leads to eburnation of bone
• Affects weight bearing joints
• Asymmetric (may only affect 1 hand)
• Swelling of DIP and PIP joints DIP (Distal Interphalangeal) and PIP (Proximal Interphalangeal) are medical terms for two specific joints in each finger
• Synovial fluid enters bone fractures leading to subchondral cysts
• Osteophytes form at margins of cartilage
Muscle weakness/ muscle fatigue
EXPECTED AGE-RELATED CHANGES
Decreased bone mass and osteoblastic activity
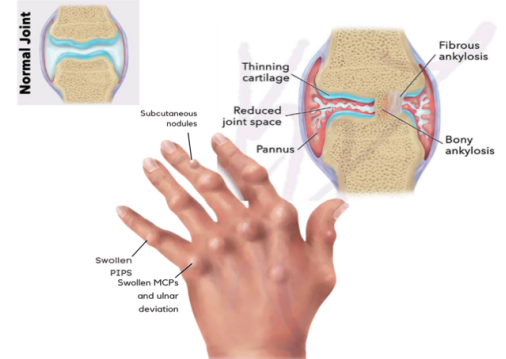
Rheumatoid Arthritis
is a collagen disease that results from an autoimmune process, affecting more women than men.
OTHERS:
• Proliferation and inflammation of synovium creates panni
• Pannus: finger-like projections that grow it joint space
• Affects hands and feet
• Symmetric (affects both hands)
• Ulnar deviation of MCP joints
• Swelling of MCP and PIP joints
• Subcutaneous nodules