IB CHEM SL midterm review (units 1-7)
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Pure substance
Chemically bonded with definite and constant composition
Compound
Molecules or lattices with fixed ratio. Have DIFFERENT properties from their elements (but same # protons)
Mixture
Variable, not constant composition, physically bonded. Each substance in a mixture retains its properties (like boil pts)
Homogenous Mixture
All substances in same “phase” w/ no visible boundary
Heterogeneous Mixture
2+ “phases” with a visible boundary
Chemical Properties
Properties in composition that change due to a chemical reaction (flammability, combustion, oxidation, acidity)
Physical Properties
Observed/Measured in a reaction (luster, density, mass, color, size, melt/boil pts, smell, texture, conductivity, electromagnetivity)
Empirical Formula
Simplest whole number ratio of ATOMS in a compiund
Linear P=T
P v T?
linear V=T
V v T
Inverse PV=1
P v V
Linear P=1/V
P v 1/V
Proton
Mass=1 Charge=+1
Neutron
Mass=1 Charge=neutral
Electron
Mass=negligible Charge=-1
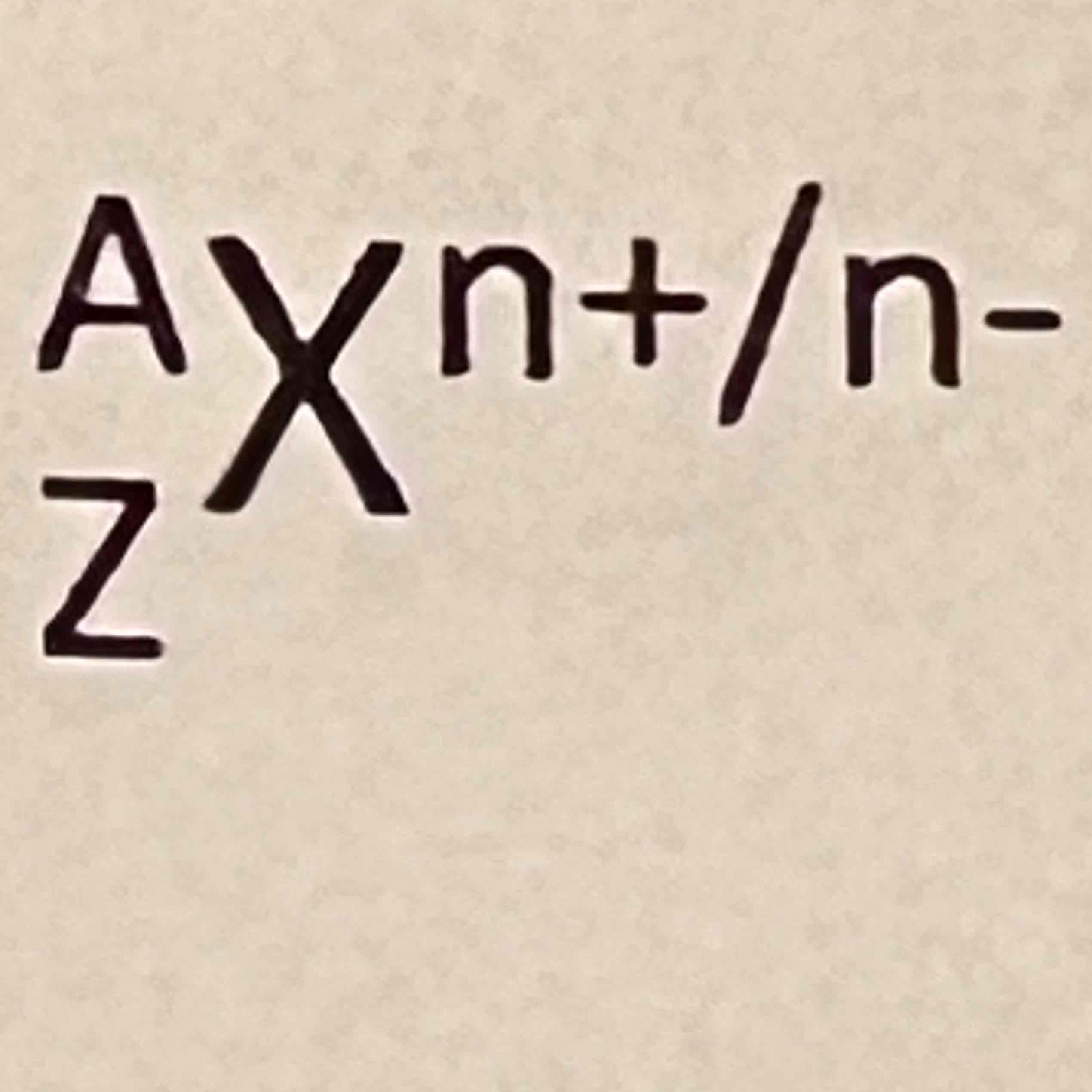
A
Mass number (pro+neu)
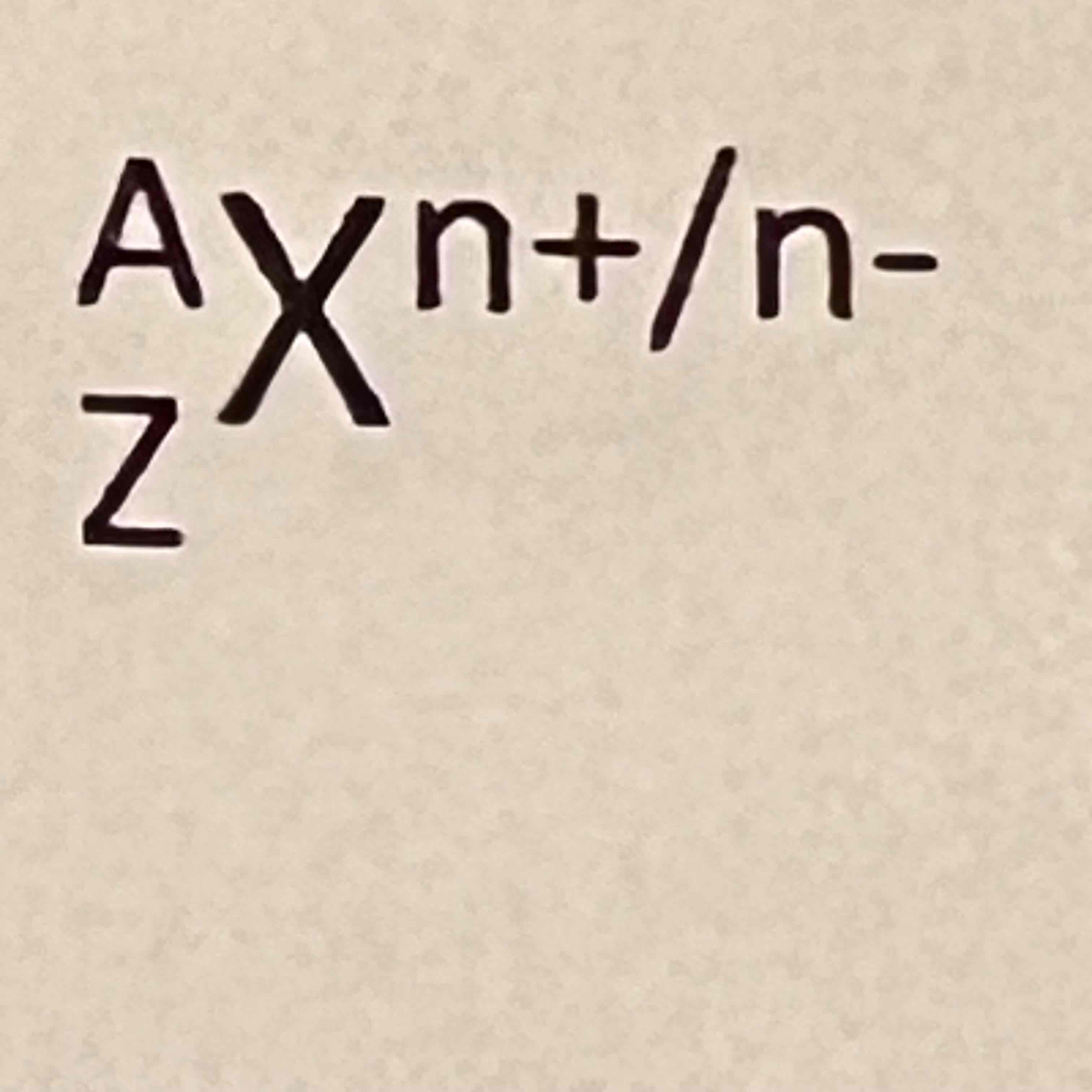
Z
Atomic number (pro)
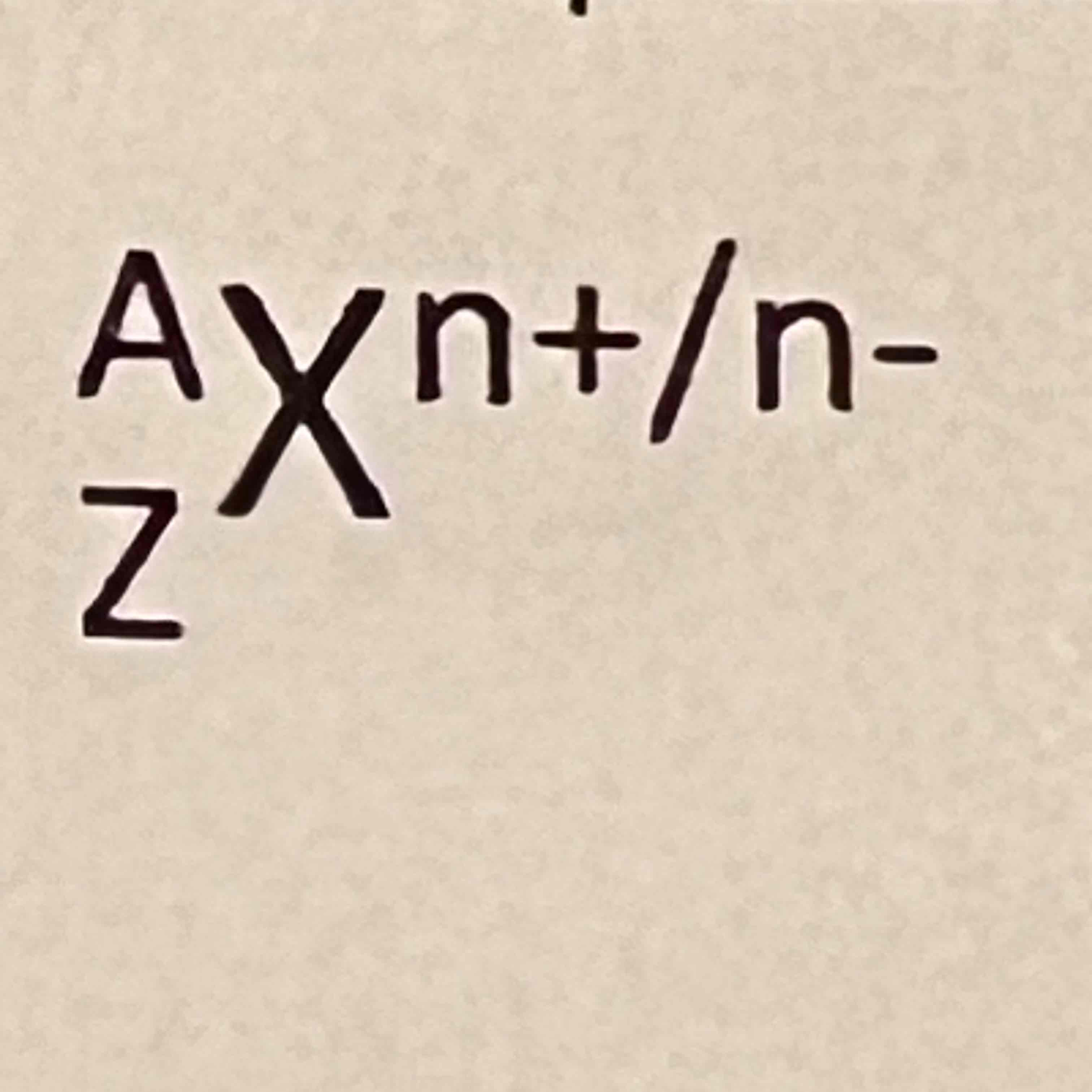
X
Element
n
Ions/charge
Isotope
Same element (protons) but different mass (neutrons)
similar chemical but different physical properties
RAM (relative atomic mass)
Weighted average of natural isotope abundances for an element
Carbon dating
14C
Radiotherapy
60Co
Diagnose diseases (medical tracers)
131 and 125 I
Released
Energy is _____ when electrons fall energy levels
Absorbed
Energy is ___ when electrons rise levels
Electromagnetic radiation / light
Y-rays, X-rays, UV, vis light, IR, microwave, radiowave
UV/ultraviolet
Big jumps/falls to/from n=1
Visible light
Medium jumps/falls to/from n=2
Infrared/IR
Small jumps/falls to/from n=3
Discrete e-s
Each element produces a line spectrum instead of a continuous spectrum because ____ exist in discrete levels. Higher levels converge at high energy, excited elements emit a light spectrum
Rows or period
You can tell an elements outermost main energy level by looking at what on the periodic table
Columns or groups
You can tell an elements outermost sub level by looking at what on the periodic table
Spin
Electrons in the same orbital must have different ____.
S orbital
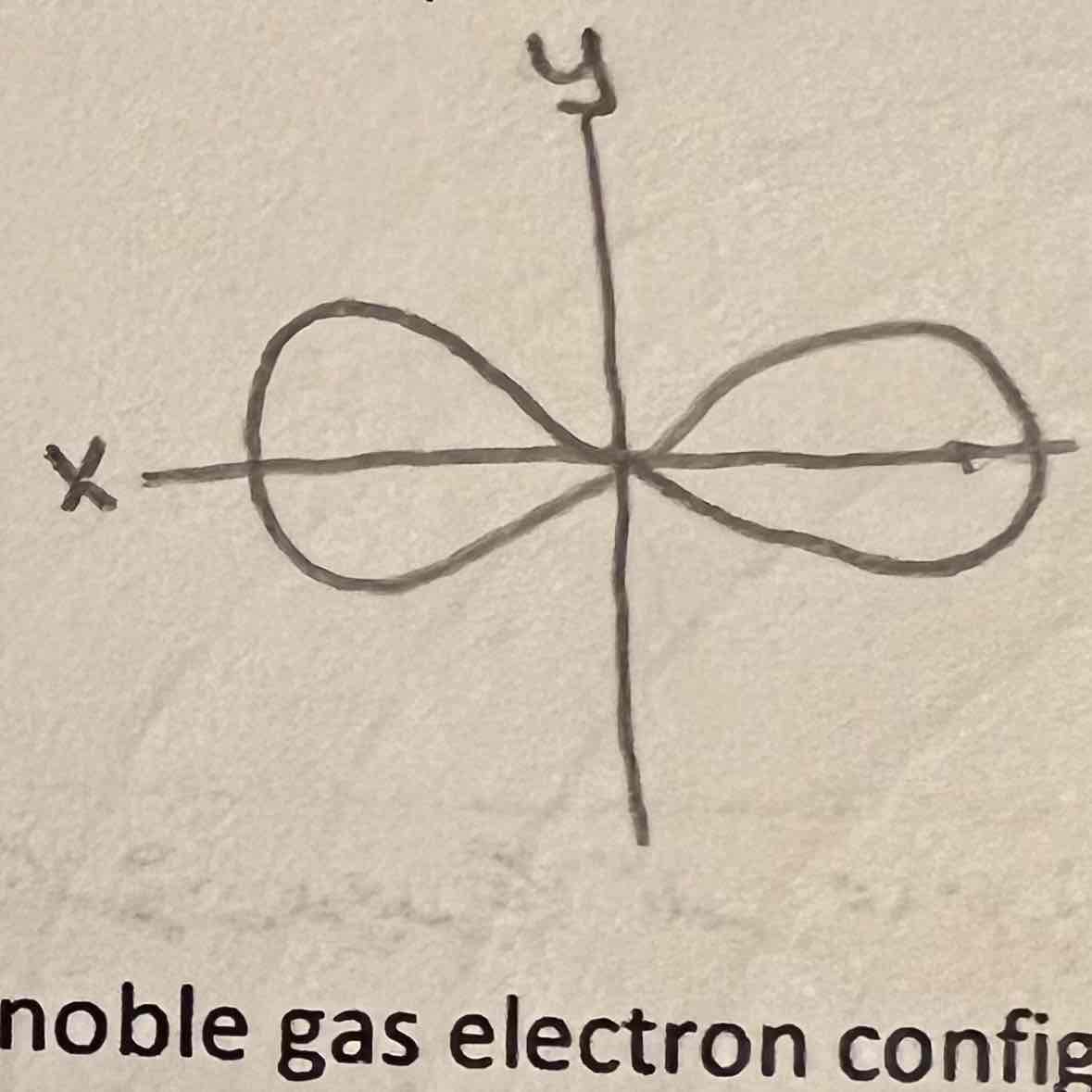
Px orbital
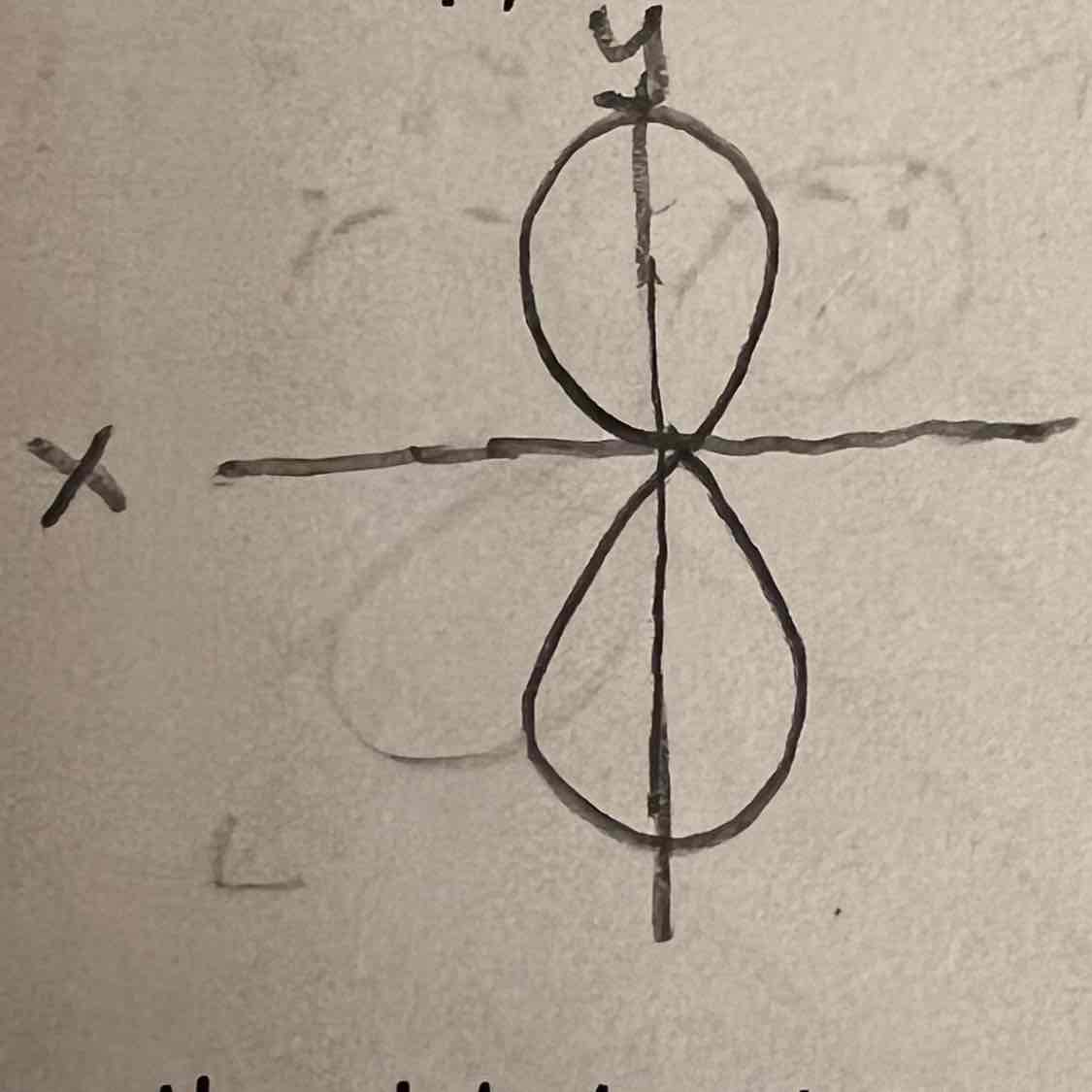
Py orbital
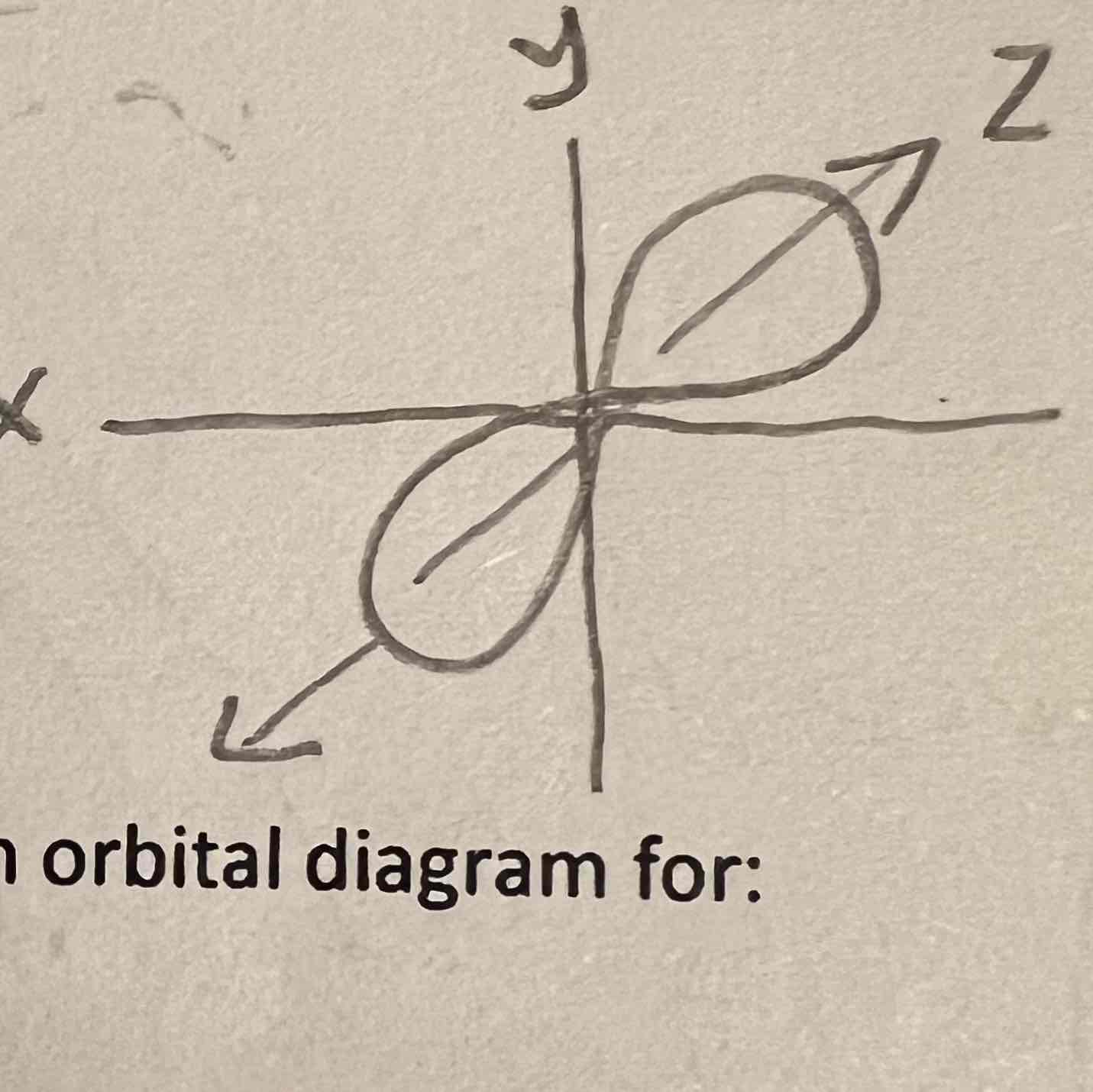
Pz orbital
Aufbau
This principle says to fill the lowest energy level first (this is why 4s fills before 3d!)
Hund
This rule says that in p and d sub levels, fill all orbitals singularly before doubling up.
REMEMBER Cr and Cu steal a 4s electron into their 3d!!!
Transition metals
____ loses electrons from 4s first when they become cations.
3 biggest factors affecting periodic trends
# of protons: ENF’s are protons pulling power on val electrons. Added protons across the period pull electrons closer.
Outermost energy level: adding levels = bigger atoms
E-E repulsion: negative electrons repel each other
Atomic radius
__ increases down a GROUP because energy levels are added.
__ decreases across a PERIOD because more protons pull the same core electrons
Ionic radius
__ increase down a GROUP b/c more energy levels
__ decrease across a PERIOD because more protons pulling electrons
Increases
Across a period, the melting point of metals ___ because atomic radius decreases, and more valence electrons and more IMFs are holding atoms together
Decreases
The melting point of metals ___ down a group because atomic radius increases and there are less IMF’s and valence electrons.
Increases
Down a group, the boiling point of halogens ___ because halogens are diatomic molecules. There are more electrons to completely fill the outer shell with valence electrons
Diatomic elements
Br I N Cl H O F
Ionization energy
__ is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms
K(g) —> K+(g) + e-
Decrease, increase
ionization energy/electronegativity/ electron affinity all ___ down a group, and ___ across a period because smaller atomic radii and they have more pull on electrons
Electronegativity
An atoms attraction of a shared pair of e-s
Electron affinity
The energy change when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom.
Cl(g) + e- —> Cl-(g)
Basic
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) —> 2NaOH(aq)
MgO(s) + H2O(l) —> Mg(OH)2(s)
Acidic
SO3(g) + H2O(l) —> H2SO4(aq)
P4H10(s) + H2O —> 4H3PO4(aq)
Amphoteric
Term for when a compound like aluminum oxide can act as either an acid or a base.
Completely steal
Ionic compounds are formed when atoms in the compound ___ electrons.
1.8
Elements forming ionic bonds should have an electronegativity difference of at least _
Ionic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between positive cations and negative anions (typically between metals and nonmetals) in a lattic
Ionic compound
Very high melt and boil point
No electrical conductivity in solids but there is in molten liquids and aqueous solutions
Soluble in polar solvents with weaker bonding
Insoluble in nonpolar solvents
Evenly share
covalent bonds form when atoms in a compound __ electrons
Covalent bonding
Electrostatic attraction between 2 nuclei and a share pair of electrons
0-1.8
Elements forming covalent bonds should have an electronegativity difference of __
Nonpolar covalent bond
0-0.5
Polar covalent bond
0.5-1.8
Increases
As electron domains decrease, bond angles …
Decrease
As unbonded electron pairs increase, bond angles
Resonance structure
Multiple Lewis structures are possible
average of bonds
The “true structure” of resonating bonds are an …
London dispersion forces
Also called temporary dipoles or induced dipoles. Non polar bonds that TEMPORARILY become polar between non polar molecules. Essentially exist between all molecules
Stronger
More linear molecules have more surface area and therefore have ___ temporary dipoles
stronger
Molecules with larger masses form __ temporary dipoles
Dipole dipole forces
Between permanently polar molecules and are stronger than dispersion forces
Hydrogen bonds
Extra strong polarities between molecules. H is attached to N/O/F, and that is bonded to another non bonding e pair on another N/O/F
MUCH stronger than dipole dipole bonds
Giant covalent structure
Infinitely repeatable structure such as diamond.
Not considered molecules because the number of atoms are VARIED- not set like in molecules.
have a very high melting point
Allotrope
Multiple forms in which an element can exist.
Ex. Graphite graphene carbon nanotube (can all conduct electricity)
Ex. O2, O3, O4, O8 (also conduct)
Low
Element forming metallic bonds tend to have __ electronegativities.
Metallic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between cation lattice and “sea” of delocalised electrons (not attached to any single atoms!)
High
Do metals have high or low melting point
Smaller cationic radii, higher ionic charges (more electrons)
Two factors that increase metallic bond strength
Delocalised electrons can move
Solid metals can conduct electricity because …
Cations can slide past each other
Metals are malleable because…
Alloy
Homogenous mixture of 2+ metals (steel bronze brass)
___ are harder/less malleable because different size cations disrupt the lattice and cations can no longer slide.
also have lower boil point because different side atoms make arrangement less regular than a pure metal and bonds are weaker
Temperature
Avg kinetic energy in C or K
Heat
Energy in J or kJ
Heat capacity
How much energy needed to raise 1g substance by 1°C
Resist
Higher specific heats mean substances ___ temp changes
Calorimeter
Device that insulates system (reaction) and surroundings (water) from outside world. Measures temp
Calorimetry assumptions
No heat lost to outside surroundings
Solutions ONLY water
Complete combustion occurred
Chemical bonds
Where energy is stored within a molecule
Break
Energy is required to ___ bonds
Form
Energy is released to ___ bonds
enthalpy change
Amount of energy gained or lost during reaction
stronger
Stable molecules contain __ bonds
Weaker
Molecules with high potential energy contain ___ bonds
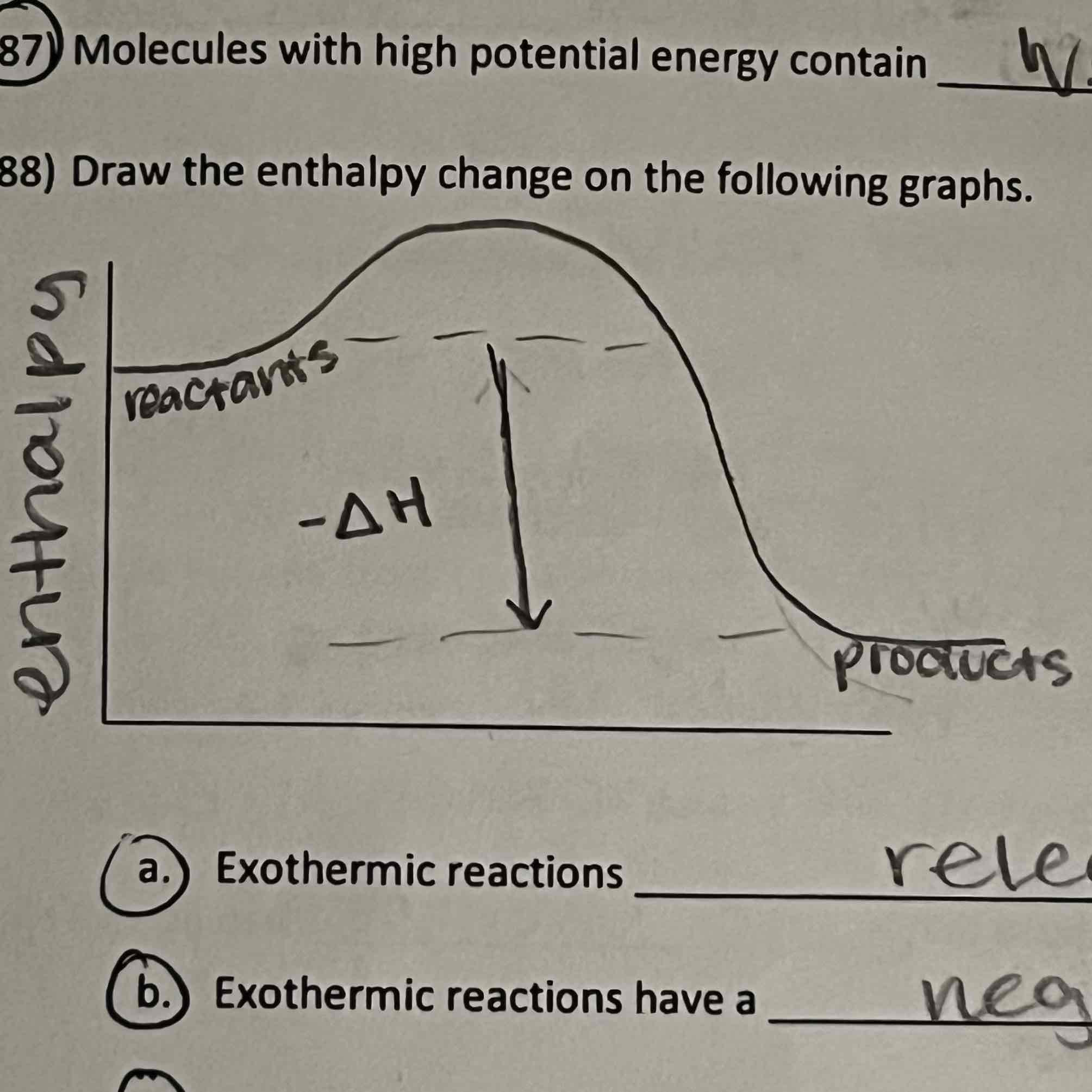
Exothermic
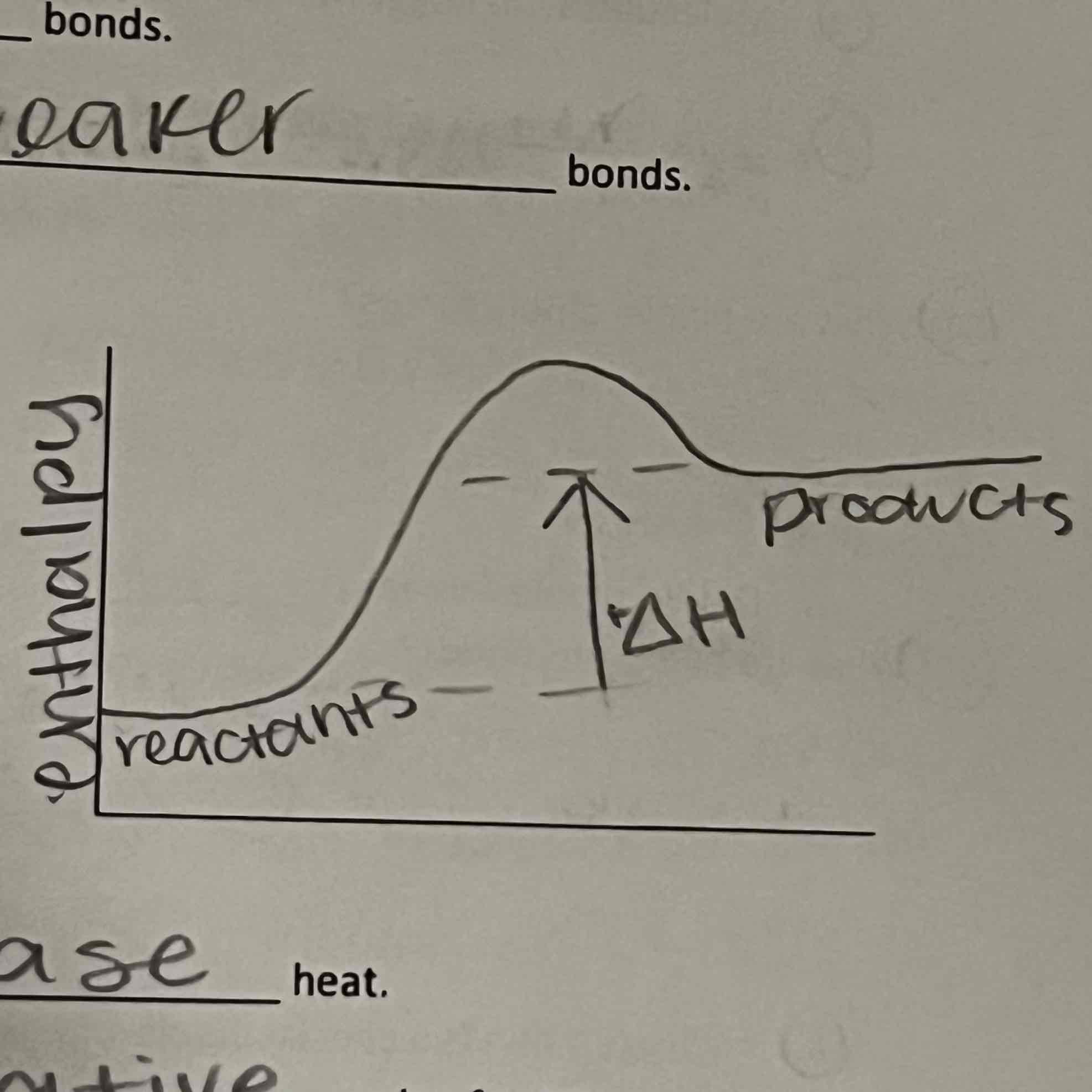
Endothermic
Release
Exothermic reactions __ heat
Absorb
Endothermic reactions ___ heat
weaker
Reactants in Exothermic reactions have __ bonds than products
Bond enthalpies
Averages across multiple compounds (in data book). Less specific than experimental calorimetery enthalpy etc