Solids (20% on final)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Primitive characterisitics
1 atom in corners (8 corners x 1/8)
52.3% packing efficiency
SN = 6
a = 2r
BCC characteristics
2 atoms
1 in center
1 on corners (8 corners x 1/8)
68% packing efficiency
SN = 8
a = (4/√3)r
atom in center makes layers NOT slide easily
FCC characteristics
4 atoms
1 on corners (8 corners x 1/8)
3 on faces (6 faces x 1/2)
74% packing efficiency
high packing efficiency allows layers to slide easily
SN = 12
a = (4/√2)r
# of tetrahedral sites in FCC and where
8
all in the center
# of octahedral sites in FCC and where
4
3 on edges (12 edges x 1/4)
1 in the center
occtant
where cations that form the interstitial alloy
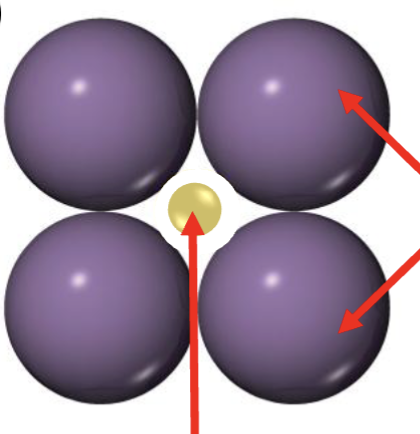
Is this stable? why or why not?
Unstable
Cation is too small to have strong attraction w/ anions
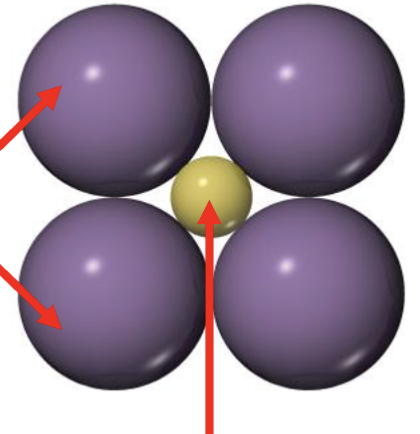
Is this stable? why or why not?
Stable
Cation fits perfectly
Maximizes cation-anion bonds
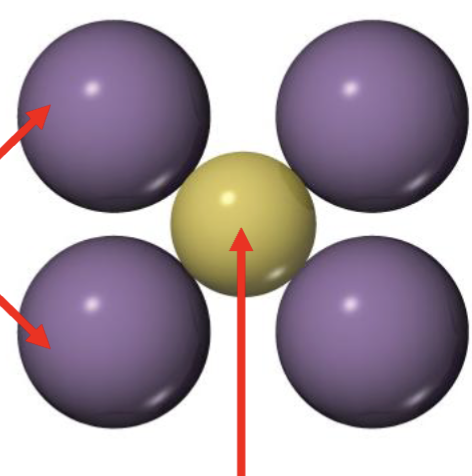
Is this stable? why or why not?
Stable
Cation is kinda big
weak anion-cation attraction
draw ideal cation fit
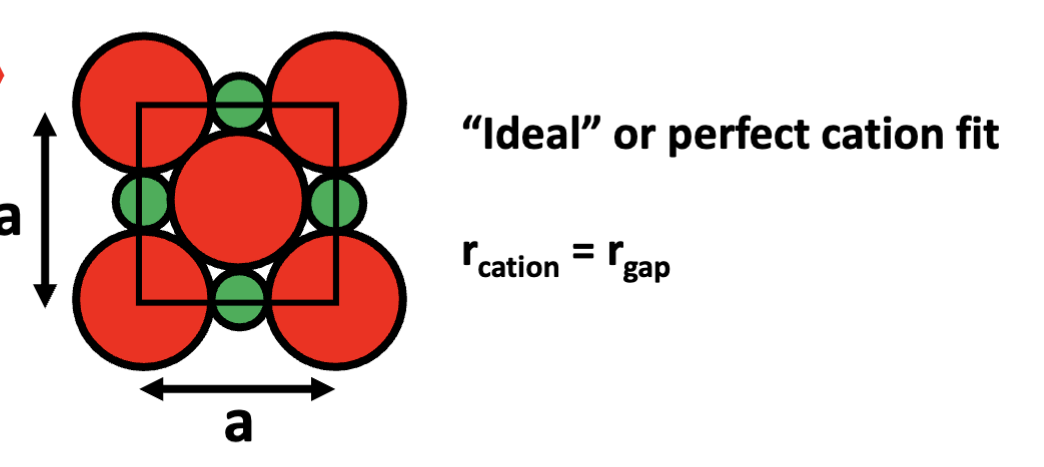
Antifluorite characteristics
radius ratio: 0.225 < r < 0.414
Tetrahedral sites (8)
SN = 4
FCC array
Cation:anion unit cell ratio = 8:4
a = 4/√3 (rx + ry)
Rock salt characteristics
radius ratio: 0.414 < r > 0.73
Octahedral sites (4)
SN = 6
FCC array
Cation:anion unit cell ratio = 4:4
a = 2rx + 2ry
CsCl crystal characteristics
radius ratio: r > 0.73
Cubic sites
SN = 8
BCC array
Cation:anion unit cell ratio = 1:1
a = (2rx + 2ry) / √3
Zinc blende
radius ratio: 0.225 < r < 0.414
Tetrahedral sites (4)
50% of tetrahedral filling due
to stoichiometry
SN = 4
FCC array
Cation:anion unit cell ratio = 4:4
a = 4/√3 (rx + ry)
radius ratio
rcation / ranion
minimum size required to occupy a gap
interstitial alloy
guest metal (super small) wedges between host metal
intermetallic alloy
when metals with strong covalent bonds form a cystalline structure
substitutional alloy
random composition; guest metal replaces some of the host metal; similar radii