FOM Week 14 LEC 120-128
1/210
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Each question labeled with lecture # (E.g. 120). Check out Amaya's Knowt Deck for Cranial Nerve facts: https://knowt.com/flashcards/77dd97c7-875d-42b1-84ab-8d05714e18a6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
(120) Anosmia
Medical condition of Smell “Blindness”
(120) Ageusia
Medical condition of Taste loss; Often coupled (and confused) with anosmia
(120) Presbyopia
Medical condition of Lens loses elasticity with age. Near-point focusing ability is reduced
(120) Cataracts
Medical condition of protein breakdown exceeding repair rate as we age. Denatured proteins build up in the lens thickening and clouding it
(120) Glaucoma
Medical condition of aqueous humour unable to drain through the Canal of Schlemm leading to stagnation and cloudiness
(120) Open-angle Glaucoma
Medical condition of the drainage angle being open but the outflow of aqueous humor being blocked at Canal of Schlemm
(120) Closed-angle Glaucoma
Medical condition of iris closing the draining angle to obstruct aqueous humour outflow instead of blockage of the Canal of Schlemm
(120) Retinal detachment
Medical Condition of reduced intraocular pressure putting retina at risk of detachment
(120) Conductive Hearing Loss
Medical condition that affects the middle ear. People speak softly thinking they are loud
(120) Sensorineural hearing loss
Medical condition that affects the inner ear. Cochlear implants used, but reclaimed sound is still crude
(120) Cause of Conductive hearing loss
Result of damage to Tympanum or Ear ossicles
(120) Cause of Sensorineural hearing loss
Result of damage to stereocilia (“hair” cells), cochlear nerve, or associated brain relays
(120) Tinnitus
Medical condition of Age-related loss of “hair” cells along cochlea. Ringing sensation is constant and often without a stimulus
(120) Benign Paroxysmal Position Vertigo (BPPV)
Medical condition that occurs when otoliths break free from utricle. Free-floating otoliths enter SCC producing conflicting signals to the brain about head orientation
(120) Nystagmus
Medical condition that is a result of a delay in the vestibulo-ocular reflex
(120) Tongue innervation from Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
posterior 1/3rd of tongue
(120) Tongue innervation from Vagus Nerve (CN X)
small regions of the tongue, oral soft palate and pharynx
(120) Tongue innervation from Facial Nerve (CN VII)
anterior 2/3rds of the tongue via chorda tympani
(120) Flavor is the coupled sense of:
Smell and Taste
(120) The Vestibulo-ocular reflex is the coupled sense of:
vision and balance
(120) Function of Sclera
blocks out light and protects against physical damage of the eye
(120) Function of Cornea
window of eye for light to enter, blocks most UV light
(120) Function of sphincter pupillae
Constricts the iris to limit light entry, parasympathetically activated
(120) Function of dilator pupillae
Expands the iris to allow light entry, sympathetically activated
(120) Ciliary Body
A ring of smooth muscle attached to the lens, responsible for deforming the lens and produces aqueous humour.
(120) Function of Ciliary Body
Contracts when viewing objects nearby so zonular fibres can loosen and lens can relax
(120) Accommodation
ability to adjust the focal point in the eye to a near object by deforming the lens
(120) Function of Utricle
Senses horizontal acceleration
(120) Function of Saccule
Senses vertical acceleration; Functions as our gravity sensor
(120) When rotating the head, the Semicircular Canals’ afferent neurons get ___ on the turning side
depolarized
(120) When rotating the head, the Semicircular Canals’ afferent neurons get ___ on the opposite side
hyperpolarized
(120) When rotating the head, the Semicircular Canals’ afferent neurons get depolarized on the _____ side
turning
(120) When rotating the head, the Semicircular Canals’ afferent neurons get hyperpolarized on the _____ side
opposite
(121) The function of the Parotid Gland is to:
Produce saliva
(121) Horner’s Syndrome
Medical Condition of damage or blockage of sympathetic pathway to head
(121) Frey’s Syndrome
Medical condition of auricotemporal nerve regrows after trauma to innervate sweat glands
(121) Symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome
Constricted pupil, lack of sweating, can’t blush
(121) This nerve induces parasympathetic activation of the convergence reflex:
CN III
(121) Symptoms of Frey’s Syndrome
Gustatory sweating
(121) The preganglionic input to the Otic ganglion is:
CN IX
(121) The preganglionic input to the Submandibular ganglion is:
CN VII
(121) The preganglionic input to the Ciliary ganglion is:
CN III
(121) The preganglionic input to the Pterygopalatine ganglion is:
CN VII
(121) The function of the Sublingual Gland is to:
Produce saliva
(121) This nerve induces parasympathetic activation of Pupil Constriction:
CN III
(121) This ganglion manages sympathetics of the head and neck:
Superior Cervical Ganglion
(121) This ganglion manages parasympathetics of the Ciliary muscle and the sphincter pupillae:
Ciliary Ganglion
(121) This ganglion manages parasympathetics of the Lacrimal and mucosal glands:
Pterygopalatine Ganglion
(121) This ganglion manages parasympathetics of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands:
Submandibular Ganglion
(121) This ganglion manages parasympathetics of the Parotid Gland:
Otic Ganglion
(121) The function of the Lacrimal Gland is to:
Produce tears
(121) The function of the Submandibular Gland is to:
Produce saliva
(121) The function of the Mucosal Glands is to:
Keep mucosa moist
(121) The preganglionic input to the Superior Cervical Ganglion is:
Sympathetic Chain
(121) This ganglion manages parasympathetics of the sweat glands:
Superior Cervical Ganglion
(121) This nerve induces parasympathetic activation of the accommodation reflex:
CN III
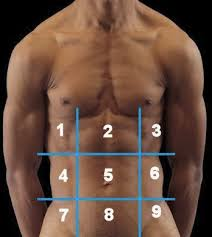
(122) #1 is the:
Right Hypochondriac Region
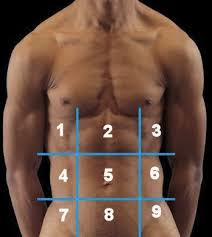
(122) #2 is the:
Epigastric Region
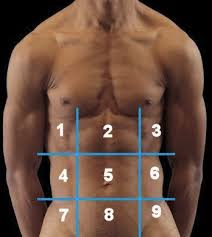
(122) #3 is the:
Left Hypochondriac Region
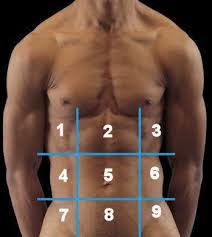
(122) #4 is the:
Right Lumbar Region
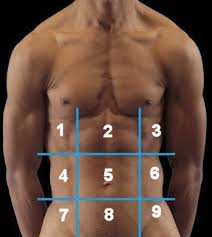
(122) #5 is the:
Umbilical Region
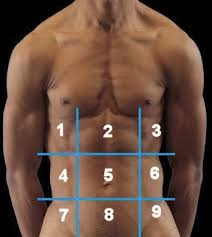
(122) #6 is the:
Left Lumbar Region
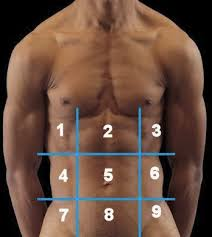
(122) #7 is the:
Right Iliac Region
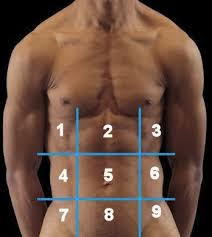
(122) #8 is the:
Hypogastric Region
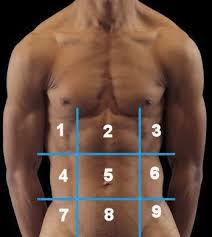
(122) #9 is the:
Left Iliac Region
(122) The first step of the GI exam is:
Inspection
(122) The second step of the GI exam is:
Auscultation
(122) The third step of the GI exam is:
Percussion
(122) The fourth step of the GI exam is:
Palpation
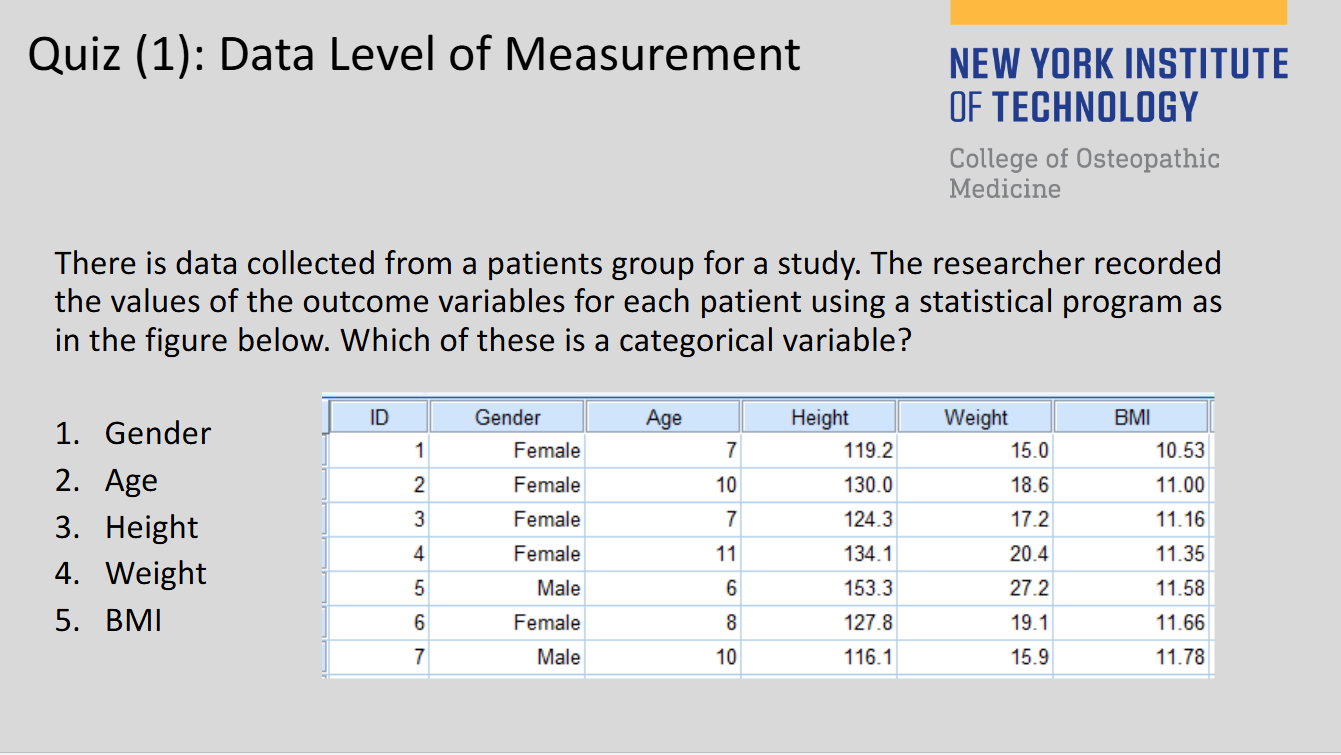
(129)
1
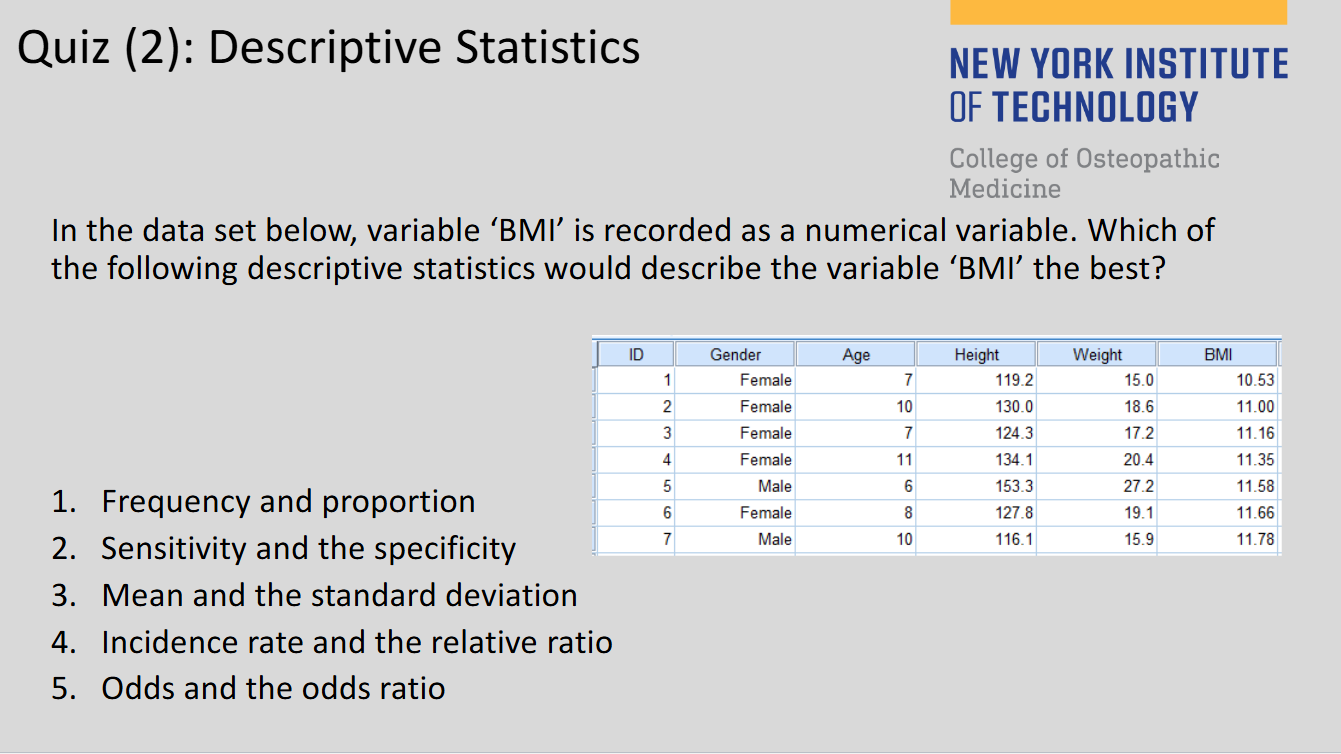
(129)
3
(129) Data with Categorical Values:
Gender, Race, Exposure/Disease status
(129) Data with numeric values:
Age, Weight, Height, A1c level, test score
(129) Descriptive Statistics for Numerical data:
mean, median, mode, variance, standard deviation
(129) Descriptive Statistics for Categorical data:
frequency, proportion, rate, ratio, prevalence, incidence rate, relative risk, odds ratio, sensitivity, specificity
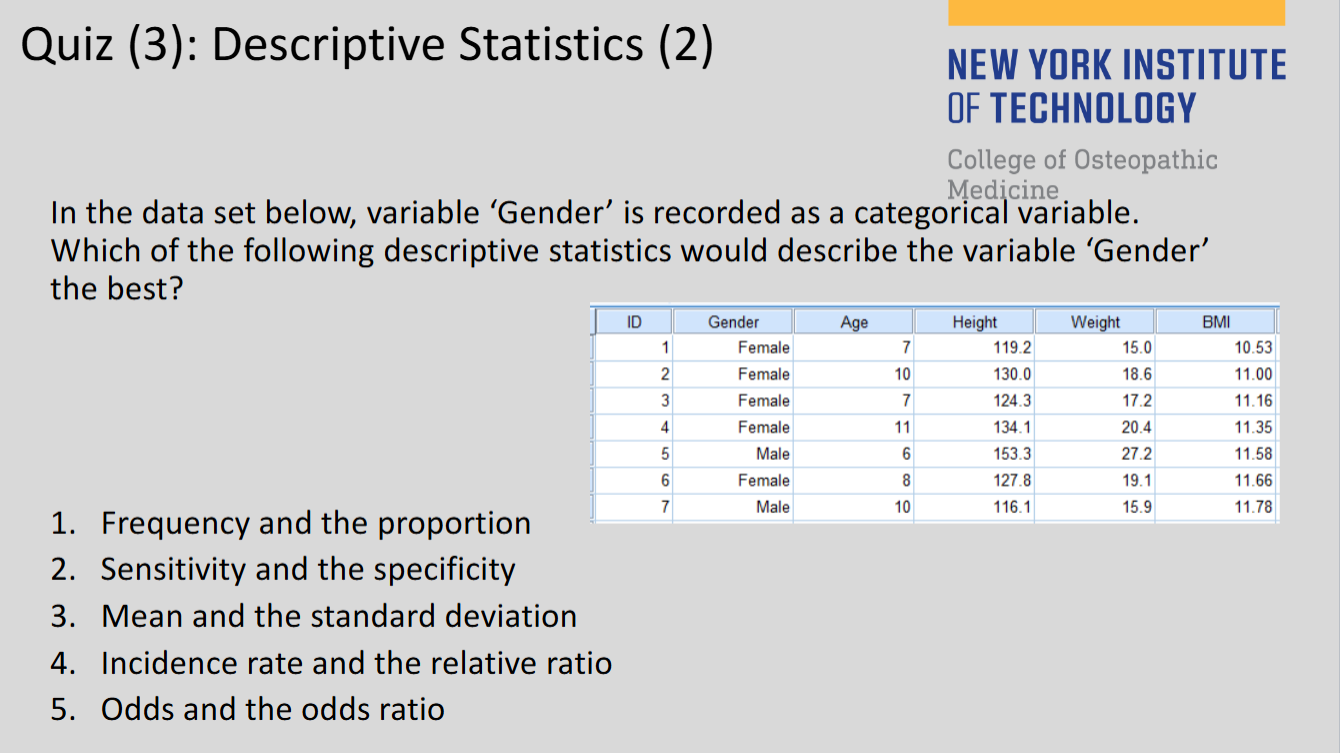
(129)
1
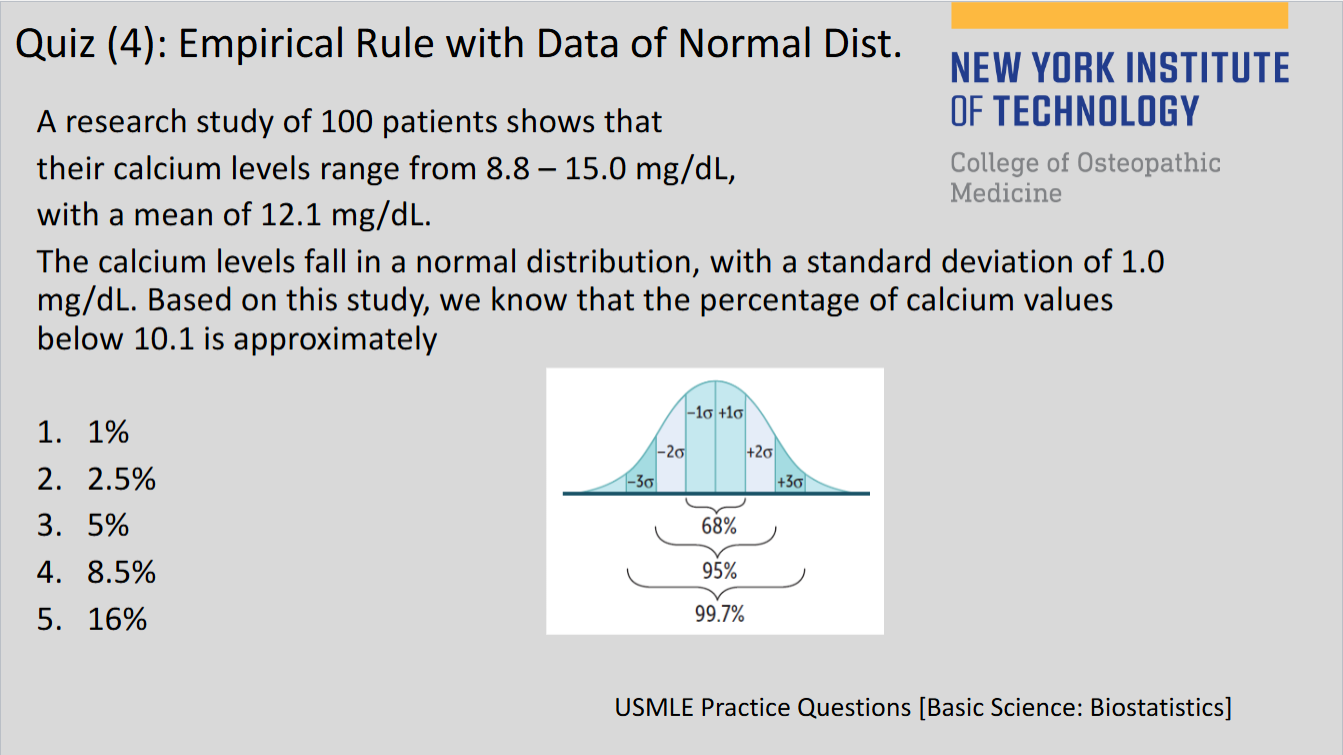
(129)
2
(129)
5

(129)
4

(129)
2

(129)
1

(129)
2
(129) If the p-value is less than the significant value you:
reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis
(129) If the p-value is greater than the significant value you:
fail to reject the null hypothesis

(129)
4

(129)
2
(129) Type I error (α):
false positive (null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected)
(129) Type II error (β):
false negative (null hypothesis is incorrectly not rejected)
(130) If you are comparing 2 groups of data and the data is parametric and independent of each other, the correct SHT is:
Independent t-test
(130) If you are comparing 2 groups of data and the data is non-parametric and independent of each other, the correct SHT is:
Mann-Whitney U test
(130) If you are comparing 2 groups of data and the data is parametric and paired/related, the correct SHT is:
Paired t-test
(130) If you are comparing 2 groups of data and the data is non-parametric and paired/related, the correct SHT is:
Wilcoxon signed-rank test
(130) If you are comparing >2 groups of data and the data is parametric and independent of each other, the correct SHT is:
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
(130) If you are comparing >2 groups of data and the data is non-parametric and independent of each other, the correct SHT is:
Kruskal-Wallis H test
(130) If you are comparing >2 groups of data and the data is parametric and paired/related, the correct SHT is:
Repeated Measures ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
(130) If you are comparing >2 groups of data and the data is non-parametric and paired/related, the correct SHT is:
Friedman test

(130)
1
(130) Parametric Data
Data that is normally distributed with equal variances
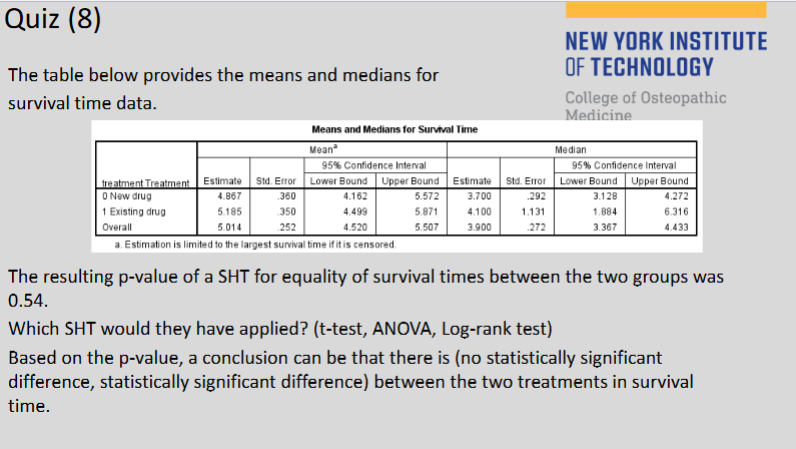
(130) Which SHT would they have applied?
Log-rank test
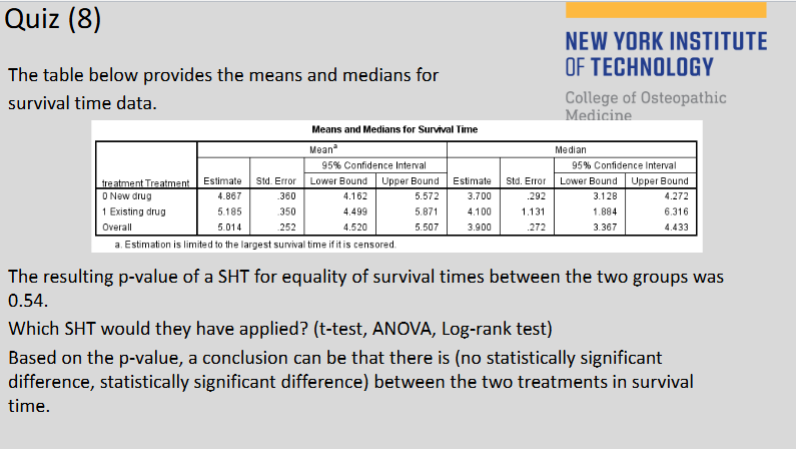
(130) Based on the p-value, a conclusion can be that there is
no statistically significant difference