MIDS 167 Midterm practice
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
normal PR interval time frame?
0.12-0.20 secs
normal QRS interval time frame?
0.08-0.12 secs
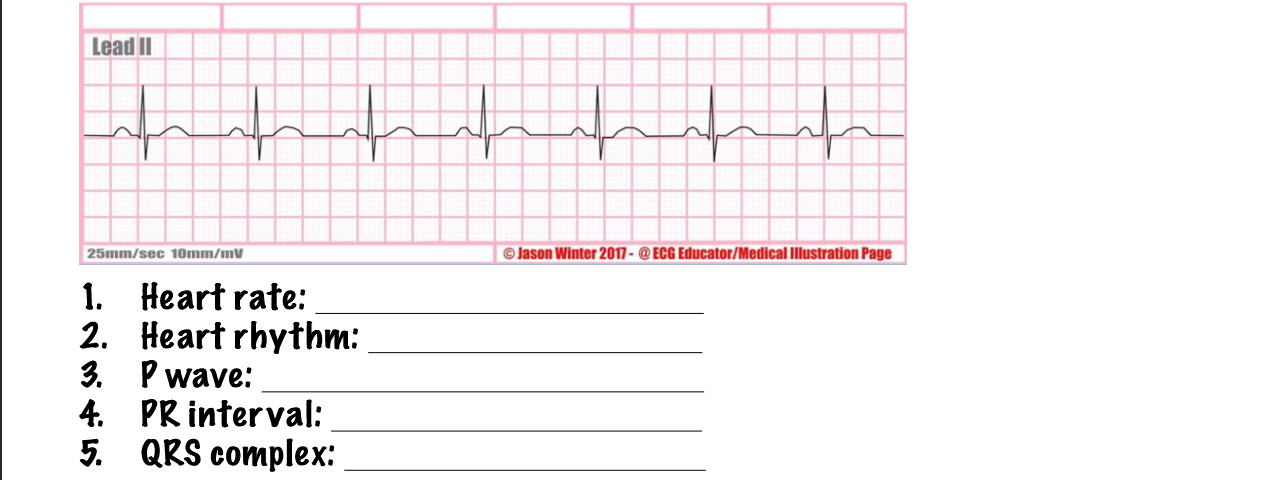
what type of rhythm is this? answer the questions
normal sinus rhythm
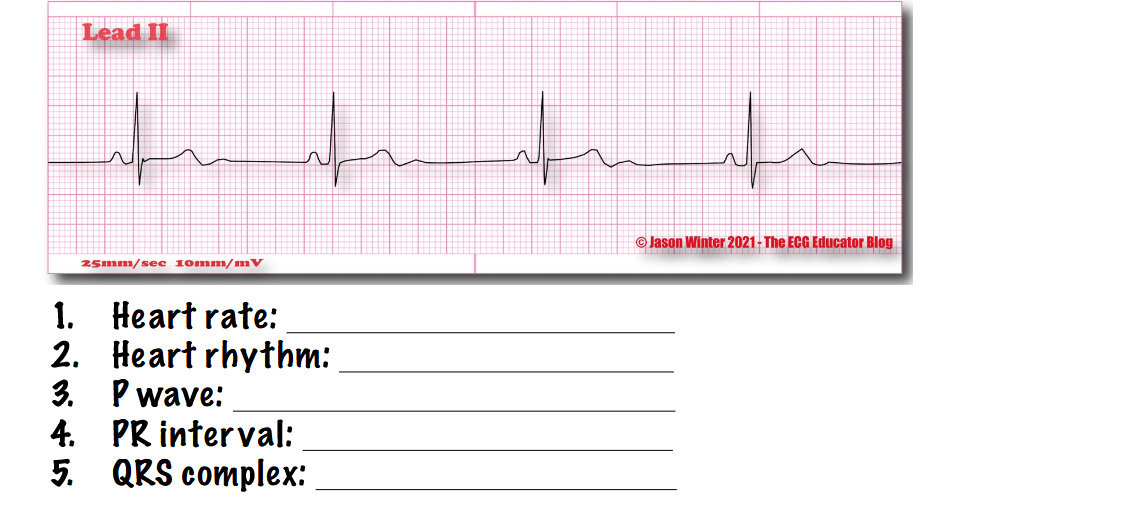
what type of rhythm is this? answer the questions
sinus bradycardia
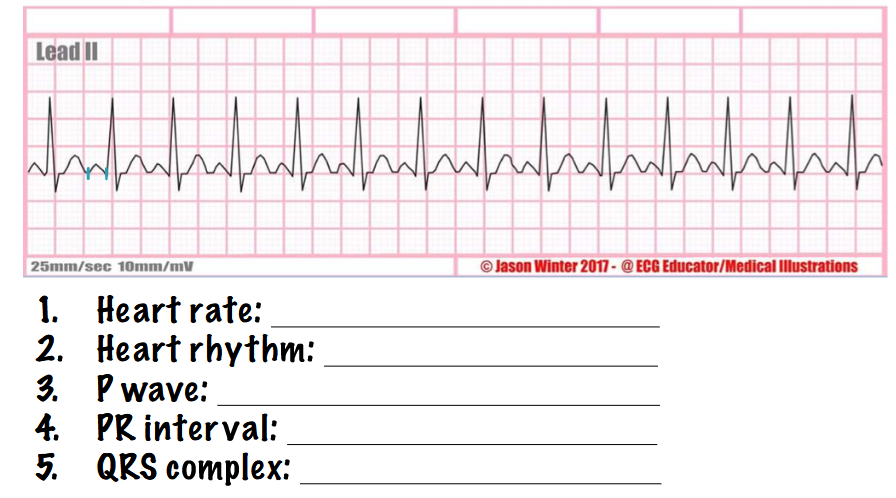
what type of rhythm is this? answer the questions
sinus tachycardia
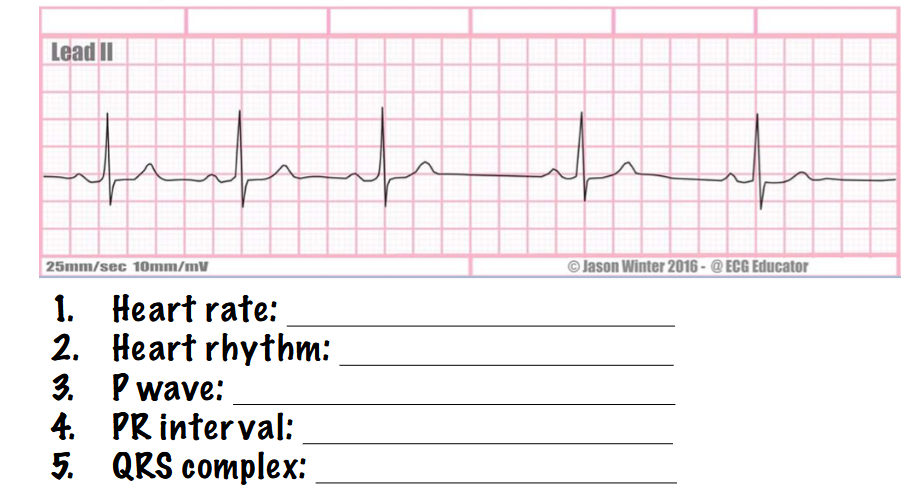
what type of rhythm is this? answer the questions
sinus arrhythmia
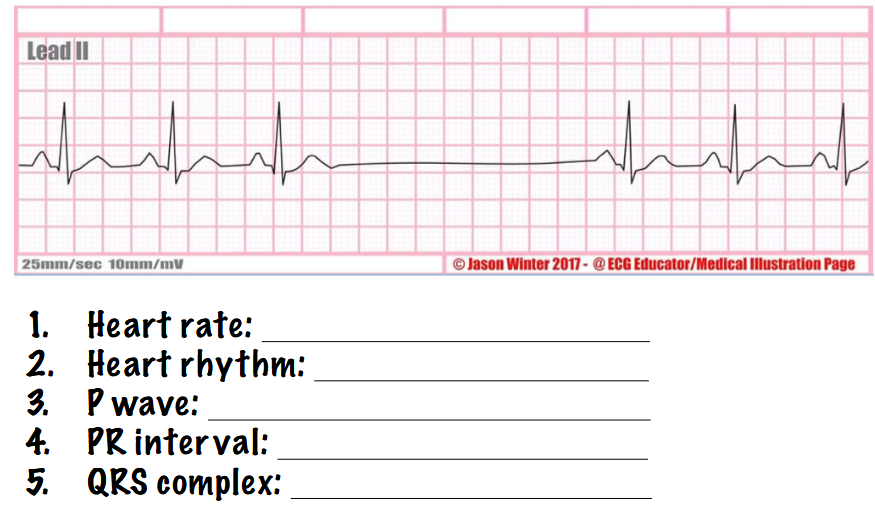
what type of rhythm is this? answer the questions
sinus arrest
Common possible cause of sinus arrhythmia?
breathing
The PR interval should normally be _____seconds or smaller.
0.20
The QRS interval should normally be ______ seconds or smaller.
0.12
The QRS complex is produced when: (u can choose more than 1)
A) The ventricles depolarize
B) The ventricles contract
C) The ventricles repolarize
a and b
The normal conduction pattern of the heart follows which sequence?
Purkinje fibers
SA node
Bundle branches
Internodal tracts
Bundle of His
AV node
2,4,6,5,3,1
The T wave on the ECG strip represents:
Heart returning to rest
The coronary circulation has how many main arteries?
2
When interpreting arrhythmias, the health care provider should remember that the most important key is the:
Patient's clinical appearance
ECG is a graphic tracing of the electrical activity of the heart but not the mechanical activity. T/F?
T
The ground lead serves to minimize __________________.
outside electrical interference
Lead II is most commonly used for cardiac monitoring because of its ability to visualize _____ waves.
P
________leads are those that have one positive electrode and one negative electrode.
bipolar
You must master the accepted parameters for each arrhythmia and then apply those parameters to each of the five steps when analyzing an ECG strip. T/F?
T
Artifact is defined as ECG waveforms from sources outside the heart. T/F?
T
The point at which the QRS complex meets the ST segment is commonly referred to as the?
j point
The term supraventricular refers to a stimulus arising above the ventricles. T/F?
T
The sharp, negative deflection that follows the R wave is called the Q wave. T/F?
F
Heart rhythms are classified as either regular or irregular. T/F?
T
The ability of cardiac cells to respond to an electrical stimulus is referred to as:
Excitability
Which characteristic is specific to the pacemaker sites of the electrical conduction system (i.e. the SA node, AV junction, and the Purkinje network fibers)?
Automaticity
The ability of cardiac pacemaker cells to generate their own electrical impulses spontaneously without external, or nervous, stimulation is known as:
Automaticity
Excitability is also referred to as:
Irritability
The ability of cardiac cells to receive an electrical stimulus and then transmit the stimulus to other cardiac cells is known as:
Conductivity
Cardiac muscle cell groups that function collectively as a unit are known as:
Syncytia
The period when repolarization is almost complete and the cardiac cell can be stimulated to contract prematurely if the stimulus is stronger than normal is known as:
The relative refractory period
Cardiac depolarization may be thought of as the period during which ________ ions rush into the cell.
sodium
At the end of cardiac depolarization, ________ ions return to the inside of the cell.
potassium
The resting state of a cardiac cell, wherein the inside of the cell is electrically negative relative to the outside of the cell, is called:
Polarized state
The point at which a stimulus will produce a cell response is called the:
Threshold
The sinoatrial node is located in the:
Right atrium
The AV node is located in the:
Right atrium
The intrinsic firing rate of the AV junction is ______ BPM
40-60
The intrinsic firing rate of the SA node is ________ BPM.
60-100
The normal conduction pattern of the heart follows the sequence:
1. SA node
2. Purkinje fibers
3. Bundle of His
4. AV Node
5. Bundle Branches
6. Internodal pathways
1,6,4,3,5,2
The intrinsic firing rate of the Purkinje network is _______BPM.
20-40
The SA node receives its blood supply primarily from the:
Right coronary artery
WHAT NUMBER OF inter-nodal tracts or pathways receive the electrical impulse as it leaves the SA node?
3
What is the specialized group of cardiac fibers conducting electrical activity from the SA node to the left atrium?
Bachmann's bundle
Purkinje network fibers are smaller in diameter than ordinary cardiac muscle fibers. T/F?
F
Can a cardiac cell respond to a stimulus during ABSOLUTE REFRACTORY period?
no
Can a cell respond during RELATIVE REFRACTORY period?
yes
What node is the gatekeeper and allows for electrical signal to be delayed to the ventricles so as to not contract with the atria?
atrioventricular (AV) node
What side of the heart is a low-pressure pump?
right
The course of blood flow through the heart and lungs is referred to as ________circulation.
pulmonary
The course of blood flow through the heart and body is referred to as ________circulation.
systemic
Cardiac output is a factor of what elements?
heart rate and stroke volume
The chief chemical neurotransmitter for the parasympathetic nervous system is:
Acetylcholine
It is important to note that blood vessels are innervated only by the ________ nervous system.
sympathetic
The chief chemical neurotransmitter for the sympathetic nervous system is:
Norepinephrine
One cardiac cycle occurs every ________ seconds.
0.8
With the exception of capillaries, all of the body's blood vessels have ____andrenergic receptors whereas the heart and lungs have _____ andrenergic receptors.
alpha, beta
an other name for mitral valve?
bicuspid
Starling's Law of the heart is also referred to as:
The rubber band theory
Stroke volume is estimated at approximately _______ml per beat.
70
The ______________ nervous system is responsible for preparation of the body for physical activity (fight or flight).
sympathetic
What is Sterling’s law? EXPLAIN
more preload (incoming blood) = more forceful stroke volume (ejected blood)
The lower chamber of the heart, with the thickest myocardium, is the:
left
The right coronary artery branches supply oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the:
Electrical conduction system
The right and left coronary arteries arise from the:
Trunk of aorta
purpose of the liquid between the epicardium and pericardium is to:
reduce friction
inflammation of the visceral (outer) layer?
pericarditis
Happens when there is accumilation of excess fluid in the pericardium?
cardiac tamponade
Three layers of the arteries and veins?
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica adventitia (externa)
what is one thing veins have that arteries don’t?
valves
Where does gas exchange happen? (blood vessel vise)
capillaries
Where does gas exchange happen? (organ vise)
alveoli in lungs
LAD meaning? (LAD artery)
left anterior descending
LCX meaning?
left circumflex
___circulation is when blood travels from the left side…
systemic
____circulation is when blood travels from the right side…
pulmonary
How long does systole last?
0.3 seconds
How long does diastole last?
0.5 seconds
_____refers to the amount pumped out of the ventricles (70mL) during one cardiac cycle.
stroke volume
_____is the amount of blood ejected out of the ____ventricle
stroke volume, left
5 steps of analyzing an ECG?
rate, rhythm, P waves, PR interval, QRS complex