CVM - Lecture 1: Mediastina, Lymph and Nerve Supply
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
- right common carotid artery
- right subclavian artery
What arises from the brachiocephalic trunk?
the parietal pleura
What makes up the lateral borders of the middle mediastinum?
sup: 2nd rib
inf: 5th intercostal space
At what level are the superior and inferior borders of the heart?
Fibrous pericardium
parietal (serous) pericardium
visceral (serous) pericardium
What are the layers of the pericardium from superficial to deep?
The visceral pericardium
Which layer does the epicardium refer to?
The musclular middle layer of the heart wall
What is the myocardium?
The epithelial inner lining of the heart, continuous with the endothelium
What is the endocardium?
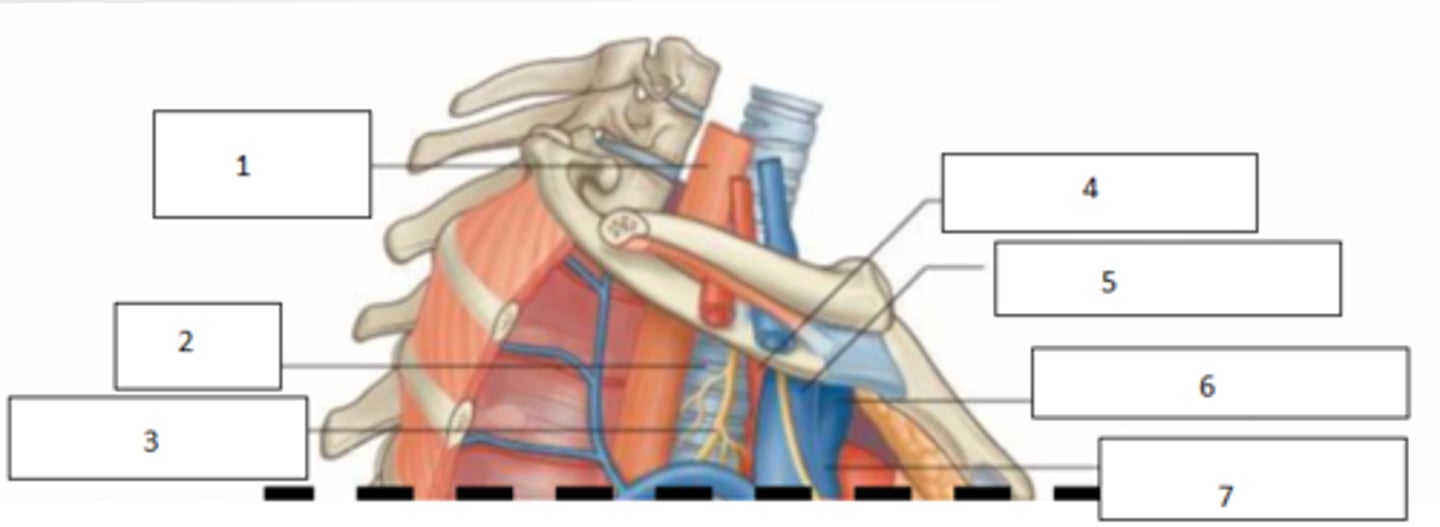
1. Left common carotid A.
2. SVC
3. phrenic nerve
4. pericardiophrenic vessels
5. diaphragm
Fill the blanks
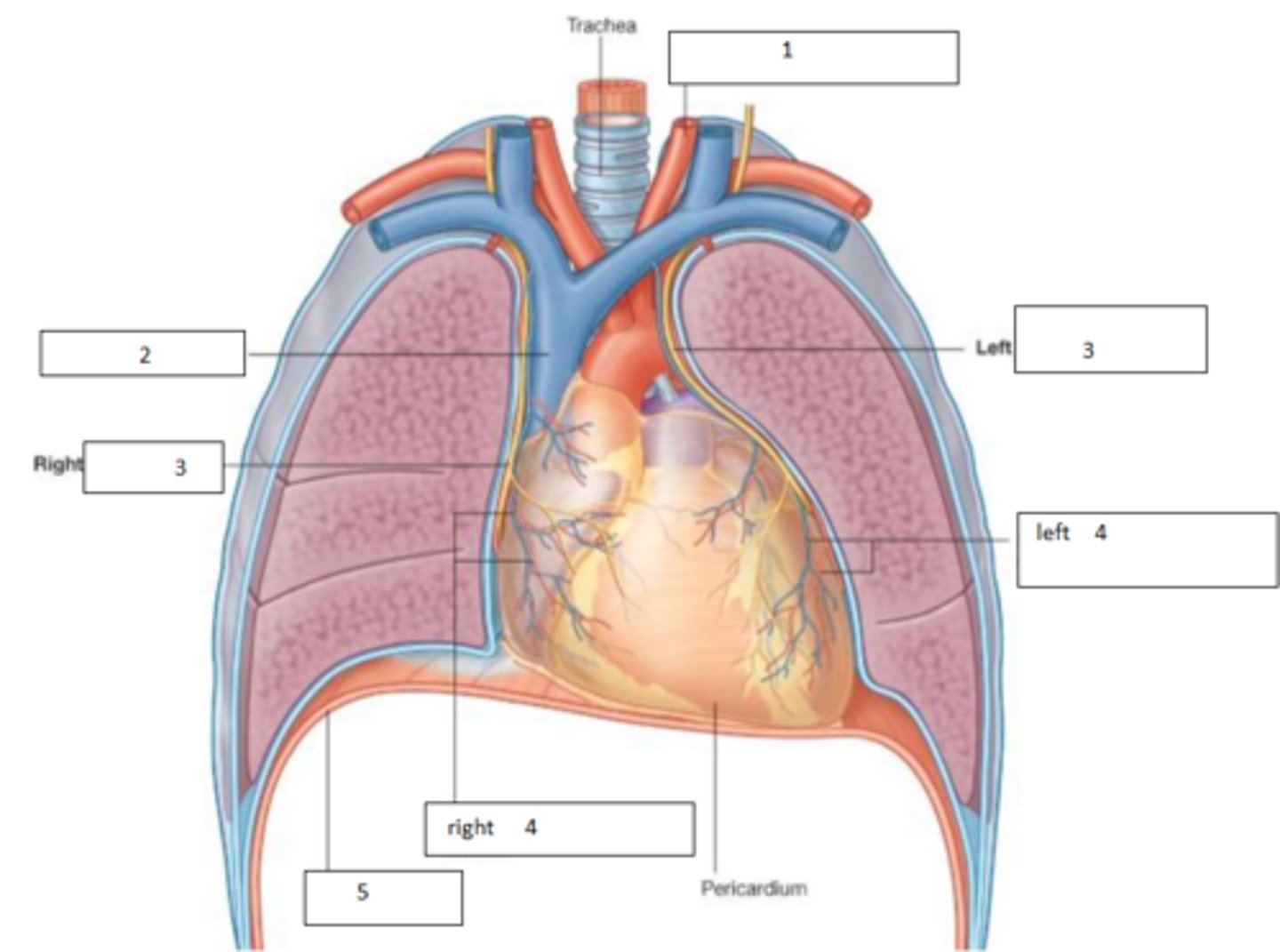
Superior Vena Cava +Inferior Vena Cava -> Right atrium -> Right ventricle -> Pulmonary arteries -> Capillary bed of lungs -> Pulmonary veins -> Left atrium -> Left ventricle -> Aorta+branches
List the order of the cardiac circuit from the greatest vein to the greatest artery
1. aortic arch
2. SVC
3. fossa ovalis
4. IVC
5. Valve of IVC
6. Valve of corona sinus
7. aperture of coronary sinus
8. auricle
9. limbus of fossa ovalis
10. crista terminalis
11. pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati)
Fill the blanks
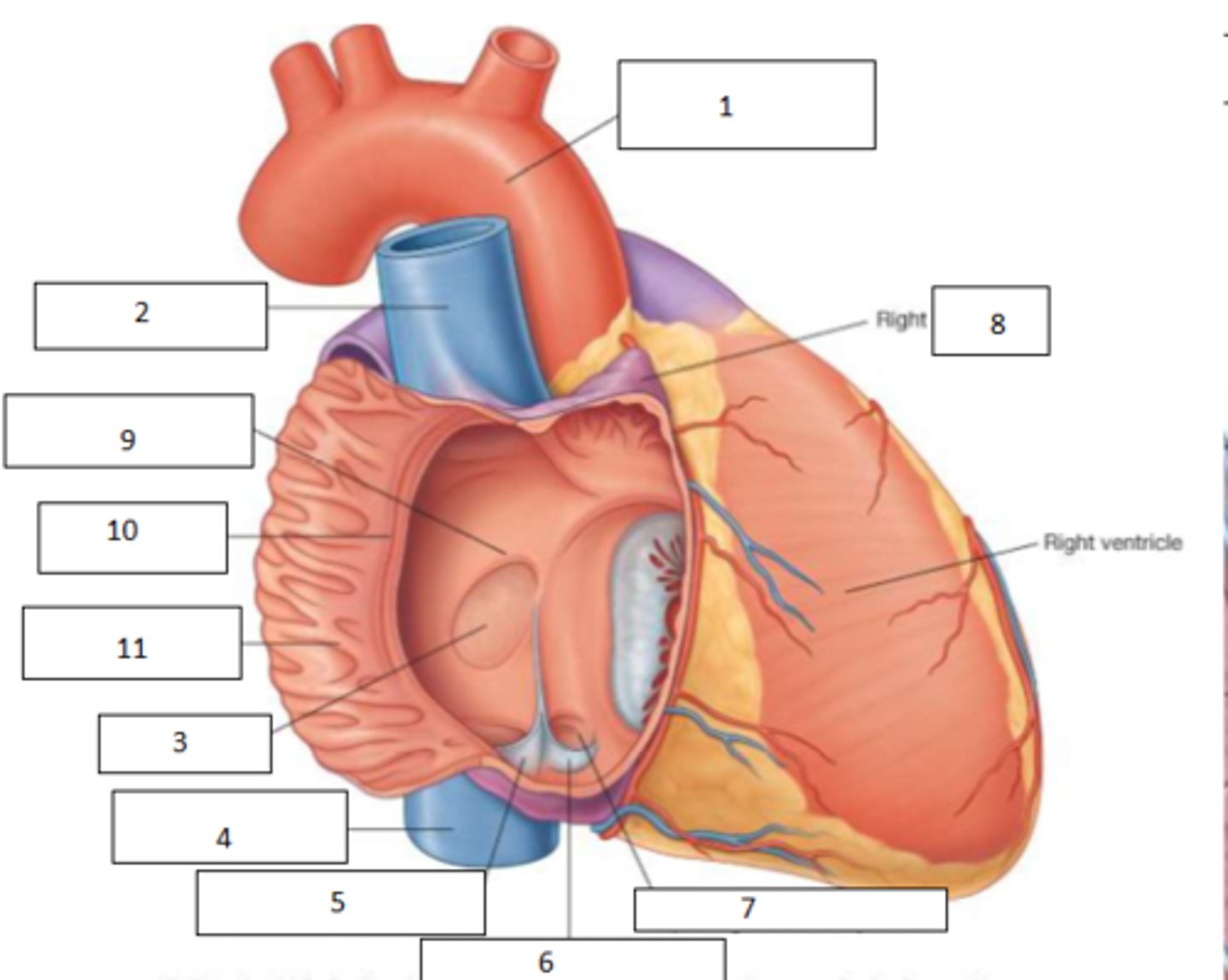
This was previously the foramen ovalis - an embryonic shunt between the two atria to bypass pulmonary circuit
What is the role of the fossa ovalis?
the tricuspid valve
What separates the RA and the RV
- cusps: anterior, septal, posterior
- chordae tendinae
- papillary muscles
- septomarginal trabecula
What makes up the tricuspid valve?
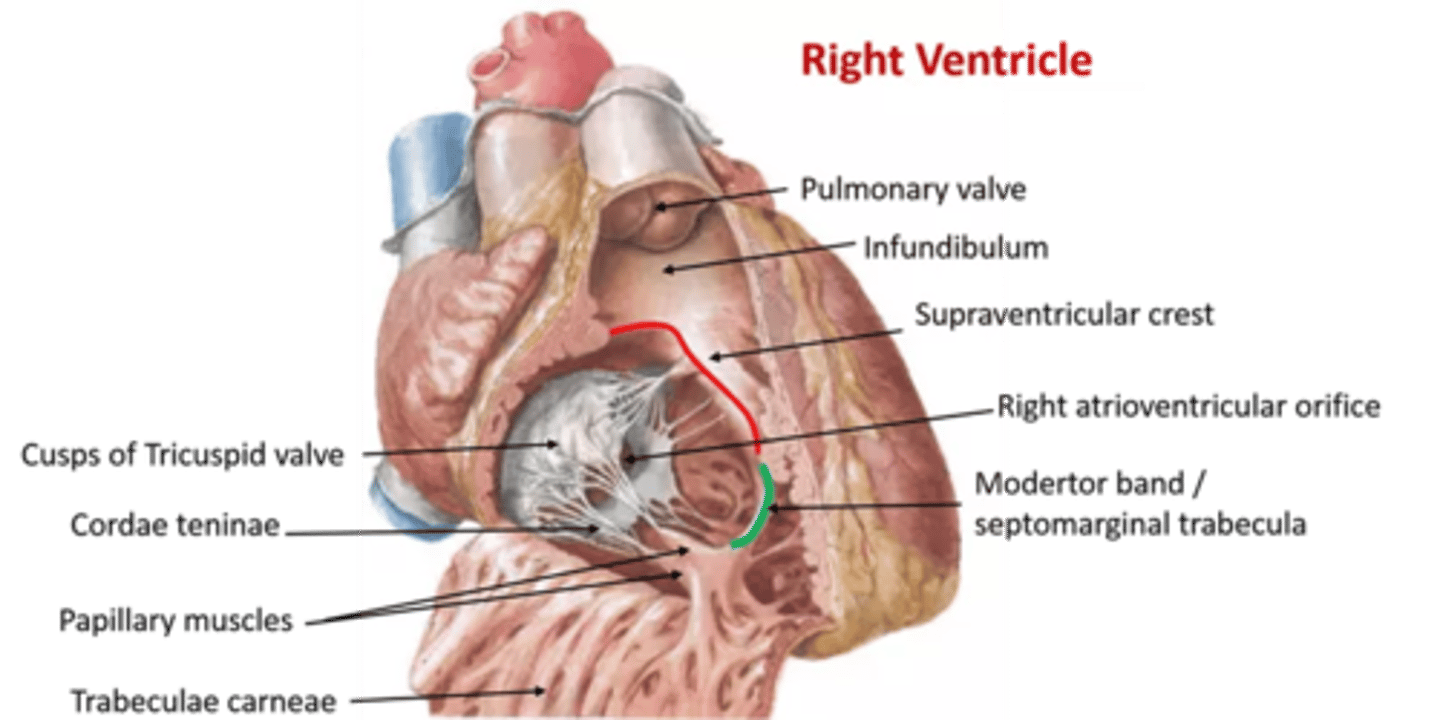
These are the muscles of the ventricular wall
What is the function of the trabeculae carnae?
Pulmonary valve: anterior+right+left semilunar cusps
What separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk?
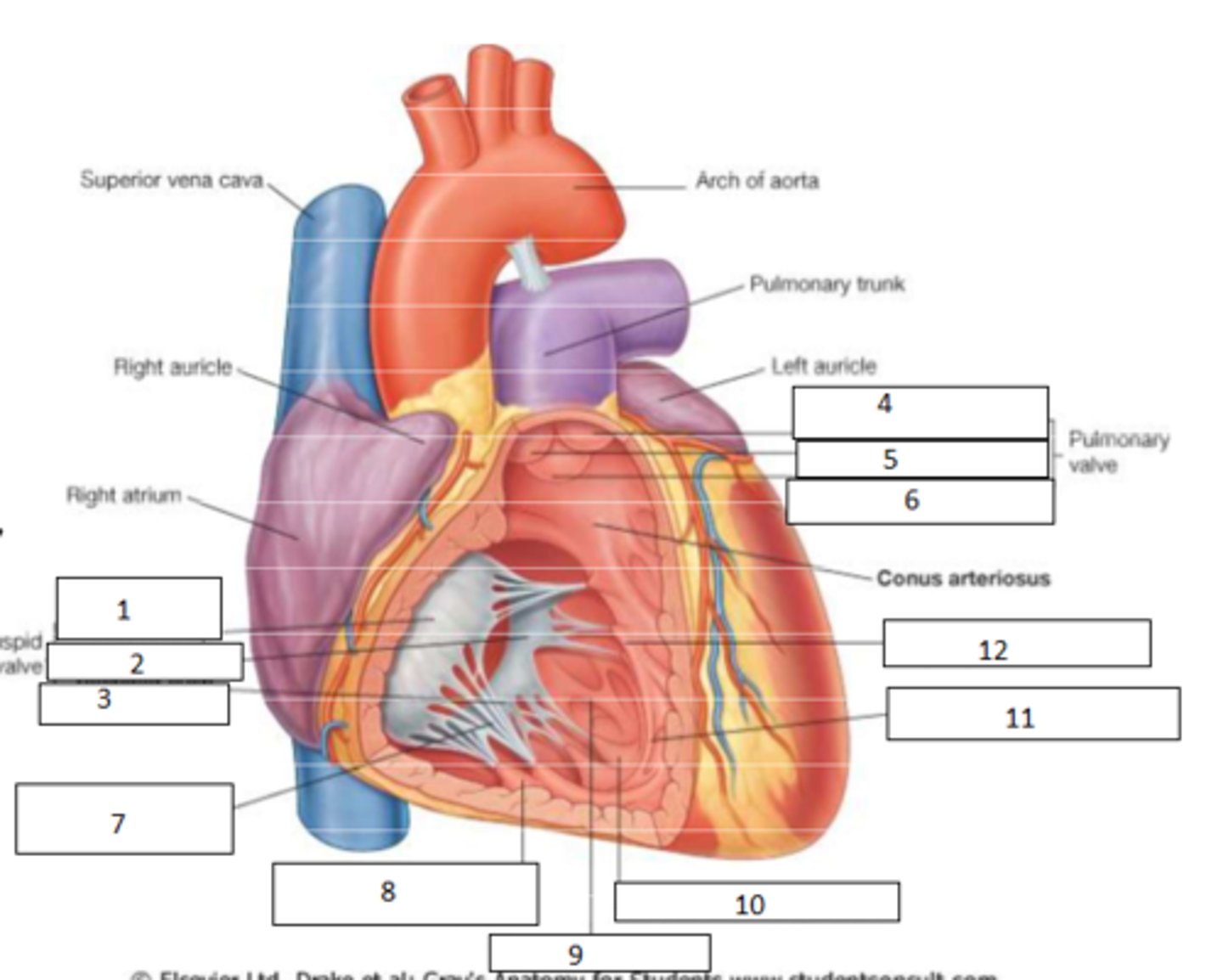
1. anterior cusp
2. septal cusp
3. posterior cusp
4. anterior semilunar cusp
5. right semilunar cusp
6. left semilunar cusp
7. chordae tendineae
8. anterior papillary muscle
9. trabeculae carneae
10. posterior papillary muscle
11. septomarginal trabecula
12. septal papillary muscle
Fill the blanks
1. pulmonary arteries
2. pulmonary veins
3. valve of foramen ovale
4. bicuspid (aka mitral) valve
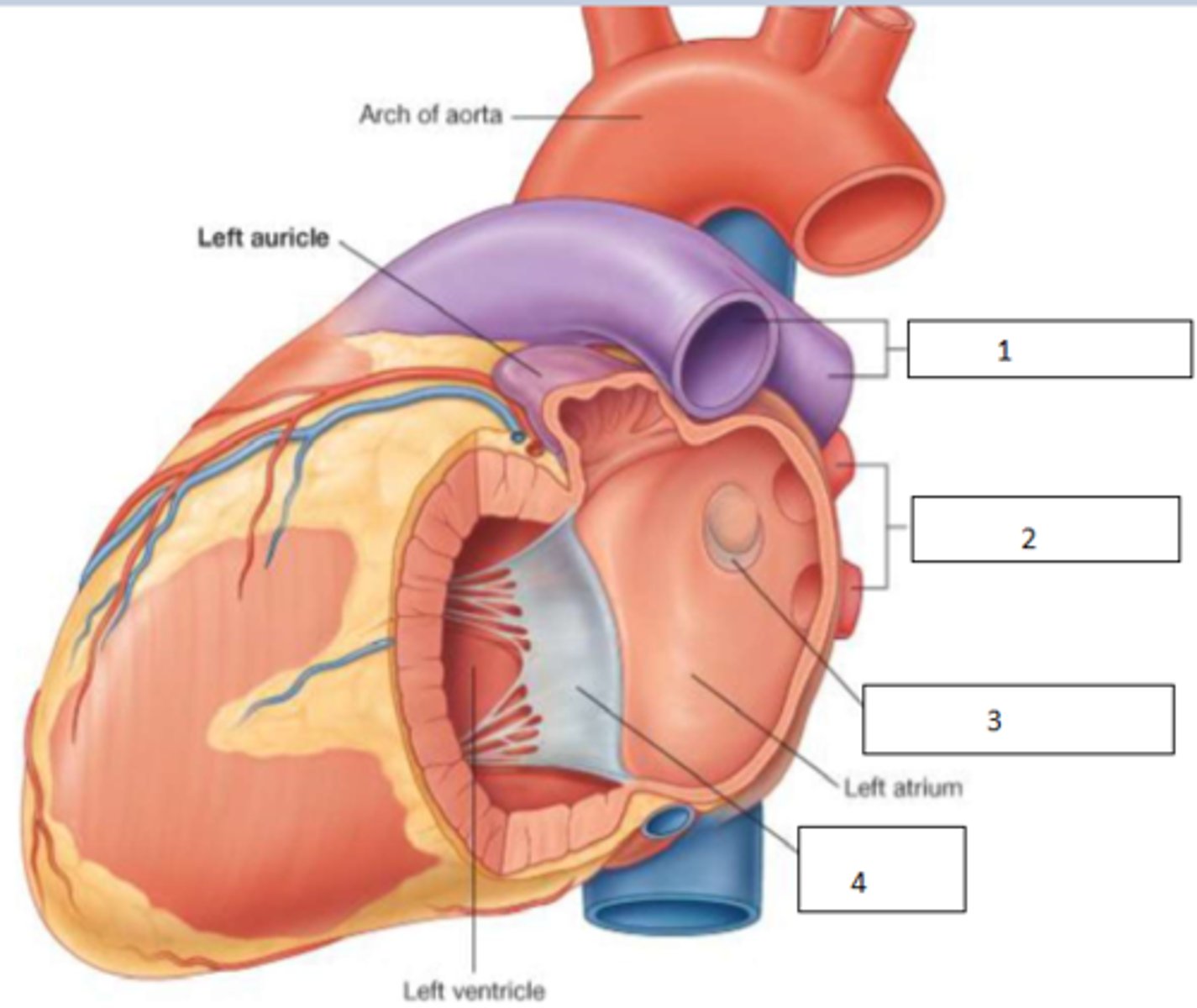
4
How many pulmonary veins are there?
- anterior cusp
- posterior cusp
Name the cusps of the mitral valve
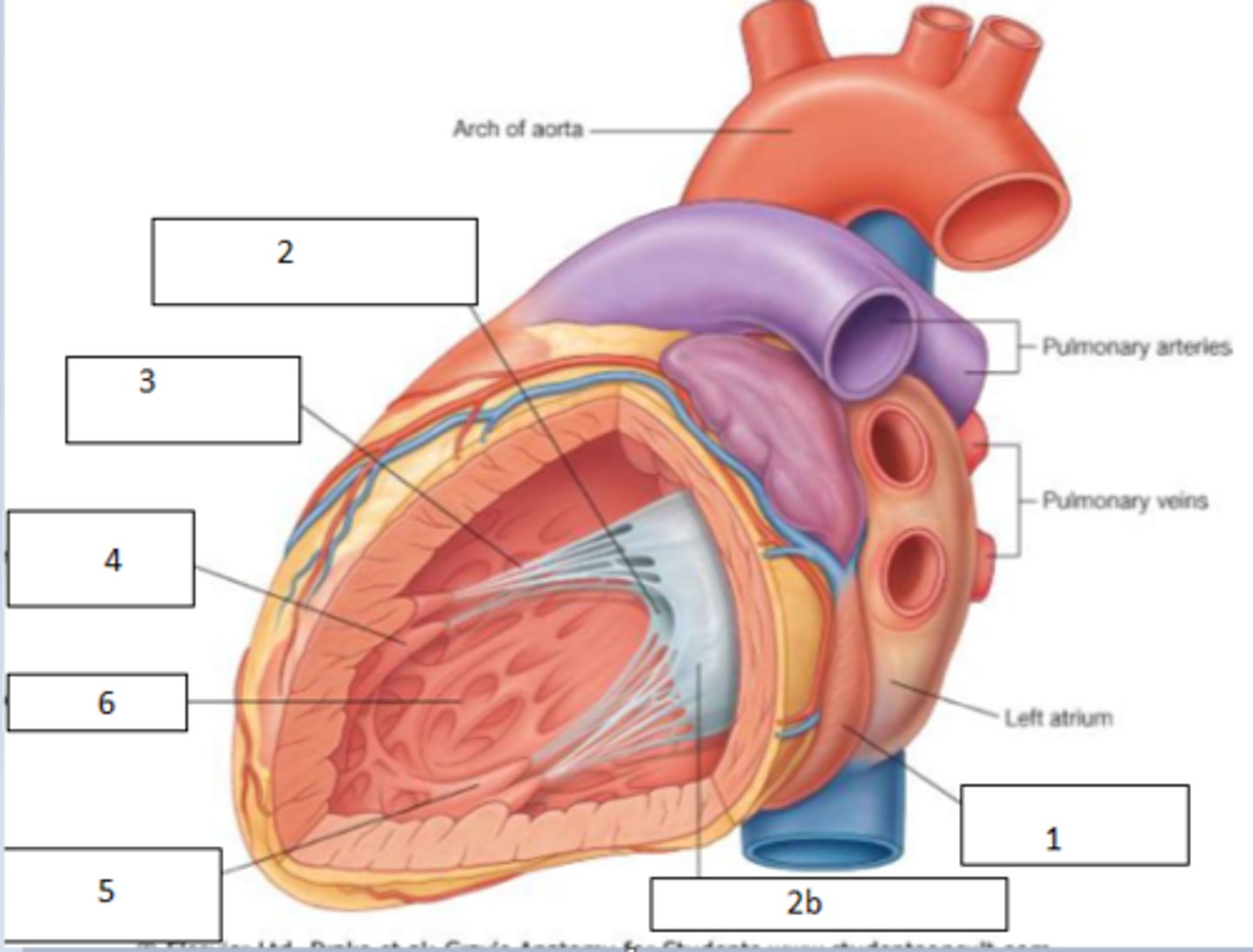
1. coronary sinus
2. anterior cusp
2b. posterior cusp
3. cordae tendinae
4. anterior papillary muscles
5. posterior paipllay muscles
6. trabeculae carnae
Fill the blanks
The aortic (semilunar) valve
What separates the left ventricle from the aorta?
- left seminlunar valve
- right semilunar valve
- posterior aortic valve
What are the cusps of the aortic valve?
active: atrioventricular valves
passive: semilunar valves
Which are the active and passive valves of the heart respectively?
- a septum separates the right and left sides physically and electrically
- 4 connective tissue rings support the valves
Describe the major fibrous structures that allow the heart to function
1. atria contract (late diastole)
2. ventricles relax and fill
3. AV valves open with papillary muscles
4. semilunar valves are shut
In diastoli, describe the activity of the: 1. atria 2. ventricles 3. AV valves 4. semilunar valves
1. atria are relaxed and fill
2. ventricles contract
3. AV valves are shut
4. Semilunar valves are forced open
In systoli, describe the activity of the: 1. atria 2. ventricles 3. AV valves 4. semilunar valves
- Sinoatrial (SA) node
- Base of SVC
Name the local electrical supply of the atria
- Atrioventricular (AV) node
- interatrial septum above tricuspid valve
- leads to AV bundle (aka bundle of His) and then branches
Describe the local nervous supply of the ventricles
ant: sternal angle (aka manubrio-sternal joint)
post: intervertebral disc between T4+T5
Name the anterior and posterior border of the Plane of Louis
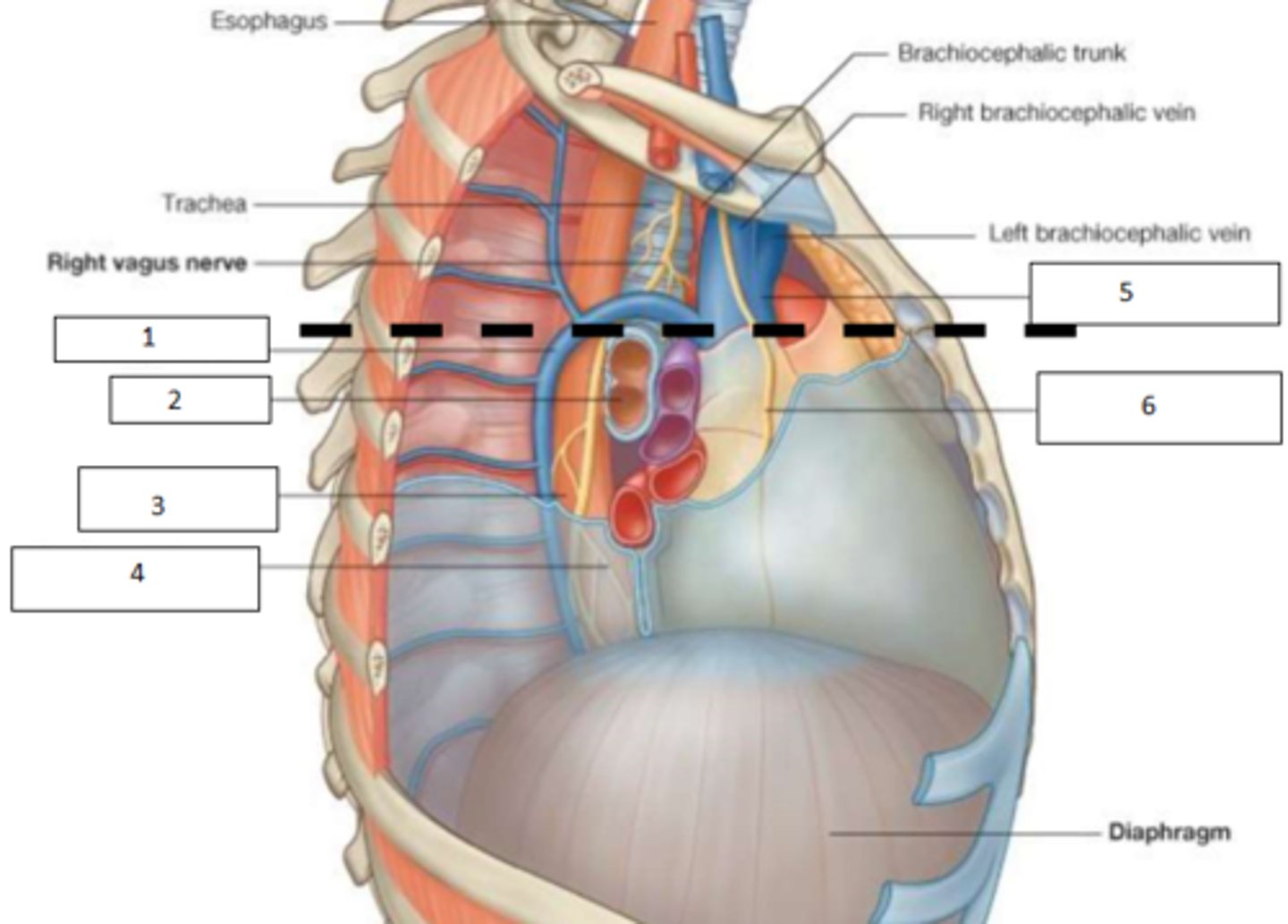
1. Oesophagus
2. Trachea
3. Vagus N.
4. Brachiocephalic trunk (aka artery)
5. Right brachiocephalic vein
6. Left brachiocephalic vein
7. Superior Vena Cava (SVC)
Fill the blanks
- Thymus
- Brachiocephalic veins (r+l)
- SVC
- Arch of Aorta: Brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid, left subclavian
- Internal thoracic vessels
- Phrenic + vagus N.
- Cardiac plexus of nerves
- Recurrent laryngeal nerves
- Trachea
- Oesophagus
- Thoracic duct (lymph)
Main contents of the superior mediastinum
- Loose CT
- Fat
- Thymus
- Lymphatics
- Sterno-pericardial ligaments
- Internal thoracic vessels
What are the main contents of the anterior mediastinum?
- Phrenic nerves
- pericardium
- heart
- cardiac plexus
- ascending aorta
- SVC
- IVC
- pulmonary trunk
- pulmonary veins
What are the main contents of the middle mediastinum?
- thoracic duct (main lymph vessel)
- azygous system of veins
- descending aorta
- oesophagus
- oesophageal plexus
- sympathetic trunk
What are the main contents of the posterior mediastinum?
Passage of thoracic duct from right to left behind oesophagus
Angle of Louis
Tracheal bifurcation
End of azygous veins into SVC
Ligamentum arteriosum
Loop of left recurrent laryngeal nerve around aortic arch
Aortic arch starts and ends
List the main features or occurrences of the plane of louis (PATELLA)
1. Azygous vein
2. Bronchus
3. Oesophagus
4. Oesophageal plexus
5. SVC
6. Right phrenic nerve
Fill the blanks
1. Left coronary artery
2. circumflex artery (branch)
3. Left anterior descending (aka left anterior intraventricular) artery
Fill the blanks
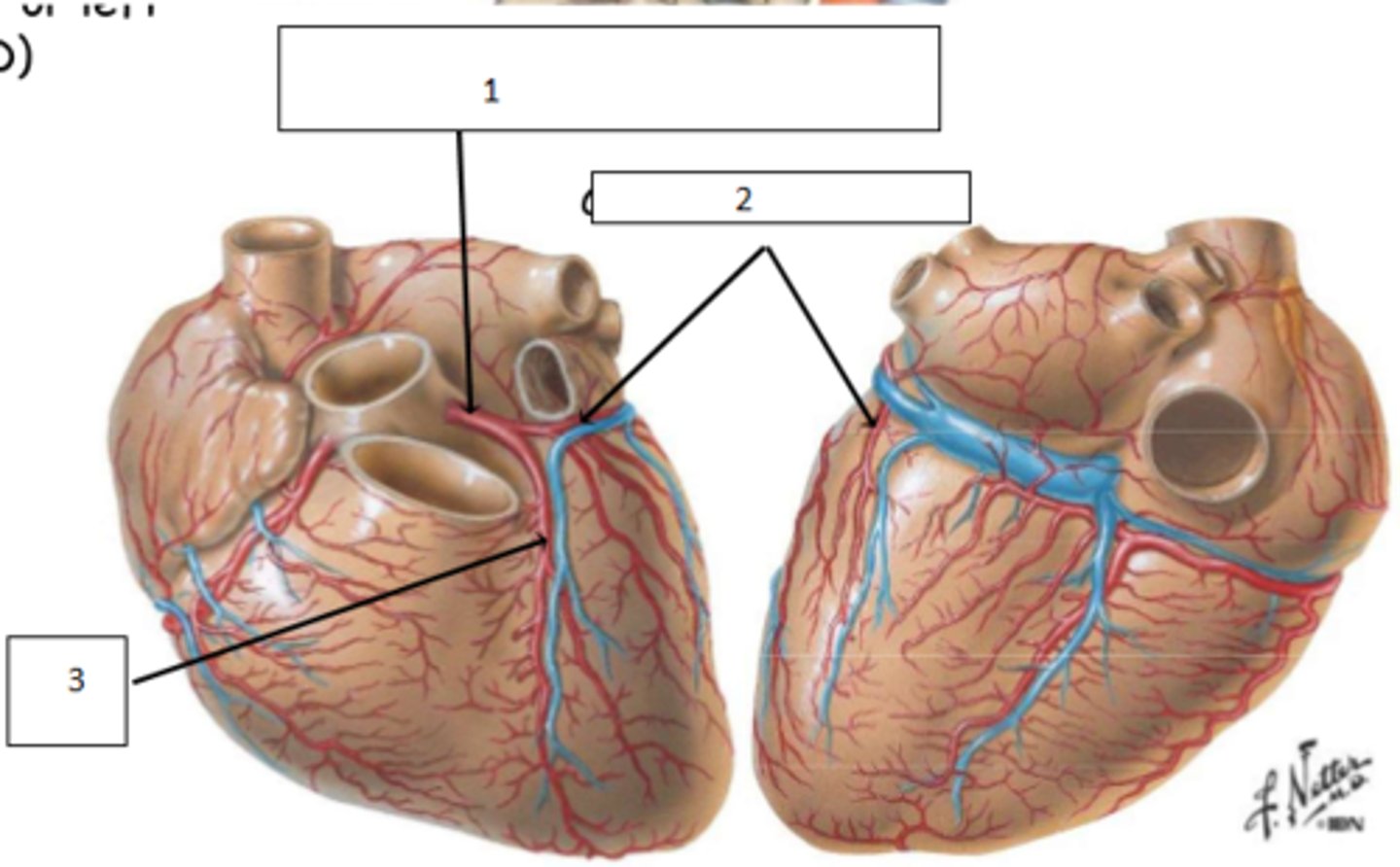
1. right coronary artery
2. posterior intraventricular artery
3. right marginal artery
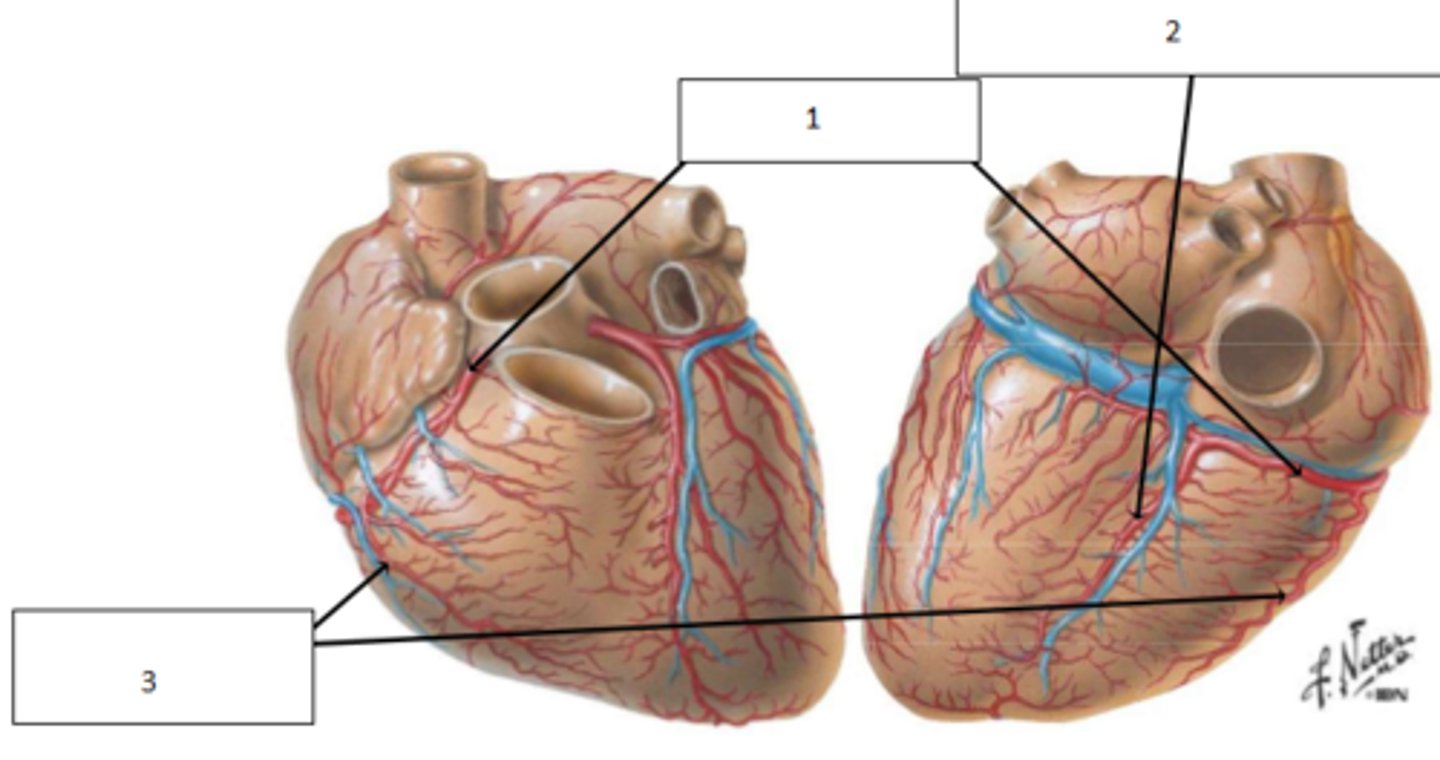
1. middle cardiac vein
2. great cardiac vein
3. small cardiac vein
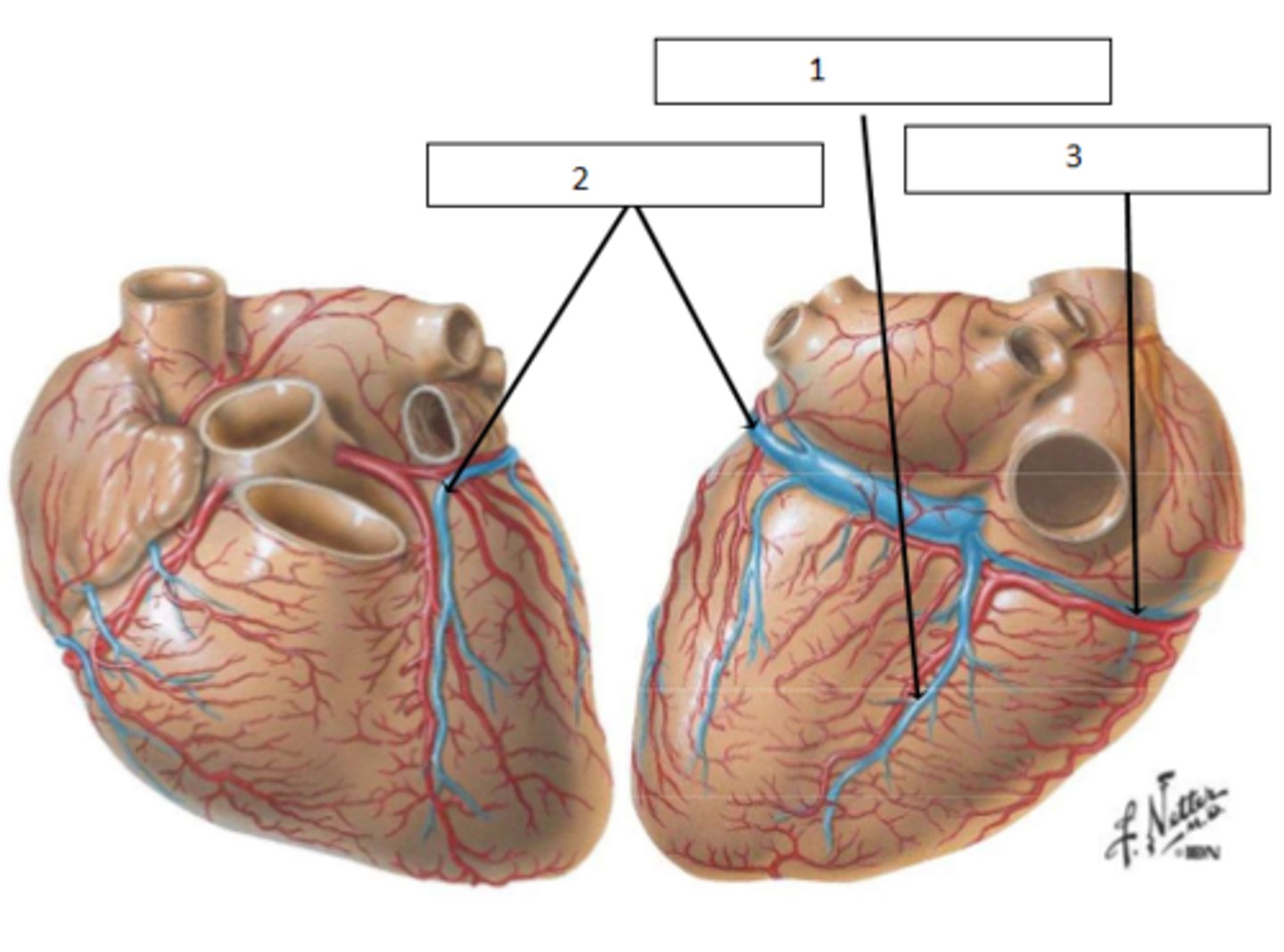
Right atrium
where does the coronary sinus drain into_
- from vagus nerve
What supplies the parasympathetic input of the heart?
- T1-T5 via sympathetic chain
What supplies the sympathetic input of the heart?
- brachiocephalic node
- tracheobronchial node
To which nodes does lymph of the heart drain?
left brachiocephalic vein
To which vein does the lymph of the heart drain?
The atria are thinner than the ventricles and the left ventricle is thicker than the right
comment on the thickness of atrial and ventricular muscle
- tunica externa/adventitia: connective tissue + elastic fibres. Blends with tissue and stabilises
- tunica media: smooth muscles + elastic fibres
- tunica intima: connective tissue+ single cell layer endothelium (SSE tissue)
Describe the 3 layers of the blood vessels