Host Resistance & Immunity
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Innate (nonspecific)
Host defenses that include first line of defense & second line of defense
body’s natural, inborn defense system provides protection against wide range of foreign invaders
Acquired (specific)
Host defenses, third line of defense
immunity develops over time in response to exposure
first line of defense
surface protection composed of anatomical & physiological barriers that keep microbes from penetrating sterile body compartments
Ex: physical barriers, chemical barriers, genetic components
second line of defense
cellular & chemical system that comes immediately into play if infectious agents make it past surface defenses
Ex: phagocytosis, inflammation, fever, antimicrobial proteins
third line of defense
includes specific host defenses that must be developed uniquely for each microbe through the action of specialized white blood cells
include active infection & passive maternal antibodies
B cells, T cells, & their effects
hematopoesis
development of white blood cells in bone marrow
macrophages & dendritic cells
What are the innate leukocytes?
basophils
release histamine which causes inflammation
nuclei with two to five lobes
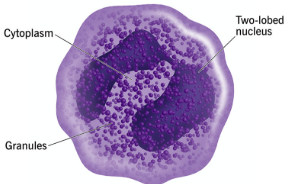
eosinophils
defend against protozoan & helminths parasites
nuclei with two to five lobes
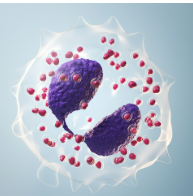
neutrophils
highly phagocytic & kill ingested microbes with lytic enzymes
nuclei with two to five lobes
B & T cells
WBCs that aren’t yet activated after leaving bone marrow become part of the adaptive immune response
Megakaryocyte
Hematopoietic stem cell > Common Myeloid Progenitor > Megakaryoblast > _____ > platelets
platelets involved in blood clotting & inflammation
mast cells
specialized tissue cells similar to basophils that trigger local inflammatory reactions & are responsible for many allergic symptoms
Hematopoietic stem cell > common myeloid progenitor > putative mast cell precursor > ___ ___
Granulocytes
Include eosinophils, basophils, & neutrophils
Hematopoietic stem cell > common myeloid progenitor > myeloblast
monocyte
blood phagocytes that rapidly leave the circulation; mature into macrophages & dendritic cells: common myeloid progenitor > monoblast > ____
macrophages - largest phagocyte ingest & kill foreign cells; strategic participants in certain specific immune reactions
dendritic cell - reside throughout tissue, processing foreign matter & presenting it to lymphocytes
Agranulocytes
No granules in cytoplasm includes:
monocytes, T cells, & B cells
T cells
perform number of specific cellular immune responses, assist B cells & kills foreign cells (cell-mediated immunity)
Hematopoietic stem cell > common lymphoid progenitor > lymphoblasts
B cells
differentiate into plasma cells & form antibodies (humoral immunity)
Hematopoietic stem cell > common lymphoid progenitor > lymphoblasts
Skin
Strong mechanical barrier, keratin
Inhospitable environment
shedding skin
pH acidic
high NaCl concentration
subject to periodic drying
mucous membranes
Form protective covering that resists penetration & traps microbes in various antimicrobial substances
Lysozyme - hydrolyzes bond connecting sugars in peptidoglycan
eye: mucous, flushing of tears, lysozyme, & secretory IgA in tears
lysozyme
hydrolyzes bond connecting sugars in peptidoglycan
Mucociliary blanket
Mucous secretions traps microbes, these microbes are transported from the lungs via mucociliary escalatory
expelled by coughing/ sneezing
salivation washes microbes to stomach
alveolar macrophages
phagocytic cells in alveoli of lungs
IgA & defensins
In the gastrointestinal tract, plasma cells secrete what two products:
Paneth cells
Cells found in the gastrointestinal tract that produces lysozyme & cryptins
low, lactobacilli, urea
Genitourinary tract unfavorable environment:
____ pH of urine & vagina
vagina has _______
_____ & other toxic metabolic end products in urine
Cationic peptides
Antimicrobial peptides divided into three classes, has the ability to damage bacterial cell membranes
first class
Cationic peptide: linear, alpha-helical peptides that lack cysteine amino acid residues
Ex: cathelicidin, produced by a variety of cells
cathelicidin
A first class cationic peptide produced by a variety of cells
second class
Defensins
cationic peptide
found inn neutrophils, intestinal Paneth cells, respiratory epithelial cells
third class
Cationic peptide: larger peptides
Ex: histatin, present in human saliva & has anti-fungal activity
Histatin
A third class cationic peptide:
present in human saliva & has anti-fungal activity
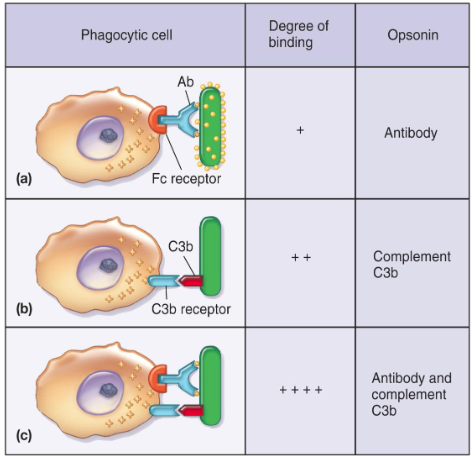
Opsonization
Process in which microbes are coated by serum components (opsonin) in preparation for recognition/ ingestion by phagocytic cells
some complement proteins are opsonins
complement activation
Proteins working in cascade pathways to eliminate pathogen
must be activated in cascade fashion
3 pathways: alternative, lectin, classical
cytokines
soluble proteins or glycoproteins released by one cell population that act as intercellular mediators or signaling molecules
3 groups based on function:
regulators in innate resistance mechanisms
regulators of adaptive immunity
stimulators of hematopoiesis
monokines
cytokines that are released from mononuclear phagocytes
lymphokines
cytokines released from T lymphocytes
interleukins
cytokins released from one leukocyte & act on another leukocyte
Colony stimulating factors (CSFs)
stimulate growth & differentiation of immature leukocytes in bone marrow
type of cytokine
Antibodies
Immunoglobulins, glycoprotein made by activated B cells (plasma cells)
serves as antigen receptor on B cell surface
Classes: IgG1, IgM, IgA2, IgD, IgE
IgM
first Ig in all immune responses
agglutination, activates complement
expressed as membrane-bound antibody on B cells
IgA
an Ig: secreted across mucosal surfaces
Tears, saliva, breast milk
IgG
involved in opsonization, neutralization of toxins
only Ig that can cross placenta
IgD
Ig that’s part of the B cell receptor complex
signals B cells to start antibody production
precipitation, opsonization, neutralization, complement fixation, agglutination
What are consequences of antigen-antibody binding? (5)
precipitation
Consequence of antigen antibody binding: cell-free molecule in solution
neutralization
Consequence of antigen antibody binding: antibodies block binding
complement fixation
Consequence of antigen antibody binding: lysing bacterial cells
agglutination
Consequence of antigen antibody binding: cross linked bacterial cell antigen
antigen
Recognized as foreign & invoke immune response (B cell activation > production of antibodies)
name comes from antibody generators
self & nonself that elicit immune response
large, complex molecules
antigenic determinant sites (epitopes)
site on antigen that reacts w/t specific antibody or T cell receptor
valence is number of epitopes on an antigen
Identification of self & foreign, diversity, specificity, memory
What are characteristics & types of specific immunity? (4)
humoral immunity
antibody mediate immunity
based on antibody activity
cellular immunity
cell-mediated immunity
based on action of specific kinds of T lymphocytes
Acquired immunity
a type of immunity that develops over time as a result of exposure to pathogens or vaccines
divided into natural vs artificial, both are further subdivided into active & passive
natural immunity
Acquired immunity through normal life experiences & not induced by medical means
active: conseq of person developing own immune response to microbe (infection)
passive: one person receiving preformed immunity made by another (maternal antibody)
artificial immunity
acquired immunity via medical procedures (immunization)
active: consequence of person developing their immune response (vaccination)
passive: consequence of one receiving performed immunity made by another (immune globulin therapy)