Axial Skeleton - Vertebral Column & Thoracic Cage
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
adult vertebral column
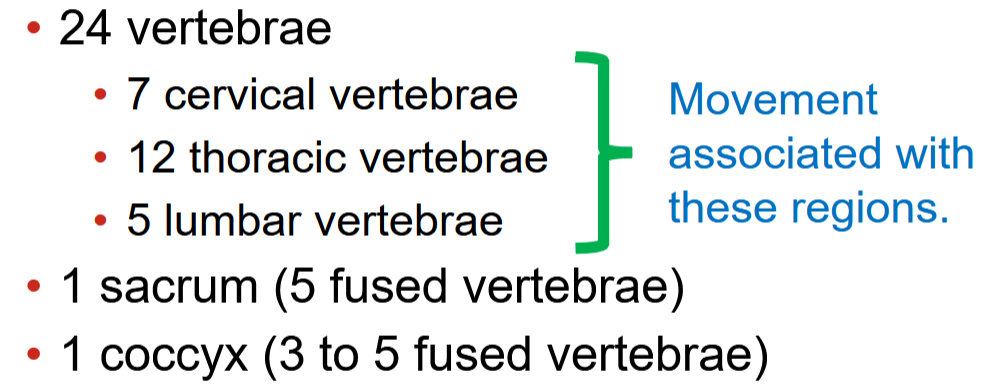
26 bones
24 vertebrae (Cervical, lumbar, thoracic)
1 sacrum
1 coccyx
Functional anatomy of the vertebral column
Encloses and protects the spinal cord
Supports the skull
Supports the weight of the head, neck, and trunk
Transfers weight to the lower limbs
Helps maintain the upright position of the body

What types of curves are in the spinal curves category?
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral
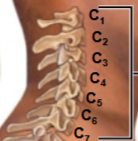
This is the first of the spinal curves / vertebrate regions. What is this region called?
Cervical
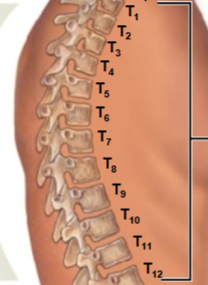
This is the second of the spinal curves / vertebrate regions. What is this region called?
Thoracic
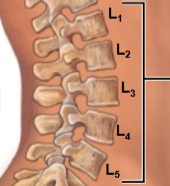
This is the third of the spinal curves / vertebrate regions. What is this region called?
Lumbar
This is the fourth and last of the spinal curves / vertebrate regions. What is this region called?
Sacral
Cervical curve / region (7 total)
A secondary curve develops as the infant learns to
balance the head on the vertebrae of the neck
Function
Support the weight of the head
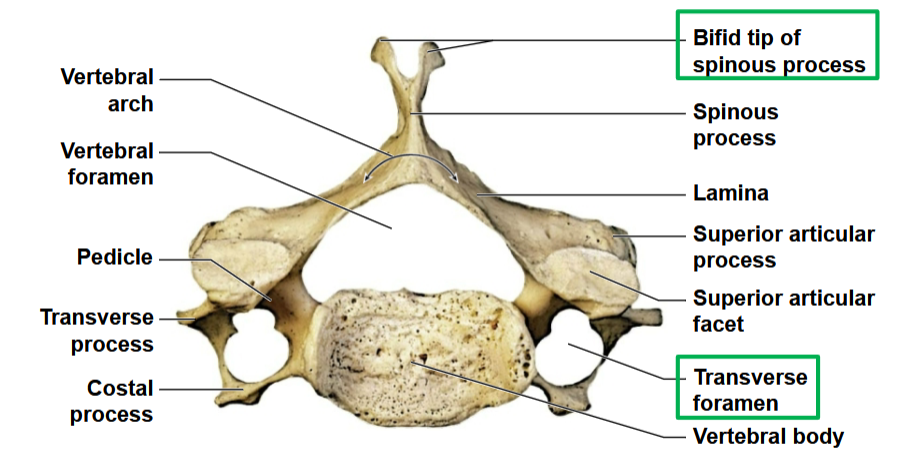
Spinous processes are bifid except for C7
All have transverse foramina
The transverse processes are fused to the costal processes
Two have specific names (C1 = atlas, C2 = axis)
Thoracic curve / region (12 total)
A primary curve accommodates the thoracic organs.
All have rib articulation points
• T1 to T8 have superior and inferior costal facets
• T9 to T12 have only one facet
• T1 to T10 have transverse costal facets
• They support the ribs
Most spinous processes point inferiorly
Lumbar curve / region (5 total)
A secondary curve balances the weight of the trunk over the lower limbs; it develops with the ability to stand.
• Support the weight of the torso
• Vertebral bodies are quite large
• Spinous process points posteriorly
Sacral curve / region
A primary curve accommodates the
abdominopelvic organs.
Includes the sacral + coccygeal regions
There is one sacrum but consists of five fused
vertebraeJoints
• Lumbosacral joint
• Sacroiliac joint
What are the movements associated with and specific to the spinal
column?
Flexion
Extension
Lateral flexion
Lateral extension
Lateral rotation
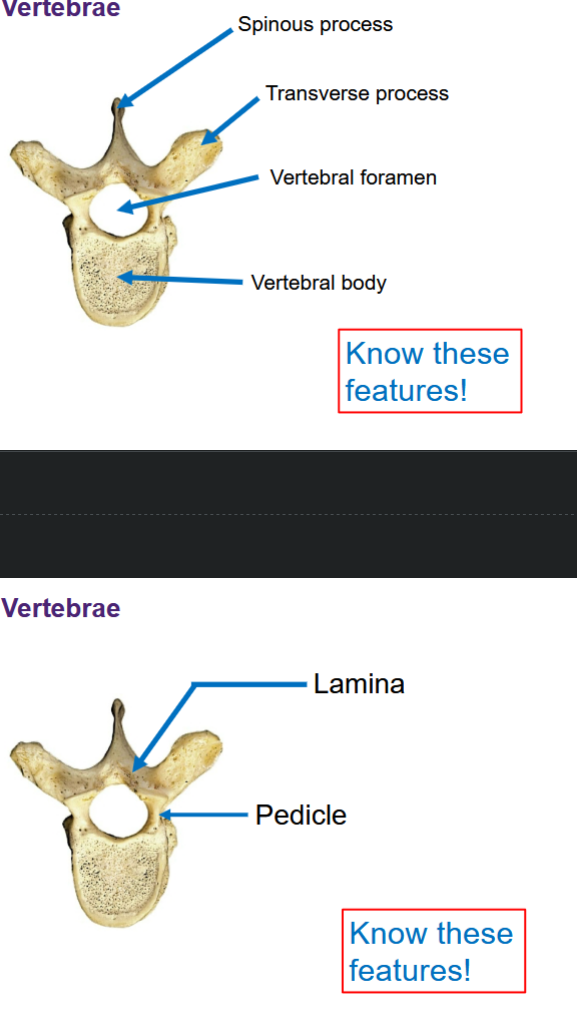
Labeled vertebrae
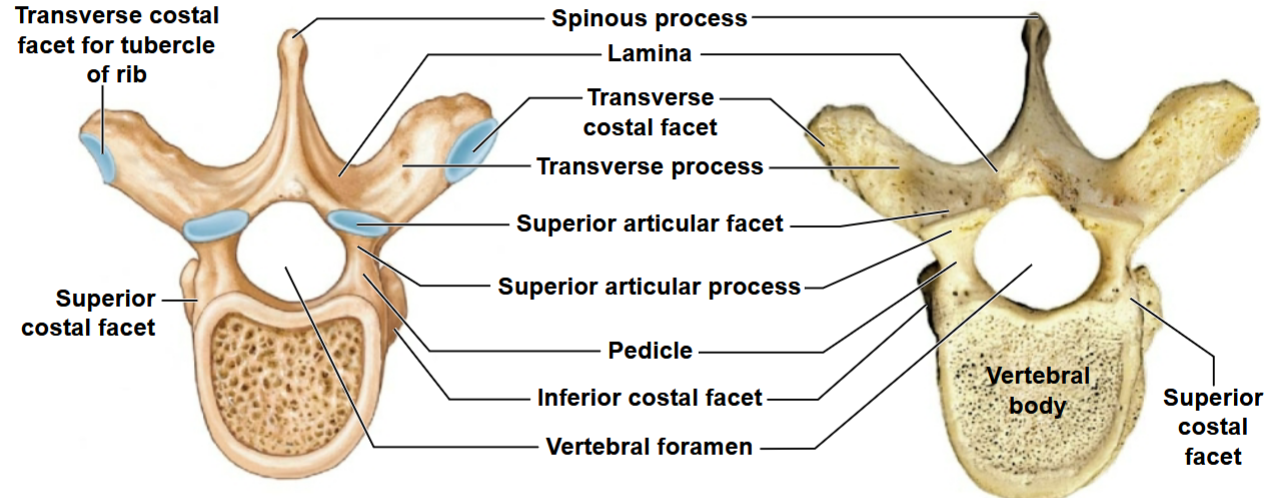
What view of the thoracic vertebrae is this?
Superior view
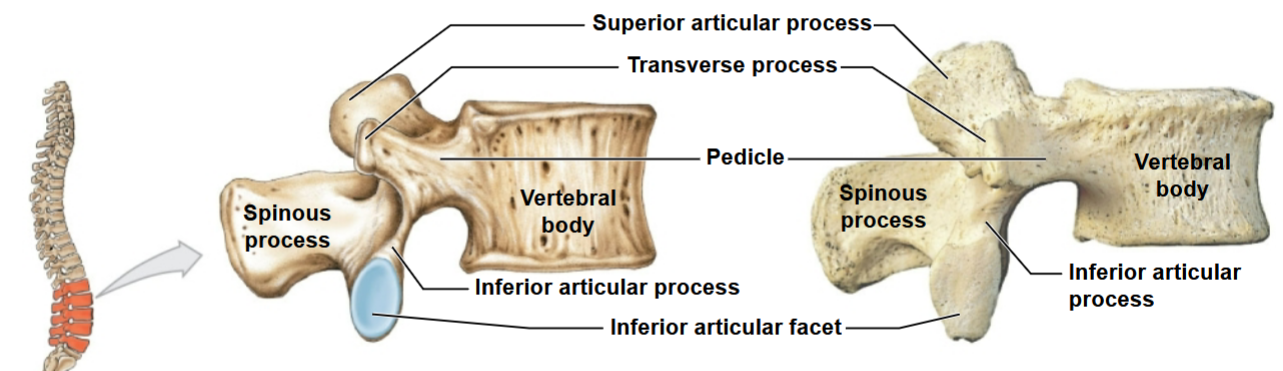
Vertebral Arch
Forms the vertebral foramen
• Made of pedicle and laminae
• Spinous process projects posteriorly
• Transverse processes project laterally
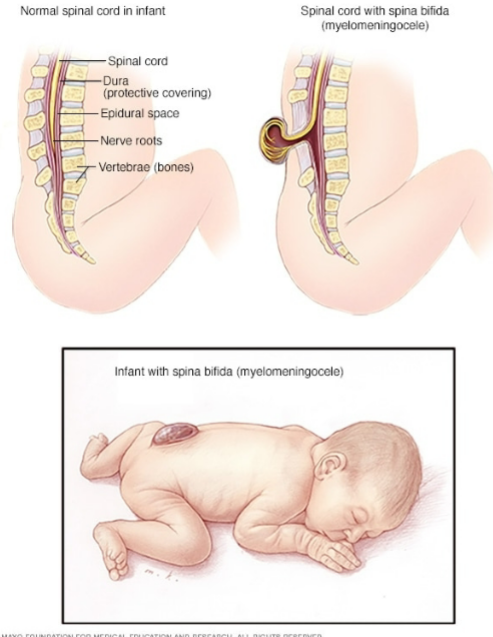
What is spina bifida?
Malformation of the structures making up the
vertebral arch, where the vertebral arch fails to
close completely
Folate deficiency can be a contributing factor
Pregnant women should take folic acid supplement as form of prevention
What are the functions and divisions of the articular processes?
Superior articular process
Inferior articular process
These allow adjacent vertebrae to join each other
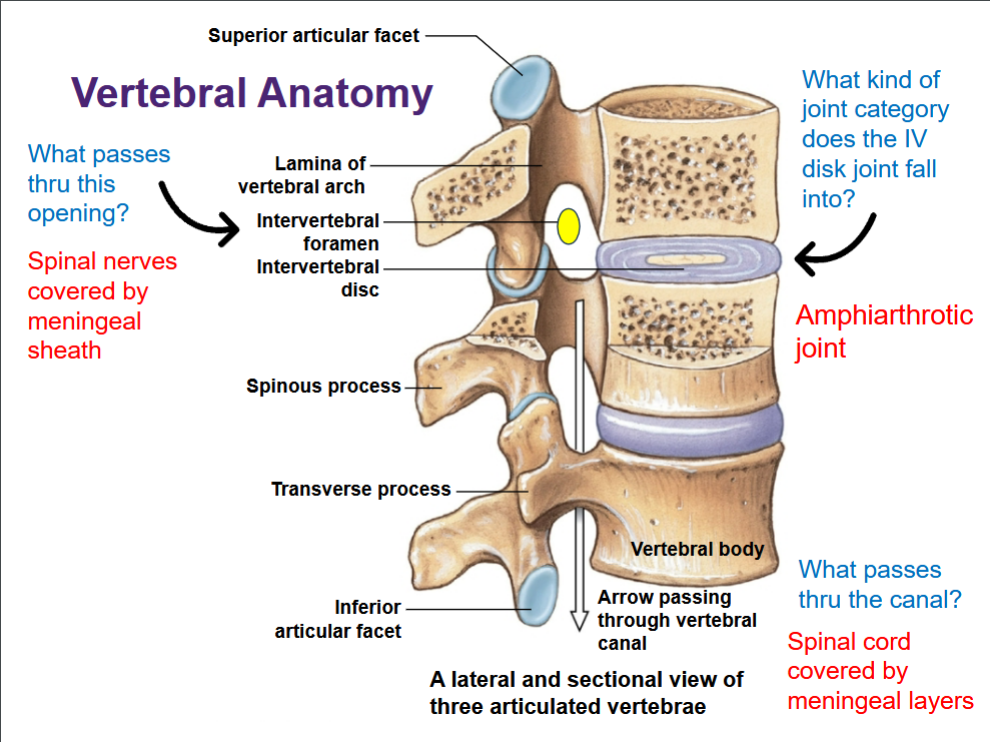
Vertebral Articulation
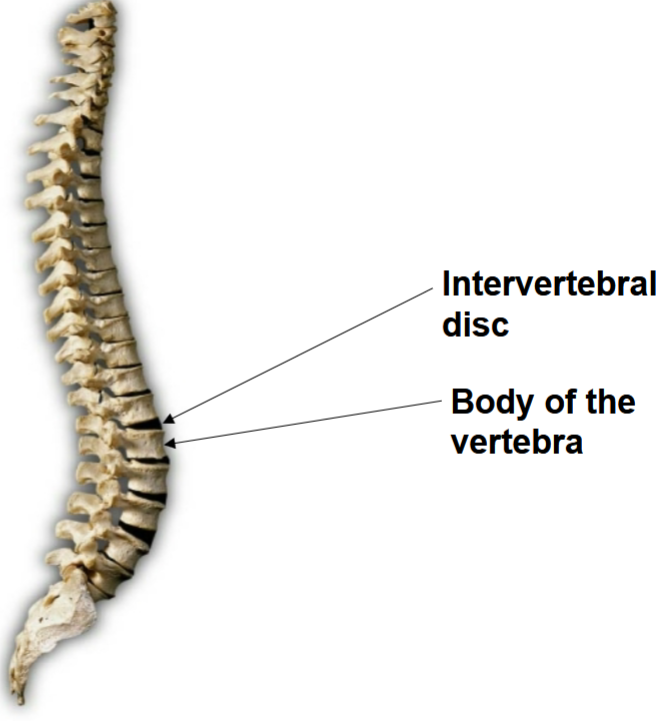
Vertebrae have articular facets and a vertebral canal
• Vertebral bodies are separated by intervertebral discs
• This results in creating a space called the intervertebral foramina
Vertebral anatomy (again labeled)
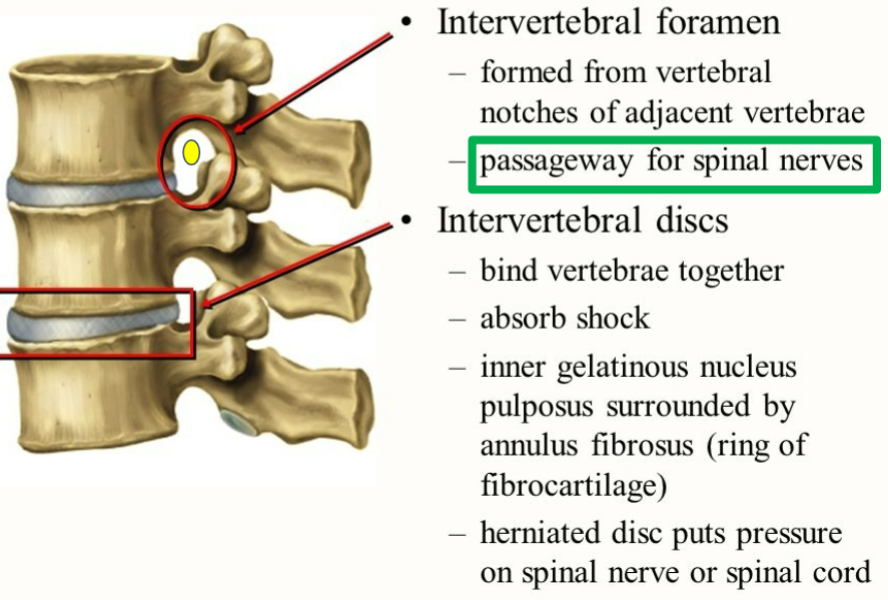
What does this represent?
intervertebral foramen and discs
What does this represent?
Superior view of cervical vertebrae
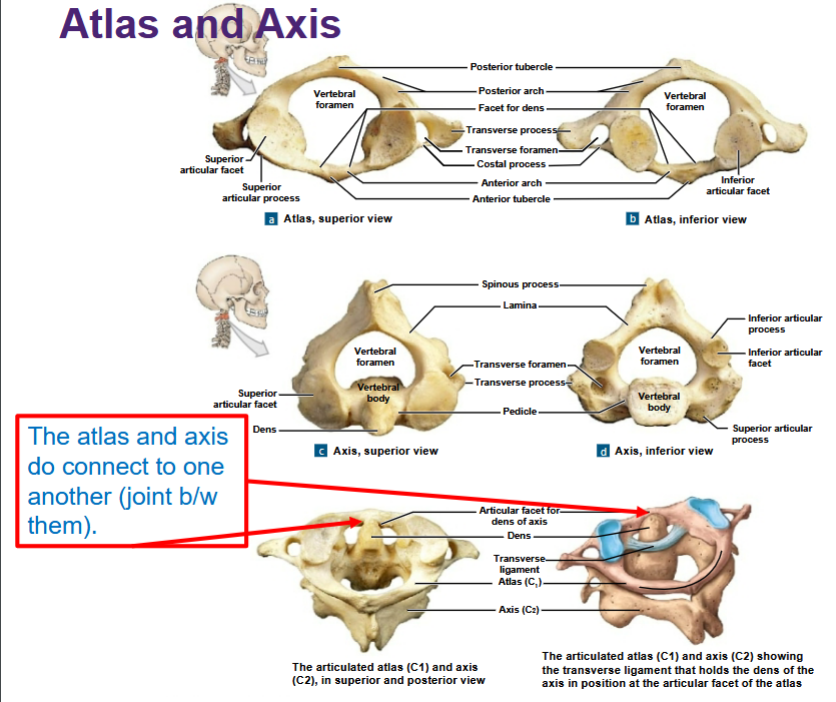
Atlas and Axis
The Atlas (C1)
• Articulates with the occipital condyles of the skull
• Does not have a body
• Consists of anterior and posterior vertebral
arches/anterior and posterior tubercles/superior
articular facets/inferior articular facets
• Has the largest vertebral foramen of all vertebrae
• Allows the head to nod in a “yes” manner
The Axis (C2)
• Has a dens
• The transverse ligament binds the dens to the atlas
• Allows the head to move in a “no” manner
Vertebral Prominens (C7)
C7 has a long prominent spinous process
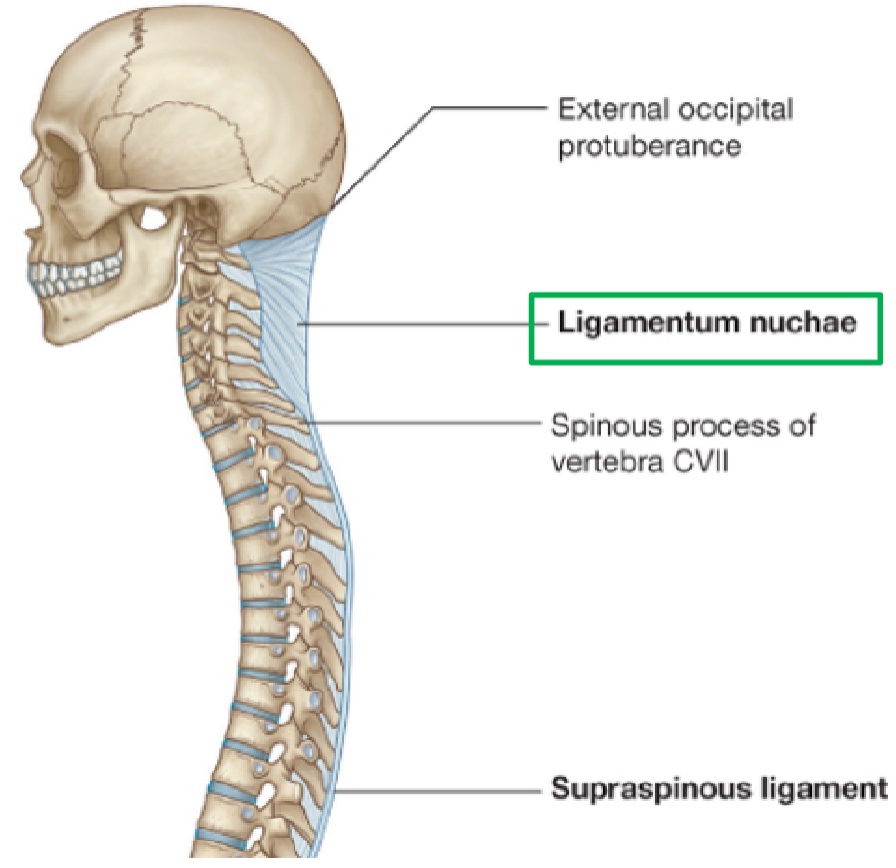
Ligamentum nuchae
• Large elastic ligament
• Begins at the vertebral prominens and extends to
the external occipital crest of the skull
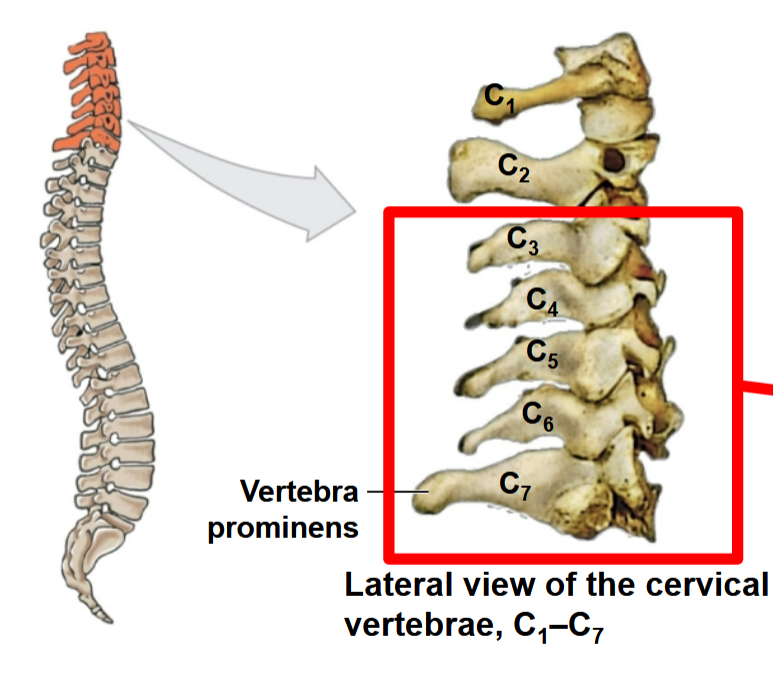
Where is the greatest range of motion in the cervical spine?
C3 to C7
Where is the Ligamentum Nuchae located?
What is represented by this image?
Lateral view of lumbar vertebra
Coccyx
Consists of three to five fused vertebrae
• Adult male coccyx points anteriorly
• Adult female coccyx points inferiorly
• coccygeal cornu – articulation with sacrum
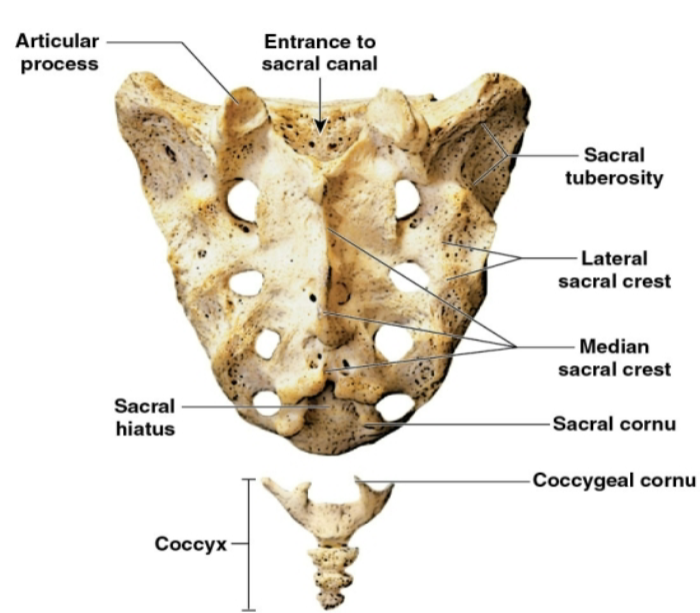
What view of the sacrum + coccyx is this?
Posterior
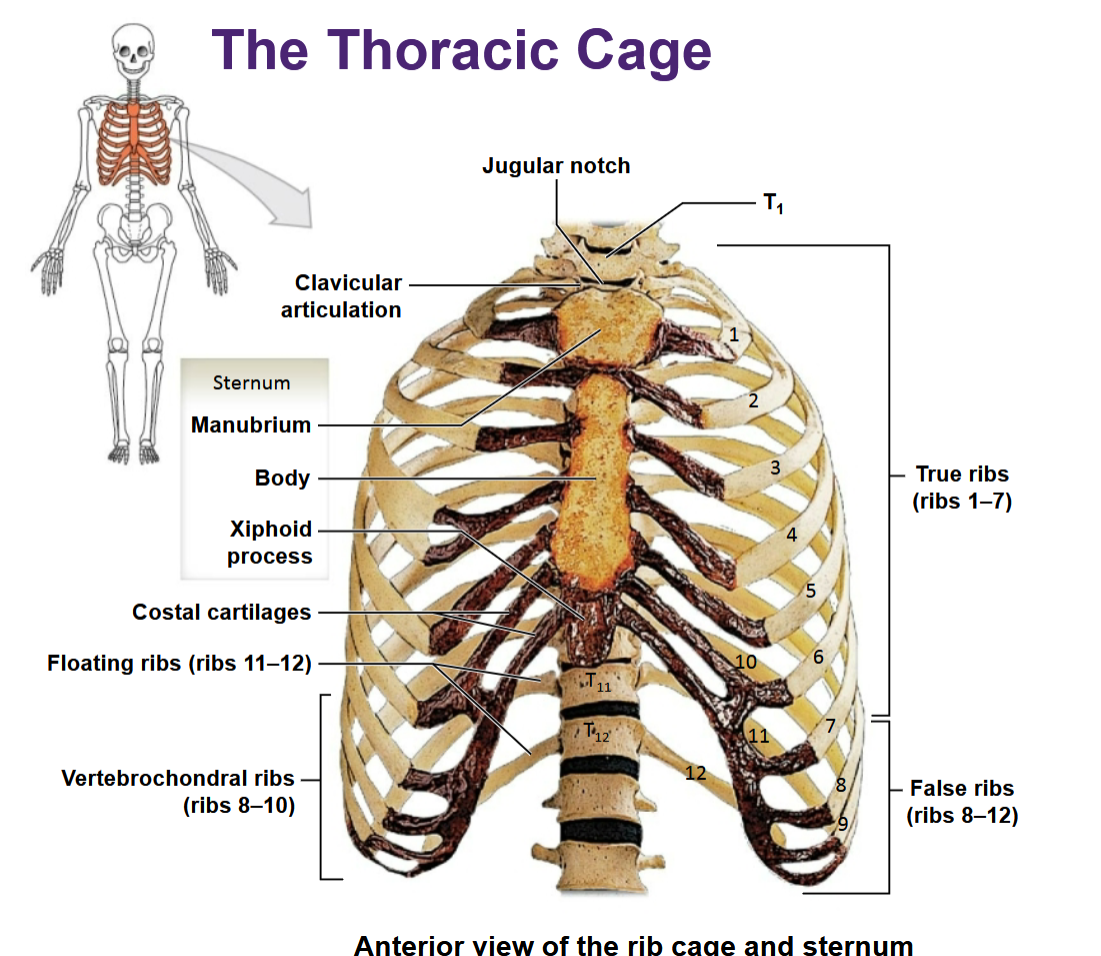
Thoracic cage
Function
• Protection
• Attachment site for muscles
Ribs
• True ribs/ vertebrosternal ribs (1-7)
• False ribs / vertebrochondral ribs (8-10)
• Floating ribs (11-12)
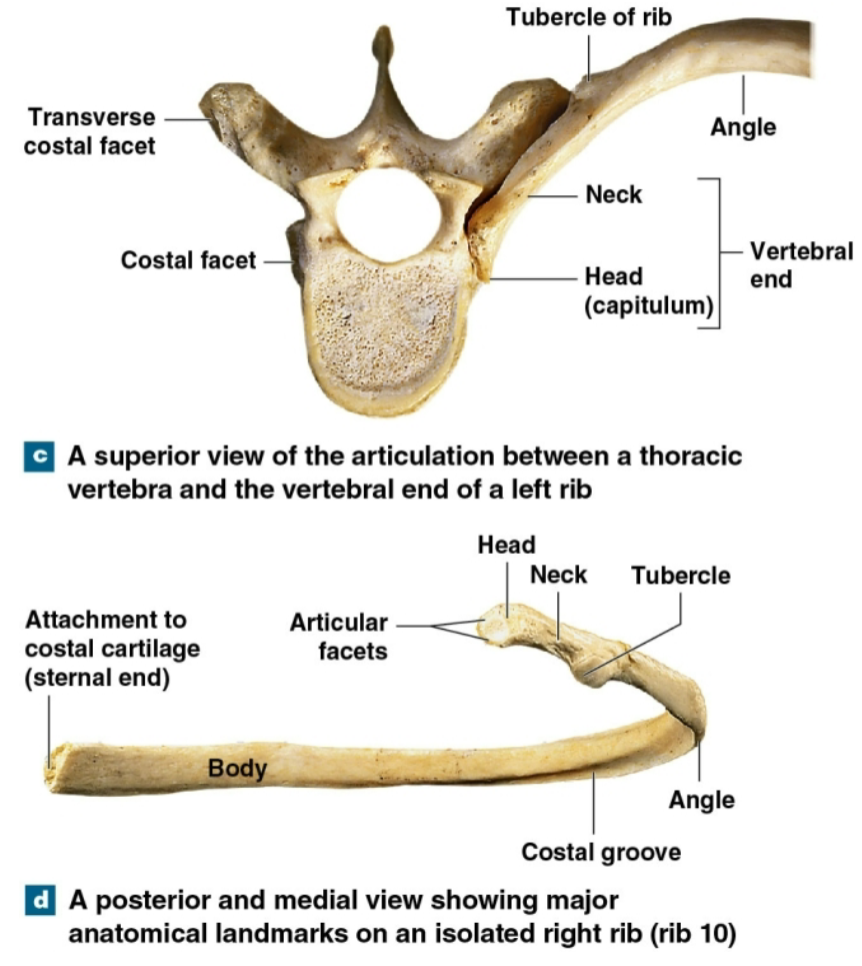
Structures of a rib
head
neck
body
tubercle
angle
costal groove
Sternal end -superior and inferior articular
facets/interarticular crest
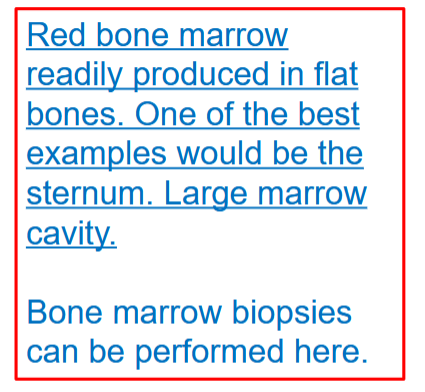
The Sternum
Consists of:
• Manubrium
• Body
• Xiphoid process
• Jugular notch
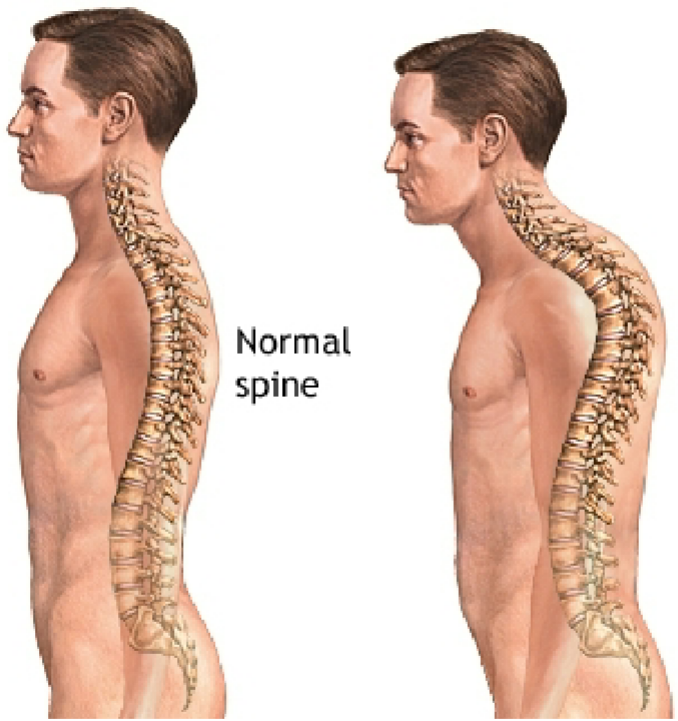
The image on the left is a “normal” spine. What is the type of spine on the left referred as?
Kyphotic spine
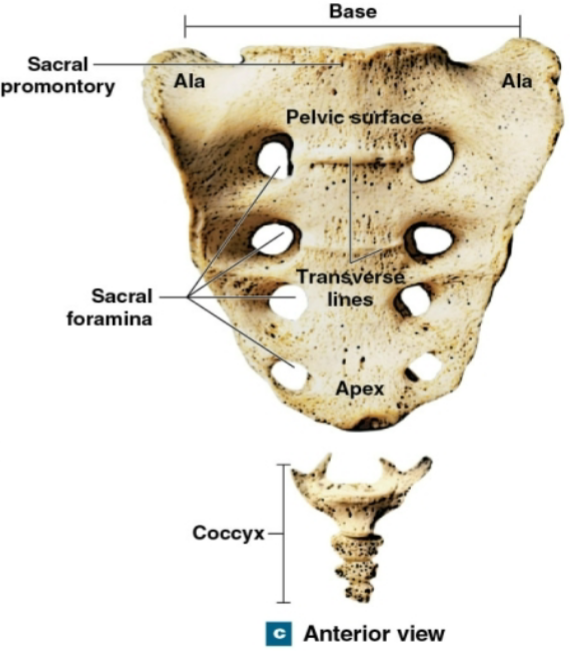
What view of the Sacrum + Coccyx is this?
Anterior view
Are false ribs directly connected to the sternum?
No; they are indirectly connected
What joint in the Sacral region do you NOT need to know?
Sacrococcygeal joint
Do the atlas (C1) and axis (C2) share a direct connection?
Yes, via a joint
What feature is unique to cervical vertebrae?
Transverse foramen