biology chapter 21 manipulating genomes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
introns - non coding DNA
exons - coding DNA
what are introns and exons?
short DNA sequences repeated many times
satellite DNA?
minisatellite: 20-50 base pairs repeated 50-100
microsatellite: 2-4 base pairs repeat 5-15 times
Different people have different numbers of repeats so different satellite patterns which is the basis of DNA profiling
minisatellite and microsatellite definition?
put DNA fragment through PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
restriction endonucleases are used to cut into small fragments at restriction sites
put onto gel and do gel electrophoresis. DNA are attracted to the positive charge and large strands move further
add a radioactive or flourescent dye to see evidence
how to produce a DNA profile?
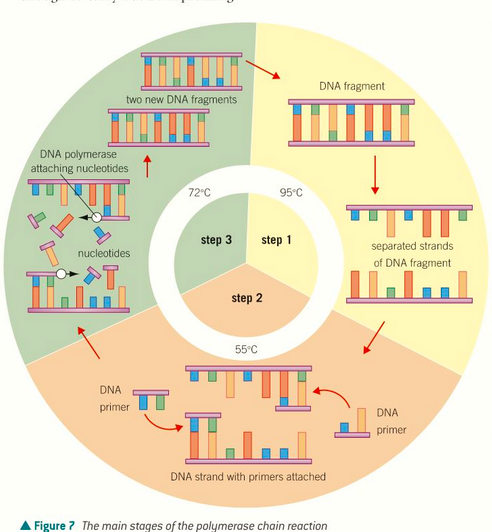
denaturation: 95 degrees to break hydrogen bonds in DNA
Annealing of primers at 55 degrees. They bind to the end of the DNA strands
At 72 degrees, synthesis of a new DNA strand with free nucleotides occurs. Done by TAQ polymerase (obtained from thermophilic bacteria in hot springs)
steps for PCR
crime scene DNA and forensics
paternity tests
analysis of risk of diseases
evolutionary relationships between species
classification/species identification
uses of DNA profiling
developed by Sanger and paved the way towards new developments
Needs a DNA sample, free nucleotides, coloured terminator bases, DNA polymerase and primer to start process
what is needed for sequencing DNA?
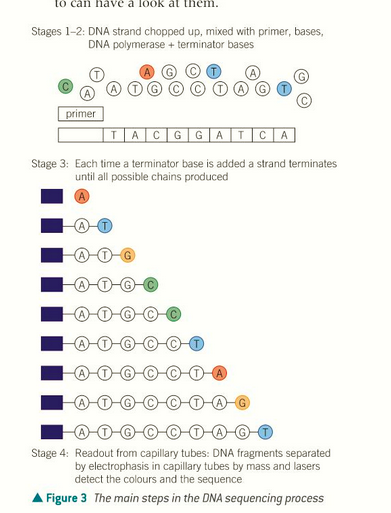
heat up to 95 to denature and break hydrogen bonds
cool to 50 and the primers will anneal
heat up to 60 and DNA polymerase starts adding free nucleotides bases
a terminator base is added and since they are missing an oxygen, they can’t form phosphodiester bonds and will stop base addition. This creates a variety of lengths of DNA.
After gel electrophoresis, direct UV light at nylon to see the lengths.
Can also do capillary sequencing and read with a laser to construct the genome
how to do DNA sequencing
fragments of DNA attached to the slide called a flow cell and replicated using PCR to form clusters
all clusters sequenced at the same time so it is cheaper and faster
Next generation sequencing/ high throughput sequencing
software needed to organise and analyse raw biological data
What is bioinformatics?
uses data from bioinformatics to build theoretical models of biological systems
what is computational biology?
analysing the genomes of pathogens to find the source of infections and the medicine needed to fight it
Identifying species with DNA barcoding
allowed us to find the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide to be predicted
How is DNA sequencing used?
design and construction of new artificial biological pathways
genetic engineering, making new genes to replace faulty ones, synthesis of whole new organisms, use of biology industrial contexts
what is synthetic biology and some techniques?
human cell DNA is extracted out and plasmid is removed from bacteria using endonucleases or reverse transcriptase
restriction endonucleases are used to cut out desired gene and same enzyme used to cut plasmid which leaves same sticky ends. DNA ligase forms bonds between gene and plasmid. This is called a recombinant plasmid.
Recombinant plasmid put into bacteria now called transgenic bacterium.
Put onto agar plate to culture it.
Genetic engineering method
they have a marker gene which is a gene that has been engineered into the plasmid and enables the scientists to see which bacteria have taken the plasmid.
Why are specific plasmids or vectors used in genetic engineering?
to show that the plasmid has the recombinant gene
if inserted successfully, marker gene will not function like the flourescence gene
what is the second marker gene used for?
culture in Ca2+ solution and heat shock which causes membrane to become permeable
electroporation to create pores with electricity
Electrofusion to fuse cells and create a polyploid cell with DNA from two cells fused
how is the plasmid with recombinant DNA put into the host cell?
mutant allele is replaced with healthy allele in somatic cells (body)
temporary solution and disease can still be passed onto offspring
what is somatic cell gene therapy?
insert healthy allele in eggs or embryo cells after fertilisation
healthy allele would be passed onto offspring
done on animals but not humans as it is done to embryos without consent
what is germ line cell gene therapy?
people were initially uncomforatble with using human genes in microorganisms but the human medicines they make are very useful.
ethical concerns of using GM bacteria?
benefits:
reduce pesticides used
increased yield
disease resistant
risks:
non pest insects might be damaged by toxins in GM plants made for pests
transferred genes for disease resistance may spread to the wild populations
biodiversity reduced when herbicides used to kill weeds
benefits and risks of GM crops?
swine fever-resistant pigs
Faster-growing salmon
Pharming:
creating animal models so animals develop certain diseases to be tested on
creating human proteons
ethical issues as they cannot give consent and could cause them harm>
how have animals been GM’d?
ethical issues?