Quantitative Analysis - Enzymatic Method
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Glucose Oxidase
Saifer Gernstenfield
Coupled enzyme reaction (Trinder’s Reaction) – Colorimetric
Measures B-D-Glucose
Indirect Measurements of glucose, based with hydrogen peroxide na na proproduce.
Kun damot na proproduce na hydrogen peroxide, damo gihapon it glucose level.
For urine and whole blood glucose rapid reagent strip testing
Also for automated methods for plasma and serum
Interference by: Uric Acid, Bilirubin, Ascorbic Acid
Increased Uric Acid, Ascorbic Acid, Bilirubin, Tetracycline, Hemoglobin and Glutathione 🡪 Falsely Low Glucose Result
ENZYMES:
Glucose oxidase
Peroxidase

Glucose oxidase - oxygen consumption
Polarographic glucose oxidase method
O2 consumption is determined by O2 electrode
Less common than hexokinase method. Commonly used for glucose meter testing
Accurate and precise method, virtually no interferences
ENZYME:
Glucose Oxidase

Hexokinase Method
Most specific and reference method
Based on formation of NADH followed by increase in absorbance at 340nm (directly proportional to glucose concentration)
Falsely Low: Gross hemolysis (inhibits peroxidase), extremely increased Bilirubin
Not affected by Ascorbic Acid and Uric Acid
Specific glucose method which employs G6PD as a second coupling step requiring Magnesium
ENZYMES
Hexokinase
G6PD

For example
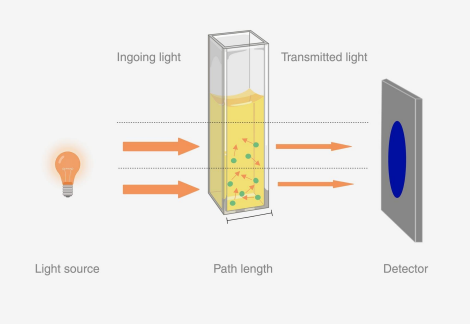
How do it measure glucose?
This is your tube, it contains serum, glucose molecules, tapos mayda kita light source, once this light passes through the tube, it ig meameasure iton intensity han light na naka pass through han tube this detector.
This detector will measure the glucose level.
Wavelenthg selector will just select the specific wavelength of glucose.
Specimen Handling
Standard clinical specimen: VENOUS PLASMA GLUCOSE
For daily monitoring: CAPILLARY BLOOD
Separate plasma from cell WITHIN 1 HOUR
Random Blood Sugar
Requested during insulin shock and hyperglycemic ketonic coma
Normal: <140 mg/dL
Fasting Blood Sugar
Fasting blood glucose should be obtained in the morning after an approximately 8 – 12 hours fast (not longer than 16 hours)
Reference Values: 70 – 100 mg/dl
Point of care testing
For daily monitoring, specimen is capillary blood
Strips impregnated with glucose oxidase and peroxidase
Principle: Color change read by Reflectance Photometry
2hr post prandial blood sugar
Glucose load of 75g (adults) or 1.75g/kg (children) of glucose is administered and a specimen is drawn 2 hours later.
Normal value: <140 mg/dL
Diabetic: >180 mg/dL
glycosylated hemoglobin
Index for long term plasma glucose control 2 – 3 months period, indicating compliance and efficacy of Diabetes Mellitus therapy