CHP 7 The Axial Skeleton (axis of the body)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
How many bones are in the human body
206
How many bones are in the axial skeleton
80
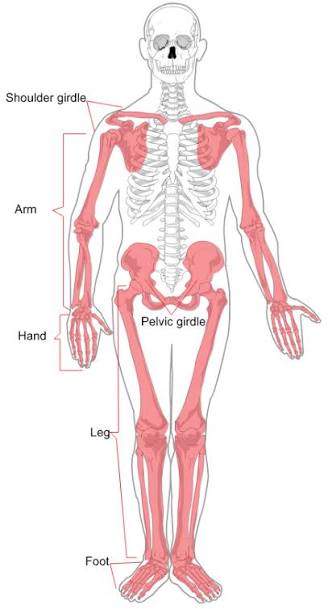
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton
126
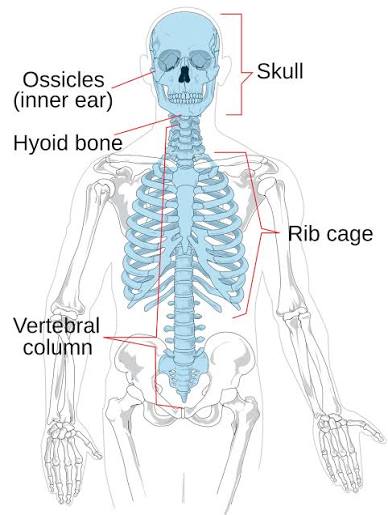
Axial skeleton
Skull (22 bones), Hyoid (1 bone), Vertebral Column (24 vertebrae + Sacrum + Coccyx)
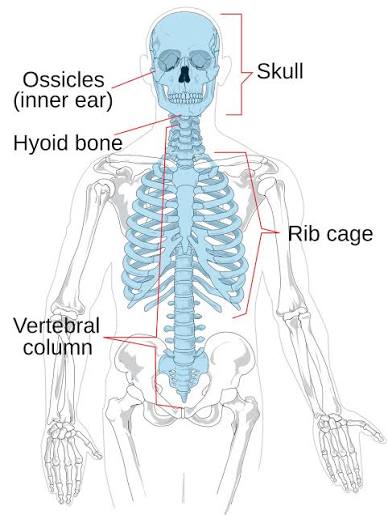
Skull
Cranium (8 bones), Facial (14 bones), * auditory ossicles (3 bones on each side)
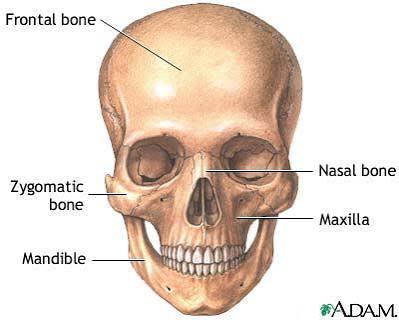
Bone classification
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular, Sesamoid, Sutral
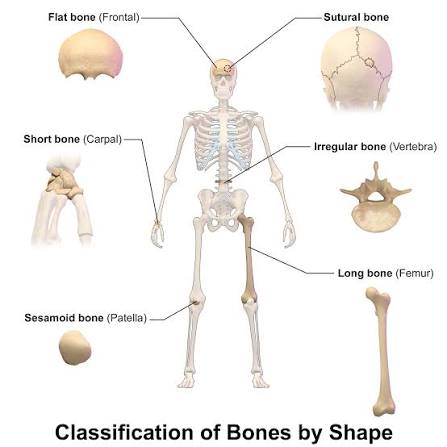
Red Marrow locations
Epiphyses of long bones, flat bones, and Irregular bones
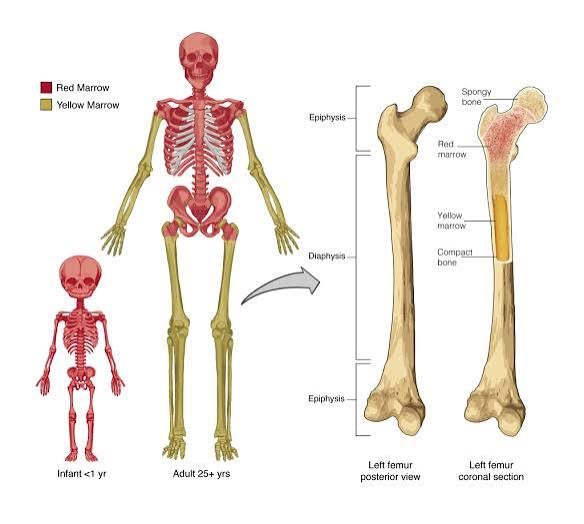
Markings: 2 main types
Depression/openings, and Processes( projections, outgrowths)
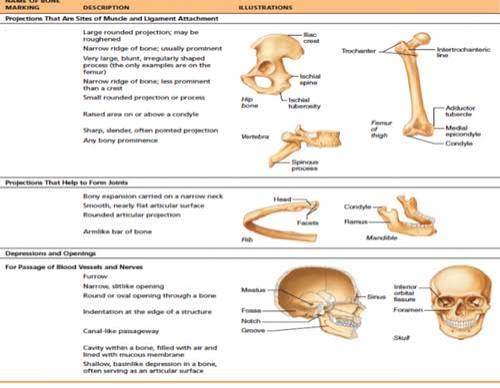
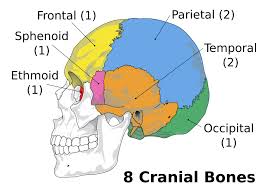
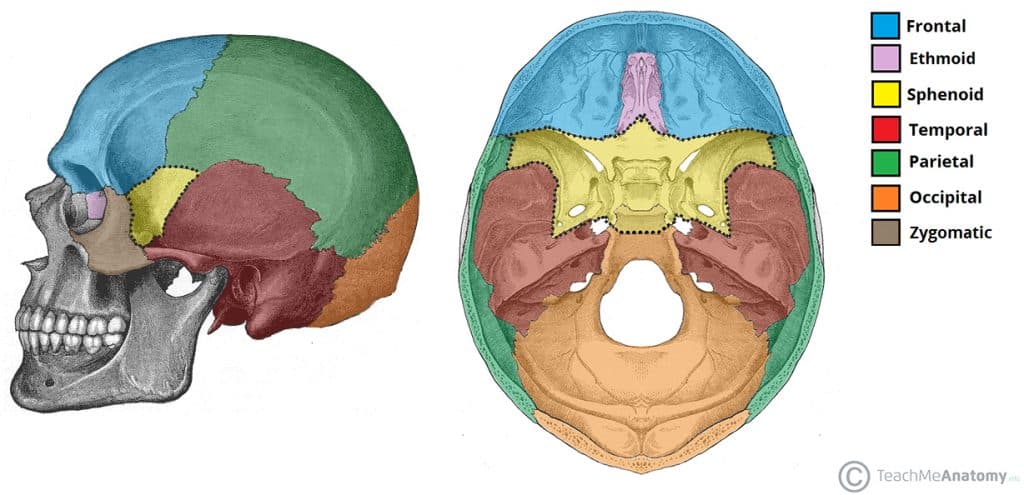
8 Cranial bones
(1) Frontal bone, (2) parietal bones, (2) Temporal bones, (1) Occipital/Sphenoid/Ethmoid
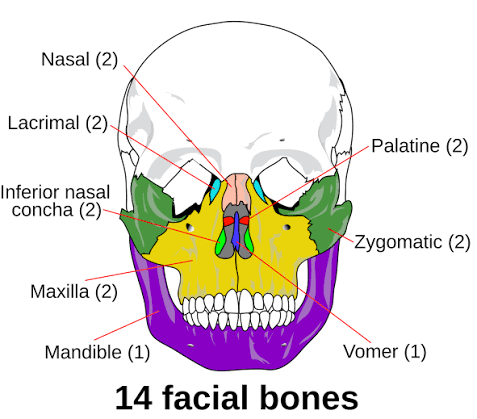
14 Facial bones
(2) Nasal bones, (2) Maxillae, (2) Zygomatic, (2) Lacrimal, (2) Palatine, (2) Inferior nasal conchae, (1) Yomer bone, (1) Mandible
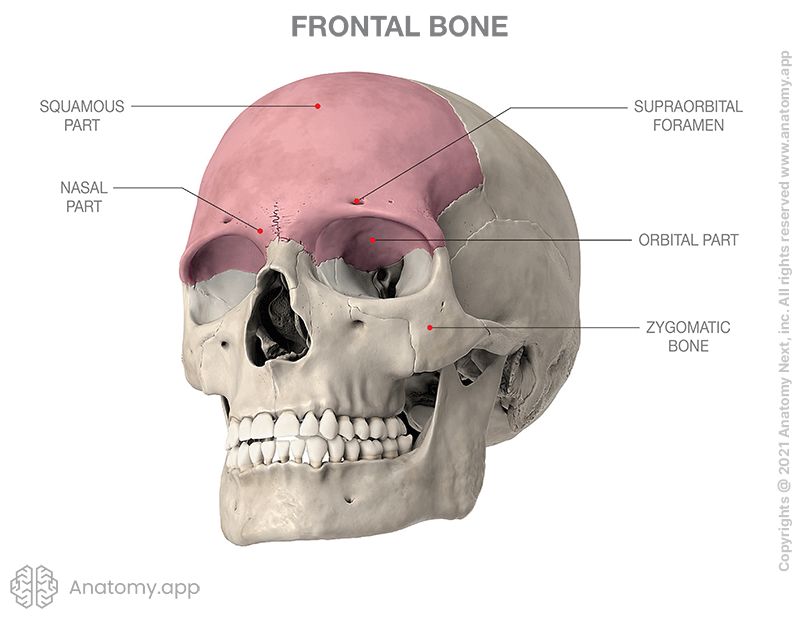
Frontal Bone
Forehead, superior roots of orbits, anterior cranial floor. “Frontal Square” forms forehead. “Supraorbital Margin” = the brow
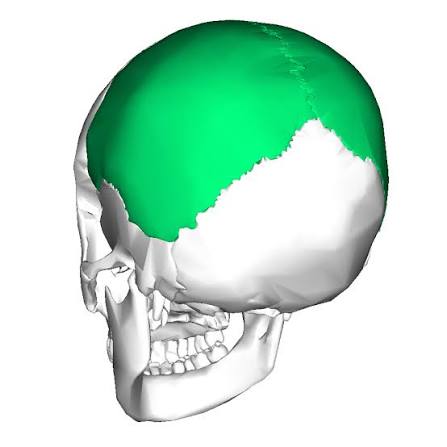
Parietal Bones (L,R)
Most of the roots & sides of the cranium
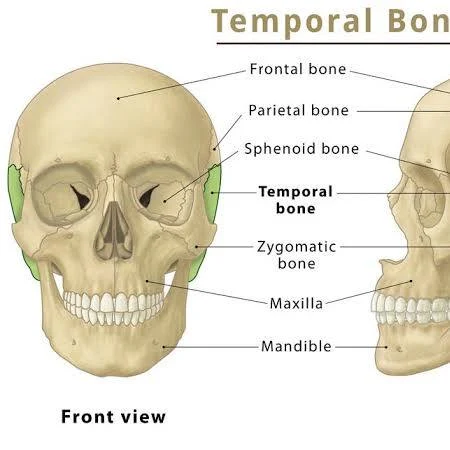
Temporal Bones (L,R)
Inferior lateral sides (and floor) of cranium. Contains “Mastoid Process” & “Syloid Process” attachments for muscle.
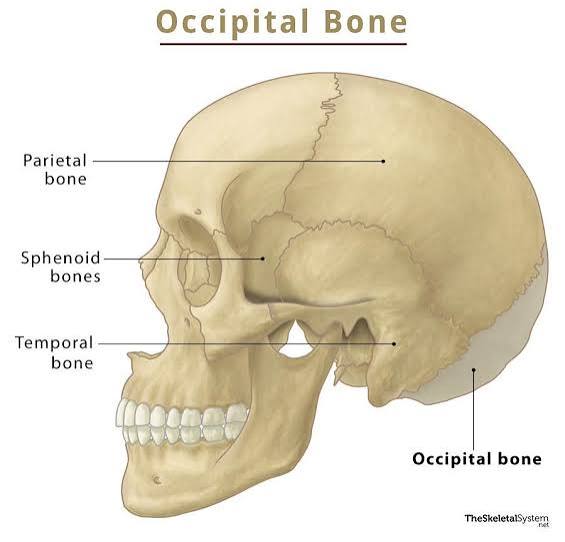
Occipital Bone
Posterior & base of cranium. Contains “foramen magnum” for spinal cord & brain stem.
Sphenoid
“Keystone of cranium” all other cranial bones articulates with it. Contains “Sella turrica” to protect pituitary. Also carotid & jugular foramen (for major vessels).
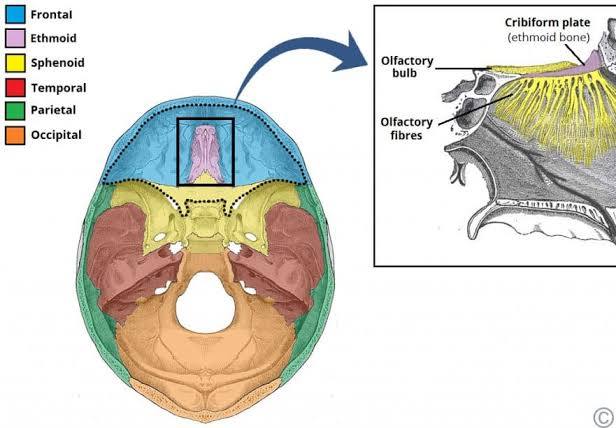
Ethmoid
Honeycomb shape (grape to walnut size). Between sphenoid & nasal bones. Houses "olfactory foramina” to accomodate olfactory nerve receptors. Air Spaces (Sinuses) + Superior, midle nasal canche.
Facial bones
14
(2) Nasal bones (Fused)
Bridge of nose
(2) Lacrimal bones
Smallest facial bones. Medial side of orbits. House lacrimal sacs/ducts
(2) Paletine bones (Fused)
Posterior hard plate
(2) Inferior Nasal conchae
Not part of the ethmoid. In the nasal cavity
(1) Yomer
Thin, triangular. Inferior portion of nasal septum
(2) Maxillae bones (Fused)
Upper jaw, face below orbits. Articulates with every facial bone except mandible. Contains “Infraorbital foramen”
(2) Zygomatic bones(L,R)
Cheek bones
(1) Mandible bone
Lower Jaw. Largest, strongest facial bones. *Only moveable facial bone. Contains “Mental foramen”
Sutures
Immovable joints found between cranial plates (bones).
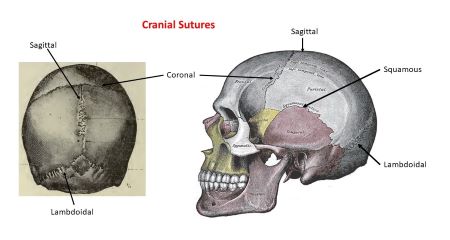
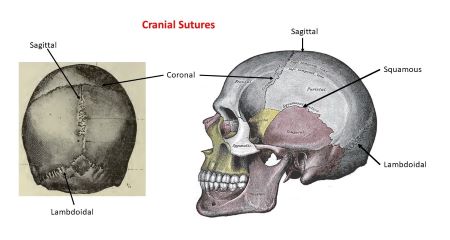
4 major sutures
Coronal, Sagittal, Lambdoid, Squamos (2-L,R)
Paranasal sinuses
Air chambers in the skull. Lined with mucus membranes.
-small or absent at birth
-develops when teeth erupts & during puberty
Paranasal Sinuses Functions
Allows for bone growth without increasing weight of the skull.
Sound Resonance
Fontanels (fontanelle)
Dense CT in unfused cranial plates at birth (“soft spots”). Bones eventually fuse and sutures are found. Allows for accommodation through birthing canal and growth after birth(Crainal & Brain).
4 Major Fontanels
1) Anterior Fontanel, 2) Posterior Fontanel, 3) Anterolateral Fontanel (L,R), 4) Posterolateral Fontanel (L,R)
1) Anterior Fontanel
Largest. Between 2 parietals and frontal bone. Diamond shaped. Closes at 18-24 months.
2) Posterior Fontanel
Between posterior parietals & occipital bone. Closes 2 months after birth
3) Anterolateral Fontanel (L,R)
Between frontal, parietal & sphenoid (on both sides). Closes at 3 months
4) Posterolateral Fontanel (L,R)
Between parietals, occipital, temporals (on both sides). Closes between 2 months to 12 months.
Hyoid bone
Horse shoe shaped. Located in neck above the larynx. Only bone that doesnt articulate with any other bones.
-Helps anchor tounge muscles (helps speech)
Vertebral column
The spine (24 vertebrae+sacrum+coccyx)
Vertebral locations
7 cervical at the top, 12 thoracic in the middle, 5 lumbar under that, sacrum & cocckyx at the bottom
Herniated disc
When annulus ruptures & nucleus pulposus protrudes from disc. Most common in lumbar area
Spina Bifida
A congenital defect of vertebral column. L5 and/or S1 vertebral lamina dont fuse normally at midline.
Spina Bifida Occulta
Less severe form of Spina Bifida
Spina Bifida Cystica
Very severe form of Spina Bifida. CNS membranes protrude through spine (vertebral column) and produce a sac with spinal membranes and nerve roots. This may interfere with natural control of urinary bladder & bowel control.
Sacrum
5 fused vertebrae. Fully fused at 16-18 years
Coccyx
4 fused vertebrae. Fully fuse at 20-30 years
Thoracic Cage(Ribs)
12 pairs of ribs. Articulate with 12 thoracic vertebrae. Anterior connects to sternum is via costal cartilage pairs 1-7 are “true ribs”, pairs 8-10 are “false ribs”, and pairs 11/12 are “floating ribs”